Recombinant Mouse TGF-beta receptor type-1 (Tgfbr1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP734134MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP734134MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP734134MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP734134MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP734134MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Tgfbr1; TGF-beta receptor type-1; TGFR-1; EC 2.7.11.30; ESK2; Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I; TGF-beta receptor type I; TbetaR-I
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transmembrane serine/threonine kinase forming with the TGF-beta type II serine/threonine kinase receptor, TGFBR2, the non-promiscuous receptor for the TGF-beta cytokines TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3. Transduces the TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm and is thus regulating a plethora of physiological and pathological processes including cell cycle arrest in epithelial and hematopoietic cells, control of mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing, extracellular matrix production, immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. The formation of the receptor complex composed of 2 TGFBR1 and 2 TGFBR2 molecules symmetrically bound to the cytokine dimer results in the phosphorylation and the activation of TGFBR1 by the constitutively active TGFBR2. Activated TGFBR1 phosphorylates SMAD2 which dissociates from the receptor and interacts with SMAD4. The SMAD2-SMAD4 complex is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it modulates the transcription of the TGF-beta-regulated genes. This constitutes the canonical SMAD-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade. Also involved in non-canonical, SMAD-independent TGF-beta signaling pathways. For instance, TGFBR1 induces TRAF6 autoubiquitination which in turn results in MAP3K7 ubiquitination and activation to trigger apoptosis. Also regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition through a SMAD-independent signaling pathway through PARD6A phosphorylation and activation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- GPR50 is a TbetaRI co-receptor with potential impact on cancer development PMID: 29572483
- TGFBR1 is a target gene of miR-22 during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. PMID: 29588073
