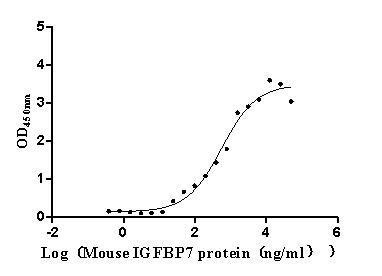
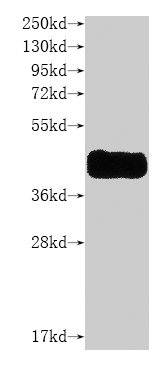
Recombinant Mouse Myogenin (Myog)
-
中文名称:小鼠Myog重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP015360MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Myog重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015360MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Myog重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015360MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Myog重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP015360MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Myog重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP015360MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Myog
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Myog; Myogenin; MYOD1-related protein
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-224
-
氨基酸序列MELYETSPYF YQEPHFYDGE NYLPVHLQGF EPPGYERTEL SLSPEARGPL EEKGLGTPEH CPGQCLPWAC KVCKRKSVSV DRRRAATLRE KRRLKKVNEA FEALKRSTLL NPNQRLPKVE ILRSAIQYIE RLQALLSSLN QEERDLRYRG GGGPQPMVPS ECNSHSASCS PEWGNALEFG PNPGDHLLAA DPTDAHNLHS LTSIVDSITV EDMSVAFPDE TMPN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Acts as a transcriptional activator that promotes transcription of muscle-specific target genes and plays a role in muscle differentiation, cell cycle exit and muscle atrophy. Essential for the development of functional embryonic skeletal fiber muscle differentiation. However is dispensable for postnatal skeletal muscle growth; phosphorylation by CAMK2G inhibits its transcriptional activity in respons to muscle activity. Required for the recruitment of the FACT complex to muscle-specific promoter regions, thus promoting gene expression initiation. During terminal myoblast differentiation, plays a role as a strong activator of transcription at loci with an open chromatin structure previously initiated by MYOD1. Together with MYF5 and MYOD1, co-occupies muscle-specific gene promoter core regions during myogenesis. Cooperates also with myocyte-specific enhancer factor MEF2D and BRG1-dependent recruitment of SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling enzymes to alter chromatin structure at myogenic late gene promoters. Facilitates cell cycle exit during terminal muscle differentiation through the up-regulation of miR-20a expression, which in turn represses genes involved in cell cycle progression. Binds to the E-box containing (E1) promoter region of the miR-20a gene. Plays also a role in preventing reversal of muscle cell differentiation. Contributes to the atrophy-related gene expression in adult denervated muscles. Induces fibroblasts to differentiate into myoblasts.