Recombinant Mouse Transcription factor HES-1 (Hes1)
-
货号:CSB-YP010307MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP010307MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP010307MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP010307MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP010307MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Hes1; Hes-1; Transcription factor HES-1; Hairy and enhancer of split 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-282
-
氨基酸序列MPADIMEKNS SSPVAATPAS VNTTPDKPKT ASEHRKSSKP IMEKRRRARI NESLSQLKTL ILDALKKDSS RHSKLEKADI LEMTVKHLRN LQRAQMTAAL STDPSVLGKY RAGFSECMNE VTRFLSTCEG VNTEVRTRLL GHLANCMTQI NAMTYPGQAH PALQAPPPPP PSGPAGPQHA PFAPPPPPLV PIPGGAAPPP GSAPCKLGSQ AGEAAKVFGG FQVVPAPDGQ FAFLIPNGAF AHSGPVIPVY TSNSGTSVGP NAVSPSSGSS LTSDSMWRPW RN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional repressor of genes that require a bHLH protein for their transcription. May act as a negative regulator of myogenesis by inhibiting the functions of MYOD1 and ASH1. Binds DNA on N-box motifs: 5'-CACNAG-3' with high affinity and on E-box motifs: 5'-CANNTG-3' with low affinity. May play a role in a functional FA core complex response to DNA cross-link damage, being required for the stability and nuclear localization of FA core complex proteins, as well as for FANCD2 monoubiquitination in response to DNA damage.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- this paper shows that epithelial Hes1 maintains gut homeostasis by preventing microbial dysbiosis PMID: 29297498
- miR-374b regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells through targeting Hes1. Overexpression of Hes1 reverses the effect of miR-374b overexpression on neural stem cells differentiation. PMID: 29902458
- Hes1 might contribute to the maturation and the cellular structure organization of biliary epithelial cells, which provides new insight into understanding the pathology of biliary atresia. PMID: 30090006
- the results raise the possibility that HES1 or other genes that affect HES1 expression could be involved in the etiology of Ectopic pancreas . PMID: 30093553