- Postnatal cartilage-specific deletion of Alk5 induced an OA-like phenotype with degradation of articular cartilage, synovial hyperplasia, osteophyte formation, subchondral sclerosis, as well as enhanced chondrocyte apoptosis, overproduction of catabolic factors, and decreased expressions of anabolic factors in chondrocytes. In addition, the expressions of PRG4 mRNA and protein were decreased in Alk5 conditional KO mice. PMID: 28716756
- Loss of ALK5 is associated with germinal matrix hemorrhage-intraventricular hemorrhage. PMID: 29456135
- this study shows that tissue-specific differentiation of colonic macrophages requires TGFbeta receptor-mediated signaling PMID: 28145440
- expression induced by IL-6 in keratinocytes PMID: 27892604
- Loss of smooth muscle cell-Tgfbr1 triggers multiple deleterious pathways, including abnormal TGFBR2, ERK, and AngII/AT1R signals that disrupt aortic wall homeostasis to cause aortic aneurysm formation PMID: 27739498
- miR-130a-3p might play a critical role in negatively regulating hepatic stellate cell activation and proliferation in the progression of nonalcoholic fibrosing steatohepatitis by directly targeting TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 via the TGF-beta/SMAD signaling pathway. PMID: 28518142
- Deletion of smooth muscle cell-specific Tgfbr1 inhibits arterial neointimal hyperplasia in short term, but promotes an undesired vascular phenotype for injured arteries. PMID: 27923978
- TGFbetaR1 signalling is needed for development of CD103(+)CD11b(+) intestinal DCs from CD103(-)CD11b(+) cells and that they contribute to the generation of Th17 and regulatory T cells. PMID: 28931816
- Overactivation of TGFBR1 drives gonadal tumor development. The TGFBR1 constitutively active mouse model phenocopies a number of morphological, hormonal, and molecular features of human granulosa cell tumors and are potentially valuable for preclinical testing of targeted therapies to treat granulosa cell tumors, a class of poorly defined ovarian malignancies. PMID: 27344183
- results indicate that CD34+ cells and signaling through ALK5 play pivotal roles in the morphogenesis of interstitial-like, peritubular-like and cord-like structures PMID: 29190781
- a surface population of Hsp90 extracellularly binds TGFbetaRI and this complex behaves as an active participant in collagen production in TGFbeta-activated fibroblasts. PMID: 27418101