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Autophagy proteins were measured to understand the molecule mechanisms. We also inhibited hypoxic autophagy and examined the changes in myogenin expression, myotubes formation, and apoptosis. PMID: 28706950
- The study demonstrates an essential role of Setd2 in myoblast proliferation and differentiation, and uncovers Setd2-mediated molecular mechanism through regulating MyoG and p21. PMID: 28130125
- Overexpression and knockdown of TLP revealed that the levels of muscle-specific myosin heavy chain and the myogenic transcription factor myogenin are downregulated by TLP. The proximal AT-rich sequence of the myogenin promoter is responsible for TLP-mediated transcriptional repression. PMID: 27680312
- This suggests that 4.1R may influence myogenesis by preventing VHL-mediated myogenin degradation. PMID: 27780863
- Findings indicate a interplay between A-kinase anchoring protein 6 (AKAP6) and myogenin. PMID: 26563778
- In summary, our results implicate that metastatic properties of some RMS subtypes might be linked to c-Myb function. PMID: 26462877
- Dach2 and Hdac9 mediate the effects of muscle activity on muscle reinnervation; Myog and Gdf5 appear to stimulate muscle reinnervation through parallel pathways PMID: 26483211
- Combining chemical with mechanical factor increases expression and there was no significant difference in MyoG expression of ESCs- and MSCs-chemical + mechanical groups PMID: 25330622
- TWIST reverses muscle cell differentiation through promoter binding and down-regulation of myogenin. PMID: 24188104
- miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation through myogenin regulation. PMID: 24385428
- P38alpha-defective, Myog-expressing myoblasts fail to form multinucleated myotubes. PMID: 22847234
- Expression of myogenin probably influences the shift from glycolytic metabolism towards oxidative metabolism in differentiating myoblasts. PMID: 24055422
- Myogenin expression and myogenesis were nearly abolished in the absence of both AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2, while enhanced AMPK activity promoted myogenesis and myotube formation. PMID: 24043309
