Recombinant Mouse Protein Wnt-4 (Wnt4)
-
货号:CSB-YP026137MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP026137MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP026137MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Wnt4; Wnt-4Protein Wnt-4
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:23-351
-
氨基酸序列SNWLYLAK LSSVGSISEE ETCEKLKGLI QRQVQMCKRN LEVMDSVRRG AQLAIEECQY QFRNRRWNCS TLDSLPVFGK VVTQGTREAA FVYAISSAGV AFAVTRACSS GELEKCGCDR TVHGVSPQGF QWSGCSDNIA YGVAFSQSFV DVRERSKGAS SSRALMNLHN NEAGRKAILT HMRVECKCHG VSGSCEVKTC WRAVPPFRQV GHALKEKFDG ATEVEPRRVG SSRALVPRNA QFKPHTDEDL VYLEPSPDFC EQDIRSGVLG TRGRTCNKTS KAIDGCELLC CGRGFHTAQV ELAERCGCRF HWCCFVKCRQ CQRLVEMHTC R
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Plays an important role in the embryonic development of the urogenital tract and the lung. Required for normal mesenchyme to epithelium transition during embryonic kidney development. Required for the formation of early epithelial renal vesicles during kidney development. Required for normal formation of the Mullerian duct in females, and normal levels of oocytes in the ovaries. Required for normal down-regulation of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the ovary. Required for normal lung development and for normal patterning of trachael cartilage rings.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- urinary Wnt4 could be a potential noninvasive biomarker for the early detection of tubular injury. PMID: 27600466
- GLP-1 promoted adipogenesis through the modulation of the Wnt4/beta-catenin signaling pathway PMID: 27504979
- Results suggest that the Wnt4 gene encodes signals that are important for various aspects of female reproductive tract development. PMID: 26721931
- Our functional study revealed that WNT4 molecules were involved in regulating zygotic cleavage and early embryogenesis PMID: 26700598
- Data indicate that a balance between supporting cell self-renewal and differentiation is maintained in the developing ovary by relative Wnt4 protein/beta-catenin and p27Kip1 protein (p27)/Forkhead box L2 (FOXL2) activities. PMID: 26939755
- decreased expression of Wnt4 in the aging thymus may be one of the molecular triggers underlying the process of age-related thymic senescence. PMID: 26397044
- Mir-29c regulates WNT4 signaling. PMID: 26484393
- Wnt4 is essential to normal mammalian lung development. PMID: 26321050
