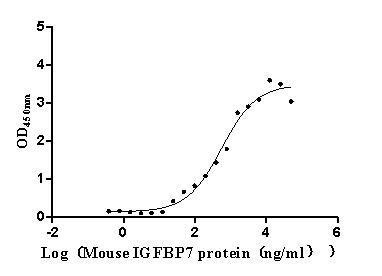
Recombinant Mouse Organic solute transporter subunit alpha (Osta), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc51a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP851240MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc51a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP851240MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc51a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP851240MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc51a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP851240MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Slc51a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP851240MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Slc51a
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Slc51a; Osta; Organic solute transporter subunit alpha; OST-alpha; Solute carrier family 51 subunit alpha
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Essential component of the Ost-alpha/Ost-beta complex, a heterodimer that acts as the intestinal basolateral transporter responsible for bile acid export from enterocytes into portal blood. Efficiently transports the major species of bile acids.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that transport of bile acid taurocholate is retained when OstB (organic solute transporter beta subunit) is truncated to contain only the transmembrane domain with 15 additional residues on each side and co-expressed with intact OstA; shorter fragments of OstB are inactive. PMID: 28455390
- These findings indicate that loss of OSTalpha protects against age-related weight gain and insulin resistance. PMID: 24381083
- Ileal FGF15 expression was directly correlated with plasma cholesterol levels and aortic cholesterol content. In contrast, plasma and hepatic cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis development were not reduced in apoE(-/-) mice deficient in Ostalpha. PMID: 23880190
- Total ileal FGF15 expression was elevated almost 20-fold in Ostalpha(-/-) mice as a result of increased villus epithelial cell number and ileocyte FGF15 protein expression PMID: 22542490
- Inactivation of FXR largely unmasked the bile acid malabsorption phenotype and corrected the bile acid homeostasis defect in Ostalpha null mice. PMID: 21691100
- Ostalpha-deficient mice efficiently eliminate excess bile acids via the feces. PMID: 21719738
- OSTalpha is localized to steroidogenic cells of the brain and adrenal gland, and it modulates DHEA/DHEAS homeostasis PMID: 20649839
- These findings indicate that loss of Ostalpha provides protection from liver injury in obstructive cholestasis through adaptive responses in both the kidney and liver that enhance clearance of bile acids into urine. PMID: 19902485
- Co-expression of mouse Ostalpha-Ostbeta, but not the individual subunits, stimulated Na(+)-independent bile acid uptake and the apical-to-basolateral transport of taurocholate PMID: 15563450
- OSTalpha and OSTbeta mRNA levels were induced in the adrenals and kidneys of wild-type, but not FXR-/-, mice PMID: 16251721
- the selective localization of OSTalpha and OSTbeta to the basolateral plasma membrane of epithelial cells responsible for bile acid and sterol reabsorption. PMID: 16317684
- In conclusion, we identified Ost-alpha/Ost-beta as a novel FXR target. Absent Ost-alpha/Ost-beta induction in CA-fed FXR(-/-) animals may contribute to increased liver injury in these animals. PMID: 16357057
- The mouse Ostalpha and Ostbeta promoters are unusual in that they contain functional FXR and LRH elements, which mediate, respectively, positive and negative feedback regulation by bile acids. PMID: 16357058
- These results indicate that expression of Ostalpha and Ostbeta are highly regulated in response to cholestasis and that this response is dependent on the FXR bile acid receptor. PMID: 16423920
- LXRalpha transcriptionally regulate mouse organic solute transporter alpha/beta via inverted repeat-1 elements shared with farnesoid X receptor PMID: 17177110
- Present as heterodimers (with Ost beta) and/or heteromultimers; the interaction between Ostalpha and Ostbeta increases the stability of the proteins and is required for delivery of the heteromeric complex to the plasma membrane. PMID: 17650074
- These data indicate that Ostalpha-Ostbeta is essential for intestinal bile acid transport in mice. PMID: 18292224
- These findings provide direct support for the hypothesis that Ostalpha-Ostbeta is a major basolateral transporter of bile acids and conjugated steroids in the intestine, kidney, and liver. PMID: 18497332
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Mainly restricted to the lateral and basal membranes of ileal enterocytes. Transported from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane upon interacting with SLC51B.
