Recombinant Mouse Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-YP803849MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Txnip; Vdup1; Thioredoxin-interacting protein; Vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:Yeast
-
分子量:46.4kDa
-
表达区域:1-397aa
-
氨基酸序列MVMFKKIKSFEVVFNDPEKVYGSGEKVAGRVIVEVCEVTRVKAVRILACGVAKVLWMQGSQQCKQTLDYLRYEDTLLLEEQPTAGENEMVIMRPGNKYEYKFGFELPQGPLGTSFKGKYGCVDYWVKAFLDRPSQPTQEAKKNFEVMDLVDVNTPDLMAPVSAKKEKKVSCMFIPDGRVSVSARIDRKGFCEGDDISIHADFENTCSRIVVPKAAIVARHTYLANGQTKVFTQKLSSVRGNHIISGTCASWRGKSLRVQKIRPSILGCNILKVEYSLLIYVSVPGSKKVILDLPLVIGSRSGLSSRTSSMASRTSSEMSWIDLNIPDTPEAPPCYMDIIPEDHRLESPTTPLLDDVDDSQDSPIFMYAPEFQFMPPPTYTEVDPCVLNNNNNNNNVQ
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:
The production of this Recombinant Mouse Txnip protein required the insertion of a DNA fragment (Txnip, 1-397aa) into the plasmid vector and the transferral of this vector into Yeast cells (the step of transformation). The cells were then cultured and induced to express the Txnip protein. This recombinant protein was fused with N-terminal 6xHis tag. Its purity is 90%+ determined by SDS-PAGE.
Txnip (Txnip or Vdup1) is a gene providing an instruction of making a protein named thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) in mus musculus (mouse). This gene has many orthologs in multiple mammals, such as human, norway rat, pig, cattle, etc. The protein encoded by this gene is also known as vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1 and belongs to arrestin family.Txnip protein inhibits the antioxidative function of thioredoxin by its enzyme inhibitor activity and leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and cellular stress. This protein is involved multiple biological processes, including cell cycle, cellular response to tumor cell, response to oxidative stress, etc.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:May act as an oxidative stress mediator by inhibiting thioredoxin activity or by limiting its bioavailability. Interacts with COPS5 and restores COPS5-induced suppression of CDKN1B stability, blocking the COPS5-mediated translocation of CDKN1B from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Inhibits the proteasomal degradation of DDIT4, and thereby contributes to the inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Functions as a transcriptional repressor, possibly by acting as a bridge molecule between transcription factors and corepressor complexes, and over-expression will induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Required for the maturation of natural killer cells. Acts as a suppressor of tumor cell growth.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- TXNIP facilitates the oxidative stress response in glomerular mesangial cells partially through AMPK pathway. PMID: 30142540
- Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) is highly induced in retinal vascular endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. Data (including data from studies using knockout mice) suggest that Txnip in retinal vascular endothelial cells plays role in diabetic retinal angiogenesis via Vegf/Vegfr2 and Akt/mTOR signaling. (Vegfr2 = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2) PMID: 29203232
- These results suggest that mitochondrial ROS-TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1beta axis activation is responsible for tubular oxidative injury, which can be ameliorated by MitoQ via the inhibition of mtROS overproduction PMID: 29475133
- crucial role in haematopoietic stem cell aging by inhibiting p38 activity via direct interaction PMID: 27929088
- Data show that p38MAPK phosphorylation significantly increased in lentivirus vector thioredoxin interacting protein (LV-GFP-TXNIP) cells. PMID: 29169415
- NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3 protein (NLRP3)-/- mice exhibited less severe non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) than WT mice, whereas thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) deficiency enhanced NLRP3 inflammasome. PMID: 28499273
- TXNIP is a direct substrate of protein kinase B (AKT) and is responsible for mediating AKT-dependent acute glucose influx after growth factor stimulation. PMID: 28591573
- Our data indicate for the first time that the inflammasome is involved in the inflammatory response and cell death in hypoxia-induced beta cells through the ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 axis in vitro. This provides new insight into the relationship between hypoxia and inflammation in T2D. PMID: 29278702
- Here the s demonstrate that thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip), which regulates glucose homeostasis in mammals, binds to fructose transporters and promotes fructose absorption by the small intestine. PMID: 27725089
- thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency alleviates diabetic renal lipid accumulation through regulation of Akt/mTOR pathway PMID: 27497988
- All-trans retinoic acid plays a key role in inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via suppressing TXNIP expression, which reduces oxidative stress levels. PMID: 28322443
- TXNIP-NFYA-SREBP2/miR-33a-AMPKalpha/CROT/CPT1/HADHB pathway is conserved in mouse, rat, and human cardiomyocytes and regulates myocardial beta-oxidation. PMID: 27199118