- RSPO1, WNT4, and beta-catenin have roles in the signaling pathway during ovarian differentiation in mice. PMID: 25187620
- The Runx-1 gene can be a Wnt-4 signalling target, and that Runx-1 and Wnt-4 are mutually interdependent in their expression. PMID: 25645944
- Progesterone and Wnt4 control stem cell function through a luminal-myoepithelial crosstalk with Wnt4 acting independent of progesterone receptor perinatally. PMID: 25603931
- significant role in supporting thymocyte development and maturation PMID: 24768153
- results suggest that Wnt4 signaling could be an attractive therapeutic target for treating osteoporosis and preventing skeletal aging PMID: 25108526
- Data indicate that Wnt4 signaling is necessary during maturation of the ovarian follicle. PMID: 24371124
- Data from several types of in vitro angiogenesis assays suggest that Wnt4 (but not Wnt1) is a potent inhibitor of capillary outgrowth; Wnt4 and Wnt1 appear to be secreted by vascular endothelial cells into extracellular matrix during angiogenesis. PMID: 22607657
- Wnt4-null and Rspo1-null pregranulosa cells transition through a differentiated granulosa cell state prior to transdifferentiating towards a Sertoli cell fate. PMID: 24036309
- Wnt4 signaling through beta-catenin stabilization is sufficient to drive spontaneous myofibroblast differentiation in interstitial pericytes and fibroblasts, emphasizing the importance of this pathway in renal fibrosis. PMID: 23766539
- Endocardial to myocardial notch1-wnt4-bmp2 axis regulates early heart valve development. PMID: 23560082
- this study identifies Rspo1 and Wnt4 as two new regulators of cell proliferation in the early gonad regardless of its sex, in addition to the specific role of these genes in ovarian differentiation. PMID: 23095882
- The repression of many female genes including Wnt4 is necessary for the bipotential gonad to adopt the male testicular fate. PMID: 22705479
- Our analyses show that Wt1, Sf1, and Wnt4 can be dosage-sensitive in mice, depending on the genetic background, and provide insights into the mechanisms of B6 XY sex reversal PMID: 22496664
- WNT4 was found to signal via the CTNNB1 pathway in Sertoli cells. PMID: 22253774
- These data reveal a new role for Wnt4 in mammalian Neuromuscular junction formation. PMID: 22253844
