Recombinant Mouse Neuropeptide Y receptor type 2 (Npy2r), partial
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP016036MO1b0
-
规格:¥2328
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
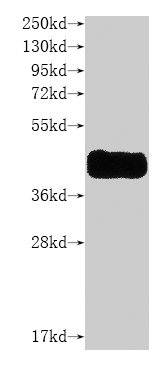
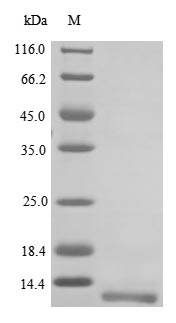
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Npy2r; Neuropeptide Y receptor type 2; NPY2-R; NPY-Y2 receptor; Y2 receptor
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:11.0 kDa
-
表达区域:1-51aa
-
氨基酸序列MGPVGAEADENQTVEVKVEPYGPGHTTPRGELPPDPEPELIDSTKLVEVQV
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for neuropeptide Y and peptide YY.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- High Npy2r expression is associated with chronic social defeat stress. PMID: 30201296
- These results indicate that endogenous PYY has a hypoalgesic effect on somatic thermal and visceral chemical pain. The effect on visceral pain seems to be mediated by peripheral Y2 receptors. PMID: 28106168
- NPY and agonists of Y2R and Y5R may be neuroprotective against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal cell death in primary cortical cell cultures after delayed treatment. A Y2R agonist not only diminished transient cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury, but also improved functional outcome after delayed treatment. Y5 and especially Y2 receptors may be promising targets for neuroprotection against ischemic damage PMID: 28057538
- Findings suggest that neuropeptide Y is expressed by distinct populations of neurons can modulate afferent and efferent projections of the central amygdala via presynaptic Y2 receptors located at inhibitory and excitatory synapses. PMID: 26365505
- confirms the critical role of Y2 signalling to control neuropeptide Y and associated pro-opiomelanocortin expression in the arcuate nuclei PMID: 26444586
- Study shows that NPY inhibits fear learning and promotes cued extinction by reducing fear expression also via activation of presynaptic Y2 receptors on central amygdala neurons PMID: 26314208
- Our results showed the altered expression of NPY, Y1R and Y2R but not Y5R in hippocampus and temporal lobe cortex of tremor rat brain. PMID: 24444822
- Data from knockout (KO) mice suggest roles for neuropeptide Y (NPY) and NPY2 receptors in fear acquisition/fear stimulus discrimination. Npy1r/Npy2r double KO mice display excessive recall of conditioned fear/impaired fear extinction. PMID: 22289084
- NPY Y2 receptors control the level of hyperactive behavior under conditions of limited food access. PMID: 21923762
- Peripheral Y2 receptor signaling is critical in the regulation of oxidative fuel selection and physical activity and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. PMID: 21546930
- NPY-Y2 receptor exerts a direct control over both the tonic and phasic release of dopamine PMID: 21055451
- Data describe the complex interaction between Y2/Y4 receptors in control of bone mass, and suggest that the reduction in cortical bone observed in the absence of leptin is due to the anti-osteogenic effect of elevated hypothalamic NPY levels. PMID: 20635164
