Recombinant Human Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C (VAPB)
-
货号:CSB-CF025790HU
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:VAPB; UNQ484/PRO983; Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C; VAMP-B/VAMP-C; VAMP-associated protein B/C; VAP-B/VAP-C
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-243
-
氨基酸序列AKVEQVLSLEPQHELKFRGPFTDVVTTNLKLGNPTDRNVCFKVKTTAPRRYCVRPNSGIIDAGASINVSVMLQPFDYDPNEKSKHKFMVQSMFAPTDTSDMEAVWKEAKPEDLMDSKLRCVFELPAENDKPHDVEINKIISTTASKTETPIVSKSLSSSLDDTEVKKVMEECKRLQGEVQRLREENKQFKEEDGLRMRKTVQSNSPISALAPTGKEEGLSTRLLALVVLFFIVGVIIGKIAL
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Participates in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response (UPR) by inducing ERN1/IRE1 activity. Involved in cellular calcium homeostasis regulation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- report on a novel mutation of p.Pro56His in VABP found in a Chinese familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pedigree and description of the clinical characteristics of the family. PMID: 28993872
- the component proteins of the machinery, OSBP, VAP, SAC1, and PITPNB, are all essential host factors for AiV replication. Importantly, the machinery is directly recruited to the RNA replication sites through previously unknown interactions of VAP/OSBP/SAC1 with the AiV proteins and with ACBD3. PMID: 29367253
- Lifelong elevation of neuronal VAPB slowed the decline of neurological impairment, delayed denervation of hindlimb muscles, and prolonged survival of spinal motor neurons. PMID: 28173107
- Study showed that alpha-synuclein perturbs endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria associations and that this involves disruption to the VAPB-PTPIP51 tethering proteins. Using a range of assays including immunoprecipitation, cellular glutathione S-transferase pull-down, proximity ligation and in vitro binding of recombinant proteins, study showed that alpha-synuclein is a direct binding partner for VAPB. PMID: 28337542
- ACBD5-VAPB interaction regulates peroxisome-endoplasmic reticulum associations. Loss of PO-ER association perturbs PO membrane expansion and increases PO movement. PMID: 28108524
- VAP-ACBD5-mediated contact between the endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes mediate organelle maintenance and lipid homeostasis. PMID: 28108526
- Effects of the combined absence of VAPA and VAPB in human cells were studied; cells lacking VAP accumulate high levels of PI4P, actin comets, and trans-Golgi proteins on endosomes. Such defects are mimicked by downregulation of OSBP, a VAP interactor and PI4P transporter that participates in VAP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum-endosomes tethers. PMID: 27419871
- this is the first study to report Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis caused by a VAPB mutation in a Chinese population. PMID: 26566915
- Our work revealed that VAP-A/B knockdown impaired the processing and secretion of PAUF, which is one of the cargo proteins of carriers of the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface. PMID: 26490117
- Heterozygous P56S Vapb knock-in mice show mild age-dependent defects in motor behaviors as characteristic features of the disease. The homozygous P56S Vapb knock-in mice show more severe defects compared with heterozygous mice reflecting the dominant and dose-dependent effects of P56S mutation. PMID: 26362257
- VAPB inhibited the degradation of DeltaF508-CFTR in the ER through interactions with the RMA1-Derlin-BAP31-VCP pathway. PMID: 26740627
- Study characterizes the human VAPB-HCV NS5B interaction and reveals that NS5B C-linker is intrinsically disordered in solution but capable of binding the human VAPB-MSP domain which overlaps with those for binding HCV NS5A and human Eph receptors. PMID: 26784321
