Recombinant Mouse Kappa-type opioid receptor (Oprk1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP016359MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP016359MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP016359MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP016359MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP016359MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Oprk1; Kappa-type opioid receptor; K-OR-1; KOR-1; MSL-1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:G-protein coupled opioid receptor that functions as receptor for endogenous alpha-neoendorphins and dynorphins, but has low affinity for beta-endorphins. Also functions as receptor for various synthetic opioids and for the psychoactive diterpene salvinorin A. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling leads to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity. Inhibits neurotransmitter release by reducing calcium ion currents and increasing potassium ion conductance. Plays a role in the perception of pain. Plays a role in mediating reduced physical activity upon treatment with synthetic opioids. Plays a role in the regulation of salivation in response to synthetic opioids. May play a role in arousal and regulation of autonomic and neuroendocrine functions.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our results indicate that the stimulation of kappa-opioid receptors in the hippocampus may ameliorate cognitive dysfunction through the activation of the cholinergic system. These findings may offer a therapeutic alternative approach in the treatment of depression patients' symptoms PMID: 29863085
- Suggest that peripheral and central MOR and central KOR may be involved in the modulation of scratching behaviour in imiquimod-treated mice. PMID: 28512665
- chronic KOR activation increased phosphorylation of NR2B subunit of NMDA at tyrosine 1472 (pNR2B NMDA) in the hippocampus, but not in the cortex. PMID: 27634008
- Pre- and postsynaptic colocalization of kappa opioid receptor and D2R supports a role for kappa opioid receptor potentiating both the D2R inhibitory autoreceptor function and the inhibitory action of D2R on efferent medium spiny neurons. Kappa opioid receptor co-activation accelerates D2R sensitization by contributing to decrease dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. PMID: 28531297