- Conditional deletion of Tgfbr1 in PTEN-inactivated endometrium leads to a disease that recapitulates invasive and lethal human endometrial cancer. PMID: 28657664
- both GDF-15 and TGF-beta1 counteract chemokine-induced integrin activation on neutrophils via the ALK-5/TGF-betaRII heterodimer. PMID: 27235139
- miR-27b is an anti-fibrotic microRNA that inhibits fibroblast activation by targeting TGFbeta receptor 1 and SMAD2. PMID: 28095798
- In the presence of gadolinium and antibeta1 integrin antibody, collagen regulated the expression levels of Tgfbr1, Tgfbr2 and Smad2/3, but did not alter the phosphorylation of p38, ERK1/2 or JNK. PMID: 27573189
- miR-22 acts as a novel negative regulator of angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by suppressing the expression of TGFbetaRI in the heart. PMID: 27997889
- TGFbetaRI inhibition in an injured adult heart could both stimulate the autocrine/paracrine activity of survivin and inhibit Wnt in CPCs to mediate cardioprotection and improve cardiac function. PMID: 26418219
- Data show that transforming growth factor-beta receptor I (Tgfbr1) was a direct target of microRNA miR-140-5p. PMID: 26657345
- Targeted early inactivation of Alk5 in mesodermal progenitors caused abnormal development and maturation of the lung that included reduced physical size of the sub-mesothelial mesoderm, an established source of specific mesodermal progenitors. PMID: 26984772
- Beclin 1 regulates neuronal transforming growth factor-beta signaling by mediating recycling of the type I receptor ALK5 PMID: 26692002
- In vascular sprouting, neuropilin-1 suppresses the stalk-cell phenotype by limiting Smad2/3 activation through Alk1 and Alk5. Notch downregulates Nrp1, thus relieving the inhibition of Alk1 and Alk5, thereby driving stalk-cell behaviour. PMID: 26081042
- Endocytic deficiency caused by ITSN knock-down modified Alk5 endocytic trafficking and enhances its degradation PMID: 25720380
- Data indicate that absence of uterine activin receptor-like kinase 5 (ALK5) resulted in reduced female reproduction due to abnormalities observed at different stages of pregnancy. PMID: 26305969
- Litomosoides sigmodontis induces TGF-beta receptor responsive, IL-10-producing T cells that suppress bystander T-cell proliferation in mice. PMID: 26138667
- constitutive activation of TGFBR1 in the mouse uterus caused defects in uterine morphology and function, as evidenced by abnormal myometrial structure, dramatically reduced uterine glands, and impaired uterine decidualization. PMID: 25505200
