Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA repair protein RAD51 (RAD51)
-
货号:CSB-YP333076SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP333076SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP333076SVG-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP333076SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP333076SVG
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:RAD51
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:RAD51; YER095W; DNA repair protein RAD51
-
种属:Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-400
-
氨基酸序列MSQVQEQHIS ESQLQYGNGS LMSTVPADLS QSVVDGNGNG SSEDIEATNG SGDGGGLQEQ AEAQGEMEDE AYDEAALGSF VPIEKLQVNG ITMADVKKLR ESGLHTAEAV AYAPRKDLLE IKGISEAKAD KLLNEAARLV PMGFVTAADF HMRRSELICL TTGSKNLDTL LGGGVETGSI TELFGEFRTG KSQLCHTLAV TCQIPLDIGG GEGKCLYIDT EGTFRPVRLV SIAQRFGLDP DDALNNVAYA RAYNADHQLR LLDAAAQMMS ESRFSLIVVD SVMALYRTDF SGRGELSARQ MHLAKFMRAL QRLADQFGVA VVVTNQVVAQ VDGGMAFNPD PKKPIGGNIM AHSSTTRLGF KKGKGCQRLC KVVDSPCLPE AECVFAIYED GVGDPREEDE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Required both for recombination and for the repair of DNA damage caused by X-rays. Its function may be modulated by interaction with other repair proteins. RAD52 interacts directly with RAD51, via its C-terminus. Forms a nucleoprotein filament with DNA as an early intermediate in recombination.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- analysis of Rad51-dependent break-induced replication in which the invading double strand break end and its donor template share a 108-base-pair homology region and the donor carries different densities of single-base-pair mismatches PMID: 28405019
- Small Rad51 and Dmc1 complexes co-occupy both ends of a meiotic DNA double strand break. PMID: 26719980
- Using single-molecule imaging to visualize Rad51, study shows that Rad51 uses a length-based recognition mechanism while interrogating dsDNA, enabling robust kinetic selection of 8-nucleotide tracts of microhomology, which kinetically confines the search to sites with a high probability of being a homologous target. PMID: 25684365
- Shu complex utilizes homologous recombination machinery for error-free lesion bypass via physical interaction with a Rad51 paralogue PMID: 24339919
- Here we show that Rad51-mediated meiotic recombination is not subject to regulatory processes associated with high-fidelity chromosome segregation PMID: 24367271
- These results support the idea that down-regulation of Rad51 activity is important during meiosis to prevent Rad51 from competing with Dmc1 for repair of meiotic DSBs PMID: 24465215