- Mechanical allodynia produced by monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) was enhanced in mice lacking KOR or PDYN gene. In contrast with the nociceptive manifestations induced by osteoarthritis, the increased microglial expression on the lumbar section of the spinal cord after MIA administration was similar in KOR-KO, PDYN-KO and WT littermates. Moreover, anhedonic- and anxiolytic-like states were revealed after MIA administration. PMID: 27567942
- The kappa opioid receptor was identified as a key player mediating the effects of buprenorphine in tests sensitive to antidepressant drugs in mice. PMID: 26979295
- This study provides the first evidence for a time- and learning-dependent property of neocortical kappa opioid receptor in facilitating acquisition and consolidation of associative memories. PMID: 28119127
- triazole 1.1 retained the antinociceptive and antipruritic efficacies of a conventional KOR agonist, yet it did not induce sedation or reductions in dopamine release in mice, nor did it produce dysphoria as determined by intracranial self-stimulation PMID: 27899527
- This study reports a cluster of compounds that are highly effective in enhancing remyelination and identifies kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) as a positive regulator for oligodendroglial differentiation, implicating KOR agonism as a potential strategy to accelerate remyelination. PMID: 27466337
- GRK2 upregulation causes kappa-opioid receptor desensitization in diabetic heart PMID: 27865836
- Study showed that Dyn-A, the endogenous kappa opioid receptor agonist, significantly hyperpolarized and inhibited neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of mouse thalamus PMID: 26056031
- Suggest that mixed cardiac ion channel blockade my mediated the antiarrhythmia actions of kappa-opioid receptor antagonist PD117,302. PMID: 26086860
- Findings suggest that activation of kappa opioid receptor (kappa-opioid receptor) reduces hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. PMID: 25186835
- kappa-Opioid receptor mediates the antinociceptive effect of nitrous oxide in mice. PMID: 25086587
- The data of this study provide evidence that KORs on VTA DA neurons are necessary to mediate KOR-mediated aversive behavior. PMID: 23921954
- Ablation of kappa-opioid receptors from brain dopamine neurons had anxiolytic-like effects. PMID: 23446450
- Natural food reward and systemic ghrelin activate Kappa opioid receptors in the ventral tegmental area. PMID: 23220294