- results suggest that melatonin confers protection against Cd-induced liver inflammation and hepatocyte death via inhibition of the TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. PMID: 28099758
- proteomic and functional analyses demonstrated that Txnip inhibits glucose transport through direct binding to glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1). An ex vivo analysis of perfused hearts further demonstrated that the enhanced functional reserve afforded by deletion of Txnip was associated with myocardial glucose utilization during beta-adrenergic stimulation. PMID: 27037370
- Thrombin activates reactive oxygen species (ROS)/thioredoxin binding protein (TXNIP)/NLRP3 signaling in BV2 microglia cells, which may indicate a mechanism that pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic contributes to the development of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). PMID: 28202418
- TxNIP appears to be an important factor in FFA-induced ROS generation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells PMID: 27702549
- Glucose exerts strong stimulatory effects on activation histone marks while having inhibitory effects on repression marks in the promoter of the TXNIP gene, and this was associated with a marked increase in expression of the proinflammatory gene in kidney. PMID: 26806835
- Diabetes induces TXNIP expressions at mRNA levels, but shows the opposite effect on GS. PMID: 27131835
- ITCH targets TXNIP for ubiquitin-proteasome degradation in cardiomyocytes and ameliorates reactive oxygen species-induced cardiotoxicity through the thioredoxin system. PMID: 26796253
- Txnip plays an important role in oxidative inflammatory response and atherosclerotic lesion development in ApoE knockout mice. PMID: 26062991
- The results indicate that a lack of TxNIP protects against diabetic nephropathy (DN) and support in vitro data that upregulation of TxNIP by glucose is a key mediator of early oxidative stress and a trigger for the development and progression of DN. PMID: 25855771
- Reactive oxygen species regulation through REDD1/TXNIP is physiological rheostat controlling stress-induced autophagy. PMID: 25916556
- These findings suggest that TXNIP is required for endothelial cell survival and homeostasis especially under stress conditions including hyperoxia. PMID: 25329456
- HG-induced NADPH oxidase activation is driven by TXNIP which subsequently triggers NALP3 inflammasome activation in podocytes and ultimately led to podocyte injury PMID: 25834832
- Data indicate that thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP)levels are induced in erythroid differentiation. PMID: 25600403
