Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 (Irak3)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-BP011811MO
-
规格:¥3168
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
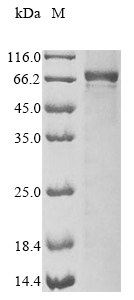
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Irak3Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3; IRAK-3; EC 2.7.11.1; IL-1 receptor-associated kinase M; IRAK-M
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
分子量:72.3
-
表达区域:1-609aa
-
氨基酸序列MAGRCGARGALSPQLLLFDLPPALLGELCGILDSCDGPLGWRGLAERLSNSWLDVRHIEKYVNQGKSGTRELLWSWAQKNKTIGDLLEVLQDMGHQRAIHLIINYGVSWTPSVQTHHELPFPSFPPEVKHACRENDPGPLEPANVTVDNVLVPEHNEKGTLQKTPISFQSILEGTKHFHKDFLIGEGEIFEVYRVDIRNQAYAVKLFKQEKKMQLKKHWKRFLSELEVLLLFRHPHILELAAYFTETEKLCLVYPYMSNGTLFDRLQCTNGTTPLSWHVRISVLIGIAKAIQYLHNTQPCAVICGNVSSANILLDDQLQPKLTDFAAAHFRPNLEQQSSTINMTGGGRKHLWYMPEEYIRQGRLSVKTDVYSFGIVIMEVLTGCKVVLDDPKHVQLRDLLMELMEKRGLDSCLSFLDRKIPPCPRNFSAKLFSLAGRCVATKAKLRPTMDEVLSSLESTQPSLYFAEDPPTSLKSFRCPSPLFLDNVPSIPVEDDENQNNHSVPPKEVLGTDRVTQKTPFECSQSEVTFLGLDRNRGNRGSEADCNVPSSSHEECWSPELVAPSQDLSPTVISLGSSWEVPGHSYGSKPMEKRCSSGLFCSEHEQSKKQ
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Putative inactive protein kinase which regulates signaling downstream of immune receptors including IL1R and Toll-like receptors. Inhibits dissociation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 from the Toll-like receptor signaling complex by either inhibiting the phosphorylation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 or stabilizing the receptor complex. Upon IL33-induced lung inflammation, positively regulates expression of IL6, CSF3, CXCL2 and CCL5 mRNAs in dendritic cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study using IL-33-induced type 2 immunity signaling in a combination of cell lines, mouse models, and primary cells from mouse models reveal critical roles of IRAK-M and PIN1 in IL-33-induced type 2 immunity. Upon IL-33-induced inflammation, activated PIN1 binds to and catalyzes cis-trans isomerization of phosphorylated IRAK-M, inducing IRAK-M stabilization and nuclear translocation. PMID: 29686383
- IRAK3 methylation may be a predictive factor in the transition from colitis to cancer. PMID: 28713897
- IRAK-M plays a crucial role in the regulation of allergic airway inflammation by modifying the function of airway epithelia PMID: 28665693
- Taken together, these results strongly support a role for IRAK-M in renal injury and identify IRAK-M as a possible modulator in driving an alternatively activated profibrotic macrophage phenotype in unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced chronic kidney disease. PMID: 28701510
- polycomb recessive complex 2 repressed the IRAK-M promoter, allowing low levels of expression; following LPS stimulation, the IRAK-M promoter is derepressed, and transcription is induced to allow its expression. PMID: 28011933
- this study shows that following Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, IRAK-M knock-out mice have enhanced lung neutrophilic inflammation and reduced bactertial load PMID: 28120642
- Data show that interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 (IRAK-M) is responsible for regulation of microbial colonization of tumors and STAT3 protein stability in tumor cells, leading to tumor cell proliferation. PMID: 27150039
- IRAK-M functions to modulate inflammatory signaling pathways and is critical in maintaining immune system homeostasis in the gut. However, increased IRAK-M is associated with increased disease pathogenesis and increased cancer severity in human patients. PMID: 27939424
- IRAK-M may also contribute to myofibroblast conversion. PMID: 26542797
- These data demonstrate LTi cells are present in the stomach and promote lymphoid follicle formation in response to infection, but are limited by IRAK-M expression. PMID: 25603827
- IL-7 reduced IRAK-M expression and attenuated immune tolerance induced by either LPS or CpGA PMID: 26218271
- the results suggest that IRAK-M may be targeted by L. donovani to inhibit TLR-mediated proinflammatory response late during in vitro infection. PMID: 26140693
- These data indicate expression of IRAK-M skews lung macrophages toward an alternatively activated profibrotic phenotype, which promotes collagen production, leading to the progression of experimental pulmonary fibrosis. PMID: 25595781
- Our study identifies the DAP12/IRAK-M/IL-10 to be a novel molecular pathway in APCs exploited by mycobacterial pathogens, allowing infection a foothold in the lung. PMID: 24172845
- This study illustrates how the modulation of innate immune pathways through IRAK-M influences the development of autoimmune diabetes. PMID: 24696448
- novel findings provide new insights into the understanding of negative regulatory mechanisms of the TLR4 signaling pathway. PMID: 23872113
- Altered gut microbiota promotes colitis-associated cancer in IL-1 receptor-associated kinase M-deficient mice. PMID: 23567778
- IRAK-M plays an important role in alcohol-induced liver injury and IRAK-M negatively regulates the innate and possibly the adaptive immune response in the liver reacting to acute insult by alcohol. PMID: 23437317
