Recombinant Mouse Neuromodulin (Gap43)
-
中文名称:小鼠Gap43重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP009231MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Gap43重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP009231MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Gap43重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP009231MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Gap43重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP009231MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Gap43重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP009231MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Gap43
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Gap43; Basp2; Neuromodulin; Axonal membrane protein GAP-43; Calmodulin-binding protein P-57; Growth-associated protein 43
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-227
-
氨基酸序列MLCCMRRTKQ VEKNDEDQKI EQDGVKPEDK AHKAATKIQA SFRGHITRKK LKGEKKGDAP AAEAEAKEKD DAPVADGVEK KEGDGSATTD AAPATSPKAE EPSKAGDAPS EEKKGEGDAA PSEEKAGSAE TESAAKATTD NSPSSKAEDG PAKEEPKQAD VPAAVTDAAA TTPAAEDAAT KAAQPPTETA ESSQAEEEKD AVDEAKPKES ARQDEGKEDP EADQEHA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:This protein is associated with nerve growth. It is a major component of the motile 'growth cones' that form the tips of elongating axons. Plays a role in axonal and dendritic filopodia induction.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- hnRNP-Q1-mediated repression of Gap-43 mRNA translation provides an additional mechanism for regulating GAP-43 expression and function and may be critical for neuronal development. PMID: 26658614
- The GASP-43 is involves in the orientation of cell division by interacting with Galphai. PMID: 26380950
- Trimethyltin decreased synaptophysin but not GAP-43 expression in the mouse hippocampus. PMID: 24001577
- Antiretroviral drugs may recruit the HuD-GAP43 pathway, potentially contributing to a response to the antiretroviral neuronal toxicity. PMID: 24565699
- KSRP modulation of GAP-43 mRNA stability restricts axonal outgrowth in embryonic hippocampal neurons. PMID: 24244461
