Recombinant Mouse Vitamin K-dependent protein C (Proc)
-
货号:CSB-YP018742MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP018742MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP018742MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP018742MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP018742MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Proc; Vitamin K-dependent protein C; EC 3.4.21.69; Anticoagulant protein C; Autoprothrombin IIA; Blood coagulation factor XIV) [Cleaved into: Vitamin K-dependent protein C light chain; Vitamin K-dependent protein C heavy chain; Activation peptide]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:42-460
-
氨基酸序列ANSFLEEMR PGSLERECME EICDFEEAQE IFQNVEDTLA FWIKYFDGDQ CSAPPLDHQC DSPCCGHGTC IDGIGSFSCS CDKGWEGKFC QQELRFQDCR VNNGGCLHYC LEESNGRRCA CAPGYELADD HMRCKSTVNF PCGKLGRWIE KKRKILKRDT DLEDELEPDP RIVNGTLTKQ GDSPWQAILL DSKKKLACGG VLIHTSWVLT AAHCVEGTKK LTVRLGEYDL RRRDHWELDL DIKEILVHPN YTRSSSDNDI ALLRLAQPAT LSKTIVPICL PNNGLAQELT QAGQETVVTG WGYQSDRIKD GRRNRTFILT FIRIPLVARN ECVEVMKNVV SENMLCAGII GDTRDACDGD SGGPMVVFFR GTWFLVGLVS WGEGCGHTNN YGIYTKVGSY LKWIHSYIGE KGVSLKSQKL
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent serine protease that regulates blood coagulation by inactivating factors Va and VIIIa in the presence of calcium ions and phospholipids. Exerts a protective effect on the endothelial cell barrier function.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data show that activated protein C signals via protease activated receptors PAR2/PAR3 to expand Treg cells, mitigating the disease in mice. PMID: 28827518
- APC modifies pulmonary fibrosis by limiting thrombin-dependent macrophage recruitment. PMID: 27295971
- Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of protein C in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice creates a condition that allows the occurrence of spontaneous atherothrombosis. PMID: 28302625