- Data suggest that activation of neurokinin 3 and kappa-opioid receptors (NK3R and KOR) excites and inhibits kisspeptin, neurokinin B (NKB), and dynorphin (KNDy neurons). PMID: 23744642
- Data (including data from KOR knockout mice) suggest that KOR modulates GABAergic synaptic responses in the central amygdala and modulates the effects of ethanol as one of multiple opioid system-dependent actions of ethanol in the central amygdala. PMID: 23587526
- hKOR activates p38 MAPK through a phosphorylation and arrestin-dependent mechanism; however, activation differs between hKOR and rKOR for some ligands PMID: 23086943
- these data suggest that endogenous prodynorphin-derived peptides sufficiently activate KOP receptors during acute seizures, and importantly in situations of reduced dynorphinergic signaling-like in epilepsy-the exogenous activation of KOP receptors might also have strong neuroprotective effects during excitotoxic events. PMID: 21391243
- Centrally administered apelin-13 elicited depression-like behavior in mice, which was mediated via APJ receptor and kappa-opioid receptor, but not CRF receptor. PMID: 22728209
- Repeated stress exposure reduces KOR inhibitory regulation on 5-serotonin (HT)neuronal excitability postsynaptically. PMID: 22956823
- results demonstrate that KOR provides important inhibitory control over presynaptic GABAergic signaling within the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis PMID: 22225848
- Macrophages express kappa opioid receptors, which signal via ERK1/2 phosphorylation and which are upregulated by proinflammatory IFN-gamma. PMID: 22424981
- The Ro1 model represents a model of communicating hydrocephalus. PMID: 22291910
- During stress exposure, kappa-opioid receptor activation is necessary and kappa-receptor activation in the amygdala alone is sufficient to increase nicotine-seeking behavior measured by conditioned place preference. PMID: 22279233
- Data indicate that the potency and selectivity of the in vitro kappa antagonism were confirmed in the tail-flick analgesia model. PMID: 21744827
- The opioid system is a new regulator of vascular development that simultaneously modifies 2 distinct vascular properties, embryonic cell differentiation and vascular pathfinding. PMID: 21460241
- we suggest NKB & dynorphin act autosynaptically on kisspeptin neurons in the arcuate nucleus to synchronize & shape pulsatile secretion of kisspeptin & drive the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone from fibers in the median eminence [neurokinin B] PMID: 19776272