- The VAPB and its interacting partners cooperatively regulate protein trafficking through the ERGIC by modulating PtdIns4P levels. PMID: 26812496
- Collectively, these results not only lead to a better understanding of hVAPB function but also point to potentially relevant targets for therapeutic intervention. PMID: 25826266
- results suggest that the binding of vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B(VAP-B) to Rab3 GTPase activating protein 1(RAB3GAP1) is implicated in the regulation of nuclear envelope formation through ER-Golgi intermediate compartment PMID: 25612670
- P56S-VAPB was found to suppress adipocyte differentiation by promoting the activation of the ATF4-CHOP pathway PMID: 25824044
- In patients with familial or sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) from Portugal, Iceland and Sweden no association is found with disease and VAMP-associated protein type B (VAPB) mutations. PMID: 23971766
- Findings provide new pathophysiological mechanisms of P56S VAPB that differentially affect the function and survival of corticospinal and spinal motor neurons in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 8. PMID: 23771029
- genetic screening for this mutation should be performed in all adult patients with lower motor neuron disease, regardless of family history because of the rarity of this disease, physicians often do not suspect it, and many cases may be missed in Brazil. PMID: 24212516
- Partial or complete loss of VAPB function leads to motor deficit but is unable to trigger a full-blown amyotrophic lateral sclerosis phenotype. PMID: 23446633
- this discovery provides a mechanism for ALS-causing VAPB mutants/variants to gain novel functions such as to mediate ER structure before significant accumulation of aggregates occurs. PMID: 23333387
- These results suggest that changes in wild type VAPB do not play a significant role in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis cases that are not caused by VAPB mutations PMID: 23281774
- Transfection of a dominant-negative form of the AAA ATPase p97/VCP stabilizes mutant VAPB, suggesting a role for this ATPase in extracting the aggregated protein from the inclusions. PMID: 22611258
- structual basis of VAPC binding to HCV NS5B PMID: 22815741
- This study screened a cohort of 755 sporadic ALS patients, 111 familial ALS patients (97 families), and 765 control subjects of Dutch descent for mutations in vesicle-associated membrane protein B (VAPB). PMID: 22878164
- VAPB promotes breast tumor growth by modulation of Akt activity. PMID: 23049696
- The binding residues have been successfully mapped out on both NS5A and VAPB, thus allowing the construct of the complex structure. PMID: 22720086
- The mutation in VAPB that causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis also causes the block of transport of nucleoporins and emerin to the nuclear envelope. PMID: 22454507
- ALS mutant VAPBP56S perturbs anterograde mitochondrial axonal transport by disrupting Ca(2+) homeostasis and effecting the Miro1/kinesin-1 interaction with tubulin. PMID: 22258555
- Loss of either VAPB or PTPIP51 perturbs uptake of Calcium by mitochondria and results in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 22131369
- T46I mutant of the hVAPB MSP domain is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 22069488
- endoplasmic reticulum stress and corruption of the proteasome function might contribute to the aberrant protein homeostasis associated with hVAPB PMID: 21998752
- VAPB protein levels are reduced in motor neurons derived form induced pluripotent stem cells of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. PMID: 21685205
- three conserved prolines in VAPA and Scs2p confers less vulnerability to mutations equivalent to the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis causing mutation as compared with VAPB, which has only two conserved prolines. PMID: 21144830