- In vivo, levels of lipogenic proteins, inflammatory molecules, PGC-1alpha, and PRMT1 were increased in the livers of HFD mice compared with those fed a chow diet, and were ameliorated in HFD Txnip(-/-) mice. PMID: 25003952
- we demonstrated that TXNIP-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells was a novel mechanism of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury PMID: 25015733
- Genetic deletion of Txnip in cells and mice led to increased protein ubiquitination and splicing of the unfolded protein response regulated transcription factor X-box-binding protein 1 at baseline as well as under endoplasmic reticulum stress. PMID: 24843047
- results demonstrate that TXNIP binding to NLRP3 is a key signaling mechanism necessary for hHcys-induced NLRP3 inflammasome formation and activation and subsequent glomerular injury. PMID: 25138219
- TXNIP is a promising new target for the development of new therapies for the treatment of retinal neurodegenerative diseases. PMID: 24283717
- The TXNIP expression is required for VEGF-mediated VEGFR2 activation and angiogenic response in vivo and in vitro. TXNIP expression regulates VEGFR-2 phosphorylation via S-glutathionylation of LMW-PTP in endothelial cells. PMID: 23718729
- We demonstrated that TXNIP impairs glucose and insulin tolerance in mice by upregulating G6pc through interaction with small heterodimer partner (SHP). PMID: 24037087
- studies have identified a novel TXNIP/miR-124a/FoxA2/IAPP signaling cascade linking the critical beta-cell signaling pathways of TXNIP and IAPP PMID: 24627476
- Data suggest that in vitro fertilization and embryo culture, even under optimal conditions, lead to long-term metabolic alterations; up-regulation of Txnip in offspring may serve as a biological markers for these ill effects. PMID: 24684304
- TXNIP regulates Src activation via regulation of VE-cadherin-SHP2-Src complex, resulting in altered endothelial cells stress fibers. PMID: 24515523
- TXNIP is a novel molecule that links NO synthesis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation during endotoxic shock. PMID: 24098117
- Nuclear factor-kappaB, c-Jun-N-terminal kinase, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 were activated much earlier and to a greater extent in Vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1 knockout mice after partial hepatectomy. PMID: 23820201
- demonstrated increased expression of TXNIP, LC3/LC3-II and p62 in renal tubular cells in diabetic nephropathy PMID: 24492284
- Txnip is a critical regulator of glucose metabolism in oocytes and is involved in maintaining cytoplasmic streaming in mouse oocytes. PMID: 23976953