- These results suggest that hyperhomocysteinemia-enhanced brain damage is associated with increased autophagy and neuronal apoptosis in Apo E(-/-) mice, in which downregulation of hes1 and hes5 is involved. PMID: 29171783
- Although Hes5-GFP and Hes1 are coexpressed in particular developmental contexts, we also noted cohorts of lens or retinal cells expressing just one factor. The dynamic Hes5-GFP expression pattern, coupled with its derepressed expression in Hes1 mutants, suggests that this transgene contains the relevant cis-regulatory elements that regulate endogenous Hes5 in the mouse lens and retina. PMID: 28675662
- there is a link between Dmrta2 modulation of Hes1 expression and the maintenance of neural progenitor cells during cortical development PMID: 28655839
- Hes-1 expression is maintained in neural progenitor territory throughout mouse neocortical development, a simple shift from Notch-independent to -dependent state makes it pleiotropic as the former maintains the neural stem cells in a non-dividing/slow-dividing state, whereas the latter is very much required for maintenance and proliferation of radial glial cells. PMID: 27405330
- inhibition of PTEN by Notch1/Hes1 in response to high glucose concentration inhibits autophagy, which is associated with the progression of fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy PMID: 29496446
- this paper shows the critical role of the Notch1-Hes1 signaling cascade in the regulation of innate immunity in acetaminophen-triggered liver inflammation PMID: 28286920
- results suggest that SCF(FBXL14) promotes neuronal differentiation by targeting HES1 for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis and that the C-terminal WRPW motif in HES1 is required for this process PMID: 29070679
- Notch signaling and Id2/3 regulate neurogenesis in a complementary manner and ID factors can induce neural stem cell maintenance and quiescence in the absence of Notch. PMID: 28974640
- that HIF-1alpha but not HIF-2alpha is able to interact with either GA-binding protein alpha or GA-binding protein beta1 PMID: 28602625
- Hes1 disruption leads to tumor regression without perturbing normal stem cell homeostasis, preclinically validating Hes1 as a cancer therapeutic target. PMID: 28536281