- Inhibition of ALK5 improved intraislet endothelial cell numbers after islet culture, but this effect was lost in the early post-transplantation period. PMID: 25429440
- SD-208, a TbetaRI kinase inhibitor, stimulated tumour growth of invasive lobular carcinoma and bone metastases. PMID: 25421310
- Absence of cardiovascular manifestations in a haploinsufficient Tgfbr1 mouse model confirm that haploinsuffciency is not the underlying genetic mechanism in human Loeys-Dietz syndrome. PMID: 24587008
- Results show that ALK5 and ALK1 play antagonistic roles in TGF-beta-induced podosome formation in aortic endothelial cells. PMID: 25266657
- MicroRNA-101 inhibited profibrogenic TGFbeta signalling by suppressing TbetaRI expression in both hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and hepatocytes. PMID: 24817606
- TGFBR1 is an essential regulator of myometrial development in mice. PMID: 24506537
- loss of Alk5 in cranial neural crest cells results in severely disrupted muscle formation PMID: 24912677
- These data provide a new paradigm for Tif1gamma in regulating the balance between lymphoid- and myeloid-derived hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) through TGF-beta signaling, leading to HSC aging. PMID: 25002492
- Inhibition of TGFBR1 rescues the muscle regenerative response in type 1 diabetic mice. PMID: 23770987
- ALK5 inhibition enhances anti-melanoma CTL responses through ubiquitin-mediated degradation of Smad4. PMID: 24127404
- ACLP stimulates the fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition by promoting SMA expression via TGFbeta signaling and promoting collagen expression through a TGFbeta receptor-independent pathway. PMID: 24344132
- Lowering serum uric acid attenuates TGF-beta1-induced profibrogenic tubular change in KK-Ay/Ta model mice with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 23307286
- results indicate that blocking the activity of TGF-beta/Smad pathway by specific inhibitor SB431542 of ALK5 promoted the releaser of large amounts of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and other pro-inflammatory cytokines from the lung tissue PMID: 23661518
- Signaling through the TGF beta-activin receptors ALK4/5/7 regulates testis formation and male germ cell development. PMID: 23342175