- data demonstrated that AMPKalpha1 but not AMPKalpha2 stimulates myogenin expression and myogenesis via phosphorylation of HDAC5 at Ser 259 and 498, which provides an important mechanisms linking AMPK to myogenic differentiation PMID: 23926128
- PI3K and AKT regulated skeletal muscle differentiation by regulating the expression of Myogenin and MCK. PMID: 23732671
- These findings indicated that TFE3 has a regulatory role in myoblast differentiation, and that transcriptional suppression of myogenin expression may be part of the mechanism of action. PMID: 23211595
- the FACT complex promotes myogenin-dependent transcription PMID: 23364797
- RAGE signaling physiologically repressed Pax7 transcription in stellite cells by upregulating myogenin, thereby accelerating muscle regeneration and limiting satellite cell self-renewal. PMID: 22328527
- alphaNAC interacts with histone deacetylase corepressors to control Myogenin and Osteocalcin gene expression. corepressors at target promoters. PMID: 23092676
- the important role of myogenin in maintaining terminal muscle cell differentiation PMID: 22235349
- TEAD factors directly induce Myogenin, CDKN1A and Caveolin 3 expression to promote myoblast differentiation. PMID: 21701496
- Ptpla regulates myogenesis through Myog. PMID: 22106411
- Myog and the signaling cascades regulating its induction following muscle denervation may represent novel targets for therapies aimed at reducing denervation-induced muscle atrophy. PMID: 21465538
- suggest a novel mechanism for transcriptional repression by TSHZ3 in which TSHZ3 and BAF57 cooperate to modulate MyoD activity on the Myog promoter to regulate skeletal muscle differentiation. PMID: 21543328
- myogenin was dispensable for muscle regeneration. Factors associated with muscle fatigue, metabolism, and proteolysis were significantly altered in mdx:Myog-deleted mice PMID: 21264243
- CTCF enhances the myogenic potential of MyoD and myogenin and establishes direct interactions with MyoD, indicating that CTCF regulates MRF-mediated muscle differentiation. PMID: 21288905
- alpha-syntrophin plays an important role in regulating myogenesis by modulating myogenin expression PMID: 21179410
- Results analyze the DNA methylation pattern of the 5'-flanking of the myogenin gene, a positive regulator of muscle differentiation with no CpG island and low CpG density, in both C2C12 muscle satellite cells and embryonic muscle. PMID: 20935518