- Notch1-Hes-1 signaling controls TLR7-induced autophagic death of macrophage via regulation of P62 in mice with lupus. PMID: 27537524
- Hes1 plays a key role in acinar cell integrity and plasticity on cellular insults. PMID: 27639167
- the RBPjkappa-dependent Notch targets HES1 and HES5 suppress chondrogenesis and promote the onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy. PMID: 27160681
- this study identifies Hes1 as a homeostatic suppressor of inflammatory responses that exerts its suppressive function by regulating transcription elongation PMID: 27322654
- This study demonstrated that Hes1 and Hes5 modulate not only maintenance of progenitor cells but also pituicyte versus neuron fate specification during neurohypophysis development. PMID: 26348989
- We found that miR-21 acts as a bidirectional switch in the formation of IPCs by regulating the expression of target and downstream genes (SOX6, RPBJ and HES1). PMID: 26655730
- Insm1-dependent Hes1 repression is required for neuroendocrine development. PMID: 26453796
- Findings suggest the strict spatio-temporal expression of Notch effector genes plays an important role during hippocampal neurogenesis and suggests that Notch1, Hes1 and Ngn2 were regulated by changing some specific CpG sites of their promoters PMID: 25701255
- Hes1-mediated Notch activity determines the plasticity of adult pancreatic duct cells and that there may exist a dosage requirement of Sox9 for keeping the duct cell identity in the adult pancreas. PMID: 25687338
- found that Hes1 was deubiquitinated and stabilized by Usp27x and its homologs ubiquitin-specific protease 22 (Usp22) and ubiquitin-specific protease 51 PMID: 25846153
- Results suggest that Hes1 represents a negative regulator of adult neurogenesis post-traumatic brain injury (TBI) and that the precise space-time regulation of Hes1 expression in the dentate gyrus may promote the recovery of neural function following TBI PMID: 25084035
- Notch signaling can directly downregulate MUC5AC promoter activity through Hes1-dependent mechanisms. PMID: 23860410
- results indicate that HES1 acts as a master repressor, the silencing of which is required for proper glucocorticoid signaling. PMID: 24300895