- Wnt4 regulates steady-state thymic cellularity by a thymic epithelial cell (TEC)-dependent mechanism. The absence of Wnt4 suppressed fetal and postnatal thymic expansion and resulted in decreased TEC numbers. PMID: 21937690
- Wnt-4 modulates canonical Wnt signaling and acts as regulator of beta-cell proliferation and inflammatory cytokine release. PMID: 21771967
- An important role of Wnt-4 in thymic senescence, is reported. PMID: 21453014
- Activation of canonical Wnt signaling was evident as indicated by increased Wnt4 activation in livers of hepatocellular carcinoma farnesoid X-knockout mice. PMID: 21430080
- These results establish a functional role for non-canonical Wnt signaling in hematopoiesis. PMID: 21541287
- Wnt4 activated the canonical beta-catenin pathway during myogenic differentiation in both myoblasts and satellite cells and negatively regulated myostatin's expression and its regulating pathways. PMID: 21248078
- Maintenance of female germ cells hinge upon a delicate balance between positive (WNT4 and beta-catenin) and negative (activin betaB) regulators derived from the somatic cells in the fetal ovary. PMID: 20454446
- WNT4 is a critical regulator not only of proper postnatal uterine development, but also embryo implantation and decidualization. PMID: 21163860
- Wnt/beta-catenin signaling occurs in proliferating vascular smooth muscle cells during intimal thickening. This is a result of Wnt4 upregulation. PMID: 21193738
- Wnt-4 deficiency allows 20% of the germ cells to initiate meiosis in the ovary, whereas meiosis is inhibited completely in the Wnt-4/Wnt-5a double mutant. PMID: 20106871
- WNT4 is required for normal antral follicle development and may act by regulating granulosa cell functions including steroidogenesis. PMID: 20371632
- Notch2 overexpression leads to ectopic Wnt4 expression and premature tubule formation. PMID: 20299358
- data indicate that Wnt4 levels must be regulated in chondrocytes for normal growth plate development and skeletogenesis PMID: 17505543
- The current results support a view that WNT4 may have a role in oocyte selection and follicle formation and maturation in human ovaries. PMID: 19962424
- Wnt4(EGFPCre)-mediated inactivation of Wnt4 function considerably reduced the amount of Wnt4 transcripts, led to a severe defect in kidney development, and caused the female embryos to undergo partial sex reversal to males PMID: 19830824
- role for Wnt-4 in the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis. PMID: 11832423