- Myogenin plays a dual role as both a regulator of muscle development and an inducer of neurogenic atrophy PMID: 20887891
- Interplay between DNA methylation and transcription factor availability: implications for developmental activation of the mouse Myog gene are discussed. PMID: 20498275
- S-adenosylmethionine-sulphate-p-toluenesulphonate (SAM) inhibits myogenin expression by delaying the demethylation of specific CpG in differentiating myoblasts PMID: 11728447
- p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-, calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, and calcineurin-mediated signaling pathways transcriptionally regulate its expression PMID: 12058061
- role of C-terminus in upregulation of MEF2C expression PMID: 12135755
- Myogenin was detected by cell culture immunostaining using the polyclonal anti-mouse myogenin. PMID: 12871697
- data indicate two distinct innervation-dependent mechanisms restrain myogenin activity: an inactivation mechanism mediated by phosphorylation of myogenin at T87 and a second mechanism that regulates myg gene activity independently of T87 phosphorylation PMID: 14966278
- Myogenin protein stability is decreased by BMP-2 through a mechanism implicating Id1. PMID: 15322112
- Myog-deleted mice were 30% smaller than control mice, suggesting that the absence of myogenin disrupted general body growth. PMID: 16407395
- a HDAC-Dach2-myogenin signaling pathway has been identified to decode nerve activity and control muscle gene expression in developing and adult skeletal muscle PMID: 17075071
- Brg1 is required for the continued production of the myogenin protein in newborn skeletal muscle tissue; the skeletal muscle phenotype is maintained by myogenin and the continuous activity of Brg1-based SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling enzymes PMID: 17194702
- caveolin-3 levels are downregulated by nitric oxide through the interaction with myogenin, the transcription factor for caveolin-3 PMID: 17519233
- transcription of Cugbp1 gene in muscle is regulated by myogenin and E proteins PMID: 17531403
- HDAC4 is a neural activity-regulated deacetylase and a key signaling component that relays neural activity to the muscle transcriptional machinery through Dach2, myogenin, and nAChR PMID: 17873280
- The results identify new target genes for myogenin and show that myogenin's target gene selectivity is not based solely on binding site sequences. PMID: 17904117
