Recombinant Rat Ciliary neurotrophic factor (Cntf)
-
货号:CSB-YP005683RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP005683RA
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP005683RA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP005683RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP005683RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:CntfCiliary neurotrophic factor; CNTF
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-200
-
氨基酸序列MAFAEQTPLT LHRRDLCSRS IWLARKIRSD LTALMESYVK HQGLNKNINL DSVDGVPVAS TDRWSEMTEA ERLQENLQAY RTFQGMLTKL LEDQRVHFTP TEGDFHQAIH TLMLQVSAFA YQLEELMVLL EQKIPENEAD GMPATVGDGG LFEKKLWGLK VLQELSQWTV RSIHDLRVIS SHQMGISALE SHYGAKDKQM
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:CNTF is a survival factor for various neuronal cell types. Seems to prevent the degeneration of motor axons after axotomy.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- endogenous SNCA plays a crucial role in spinal neuronal survival, in which the underlying mechanism may be linked to the regulation both apoptotic genes (Caspase7/9) and CNTF. PMID: 27581683
- Activation of CNTF/CNTFRalpha signaling pathway by hRheb(S16H) transduction of dopaminergic neurons PMID: 25799580
- FGF-2 down-regulated the expression of endogenous CNTF. PMID: 23271288
- CNTF induces a decrease in the sodium current and an increase in resting potential as in sodium inversion potential. PMID: 23665214
- Hence we can conclude that increase in the expression of ciliary neurotropic factor gene, as a nerve growth factor, following ultrasound radiation, can be considered as the reason of the effect of ultrasound on the rate of injured nerve regeneration. PMID: 23982826
- NO signaling induces CNTF expression in astrocytes that favors the beneficial outcomes of reactive astrogliosis in vivo. PMID: 23264628
- The data strongly suggested that intracellular ciliary neurotrophic factor may directly modulate proopiomelanocortin gene expression via the activation of ciliary neurotrophic factor receptors in the cell nucleus. PMID: 22146310
- The results of this study showed taht increased CNTF and CNTFR complex in the sprouting, metabolically active supraoptic nucleus are related directly to the sprouting response and not the increase in neurosecretory activity. PMID: 22037350
- CNTF promotes motor reinnervation of the MCN stump after its end-to-side neurorrhaphy with ulnar nerve and improves functional recovery of the biceps brachii muscle. PMID: 21696588