- Ligand-directed c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation disrupts opioid receptor signaling PMID: 20534436
- These results show that kappa opioid receptor system has different effects after pIONL in CNS and PNS: KOR activation promotes CNS astrocytosis and microglial or stem cell proliferation but inhibits macrophage proliferation in PNS. PMID: 20109235
- Kappa opioid receptor contributes to EGF-stimulated neurite extension in development. PMID: 20133770
- Corticotropin Releasing Factor and dynorphin/KOR systems may coordinate stress-induced anxiety behaviors and aversive behaviors via different mechanisms. PMID: 20052275
- Kappa opioid receptor binds to Sp1 and inhibits the ERK pathway PMID: 12171913
- A negative regulatory pathway for KOR transcription involves a putative enhancer region in its 3'-UTR. KOR mRNAs using the second poly(A) is more stable than that using the first poly(A). PMID: 12237335
- KOR-/- animals produced significant higher levels of antigen-specific total Ig, IgM, IgG1 and IgG2a antibodies. Endogenous activation of kappa-opioid receptors may exert a tonic inhibition of antibody response. PMID: 12507774
- The difference in alcohol preference between B6 and BALB/cJ strains is not correlated with polymorphisms of Oprk1; DBA/2J mice (alcohol-avoiding) show expression of Oprk1 mRNA subtypes (alternatively spliced) that are different from B6 and BALB/cJ. PMID: 12657375
- No impairment in spatial learning in kappa opioid receptor mutants or in mossy fibers in CA3 hippocampal region long-term potentiation. PMID: 12884965
- The 5'- and 3'-untranslated regions of KOR, either alone or in combination, are able to mediate transport of mRNAs to processes of P19 embryonal carcinoma neurons and axons of dorsal root ganglia. PMID: 12920195
- Collectively, the high potency and efficacy and the relative abundance suggest that Big Dynorphin may play a role in the kappa opioid receptor-mediated activation of G proteins. PMID: 16515546
- The present study demonstrated that morphine can produce thermal antinociception via the kappa opioid receptor in the spinal cord in the absence of the mu opioid receptor. PMID: 16530171
- opioid modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity may play an important role in embryonic stem cell fate decisions by directing the cells to specific lineages PMID: 16954126