- Data from studies in knockout mice suggest that signaling through Y2 receptor prevents development of long-term anxiety-/depression-like behaviour caused by acute immune challenge. Study includes comparison with Y4 receptor knockout mice. PMID: 19939871
- Taken together, this work demonstrates the critical roles of Y2 and Y4 receptors in the regulation of body composition and energy metabolism, highlighting dual antagonism of Y2 and Y4 receptors as a potentially effective anti-obesity treatment. PMID: 20881101
- PYY/PYY(3-36) potently inhibits basal and stress/serotonin/cholinergic-stimulated propulsive colonic motor function in conscious mice, likely via Y(2) receptors PMID: 19892938
- data reveal an anti-osteogenic effect of Y2 receptors on hypothalamic NPY-expressing neurons on trabecular but not on cortical bone PMID: 20613867
- In Y2 knockout mice motor activity in the antrum was more affected than that in the duodenum, and both fed and fasted motor activities were affected in the antrum. PMID: 20501433
- Results indicate that NPY Y2 receptor agonists inhibit diarrhea in mice by not only reducing intestinal fluid secretion, but also slowing colonic transit. PMID: 19925840
- results are evidence of the highly site-specific nature of the Y2-mediated function of NPY in the modulation of anxiety- and depression-related behavior. PMID: 20445054
- Y2 depletion influences a range of behaviours, which are potentially relevant for schizophrenia-related research PMID: 19879900
- These findings attest to a differential role of Y2 and Y4 receptor signalling in the circadian control of behaviours that balance energy intake and energy expenditure. PMID: 19781771
- Role of neuropeptide Y Y(2) receptors in modulation of cardiac parasympathetic neurotransmission PMID: 11786149
- hypothalamic Y2 receptors are involved in a tonic inhibition of bone formation. PMID: 11927618
- role in body weight regulation PMID: 12072562
- Y2 receptor participates in cholesterol and glucose homeostasis of obese mice PMID: 12126735
- PYY(3-36) inhibits food intake in mice but not in Y2r-null mice, which suggests that the anorectic effect requires the Y2R PMID: 12167864
- Deletion of this receptor results in blockage of NPY-induced angiogenesis and delayed wound healing. PMID: 12730369
- NPY Y(2) receptors may play an inhibitory role and supports the hypothesis that Y(2) receptors are involved in the regulation of anxiety-like behaviours by NPY PMID: 12742262
- tonic activation of submucosal Y(2) receptors could indirectly reduce mucosal ion transport in the colon, while direct activation of Y(2) receptors on longitudinal muscle results in contraction PMID: 12813010
- deletion of the Y2 receptor has revealed an important role of Y2 receptors in the generation of anxiety-related and stress-related behaviours in mice PMID: 12859347
- Y2 and Y4 receptors have roles in adiposity and bone mass PMID: 12861009
- High levels of NPY-Y2R expression in the preoptic nuclei suggest involvement of Y2R in the regulation of reproductive behavior, whereas Y2R expression in arcuate, dorsomedial, and perifornical nuclei may be relevant to feeding and body weight control. PMID: 14755515