- Sympathetic neurons respond to stretch with an upregulation of VEGF, which is mediated by the NGF/CNTF and TrkA signaling pathway paralleled by HIF-1alpha expression. PMID: 21640078
- CNTF induces regeneration of cone outer segments in a rat model of retinal degeneration PMID: 20209167
- The CNTF mRNA in the distal stumps of injured spinal cords increased significantly on postoperation days 1-3, then returned to normal level on day 14. PMID: 19626993
- activates spinal cord astrocytes, stimulating their production and release of fibroblast growth factor-2, to increase motor neuron survival PMID: 11771938
- CNTF promotes the outgrowth of embryonic cranial motor neurons in isolated stage E12 hindbrain explants. PMID: 11932952
- CNTF is expressed in the rat pineal gland and eyes during embryonic development and supports the in vitro survival of neonatal sympathetic neurons, which innervate pineal glands immediately after birth. PMID: 11973480
- Retinoic acid had no significant effect on the expression of this protein in OLN-93 oligodendrocytes. PMID: 12397370
- CNTF affects adipocyte gene expression, and the specific receptor for this cytokine is induced in rodent models of obesity/type II diabetes PMID: 12424252
- In olfactory bulb, ciliary neurotrophic factor is localized to ensheathing cell nuclei, cell bodies and axon-enveloping processes; additionally, individual axons of olfactory neurons are CNTF immunoreactive. PMID: 12849744
- Our novel findings of increased cardiac CNTF and cardiopulmonary MCP-1 mRNA indicate a role for these factors in the pathogenesis of heart failure. PMID: 12950323
- Results show that ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and its receptor (CNTFRalpha) are differentially regulated in hippocampal neurons and reactive astrocytes following kainic acid injection. PMID: 15179044
- CNTF and its receptors are differentially expressed after optic nerve transection and could help delay retinal ganglion cell death in such a stressful environment. PMID: 15193523
- data suggest CNTF decreases lean body weight through a combination of appetite inhibition & ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway activation; findings show that CNTF is at least in part responsible for anorexia & weight loss found with neuronal injury PMID: 15304243
- CNTF-CNTFRalpha activates the JAK/STAT pathway leading to enhanced Cx43 expression and intercellular coupling PMID: 15342787