- These findings reveal a novel biological function and mechanism of the protein C pathway in which protein S and the aPC-cleaved form of fV are cofactors for anti-inflammatory cell signaling by aPC in the context of endotoxemia and infection PMID: 26341257
- activated PC-EPCR-PAR1 signaling promotes hematopoietic stem cell retention in bone marrow. PMID: 26457757
- impaired EPCR/protein C-binding interactions not only result in procoagulant and proinflammatory effects, but also impact hematopoiesis PMID: 26045607
- SOD prevents thrombomodulin methionine oxidation, promotes protein C activation, and protects against arterial and venous thrombosis in mice. PMID: 26069236
- sPLA2-V plays a thrombogenic role by impairing the ability of EPCR to promote protein C activation. PMID: 25069533
- Data identify anticoagulant activated protein C as a "metaplastic molecule", capable of shifting the threshold of LTP towards further potentiation PMID: 24753100
- Histones regulate activated protein C formation in a manner similar to PF4 and suggest heparinoids may be benificial in sepsis. PMID: 24177324
- EPCR and APC play a limited role in the host response during pulmonary tuberculosis. PMID: 23348224
- Inhibition of the anticoagulant function of activated protein C does not interfere with its protective role during Gram-negative pneumosepsis, suggesting a more prominent role for cytoprotective effects of APC . PMID: 23216621
- RNA interference of Serpinc1 and/or Proc allows for evaluation of the function of these genes in vivo and provides a novel, controlled mouse model for spontaneous venous thrombosis. PMID: 23550037
- Activated protein C ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by epigenetically inhibiting the redox enzyme p66Shc. PMID: 23267072