- Rad51 protein overexpression induces resistance to DNA-damaging agents. PMID: 24741789
- Srs2's DNA-unwinding activity is greatly suppressed when Rad51 filaments form on duplex DNA. PMID: 23939144
- FBH1 restraining RAD51 DNA binding under unperturbed growth conditions to prevent unwanted or unscheduled DNA recombination. PMID: 24108124
- mechanism of Rad51 stabilization is inferred by our high-resolution crystal structure, which reveals Psy3-Csm2 to be a structural mimic of the Rad51-dimer, a fundamental unit of the Rad51-filament PMID: 23575680
- study provides biochemical evidence that Rad51 acts as an accessory factor with Mei5-Sae3 for Dmc1-mediated joint molecule formation during meios; Rad51 is a multifunctional protein that catalyzes recombination directly in mitosis and indirectly, via Dmc1, during meiosis PMID: 22955832
- Novel attributes of Hed1 affect dynamics and activity of the Rad51 presynaptic filament during meiotic recombination. PMID: 22115747
- Mutating Rad51 Ser 192 to Ala or Glu confers hypersensitivity to DNA damage and homologous-recombination defects. PMID: 21738226
- propose that the Shu complex shifts the balance of repair toward Rad51 filament stabilization by inhibiting the disassembly reaction of Srs2 PMID: 21372173
- determined Mei5-Sae3 interacts with the Rad51 recombinase through the N-terminal domain of Mei5 PMID: 21543267
- Rad51 inhibits translocation formation by non-conservative homologous recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PMID: 20686691
- RAD51-dependent BIR does not require special facilitating sequences that are required for a less efficient RAD51-independent process. PMID: 15657422
- Gly-103 in the N-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 protein is critical for DNA binding PMID: 15908697
- Yeast cells lacking the SGS1 DNA helicase and the MUS81 structure-specific endonuclease display a synthetic lethality that is suppressed by loss of the RAD51 recombinase. PMID: 16193328
- Dmc1p and Rad51p are loaded to the DNA repair site in an independent manner. PMID: 16341884
- The Rad51-lysine191arginine ATPase-defective mutant either forms an altered filament or is defective in turnover, resulting in a reduced pool of free protein available for DNA binding. PMID: 17030607
- The processing of double-strand breaks and binding of single-strand binding proteins RPA and Rad51 modulate the formation of ATR-kinase foci. PMID: 18003698