- Hes1 upregulation contributes to the development of FIP1L1-PDGRA-positive leukemia in blast crisis. PMID: 24486648
- delivery of siRNA to Hes1 and Hes5 using a transfection reagent or siRNA to Hes1 encapsulated within nanoparticles increased hair cell numbers in non-toxin treated organotypic cultures of cochleae and maculae PMID: 23850665
- Curcumin reduced arginase activity and up regulated TGF-beta1 and HES-1 transcripts in mice. PMID: 22982865
- Hes1 and Hes5 regulate vascular remodeling and arterial fate specification of endothelial cells in the development of the brain; they are critical transducers of Notch signals in brain vascular development. PMID: 23871867
- Our data indicate that the development of pharyngeal organs and survival of neural-crest-derived mesenchyme in pharyngeal arches are critically dependent on Hes1. PMID: 23686616
- Hes-1 downregulation allows PDX-1 to act as a major determinant of cholangiocyte proliferation in response to cholestatic injury. PMID: 23207146
- miR-1 promotes the differentiation of MSCs into cardiac lineage in part due to negative regulation of Hes-1 PMID: 23509692
- Data indicate that Notch1 and Notch2 are expressed and localized in the nuclei of the label-retaining cells (LRCs), and the expression of Notch-inducible genes, Hes1 and Hey2, was elevated in LRCs. PMID: 23199335
- In the postnatal retina, NOTCH2, as well as the Notch downstream genes, HES1 and SOX9, were detected in VSX2/Cyclin D1/SOX2-expressing cells in the postnatal retina, and in the mature retina NOTCH2 was most abundant in Muller glia PMID: 23277114
- Differential expression of Hes1 between hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoietic progenitor cells resulted in the distinct responses of these cells to the leukemic condition. PMID: 23255132
- Spatial stochastic modelling of the Hes1 gene regulatory network: intrinsic noise can explain heterogeneity in embryonic stem cell differentiation PMID: 23325756
- The results indicate that Jagged-1-Hes-1 signaling can suppress the skewing of CD4+ T cells toward Th17 cells via RORgammat, for which Hes-1 may be crucial. PMID: 23489689
- Notch-Hes1 pathway regulates ovarian somatic cell development, which is necessary for oocyte survival and maturation. PMID: 23274689