- Polyphosphate can elicit potent pro-inflammatory responses through the activation of NF-kappaB, which are counteracted by activated protein C. PMID: 22372856
- The aPC mechanism of action is complex, involving induction of Treg differentiation, inhibition of inflammation, and possibly direct cyto-protective effects on beta cells. PMID: 22447930
- We conclude that activated protein C generation and function can be modulated by changes in phospholipid occupancy of its endothelial cell receptor. PMID: 22167755
- Findings show that the protein C (PC) pathway is a unique system involved in controlling intestinal homeostasis and inflammation by regulating epithelial barrier function. PMID: 22109555
- Endogenous PC has strong effects on the host response to lethal influenza A infection, inhibiting pulmonary coagulopathy and inflammation on the one hand, but facilitating neutrophil influx and protein leak and accelerating mortality on the other hand. PMID: 21330465
- Endogenous protein C inhibits activation of coagulation and transiently lowers bacterial outgrowth in murine Escherichia coli peritonitis PMID: 21251201
- endogenous APC is essential for immune-mediated cancer cell elimination PMID: 21420234
- Age-dependent vulnerability to endotoxemia is associated with reduction of anticoagulant factors activated protein C and thrombomodulin. PMID: 20348393
- endogenous acute coagulopathy is mediated by the activation of the protein C pathway PMID: 19333141
- These findings show a new function for the thrombomodulin-protein C system in controlling the growth and survival of trophoblast cells in the placenta, which is essential for the maintenance of pregnancy. PMID: 12579195
- surviving Thrombomodulin pro/pro mice displayed increased lung inflammation accompanied by higher mycobacterial loads in liver and spleen PMID: 16014564
- directly links host endogenous levels of PC with various coagulation, inflammation, and hemodynamic end points following a severe acute inflammatory challenge PMID: 17047151