- CNTF/CPT-cAMP-induced retinal ganglion cell survival & axonal regeneration are a result of multiple pathway actions, with PKA as an essential component, but these pathways can function in an antagonistic manner under different conditions. PMID: 15574731
- CNTF expression is up-regulated from the day following intracerebral hemorrhage, with increased expression observed in brain tissue surrounding the hematoma lesion and white matter structures in association with astroglial proliferation. PMID: 15755520
- in skeletal muscle, CNTF can rapidly decrease sodium currents by altering inactivation gating, probably through an intracellular PKC-dependent mechanism that could lead to decreased membrane excitability PMID: 15831538
- Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents acute lipid-induced insulin resistance by attenuating ceramide accumulation and phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in peripheral tissues PMID: 16396984
- A notable decrease in ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) was demonstrated by Western blot after ammonia treatment, concurring with the reduction in CNTF mRNA observed in DNA microarrays. PMID: 16483693
- Ciliary neural trophic factor may mimic leptin's effects in skeletal muscle [comment] PMID: 16617151
- Results indicate that Sox10 is necessary and sufficient for regulating ciliary neurotrophic factor expression in the peripheral nervous system. PMID: 16684879
- Three-dimensional reconstructions of CNTF-immunoreactive axonal bulbar projections of these neurons revealed an ordered bilaterally symmetric pattern. PMID: 16999202
- The CNTF signaling pathway acts via regulation of nitric oxide production to modulate developmental programmed cell death of postmitotic rod precursor cells. PMID: 17054938
- Co-administration of ciliary neurotrophic factor with its soluble receptor protects against neuronal death and enhances neurite outgrowth. PMID: 18086669
- Cntf negatively regulates the phototransduction machinery in rod photoreceptors: implications for light-induced photostasis plasticity. PMID: 18188971
- Differentiation of TsAM5D chromaffin cells by glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) plus CNTF at 39 degrees C become dependent solely on nerve growth factor (NGF) for their survival and neurite outgrowth. PMID: 18293415
- CNTF can increase microglial phagocytosis through a calcium-mediated pathway. Our results also suggest that the upregulation of alphav integrin by CNTF could be involved in the increased phagocytotic activity of microglia. PMID: 18401707