- Results indicate that Rad51 and Dmc1 filaments are essentially identical with respect to several structural parameters, including persistence length, helical pitch, filament diameter, DNA base pairs per helical turn and helical handedness. PMID: 18535008
- Rad51 presynaptic filaments are sufficient to locate a homologous sequence and form initial joints, even on the surface of a nucleosome. PMID: 18570881
- an additional role of Rad51 might be to protect eukaryotic genomes from instabilities by preventing chromosomal rearrangements PMID: 18755201
- Data show that during Rad51 polymerization, recombinase proteins moved all the nucleosomal arrays in front of the progressing filament; this had a powerful remodeling effect, as Rad51 destabilized the nucleosomes along considerable stretches of DNA. PMID: 18982066
- Findings suggest that loop 2 contributes to the primary DNA-binding site in Rad51, controlling filament formation and ATPase activity. PMID: 19033358
- Mph1, but not a helicase-defective variant, dissociates Rad51-made D-loops PMID: 19136626
- BIR defect observed for rad51 mutants is due to strand invasion failure, whereas the Pol delta complex mutants are proficient for strand invasion but unable to complete extensive tracts of recombination-initiated DNA synthesis. PMID: 19139272
- Rad51 spreads chromosome-wide bidirectionally from the DNA double-strand breaks but selectively only on the broken chromosome PMID: 19217407
- Data show that Rad51 readily dissociates from DNA in the presence of ADP or in the absence of nucleotide cofactor, but that free ATP in solution confers a fivefold increase in the stability of the nucleoprotein filaments. PMID: 19327367
- ssDNA annealing promoted by Rad52 is preceded by aggregation of multiple replication protein-A (RPA)-ssDNA complexes with Rad52, and Rad51 inhibits this aggregation. PMID: 19445949
- that a physical interaction between Rad51 and the C-terminal region of Srs2 triggers ATP hydrolysis within the Rad51 filament, causing Rad51 to dissociate from DNA. PMID: 19595720
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome. Note=Localizes as foci on meiotic chromosomes.
-
蛋白家族:RecA family, RAD51 subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: sce:YER095W
STRING: 4932.YER095W
Most popular with customers
-
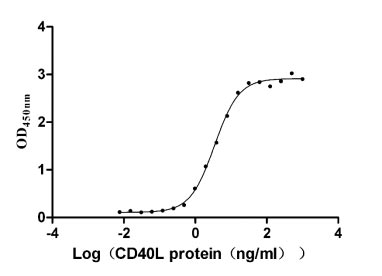
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
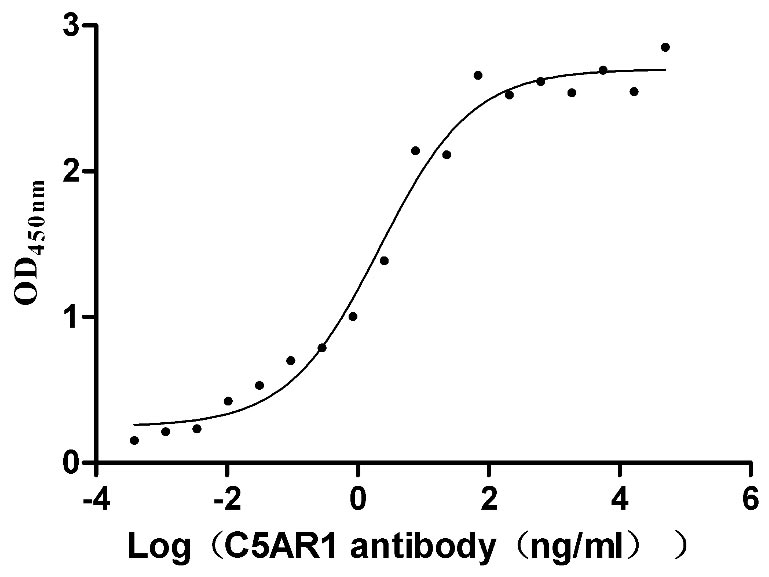
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
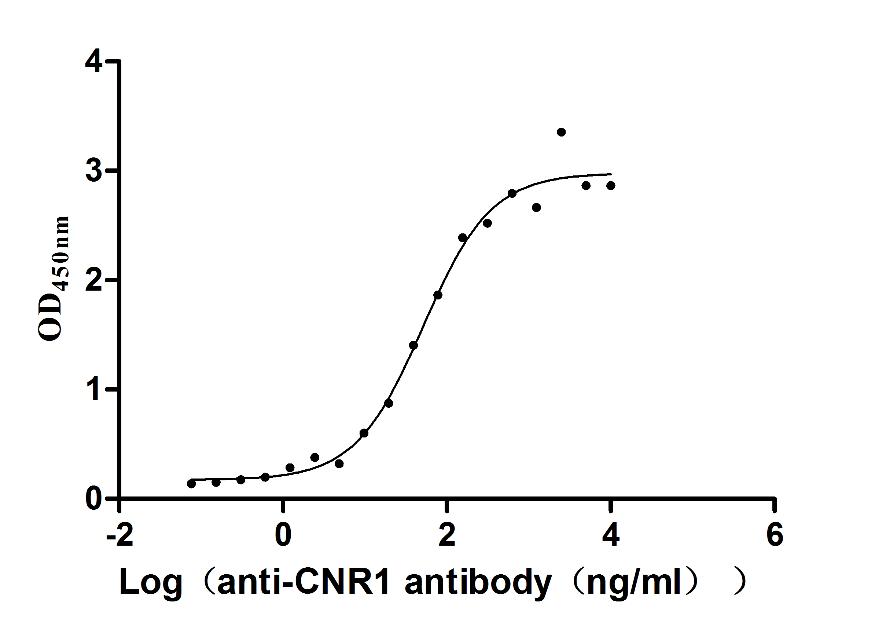
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
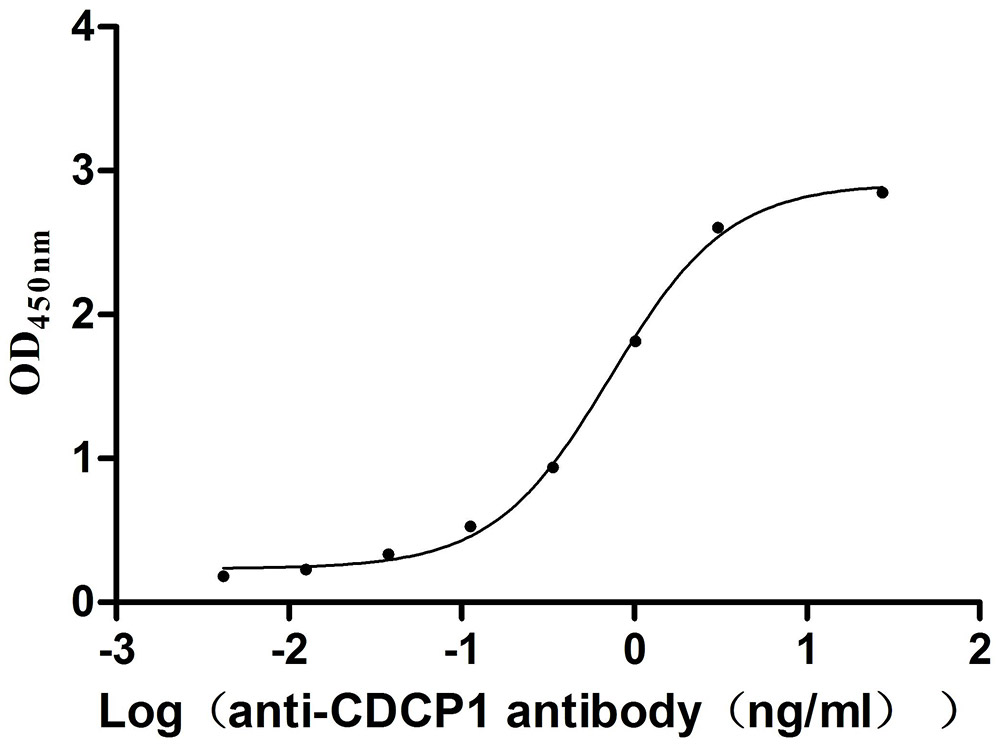
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)



-AC1.jpg)