- IL-10 plays a protective role in nonhematopoietic cells by suppressing the ability of exogenous IL-1beta to inhibit IGF-I-induced myogenin and myosin heavy chain expression in myoblasts PMID: 18270299
- Despite a lack of skeletal muscle defects in Myog-deleted mice during postnatal life and differentiation of Myog-deleted adult muscle stem cells, the loss of myogenin profoundly altered gene expression in muscle stem cells and adult skeletal muscle. PMID: 18721801
- properties of a TAF3/TRF3 complex in directing transcription initiation at the Myogenin promoter. PMID: 18851836
- Ski is necessary for muscle terminal differentiation and that it exerts this role, at least in part, through its association with Six1 and Eya3 to regulate the Myog transcription PMID: 19008232
- PAX3 mRNA is an Staufen 1-mediated mRNA decay target whose decay promotes myogenesis whereas myogenin mRNA is a classical nonsense-mediated mRNA decay target encoding a protein required for myogenesis PMID: 19095803
- HDAC4/myogenin positive feedback loop that coordinates gene induction and repression underlying muscle phenotypic changes after muscle denervation. PMID: 19109424
- Results suggest that MAFbx functions as an F-box protein in the SCF complex for ubiquitination of myogenin. PMID: 19631210
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Note=Recruited to late myogenic gene promoter regulatory sequences with SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A and SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling enzymes to promote chromatin-remodeling and transcription initiation in developing embryos.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in myoblast cells. Expressed weakly in myotubes (at protein level). Expressed strongly in denervated muscles and in satellite cells isolated from denervated muscles. Expressed weakly in innervated muscle and in satellite cells isolated from inne
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:17928
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000027730
UniGene: Mm.16528
Most popular with customers
-
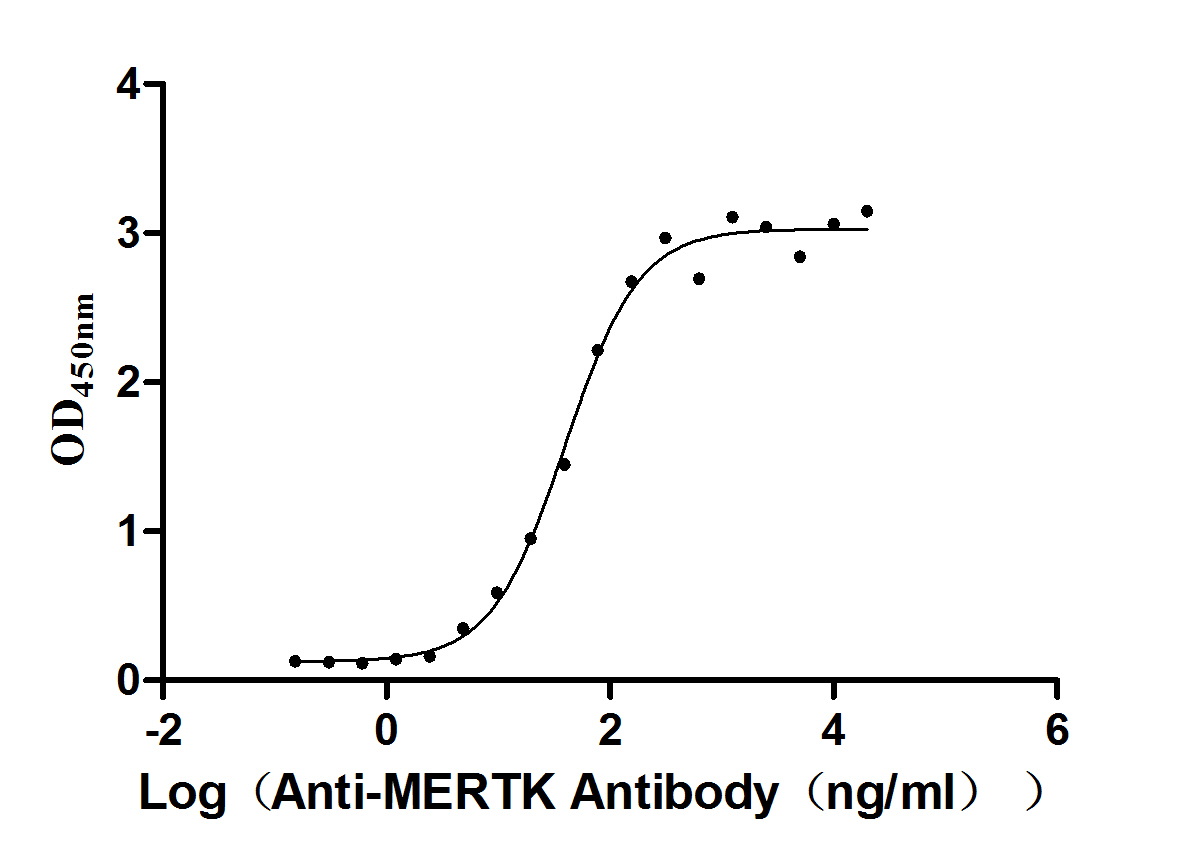
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
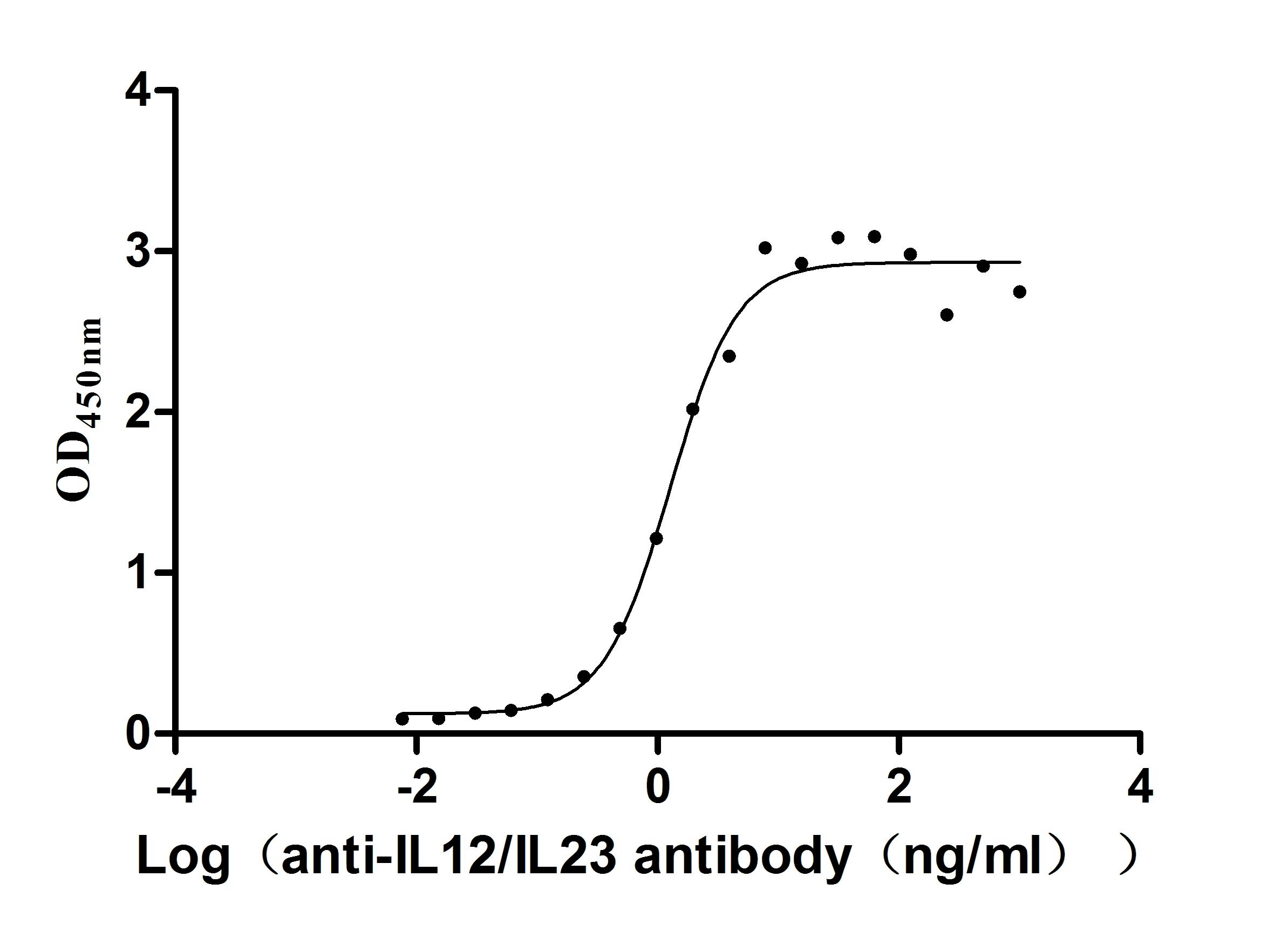
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
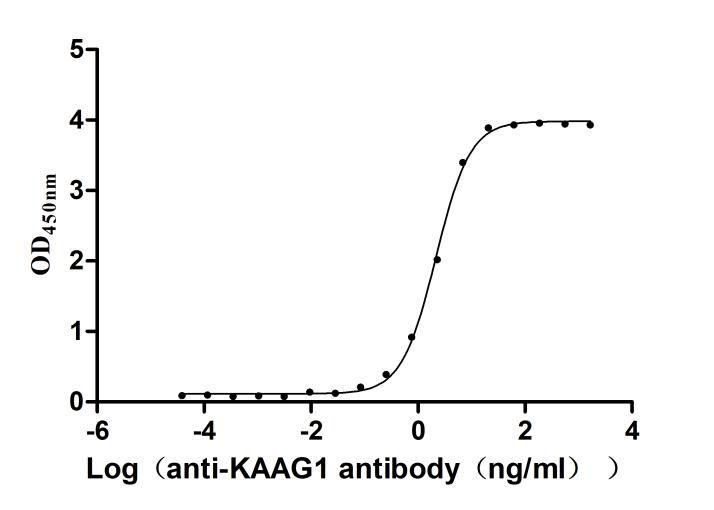
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)