- newly identified mutation in human FALS has a pathogenic effect, supporting and reinforcing the role of VAPB as a causative gene of ALS. PMID: 20940299
- Mutations in SOD1, ANG, VAPB, TARDBP and FUS genes have been identified in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 20577002
- Adeno-associated viral-mediated over-expression of both wild-type and mutated form of human VAPB selectively induces death of primary mouse motor neurons, albeit with different kinetics. PMID: 20477942
- study reports the first identification of the p.P56S mutation in the VAPB gene in a non-Brazilian patient PMID: 20447143
- VAPB mRNA levels were decreased in the spinal cord of ALS patients compared to controls and Expression of VAPB mRNA and protein was predominantly localised to large motor neurones. PMID: 18701194
- Pro56Ser mutation of VAPB lead to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by eliminating the native protein structure. PMID: 20377183
- these results demonstrate that the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis -linked VAPB mutant causes dramatic ER restructuring that may underlie its pathogenicity in motoneurons. PMID: 20008544
- the mechanism by which VAP-B(P56S) aggregates are formed and induce familial motor neuron diseases PMID: 20207736
- under conditions of proteasomal inhibition, as encountered in many neurodegenerative diseases including ALS, variant VAPB proteins might accumulate in affected cells and contribute to ALS pathogenesis. PMID: 20227395
- evidence that Nir (Nir1, Nir2, and Nir3)-VAP-B interactions are mediated through the conserved FFAT (two phenylalanines (FF) in acidic tract) motif present in Nir proteins PMID: 15545272
- Regulation of ceramide transport protein by oxyste rbinding proteins, sterols, and VAMP reveals a novel mechanism for integrating sterol regulatory signals with ceramide transport and sphingomyelin synthesis in the Golgi apparatus. PMID: 16571669
- Frequency of the detected exon variation in the VAPB gene was not significantly different between patients and controls. VAPB mutations are not a common cause of adult-onset sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 16729899
- Overexpression of wild type VAPB promotes unfolded protein response, which is a reaction of the endoplasmic reticulum to suppress accumulation of misfolded proteins. PMID: 16891305
- it is suggested that VAPB mutations do not significantly contribute to the genetic causes of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK and Northern Europe PMID: 17536055
- P56S mutation in VAP-B may lead to a less stable interaction of this endoplasmic reticulum protein with at least two other proteins: tubulin and GAPDH. PMID: 17540579
- VAPB is abundant in motor neurons and the P56S substitution causes aggregation of mutant VAPB in immobile tubular ER clusters, perturbs FFAT-motif binding, and traps endogenous VAP in mutant aggregates, which may cause motor neuron degeneration. PMID: 17804640
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 8 (ALS8); Spinal muscular atrophy, proximal, adult, autosomal dominant (SMAPAD)
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type IV membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:VAMP-associated protein (VAP) (TC 9.B.17) family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous. Isoform 1 predominates.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 12649
OMIM: 182980
KEGG: hsa:9217
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000417175
UniGene: Hs.182625
Most popular with customers
-
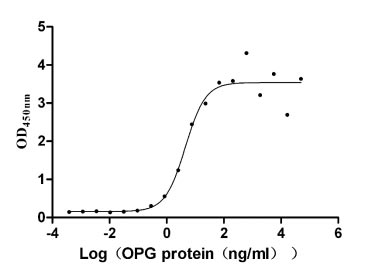
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
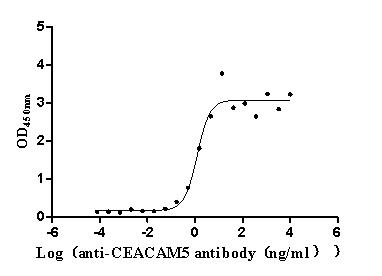
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
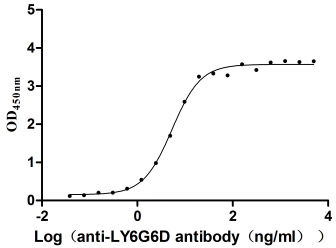
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
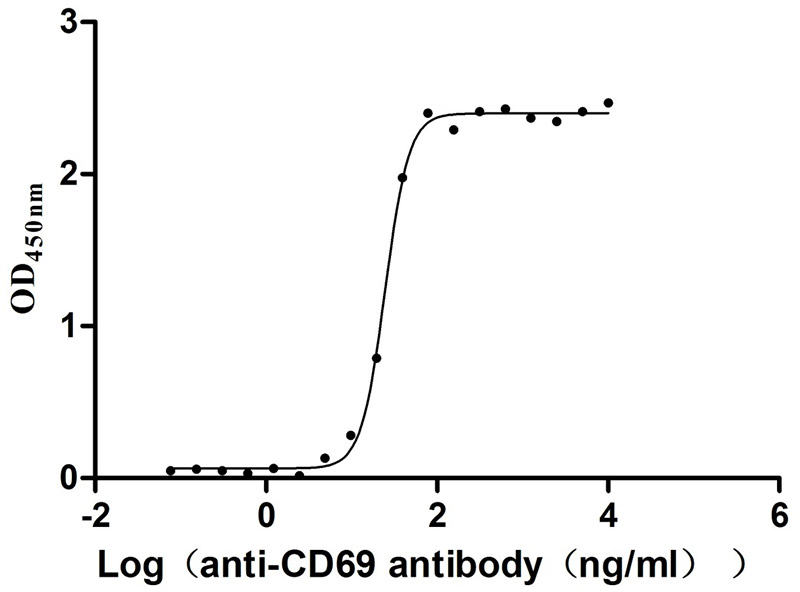
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)




-AC1.jpg)