- These findings suggest that, although kappa opioid receptors can hyperpolarize dopamine neurons, they also suppress dopamine release by direct actions at the release site. PMID: 17122312
- provided evidence for mRNA transport and regulation of presynaptic protein synthesis of nonstructural proteins like KOR in primary sensory neurons PMID: 17167054
- MOR and KOR are important in skin homeostasis, epidermal nerve fiber regulation, and pathophysiology of itching PMID: 17185983
- Results support the hypothesis that KOR activation induces spinal astrocyte proliferation, which may contribute to cellular reorganization after sciatic nerve damage. PMID: 17344394
- Changes in kappa opioidergic receptor expression in brain regions may be involved in the long-term consequences of stroke and could be used as biomarker of neuronal alteration through the use of imaging techniques in the clinic. PMID: 17676326
- Co-treatment with ultra-low-dose naltrexone or nor-binaltorphimine may selectively block signaling by endogenous GM1-sensitized excitatory kappa opioid receptors, unmasking inhibitory kappa opioid receptor signaling. PMID: 17692296
- provides evidence for a microtubule-dependent, active axonal kappa opioid receptor mRNA-transport process that involves Copb1 and can stimulate localized translation PMID: 17698811
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
组织特异性:Detected in brain (at protein level). Brain (neocortex, hippocampus, amygdala, medial habenula, hypothalamus, locus ceruleus, and parabrachial nucleus).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:18387
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000027038
UniGene: Mm.7977
Most popular with customers
-
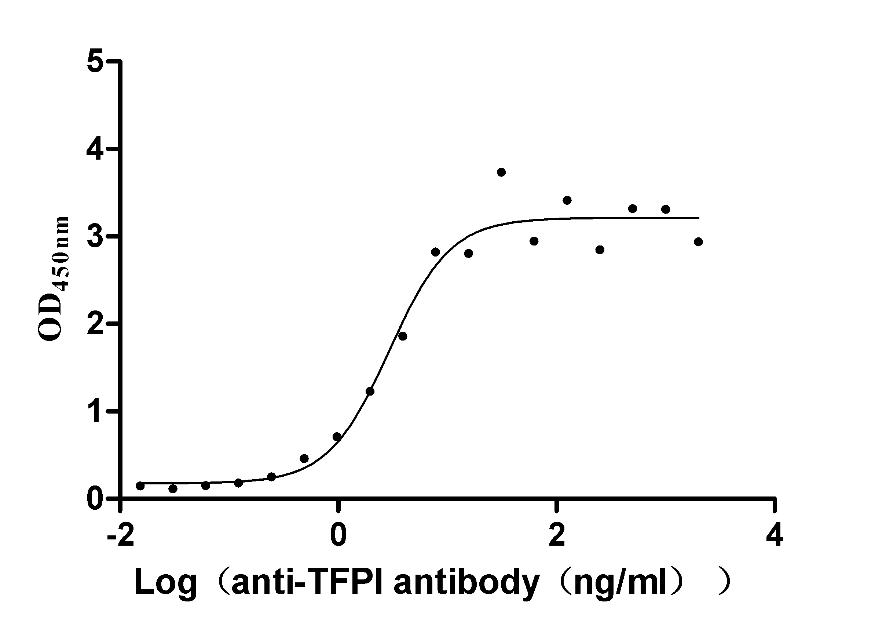
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
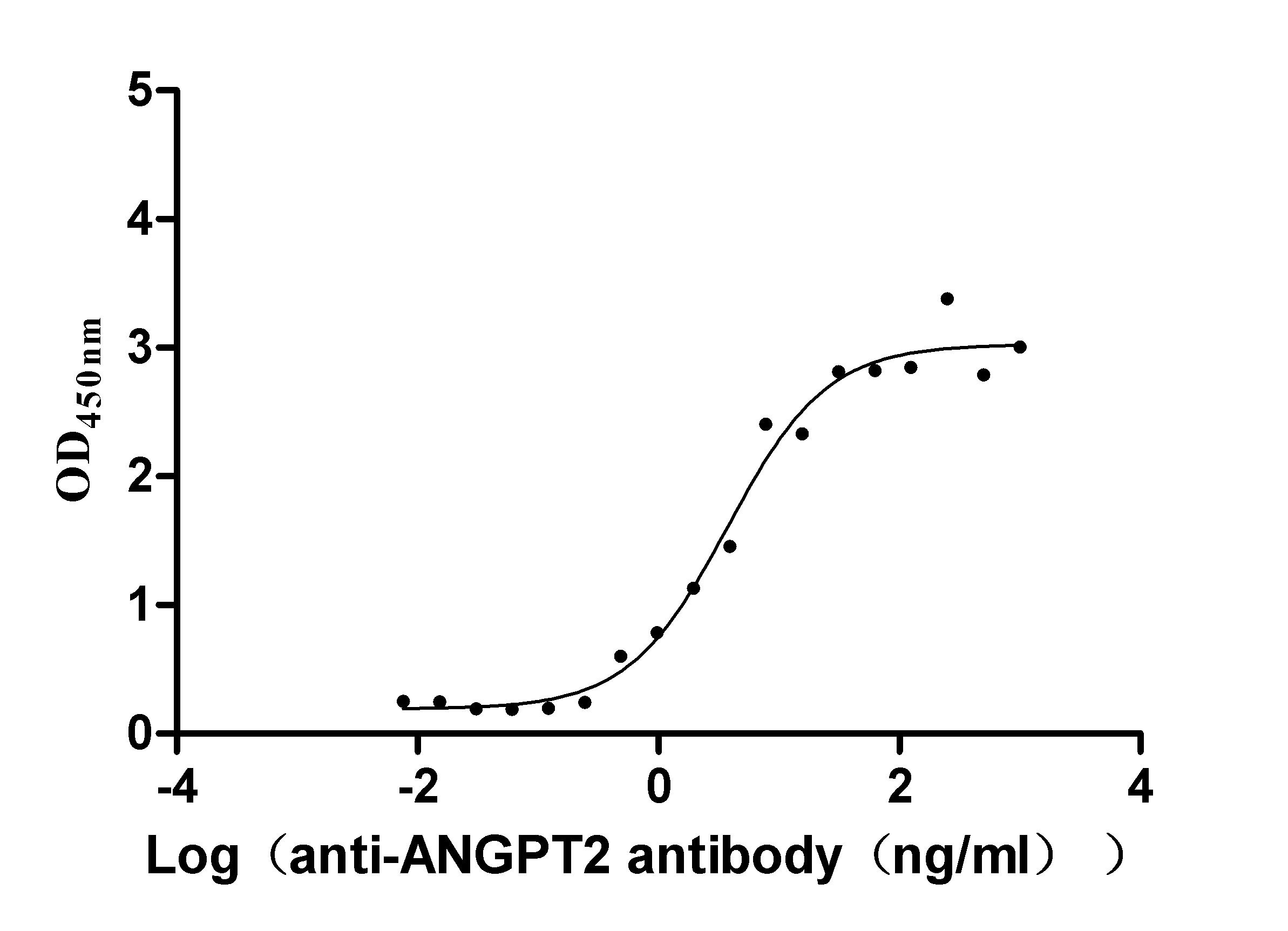
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
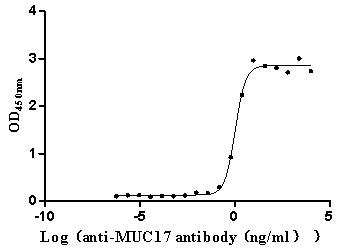
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
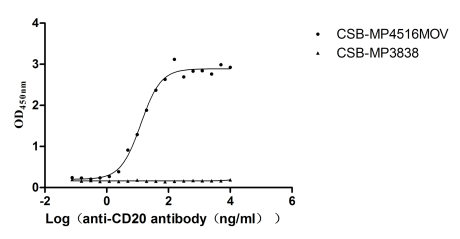
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
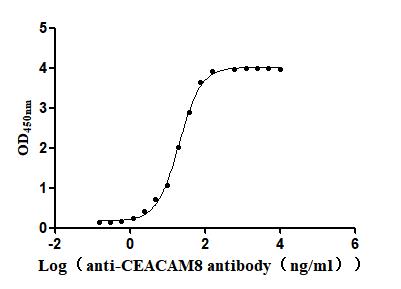
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
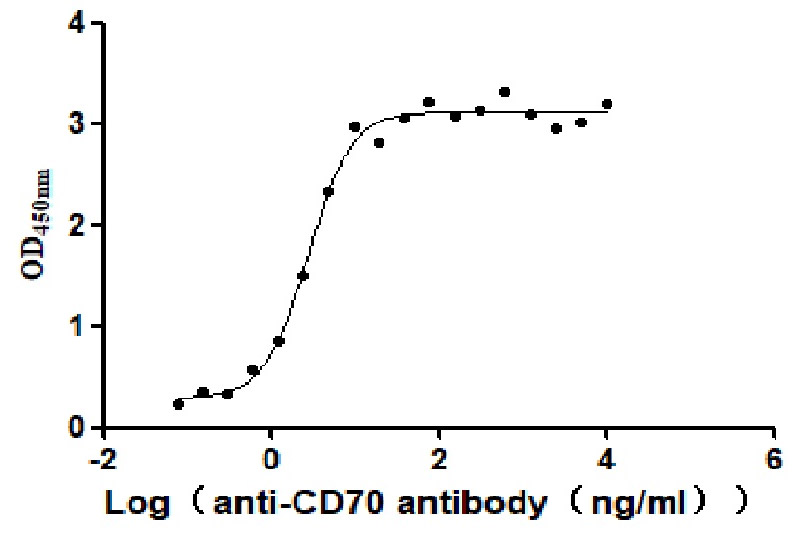
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
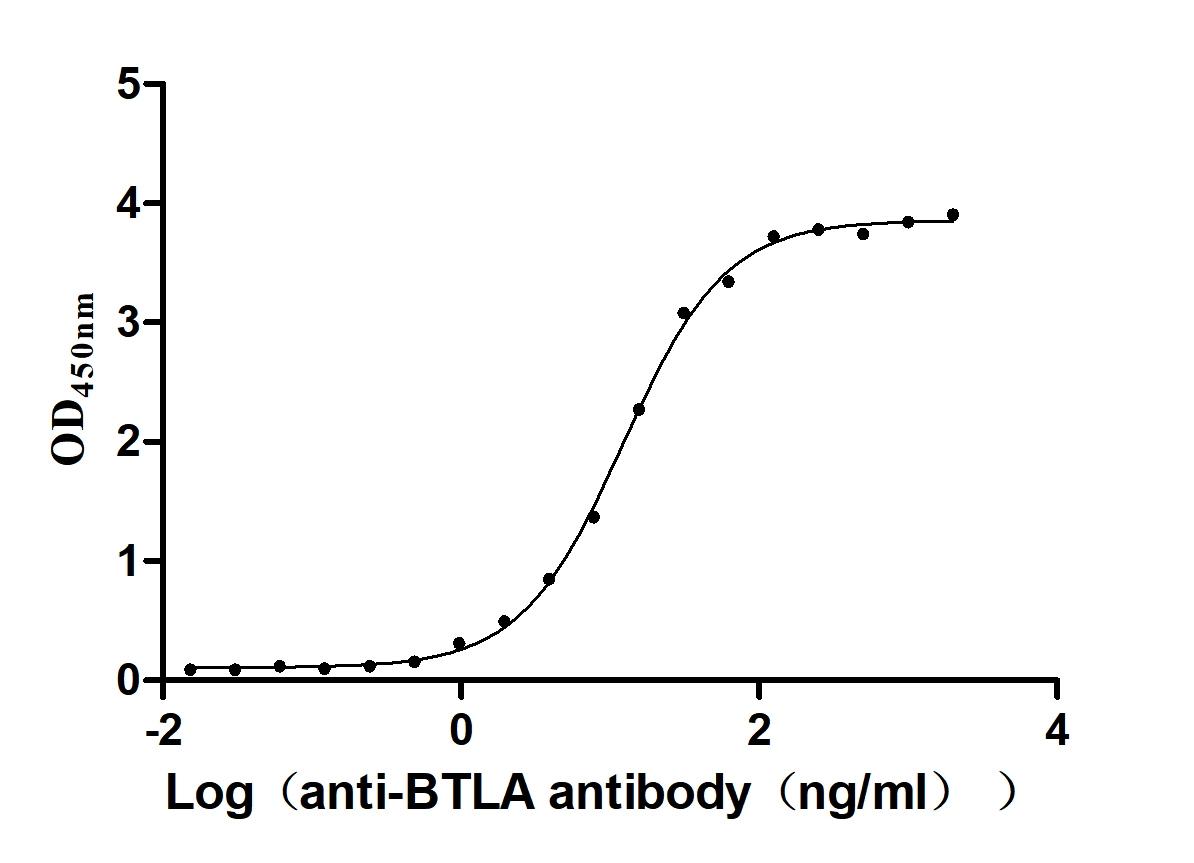
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)