- these findings suggest that GAP-43 is dynamically involved in early postnatal and adult hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic connectivity, possibly contributing to the GAP-43+/- behavioral phenotype. PMID: 24576816
- In this review, GAP-43 in vivo knockdown in olivary neurons leads to the atrophy of their climbing fibers and a reduction in the ability to sprout toward surrounding denervated Purkinje cells. PMID: 23441024
- GAP-43 is required to sustain synaptic stability and promote the initiation of axonal regrowth PMID: 23754371
- In vitro results indicated that GAP43 is indeed expressed in both myoblasts and differentiating myotubes, and its cellular localization changes dramatically during maturation. PMID: 23308181
- Initial emergence of hollows in the somatosensory cortex is no different between GAP43 heterozygous mice and nonheterozygous littermate controls; however, the emergence of sides and septa is delayed by 2 days. PMID: 22759196
- This study demonistrated that neuronal responses to netrin-1 have been directly demonstrated to require GAP-43. PMID: 23085079
- Dynamic palmitoylation links cytosol-membrane shuttling of acyl-protein thioesterase-1 and acyl-protein thioesterase-2 with that of proto-oncogene H-ras product and growth-associated protein-43 PMID: 23396970
- Nos2 deficiency promotes medulloblastoma development in Ptch1(+/-) mice through retention of proliferating GCPs in the external granular layer due to reduced Gap43 expression PMID: 22438824
- GAP-43 expression in the mucosal myenteric plexus was markedly reduced in the small intestines of Neodiplostomum seoulense-infected mice. PMID: 22451741
- These data suggest the efficient transcription of the distal promoter of Gap43 is an important mark for the transition of P19 cells from the progenitor stage into neuronal differentiation. PMID: 21938722
- GAP-43 is essential both to maintain climbing fibres structure in non-traumatic condition and to promote sprouting after partial lesion of the inferior olive. PMID: 21695168