- Hes1 repressor is essential regulator of hematopoietic stem cell development downstream of Notch signaling. PMID: 23267012
- Hes1 expression dynamics in developing brain is regulated by MicroRNA9. PMID: 23134481
- MicroRNA-9 Modulates Hes1 ultradian oscillations by forming a double-negative feedback loop. PMID: 22840391
- The results suggest that Hes1 plays a critical role in regulating the development of neural crest derivatives in the mouse cervical region. PMID: 22689348
- These results point to HES1, via repression of PTEN, and c-Myc as critical mediators of Notch function at the beta-selection checkpoint. PMID: 22649105
- the expression levels of Hes1 transcripts were also significantly decreased in denervated eyes. PMID: 22232434
- in Apc mutation-induced intestinal tumors, inactivation of Hes1 was sufficient for reducing tumor cell proliferation and inducing differentiation of tumor cells; results indicate Hes genes cooperatively regulate intestinal development and homeostasis PMID: 22318232
- seven conserved DNA sequence blocks, representing the hes1 promoter and six novel cis-regulatory modules PMID: 22167192
- The co-repressor recruitment mediated through WRPW domain of Hes-1 has contributed to the repressive effect. PMID: 21744064
- Hes1, Atoh1, and Gfi1b form a fate-determining Notch signaling driven ternary switch in the developing intestinal epithelium. PMID: 22185794
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Expressed at high levels in undifferentiated neural precursor cells, but the level of expression decreases as neural differentiation proceeds.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:15205
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000023171
UniGene: Mm.390859
Most popular with customers
-
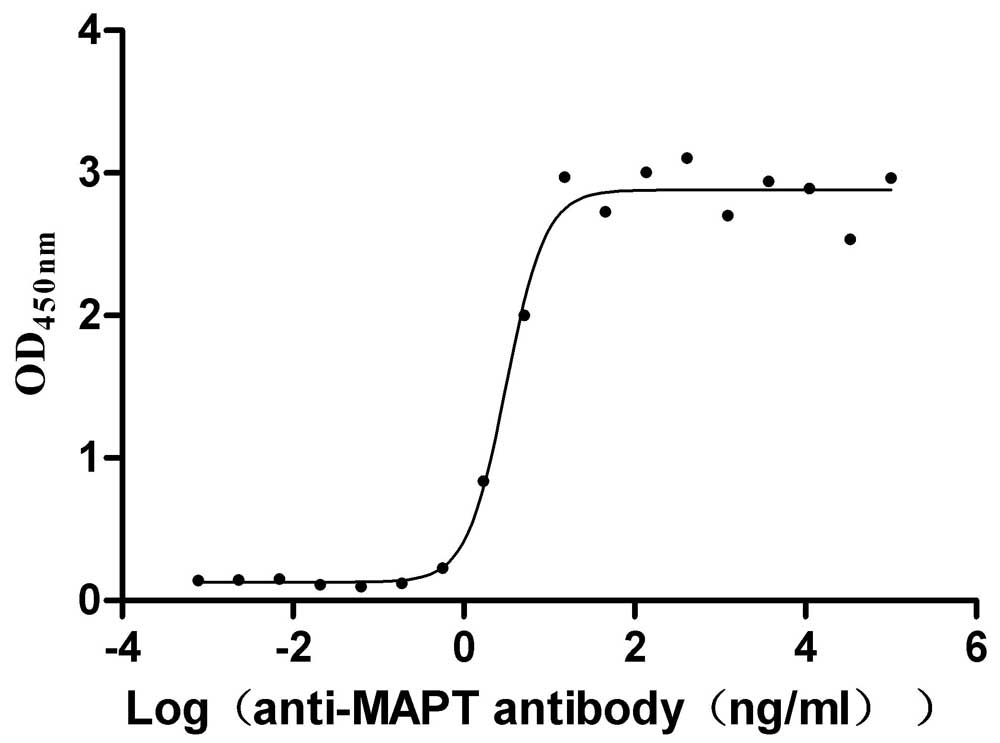
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
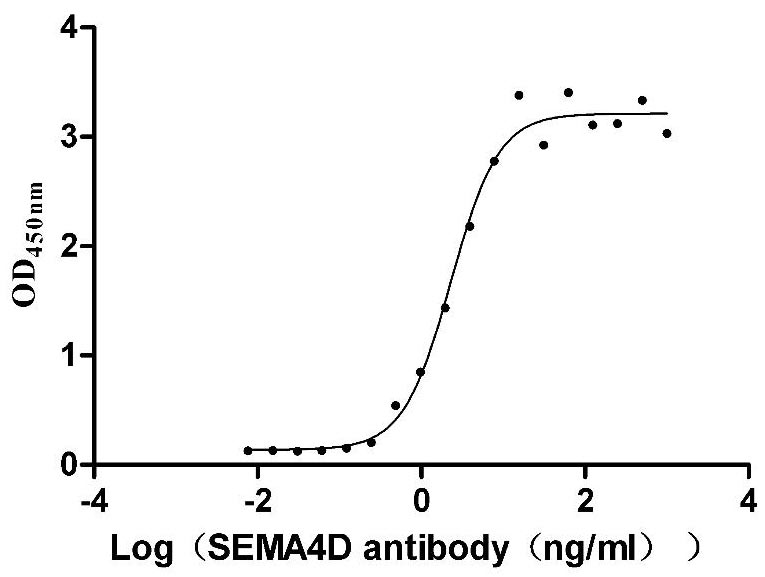
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
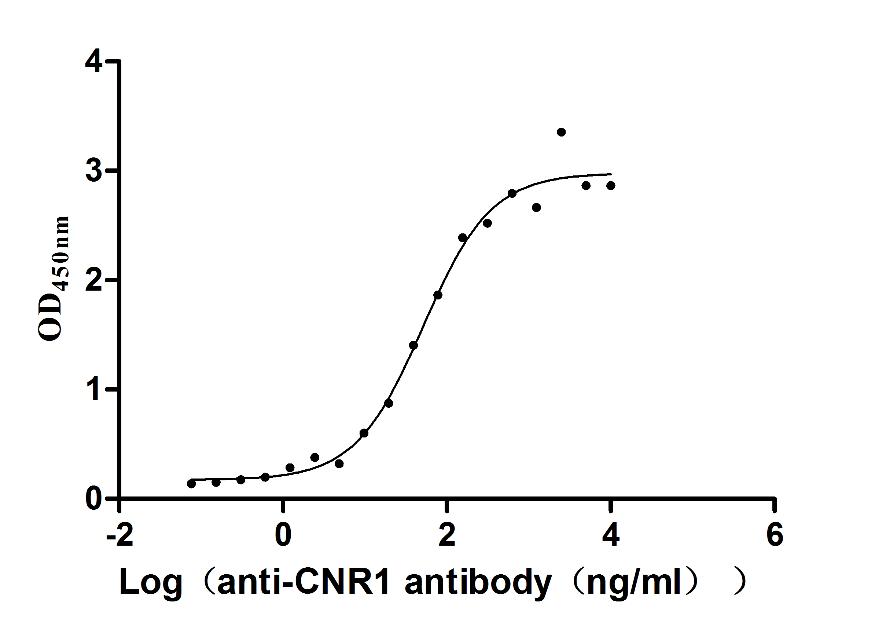
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
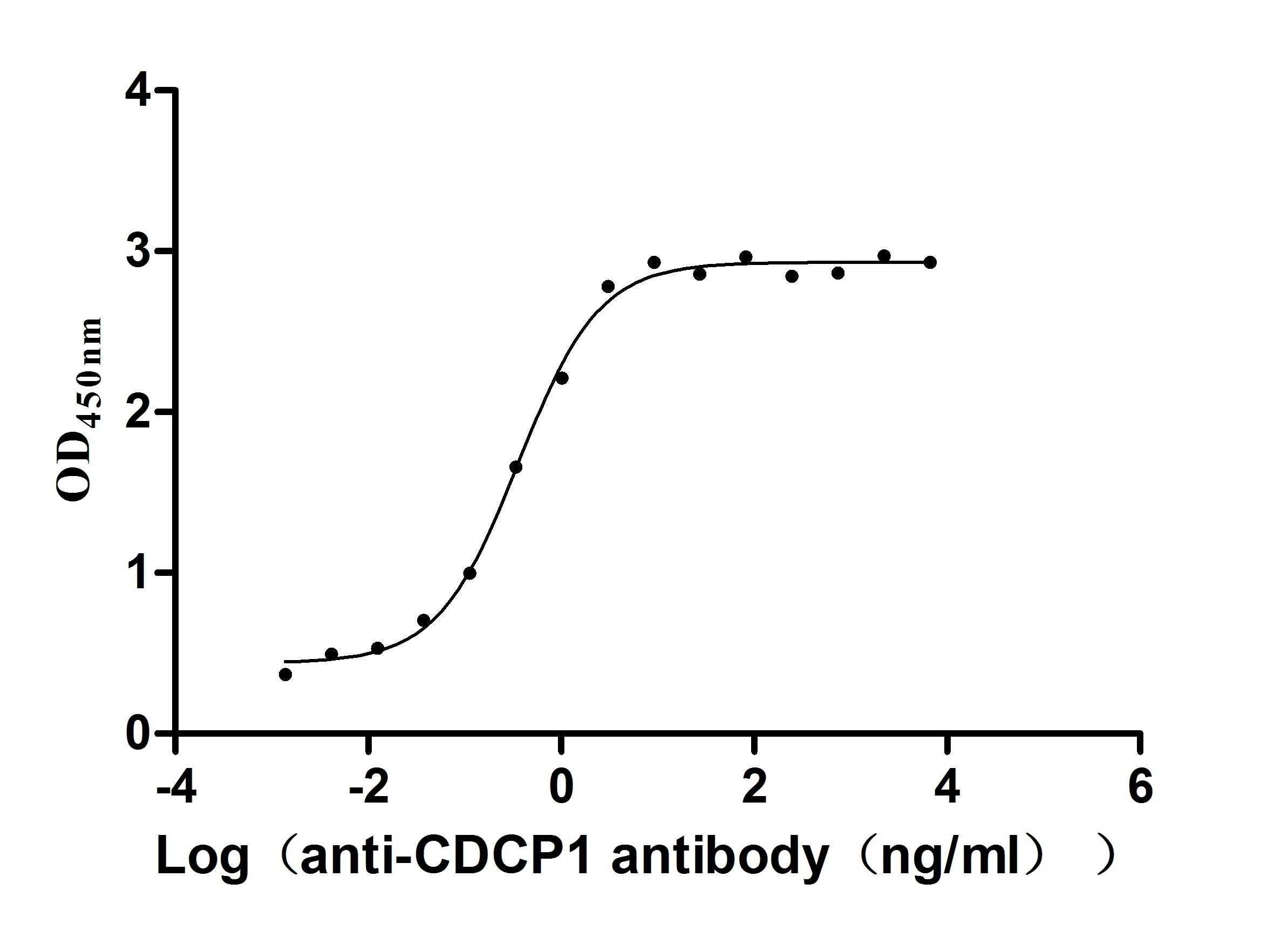
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)