- NPY Y2-/- mice displayed a deficit on the probe trial in the Morris water maze task, and exhibited marked deterioration in object memory 6 h, but not 1 h, following initial exposure in the object recognition test PMID: 14997009
- Results provide strong evidence for the role of the Y2 receptor mediating neuropeptide Y subjective day phase-advance shifts in mice. PMID: 15619538
- Taken together, these data suggest that, in mice, both Y2 and Y5 receptors regulate hippocampal seizures in vitro, while activation of Y5 receptors in extra-hippocampal regions reduces generalized seizures in vivo. PMID: 15979311
- These results demonstrate that the NPY Y2R is associated mainly with both peptidergic and nonpeptidergic small, presumably nociceptive, neurons projecting to the superficial layers of the dorsal horn. PMID: 16025447
- A role is indicated for NPY-Y2 receptors in the accumulation of adipose tissue in the hypogonadal state; hypothalamic Y2 receptors constitutively restrain osteoblastic activity even in the absence of sex hormones. PMID: 16785231
- The Y2-mediated anabolic pathway stimulates cortical and cancellous bone formation. PMID: 16995815
- The widespread distribution of Y2R-positive cell bodies and fibers suggests that NPY signaling through the Y2R is common in the mouse brain. PMID: 16998904
- Release of NPY tonically inhibits synaptic transmission in mice and its effects are mediated by Y2 receptor activation. However, both NPY and BIIE0246 were much less effective in mice than in rats. PMID: 17027162
- fasting inhibits the somatotropic axis via direct action on Y2 receptors in the Arcuate nucleus and indirectly inhibits the gonadotropic axis via Y4 receptors. PMID: 17272395
- Diet-induced obese mice had low plasma PYY, which may have caused compensatory up-regulation of PYY and Y2 receptor densities in medulla. PMID: 17615145
- activation of neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract following administration of T2R agonists to the GI tract involves CCK(1) and Y(2) receptors located on vagal afferent terminals in the gut wall PMID: 18003792
- Data show that the replacement of a high-fat diet with a low-fat diet was associated with a significant lowering of ventromedial hypothalamic neuropeptide Y Y2 receptor binding, and also a lowered plasma PYY level. PMID: 18357520
- Mice lacking Y2 receptors exhibited reduced neuronal activation when compared to WT animals in response to the emotional stressors. PMID: 19084906
- critical role for neuropeptide Y/neuropeptide Y2 receptor interactions in adipogenesis PMID: 19182605
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:18167
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000096595
UniGene: Mm.1433
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Growth hormone receptor (GHR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
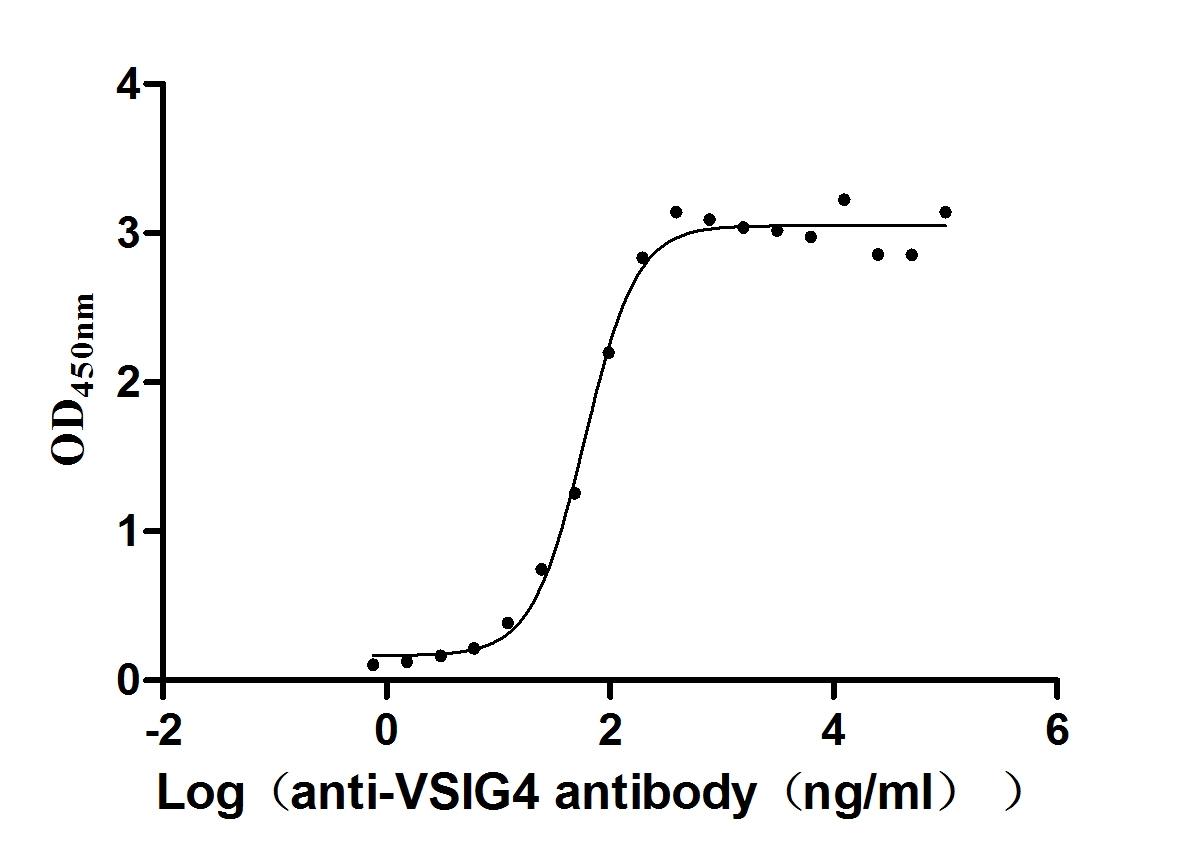
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
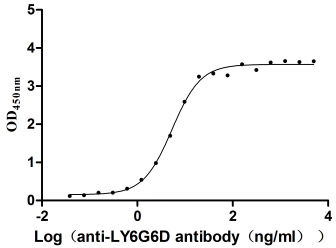
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
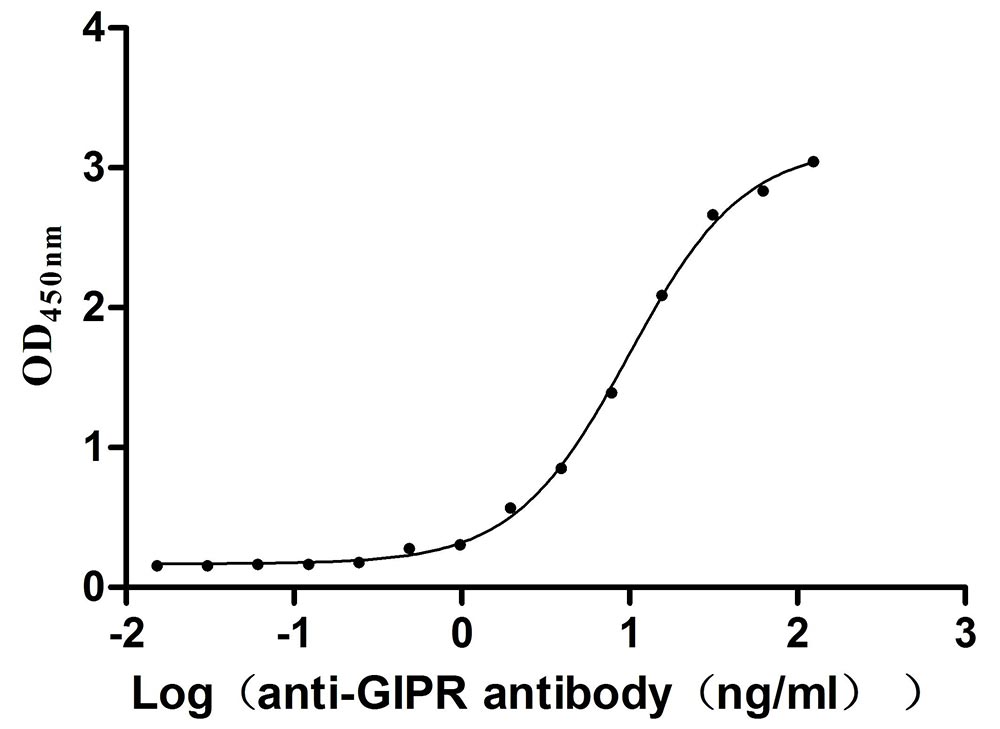
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


-AC1.jpg)