- The Gap43 and Pten network highlights the covariance of gene expression and forms a molecular network associated with axonal outgrowth in the adult retina. PMID: 21655357
- Results suggest that GAP-43 might link the cell membrane and spindle pole and consequently participate in controlling cleavage orientation during cell division. PMID: 21345365
- all the effects of environmental stimulation are amplified if the afferent Purkinje axons are endowed with enhanced intrinsic growth capabilities, induced by overexpression of GAP-43 PMID: 21304956
- Mice lacking one allele for GAP43 displayed resistance to change, stress-induced behavioral withdrawal and anxiety. GAP43 deficiency leads to the development of a subset of autistic-like behaviors. PMID: 20707874
- This study suggested abnormal postsynaptic differentiation in GAP-43 HZ cortex during early barrel development, followed by adaptive compensation and partial phenotypic rescue. PMID: 19915093
- permanently dephosphorylated GAP-43 may disrupt normal axonal fasciculation which gives rise to the ectopic growth into distal stratum oriens PMID: 19437419
- first evidence that links increased GAP-43 expression with growth of central axons; findings raise questions about the properties of granule cells and the mossy fiber mechanisms that differentially regulate axonal remodeling in the adult hippocampus PMID: 19650124
- GAP-43 promotes axon growth by multiple synergistic mechanisms that potentiate the intrinsic motility of the elongating processes, while reducing their sensitivity to environmental inhibition. PMID: 19895561
- Palmitoylcarnitine modulates the interaction of protein kinase C delta with GAP-43. PMID: 12061781
- While GAP-43 is not necessary for LTP induction, its phosphorylation may regulate presynaptic properties, thereby affecting synaptic plasticity and the induction of LTP in the hippocampus. PMID: 12099903
- Accumulation of GAP-43 along precise axon segments disrupts the normal axon-glia interaction and enhances the retraction of oligodendrocytic processes to facilitate the outgrowth of neuritic sprouts. PMID: 15009129