- wnt-4 is expressed at distinct stages of follicular development. PMID: 11861511
- results point to a role for Wnt-4 in adrenal gland development and function PMID: 12399432
- Wnt4 signaling mediates the increased expression of Dax-1 as the ovary becomes sexually differentiated PMID: 12554773
- Wnt-4 dependent signaling cascades regulate steroidogenic factor-1-dependent transcription of genes in adrenal cortex PMID: 12732619
- Data show that the role of WNT4 in gonad development is to pattern the sex-specific vasculature and to regulate steroidogenic cell recruitment. PMID: 12835383
- Wnt4 mRNA is expressed in a decreasing anterior-to-posterior gradient in the floor plate; commissural axons lacking the Wnt receptor Frizzled3 displayed anterior-posterior guidance defects after midline crossing PMID: 14671310
- matrilysin may have a role in renal tubular injury and progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and Wnt4 may regulate matrilysin expression in the kidney PMID: 15149334
- germ cells in the ovarian cortex are almost completely lost in both Wnt4 and follistatin null gonads before birth PMID: 15162500
- Wnt-4 binds both canonical and noncanonical Frizzled receptors, thereby activating Wnt signaling pathways that may each contribute to kidney tubulogenesis. PMID: 15265686
- Results identify WNT4 as a new factor involved in the mammalian testis determination pathway and show that genes can have a specific but distinct role in both male and female gonad development. PMID: 15581876
- Wnt-4 signaling normally acts to suppress testosterone biosynthesis in the female, and that testosterone is the putative mediator of the masculinization phenotype in Wnt-4-deficient females PMID: 15932923
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
-
蛋白家族:Wnt family
-
组织特异性:In adults in lung and brain.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:22417
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000036580
UniGene: Mm.20355
Most popular with customers
-
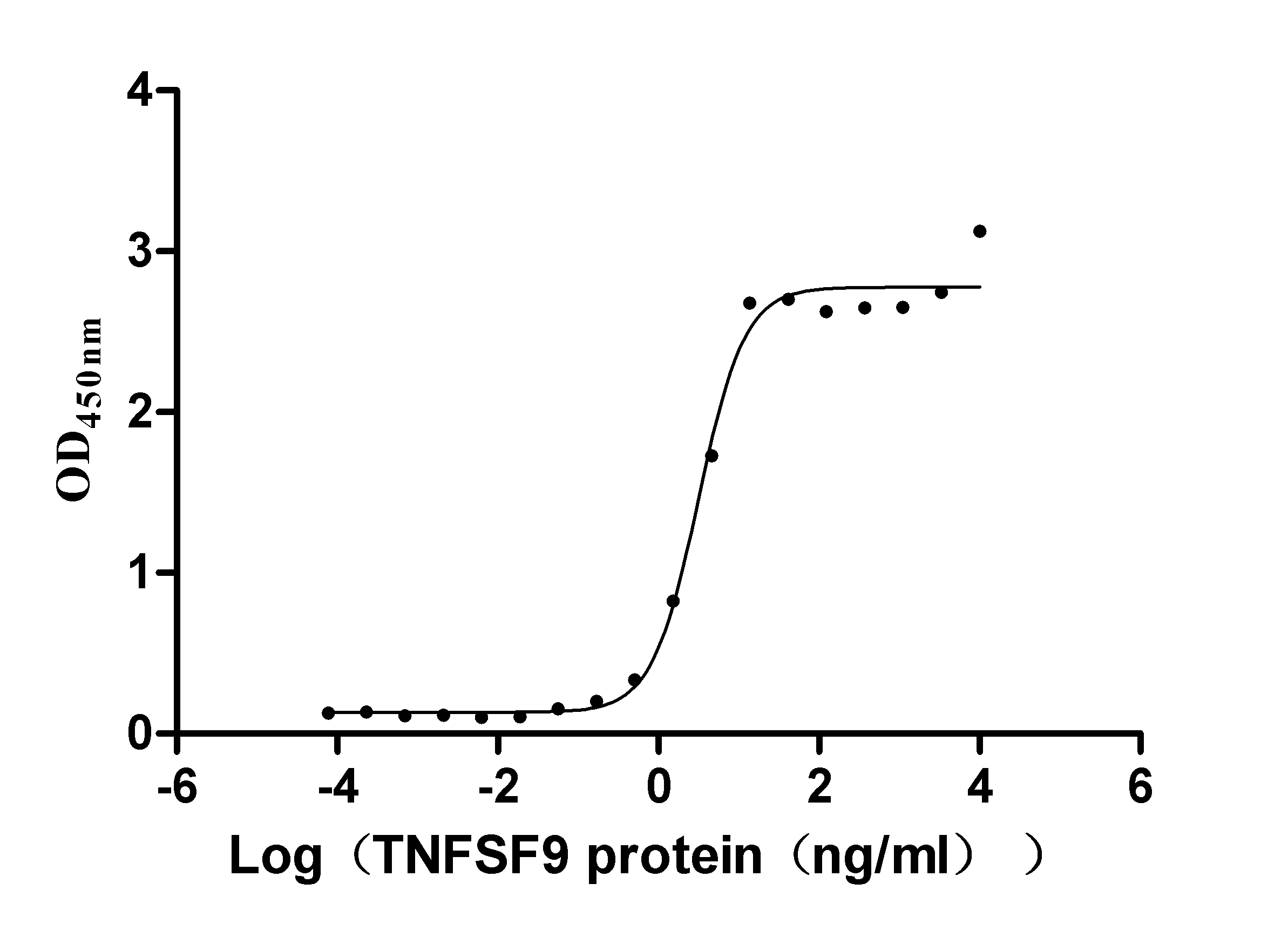
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
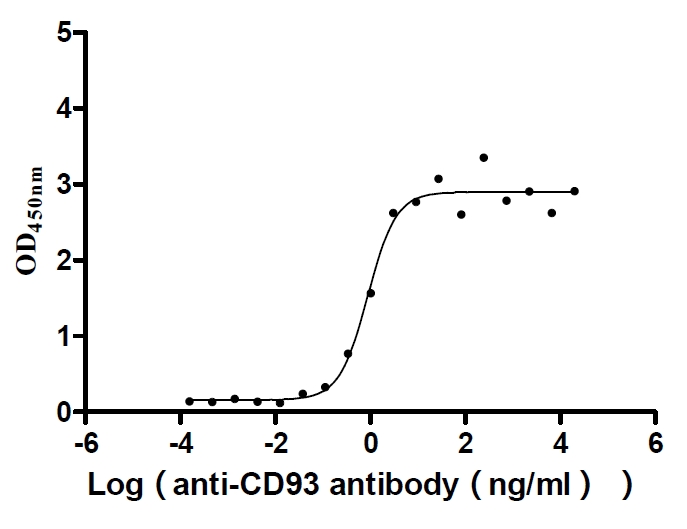
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
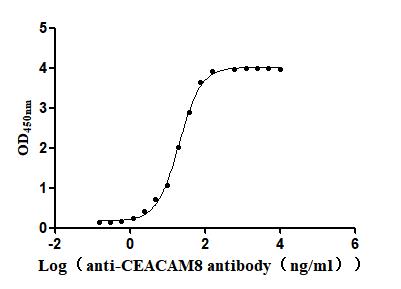
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
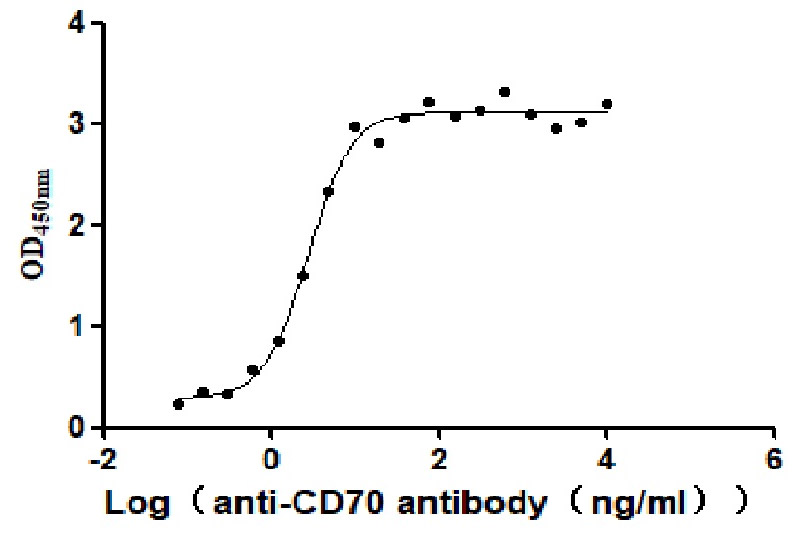
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)