- Data show that both ciliary neurotrophic factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 are present in regions of elevated oligodendrocyte progenitor cell proliferation and generation after spinal cord injury and may play a role in injury-induced gliogenesis. PMID: 18615534
- increased CNTF occurs in response to conditions which induce high levels of phagocytic activity by perivascular cells in the axotomized neurohypophysis PMID: 18805412
- CNTF may act as a protective factor against weight gain during hypercaloric diet and could account for individual differences in the susceptibility to obesity. PMID: 18950628
- study showed CNTF is up-regulated by ammonia exposure, through mediation of p38 MAPK activation in astrocytes; also observed that SAPK/JNK & Erk1/2 activations in oligodendrocytes & neurons also play indirect roles in CNTF synthesis by astrocytes PMID: 18992343
- studies indicate that CNTF can activate microglia and dendritic-like microglia similar to interleukin-6 (IL-6); however, unlike IL-6, CNTF does not stimulate the expected signaling pathways in microglia, nor does it appear to require gp130 PMID: 19267906
- CNTF could promote axon regeneration, Schwann cell migration, monocyte infiltration and activation. CNTF might also indirectly promote axonal regeneration by further activating the JAK-STAT3 pathway. PMID: 19289286
- Data demonstrate that CNTF is a potent axon growth-promoting factor for mature retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), and that exogenously applied CNTF stimulates RGCs indirectly via a mechanism that depends on astrocyte-derived CNTF. PMID: 19332123
- The effect of gp130 stimulation on glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in primary hippocampal neurons PMID: 12150983
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:CNTF family
-
组织特异性:Nervous system.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:25707
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000016690
UniGene: Rn.6067
Most popular with customers
-
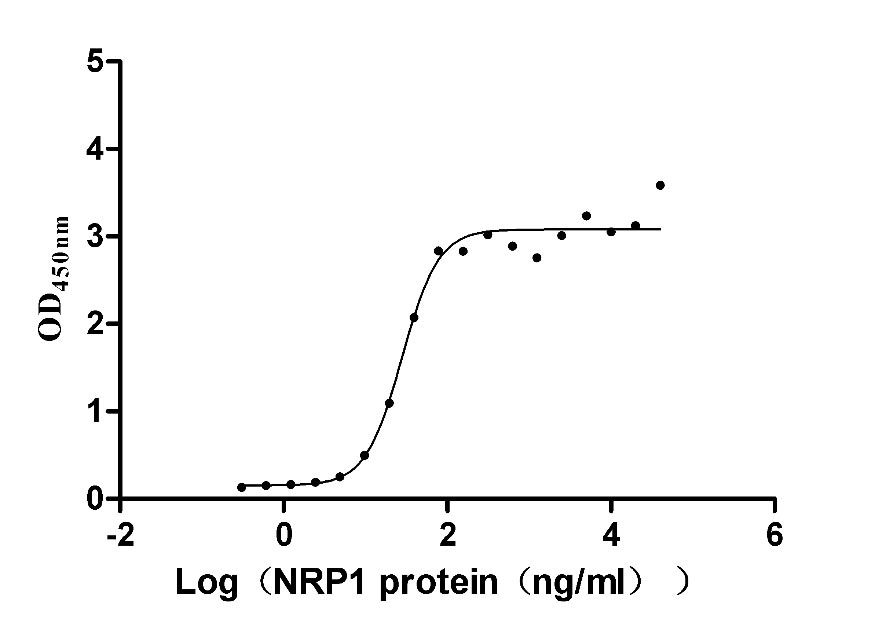
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
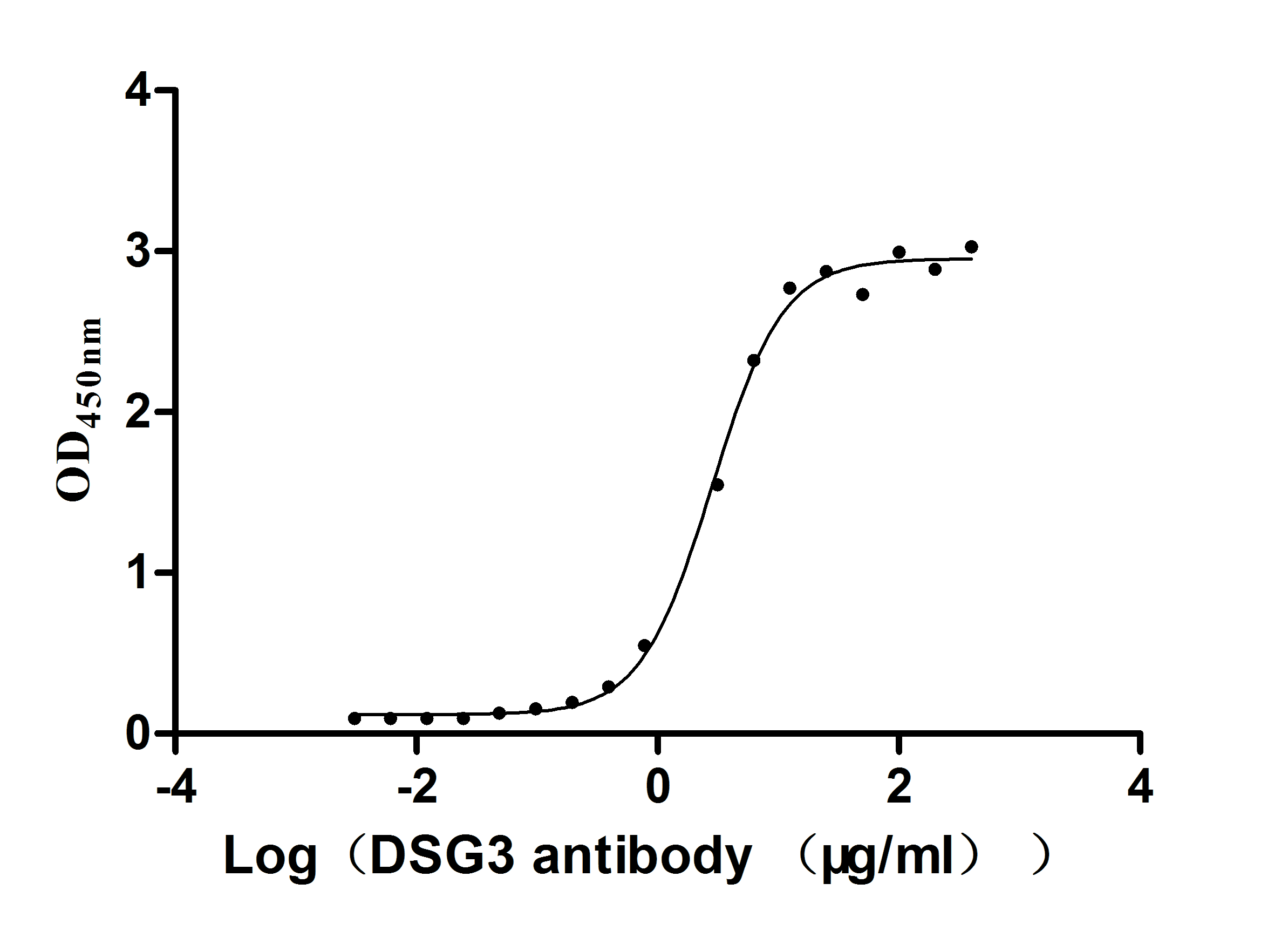
Recombinant Mouse Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
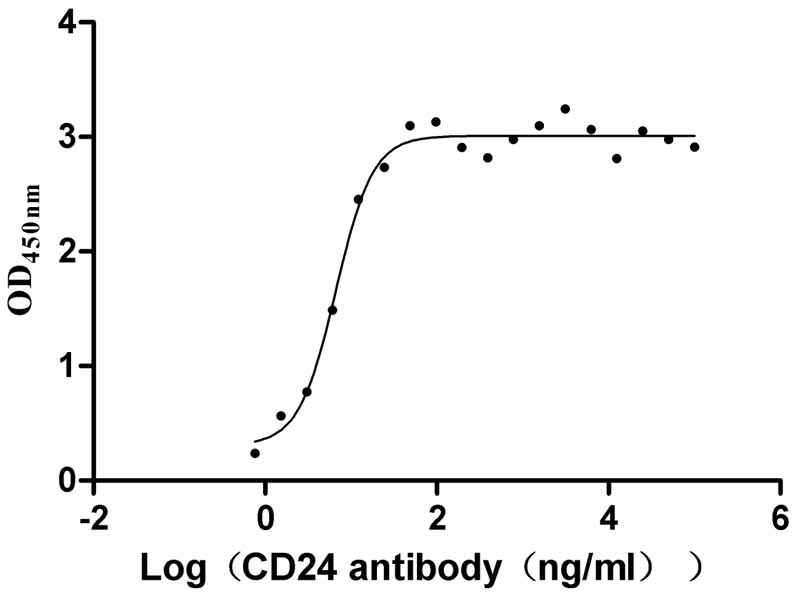
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
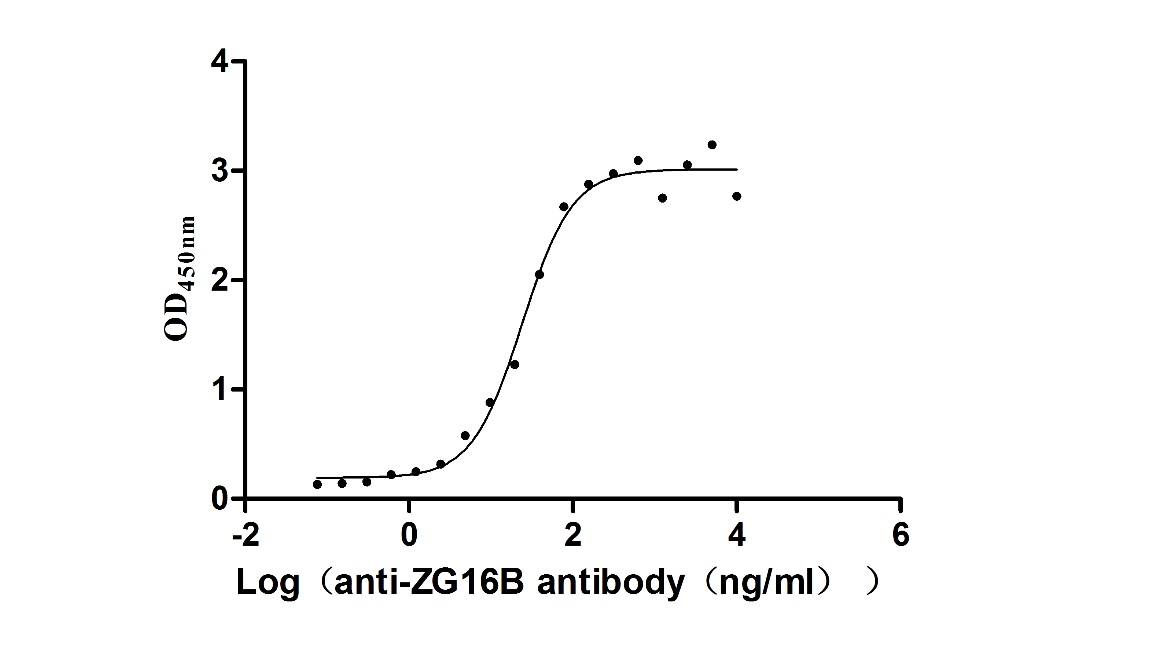
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)