- These data implicate a critical role for TXNIP in diabetes-related impairment of ischemia-mediated angiogenesis and identify TXNIP as a potential therapeutic target for the vascular complications of diabetes. PMID: 24198286
- TXNIP is a regulator of p53 and plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of the hematopoietic cells by regulating intracellular ROS during oxidative stress. PMID: 23823478
- TXNIP controls microRNA expression and insulin production and miR-204 is involved in beta-cell function. PMID: 23975026
- tnxip is responsible for mediating substrate feedback inhibition and is a potential target for modulating creatine homeostasis PMID: 23715727
- an overview of TXNIP protein and function PMID: 22750447
- Suppression of Txnip by lipopolysaccharide is accompanied by a decrease of the glucose sensing transcription factor MondoA in the nuclei. PMID: 23520550
- Data indicate that Txnip expression is increased in the hypothalamus of Gpr50-/- mice during torpor. PMID: 23584857
- The effect of hypoxia on TXNIP expression is mediated via the inhibition of the 4E-BP1/eIF4E axis of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTORC1). PMID: 23454121
- Upregulation of Trx1 by Na2S therapy in the setting of heart failure sets into motion events which ultimately leads to the attenuationof left-ventricular remodeling. PMID: 23349187
- VDUP1-deficient mice wereresistant to P. aeruginosa-induced bacteremic shock. It promoted neutrophil recruitment into the peritoneal cavity & impeded the phagocytosis of non-opsonized P. aeruginosa by the PI 3-kinase pathway in macrophages. PMID: 23246829
- Nrf2 is a key gatekeeper of Txnip transcription, suppressing both its basal expression and MondoA-driven induction to control the thioredoxin redox signaling in diabetes. PMID: 22869588
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Arrestin family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitously expressed.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:56338
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000102710
UniGene: Mm.410189
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-18.2 (CLDN18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
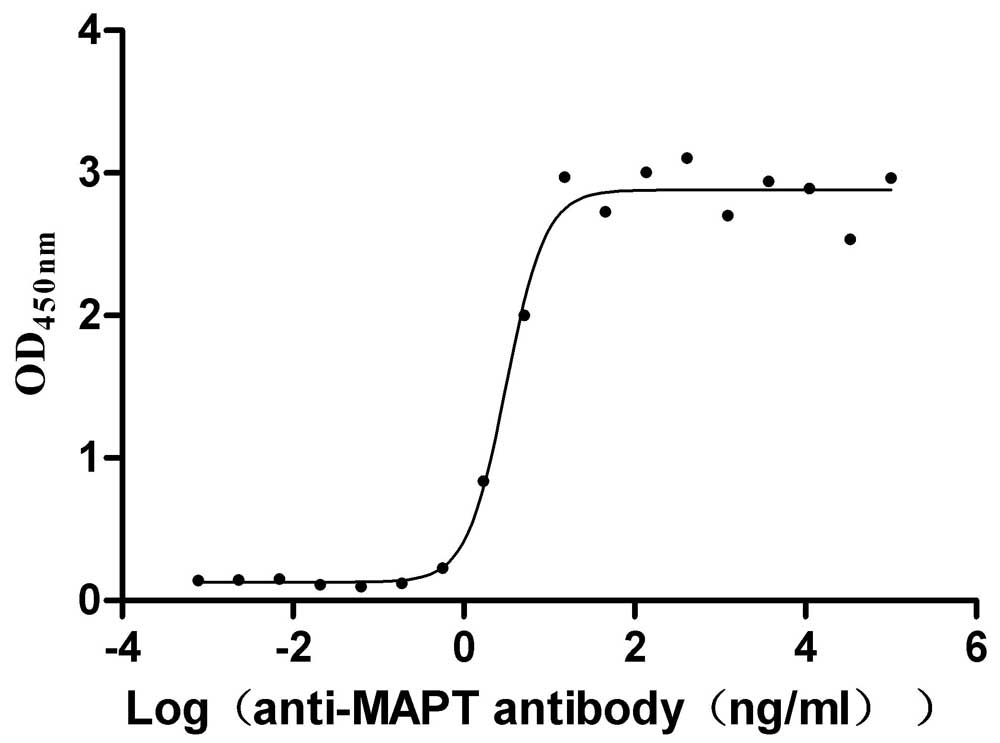
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
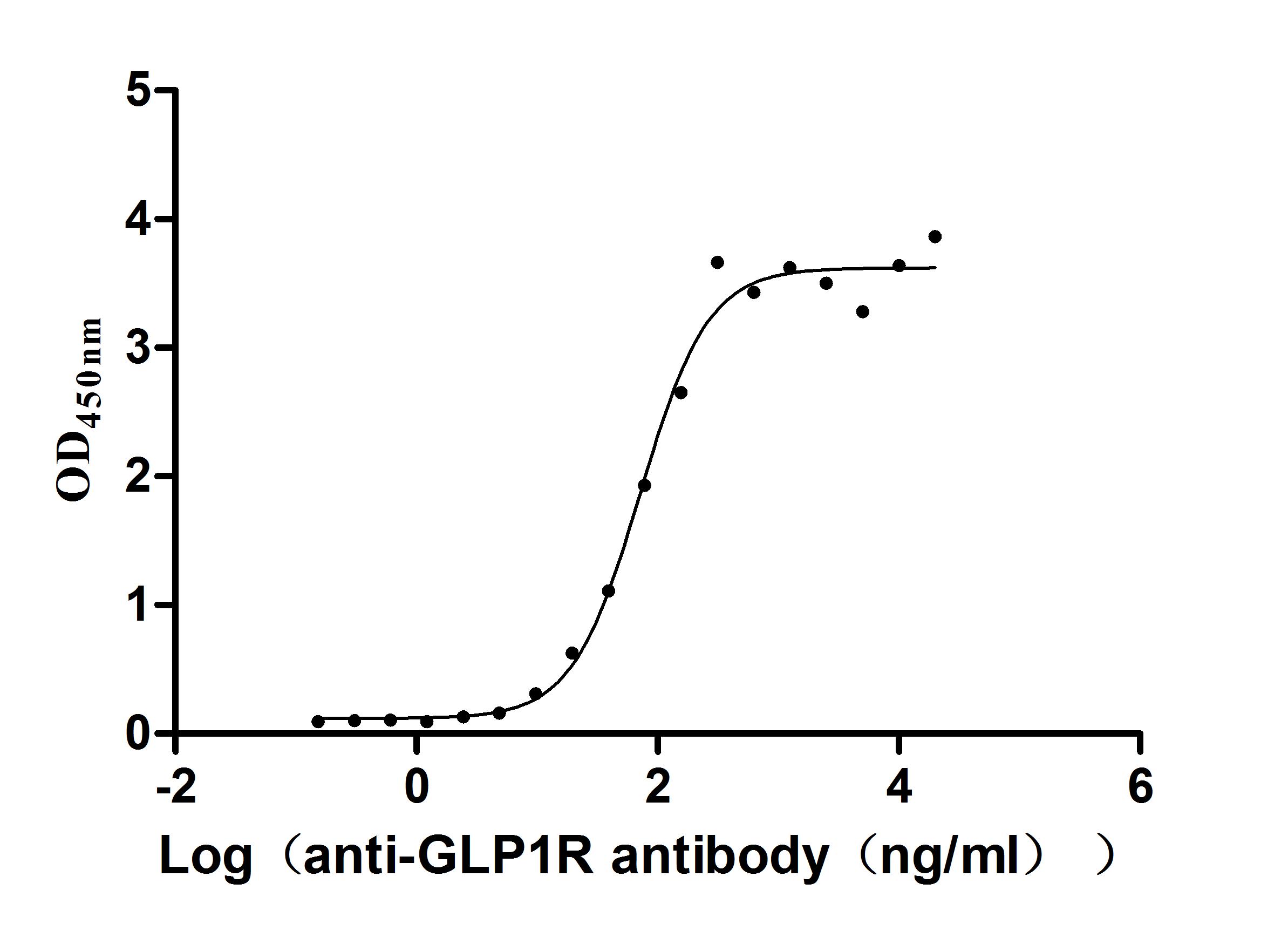
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
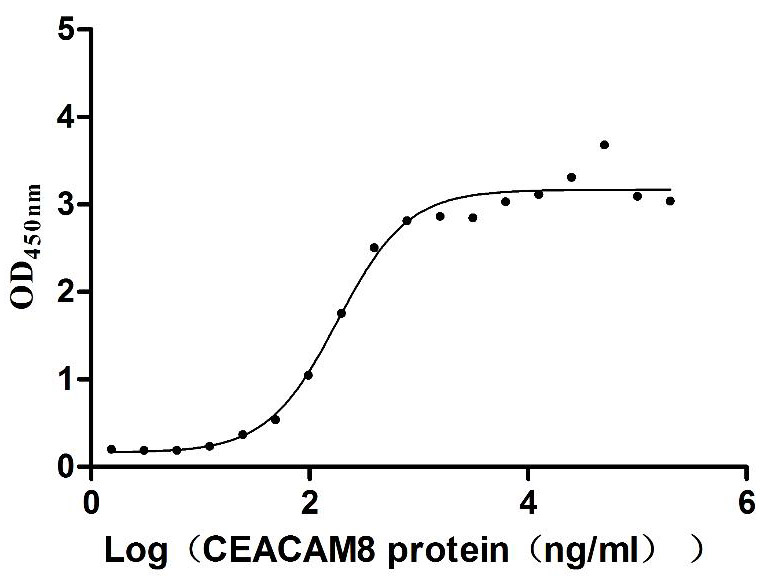
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
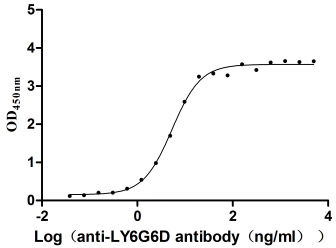
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)



-AC1.jpg)