- This study identified two distinct pathways that regulate adult beta-cell proliferation. PMID: 23248173
- TGFbeta receptor I subunit activin-like kinase (ALK)5 signaling and signal-transducing protein Smad3 nuclear accumulation are required for optimal enhancement of lipopolysaccharide plus interferon gamma-induced nitric oxide production in astrocytes by TGF-beta1. PMID: 20607716
- We show that a TbetaRI kinase inhibitor, Ki26894, restores impaired myoblast differentiation in vitro caused by activin, myostatin, and TGF-beta1, as well as CAV3(P104L). PMID: 22584670
- Results uncover USP4 as an important determinant for crosstalk between TGF-beta/TGF-beta type I receptor and AKT signalling pathways. PMID: 22706160
- Results identify a molecular mechanism that explains the cell-type specific aspects of signaling by myostatin, ALK4, ALK5, and other TGF-beta family members. PMID: 22202673
- alveolar epithelial cell can acquire a mesenchymal phenotype following injury in vivo and implicate type I collagen as a key regulator of EMT in them through signalling via Alk5. PMID: 21984393
- TGFBR1 is required for female reproductive tract integrity and function, and disruption of TGFBR1-mediated signaling leads to catastrophic structural and functional consequences in the oviduct and uterus. PMID: 22028666
- partial activation of TGFBR1 signaling may lead to accelerated chondrogenesis in vitro, the development of cartilage islands in vivo, and regenerative healing of ear wounding in mice. PMID: 21841138
- Lipoic acid induced upregulation of Il12a (2.1-fold) and downregulation of Tgfbr1 (4.3-fold) and Il17a (11.3-fold), which may reduce bone resorption. PMID: 21530805
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction, tight junction. Membrane raft. Cell surface.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, TGFB receptor subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:21812
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000007757
UniGene: Mm.197552
Most popular with customers
-
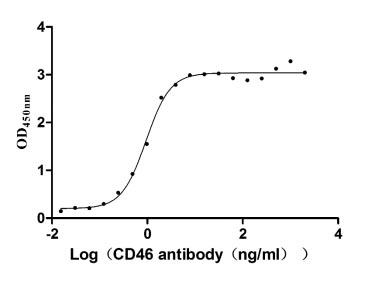
Recombinant Human Membrane cofactor protein (CD46), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
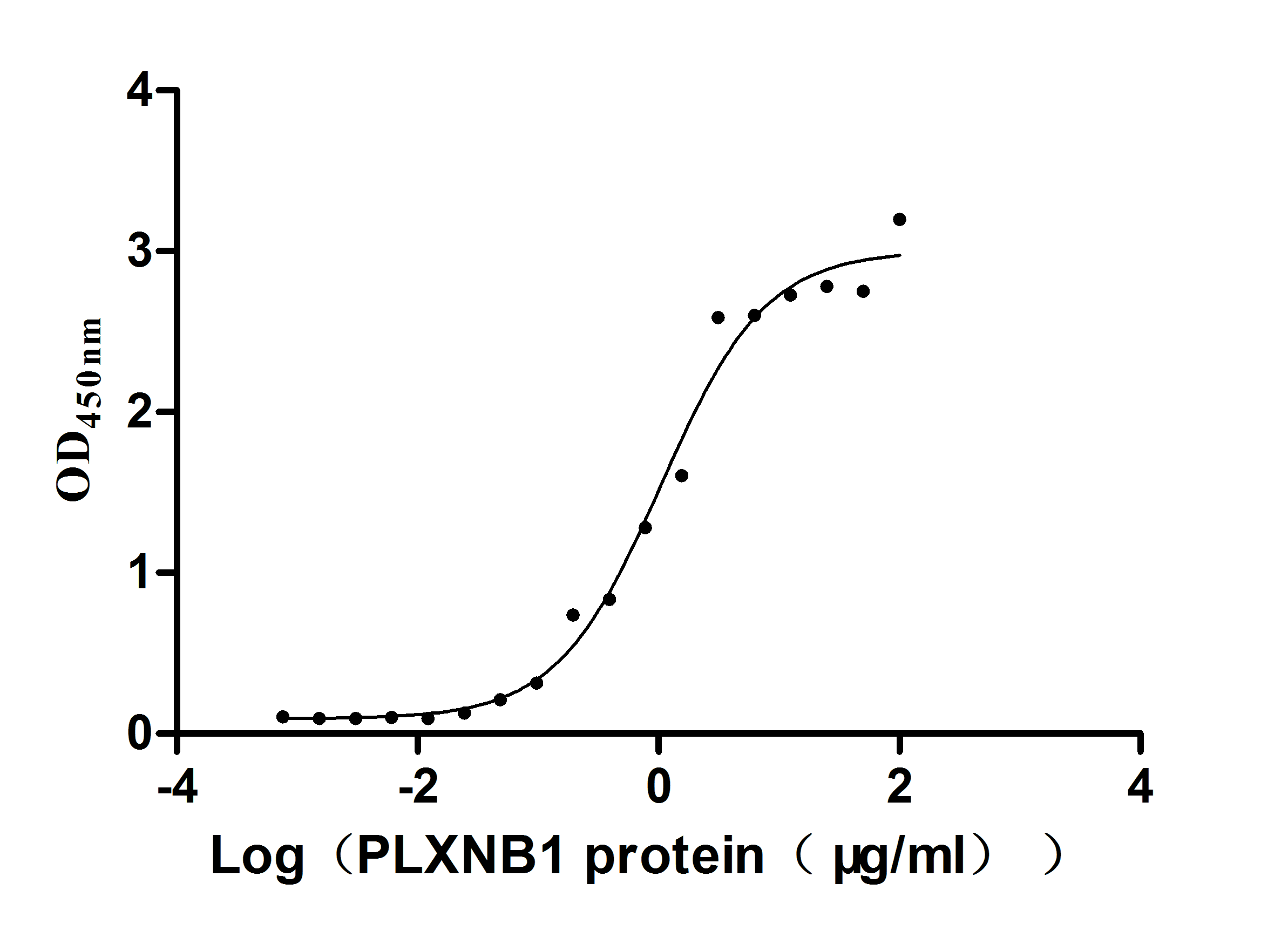
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
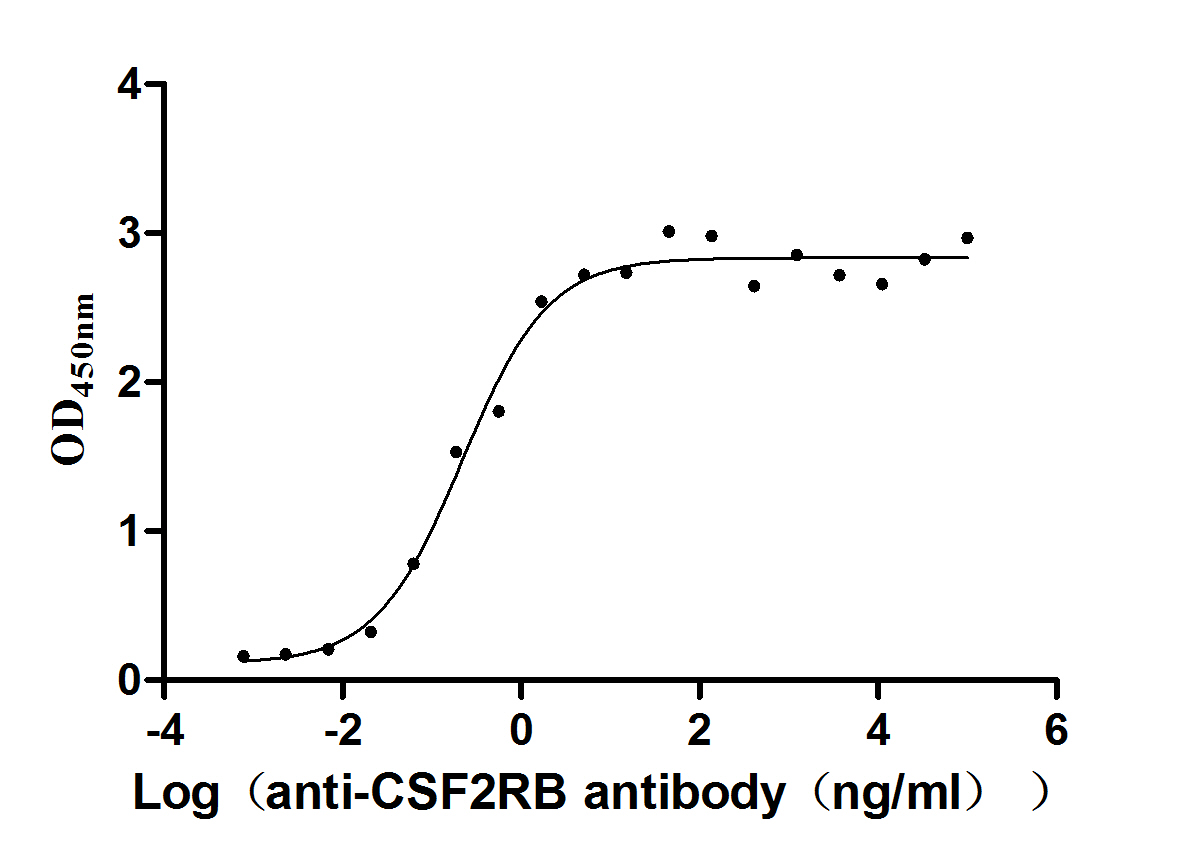
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
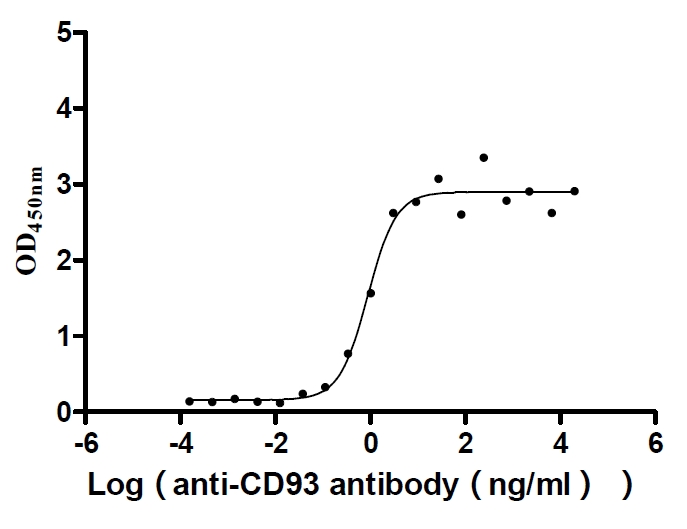
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)