- in the presence of a limited level of the anticoagulant, PC, placental homeostasis can be restored by reducing TF expression, thus facilitating proper embryonic implantation PMID: 18647222
- species specificity in the effects of pregnancy on the major determinants of the protein C system; Pregnancy causes a decrease in APC resistance in mice, which can be explained by the elevation of protein S levels and increased TFPI activity in plasma. PMID: 19036061
- An important role for the aPC/EPCR pathway in reducing metastasis via inhibition of tumor cell adhesion and transmigration. PMID: 19188668
- Protection of vascular barrier integrity by activated protein C in murine models depends on protease-activated receptor-1. PMID: 19350118
- activated PC is barrier-protective in ventilator lung injury and endothelial PC receptor is a critical participant in APC-mediated protection PMID: 19363121
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted. Golgi apparatus. Endoplasmic reticulum.
-
蛋白家族:Peptidase S1 family
-
组织特异性:Plasma; synthesized in the liver.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:19123
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000132226
UniGene: Mm.2786
Most popular with customers
-
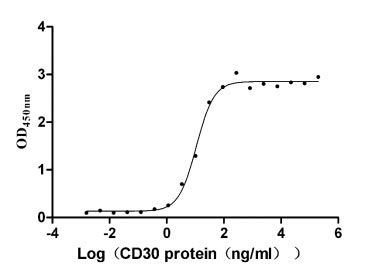
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
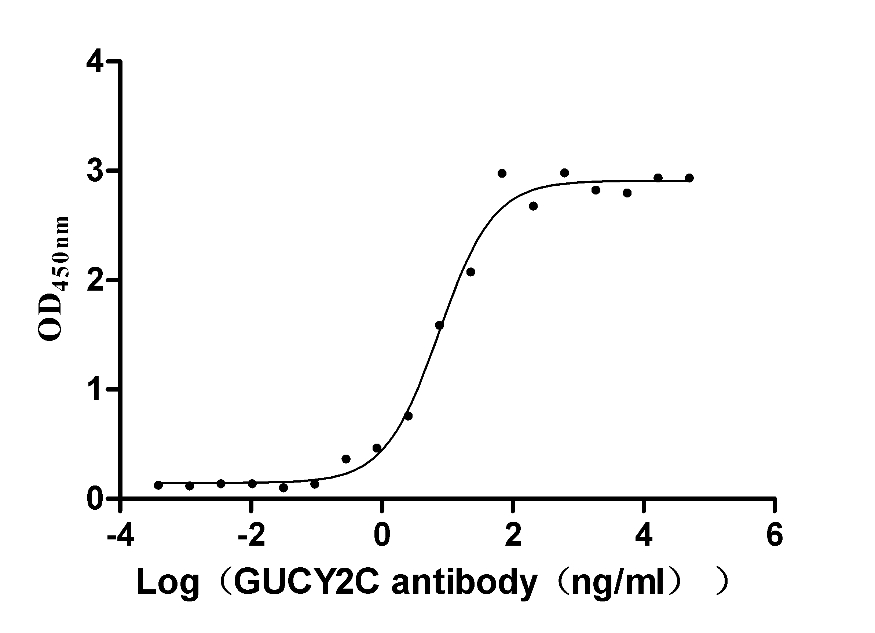
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
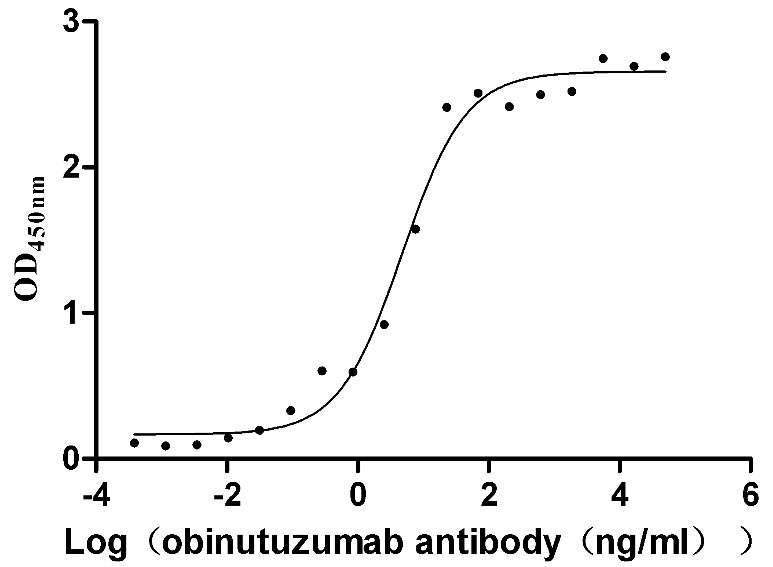
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
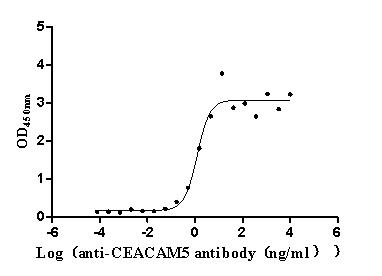
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
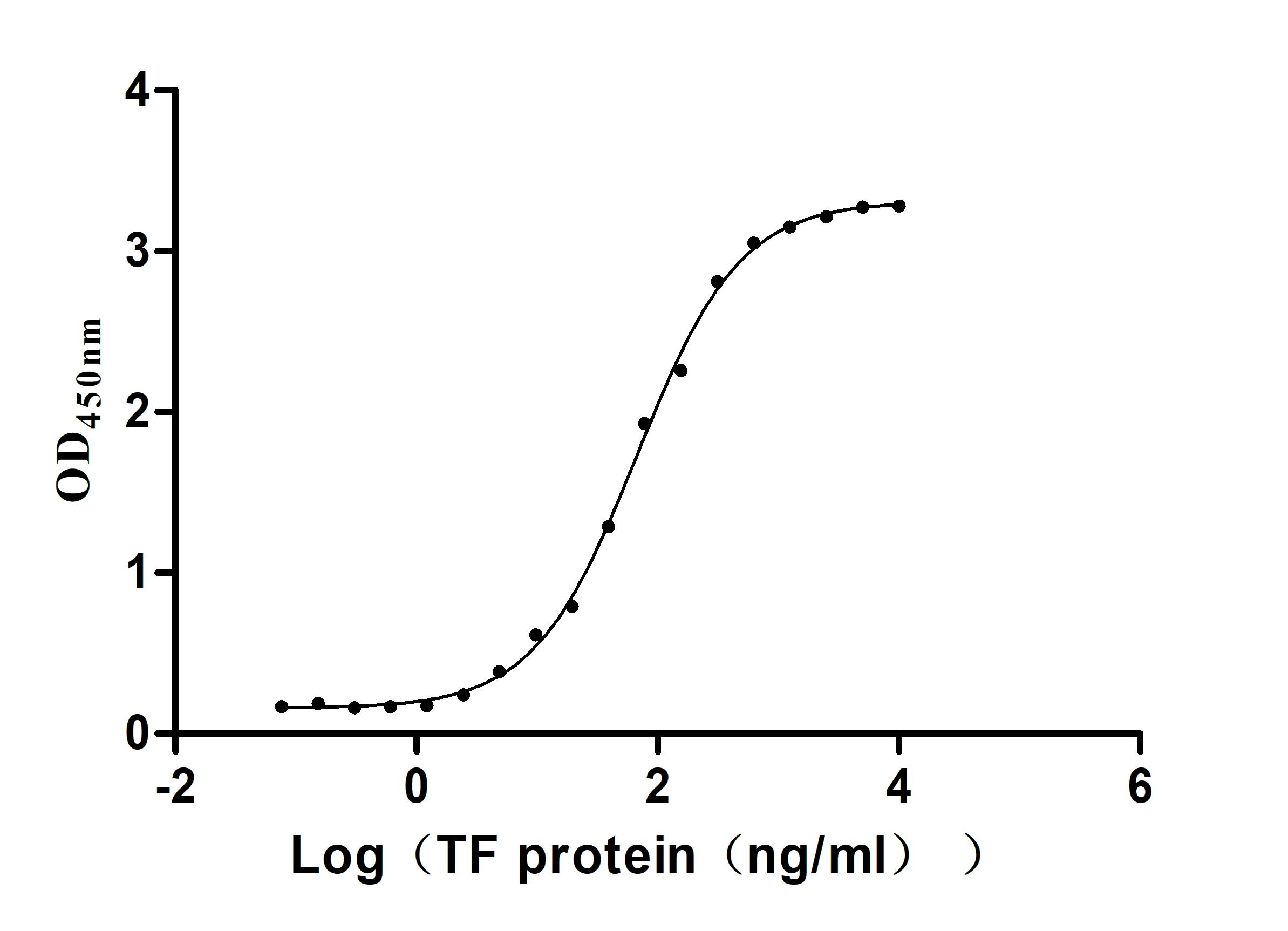
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
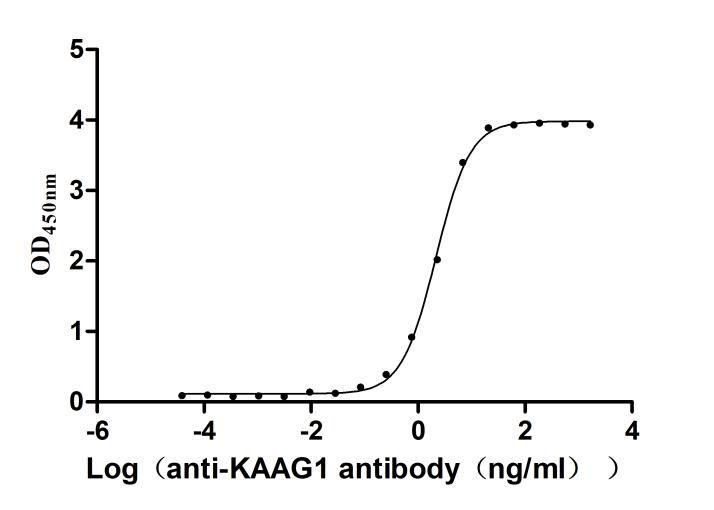
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)