-
蛋白家族:OST-alpha family
-
组织特异性:Present at high levels in ileum. In ileum, it is restricted to the apical domain on the mature villus enterocytes with little detectable expression in the goblet cells or crypt enterocytes (at protein level). Expressed in kidney but not in heart, brain, l
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:106407
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000046286
UniGene: Mm.476915
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Paguma larvata Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Paguma larvata (Masked palm civet)
-
Recombinant Mouse Semaphorin-4D (Sema4d), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
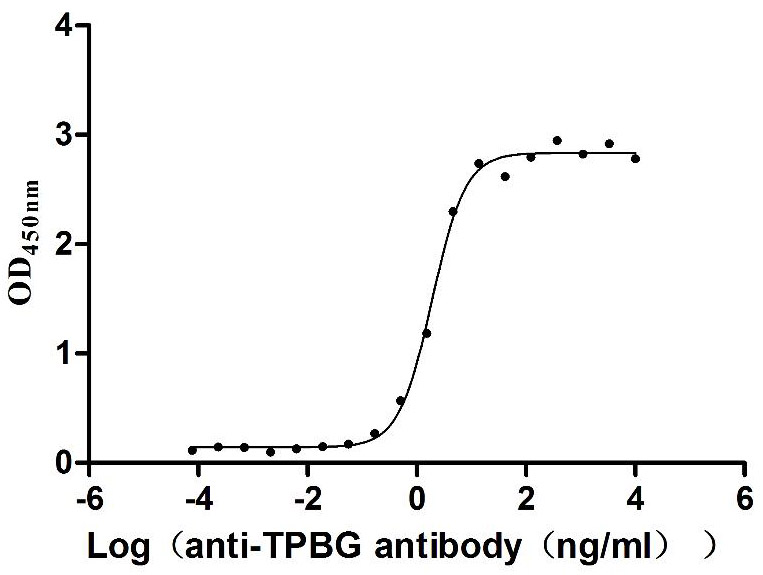
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
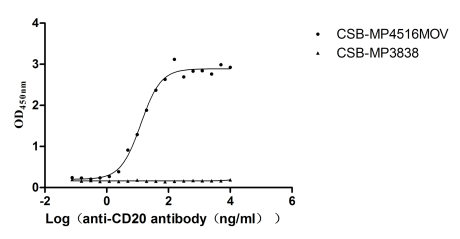
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
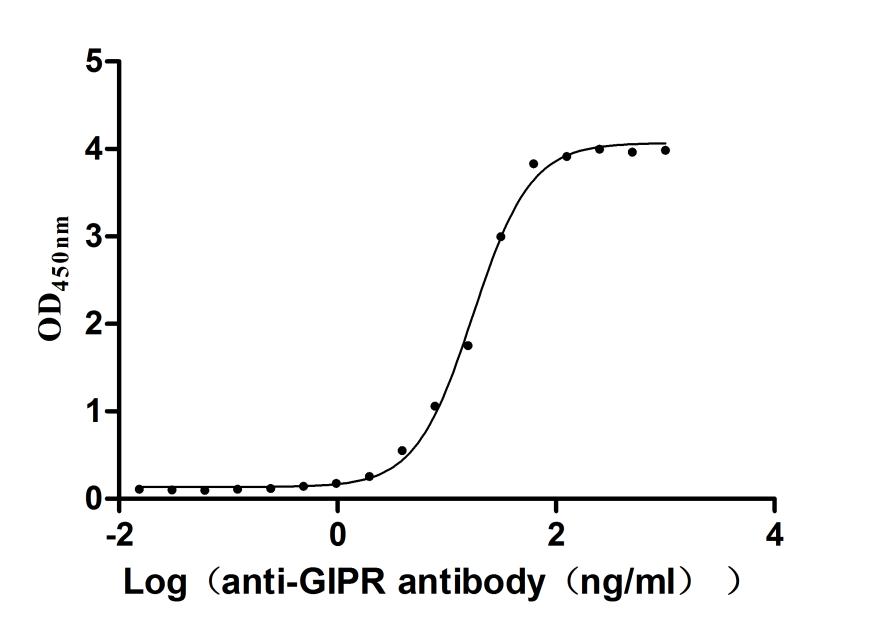
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)