- nNOS-positive cells were surrounded by GAP-43 labeled regions that appeared to be presynaptic boutons. PMID: 15148562
- After status epilepticus in mice, early loss of GAP-43 and strong CD44 induction in the IML correlated with hilar cell loss and subsequent MFS. PMID: 15191797
- GAP-43 expressed in multipotent precursors is required for appropriate cell fate commitment, and its absence affects astrocyte as well as neuronal differentiation. PMID: 15234344
- Older transgenic animals overexpressing human S100B show more GAP-43 staining than control animals, suggesting synaptic remodeling could take place. PMID: 15306236
- The present results provide strong evidence for a pivotal role of hippocampal GAP-43 in the bidirectional regulation of mnemonic processing. PMID: 15390153
- GAP-43 is necessary for the development and function of a variety of neuronal systems. PMID: 15541878
- GAP-43 and L1 coexpressed in Purkinje cells act synergistically to switch these CNS neurons into a regeneration-competent phenotype and serve as a key regulator of the regenerative ability of intrinsic CNS neurons in vivo. PMID: 16195382
- modulator I repressed GAP-43 gene expression from the proximal promoter in non-neuronal cells; also, a novel stimulative element is immediately downstream of modulator I PMID: 16794332
- role of GAP-43 protein levels in regulating memory function PMID: 17554085
- GAP-43 plays a functional role in regulating neurotransmitter release, as determined in knockuot mice. PMID: 17581849
- GAP-43 is required to link centrosome position to process outgrowth and regulate neuronal polarity. PMID: 18235238
- an unregulated expression of HuD disrupts mossy fiber physiology in adult mice in part by altering the expression and phosphorylation of GAP-43 and the amount of free calmodulin available at the synaptic terminal PMID: 18493953
- TNF-alpha acts as an inducer of axonal growth into degenerated discs, as evidenced by decreased GAP-43 immunoreactivity in mice receiving TNF-deficient nucleus pulposus injections. PMID: 18552668
- the phosphorylation state of a single site on GAP-43 differentially regulates performance of three different memory-associated tasks. PMID: 18727047
- Multiple effects of GAP-43 on cerebellar development suggest that it is a critical downstream transducer of signaling. mechanisms PMID: 18777197
- NFAT-3 has a role as a direct transcriptional repressor of GAP-43 expression PMID: 19443652
- Our data demonstrate that expression of GAP-43 in fibroblasts results in lengthening of the cell cycle compared to control fibroblasts. The mechanism by which GAP-43 mediated this effect involved increasing the time spent in the G(1) phase. PMID: 19589379
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell projection, growth cone membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell junction, synapse. Cell projection, filopodium membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Perikaryon. Cell projection, dendrite. Cell projection, axon. Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Neuromodulin family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the hippocampus (at protein level). Expressed in the dorsal root ganglion and the spinal cord (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14432
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000099881
UniGene: Mm.1222
Most popular with customers
-
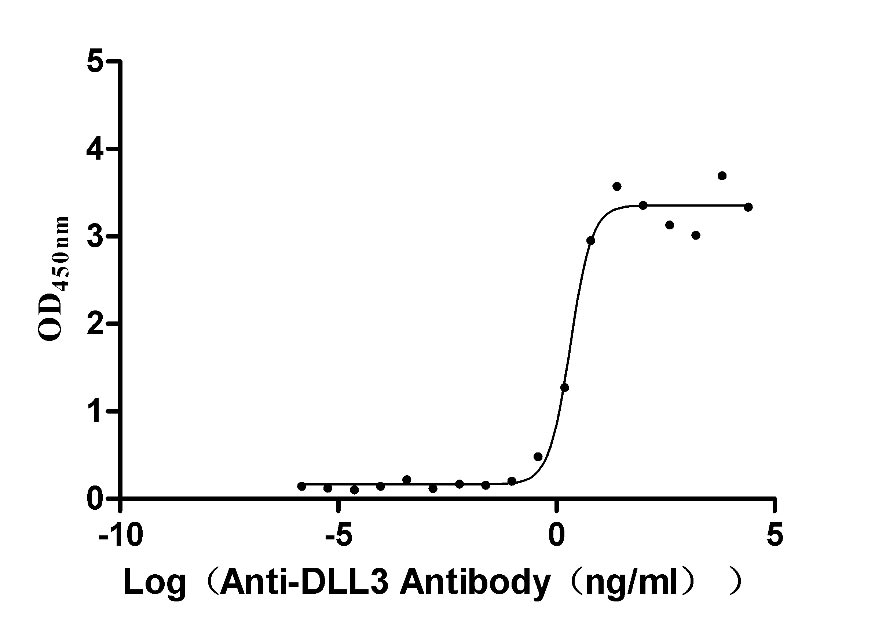
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
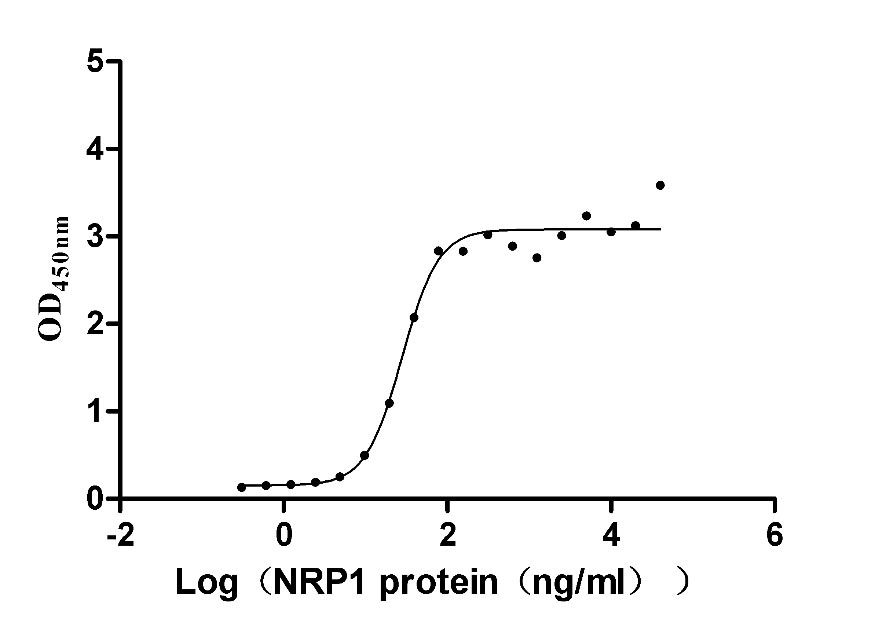
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
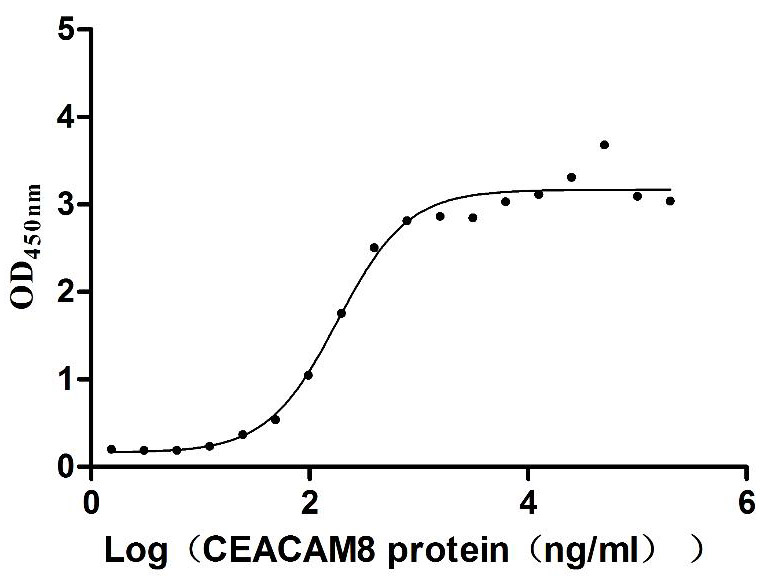
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
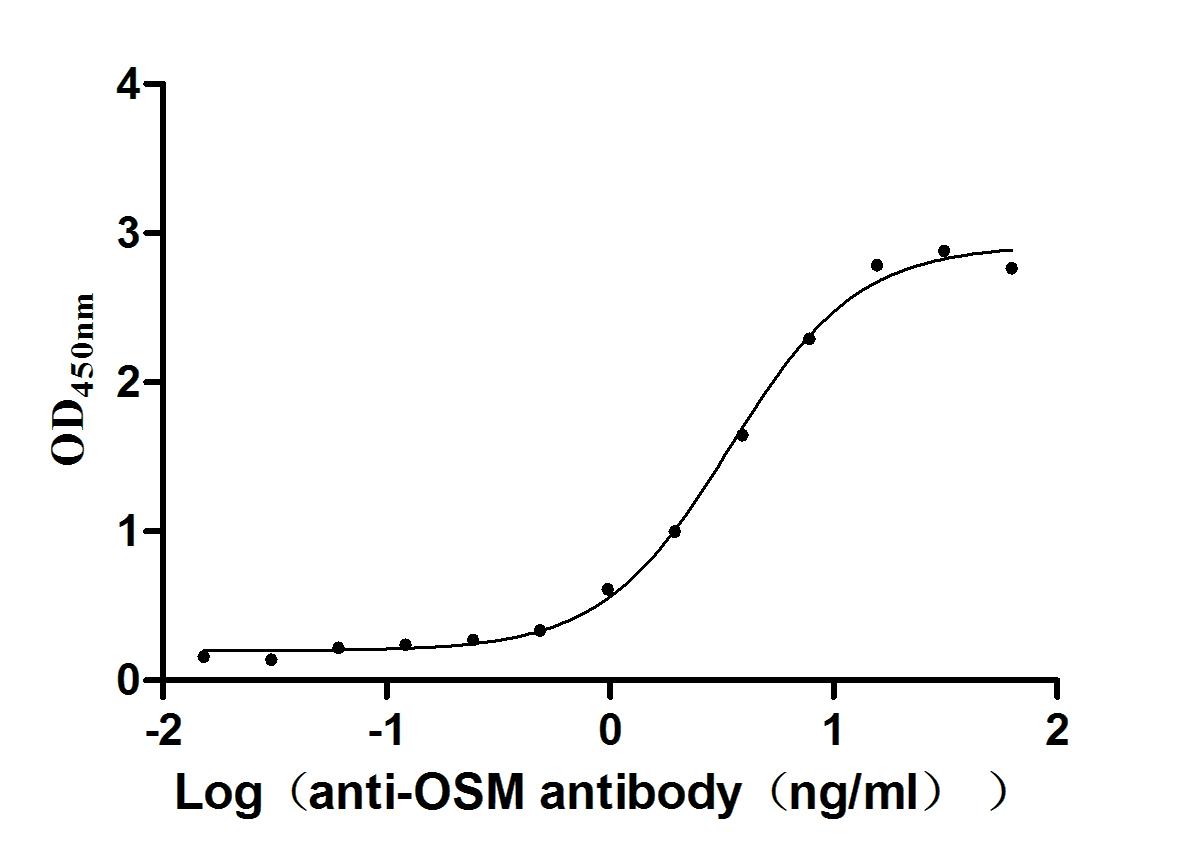
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
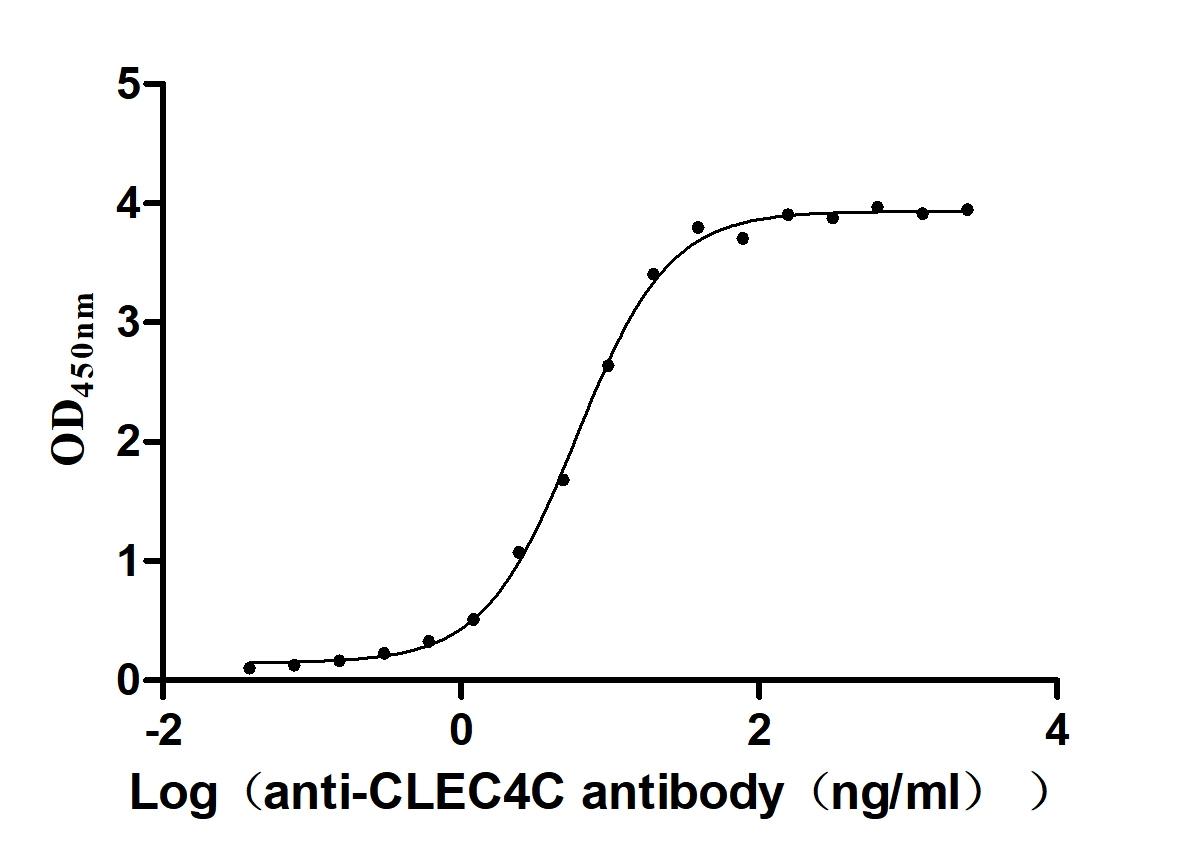
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
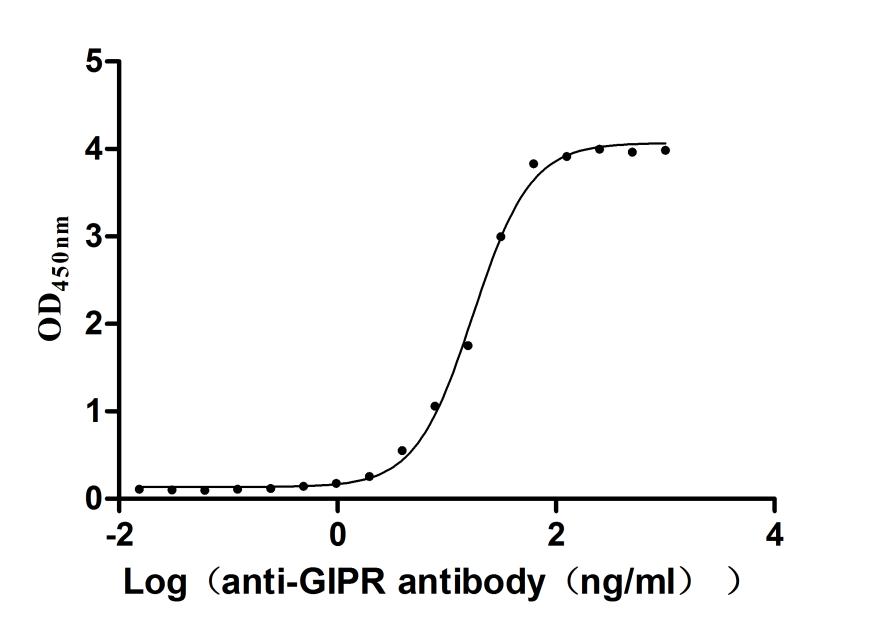
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
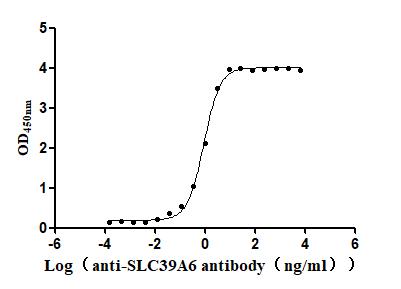
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)