- debris-induced IRAK-M decreases foreign body reactions, but at the same time, the over-expression of IRAK-M may also be detrimental on local intrusion of PAMPs or bacteria PMID: 22941946
- IRAK-M mediates TLR7-induced MEKK3-dependent second wave NFjB activation to produce inhibitory molecules PMID: 23376919
- IRAK-M impairs host defense during pneumonia caused by a common gram-negative respiratory pathogen. PMID: 22729155
- Along with endotoxin, bacterial sonicate is able to induce refractory tolerance in BM-DCs, and IRAK-M plays a role in modulating cell surface expression of MHC class II and CD80 and release of IL-10 during this tolerance. PMID: 22472665
- These data suggest that IRAK-M impairs host defense during pneumococcal pneumonia at the primary site of infection at least in part by inhibiting the early immune response. PMID: 22492852
- The upregulation of IRAK-M in macrophages is involved in the local immunosuppression around implants, and may contribute to septic and aseptic implant loosening. PMID: 21987497
- Endotoxin tolerization in vivo blocked TLR4-driven IRAK4 phosphorylation and activation in macrophages, while increasing expression of IRAK-M, SHIP-1, A20 mRNA, and A20 protein. PMID: 21934070
- These data identify a previously unknown function of IRAK-M :suppression of TLR7-mediated autoimmunity-and mutant IRAK-M as a previously unknown genetic risk for murine SLE. PMID: 21875872
- Role of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-M (IRAK-M) in priming of immune and inflammatory responses by nitrogen bisphosphonates. PMID: 21690387
- By facilitating IRAK-M expression, DNAX-activation protein (DAP)12 functions to negatively regulate lipopolysaccharide-induced liver dendritic cell maturation. PMID: 21257958
- Loss of IRAK-M is associated with colitis. PMID: 20848470
- IRAK-M is bound to caspase (CASP)-6 in a complex located near the plasma membrane in resting cells, and the components of this complex redistribute to nucleus and cytoplasm after neutrophil stimulation. PMID: 21098228
- findings indicate that systemic sepsis induces epigenetic silencing of cytokine gene expression in lung macrophages, and IRAK-M appears to be a critical mediator of this response PMID: 20585389
- manipulation of IRAK-M levels can increase the potency of DC vaccines by enhancing their Ag-presenting function, migration, and longevity PMID: 20817880
- these findings suggest that IRAK-M negatively regulates the alternative NFkappaB pathway in a ligand-specific manner. PMID: 19809574
- These data suggest that the absence of IRAK-M in the hematopoietic compartment post-bone marrow transplantation enhances pulmonary host defense and mitigates alveolar macrophage sensitivity to the inhibitory effects of PGE(2 PMID: 20439918
- IRAK-M is critical to preventing deleterious neutrophil-dependent lung injury during influenza infection of the respiratory tract. PMID: 20042589
- Endotoxin tolerance was significantly reduced in macrophages from IRAK-M knockout mice. IRAK-M regulates TLR signaling and innate immune homeostasis. PMID: 12150927
- induction of IRAK-M and inhibition of kinase activity of IRAK-1 are crucial to PGN-induced tolerance in macrophages PMID: 14660668
- IRAK-M is a key regulator of the bone loss that is due to osteoclastic resorption of bone. PMID: 15809356
- IRAK-M induction negatively regulates Toll-like receptor-dependent interleukin-12 p40 production in macrophages in the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan PMID: 16263713
- These findings indicate that IRAK-M selectively attenuates p38 activation and inhibits innate immunity through stabilizing MKP-1. PMID: 17379480
- IRAK-M is directly involved in the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune signaling processes, and deletion of IRAK-M enhances host anti-tumor immune response. PMID: 17477969
- reduced expression of IRAK-1 and increased expression of IRAK-M after CpG DNA pretreatment resulted in the hyporesponsiveness of macrophages that leads to the protection of mice from hepatic injury and death caused by CpG DNA/D-GalN. PMID: 18378686
- Tolerance to intraluminally administered LPS in the lymphocyte recruitment process was induced by enterobacteria, possibly via the induction of IRAK-M and TGF-beta. PMID: 19225984
- The expression of IRAK-M as a negative regulator of TLR7 signaling was markedly augmented in immune tolerant macrophage-like cells while the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-1 functioned normally. PMID: 19251253
- IRAK-M is a major mediator of globular adiponectin-induced endotoxin tolerance in primary macrophages PMID: 19414798
- TREM-1 activation beneficially impacts pulmonary IRAK-M expression PMID: 19596984
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, Pelle subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in inflamed lung macrophages (at protein level). Expressed in dendritic cells (at protein level). Highly expressed in liver and thymus and at lower levels in heart, brain, spleen and kidney.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:73914
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000020448
UniGene: Mm.146194
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
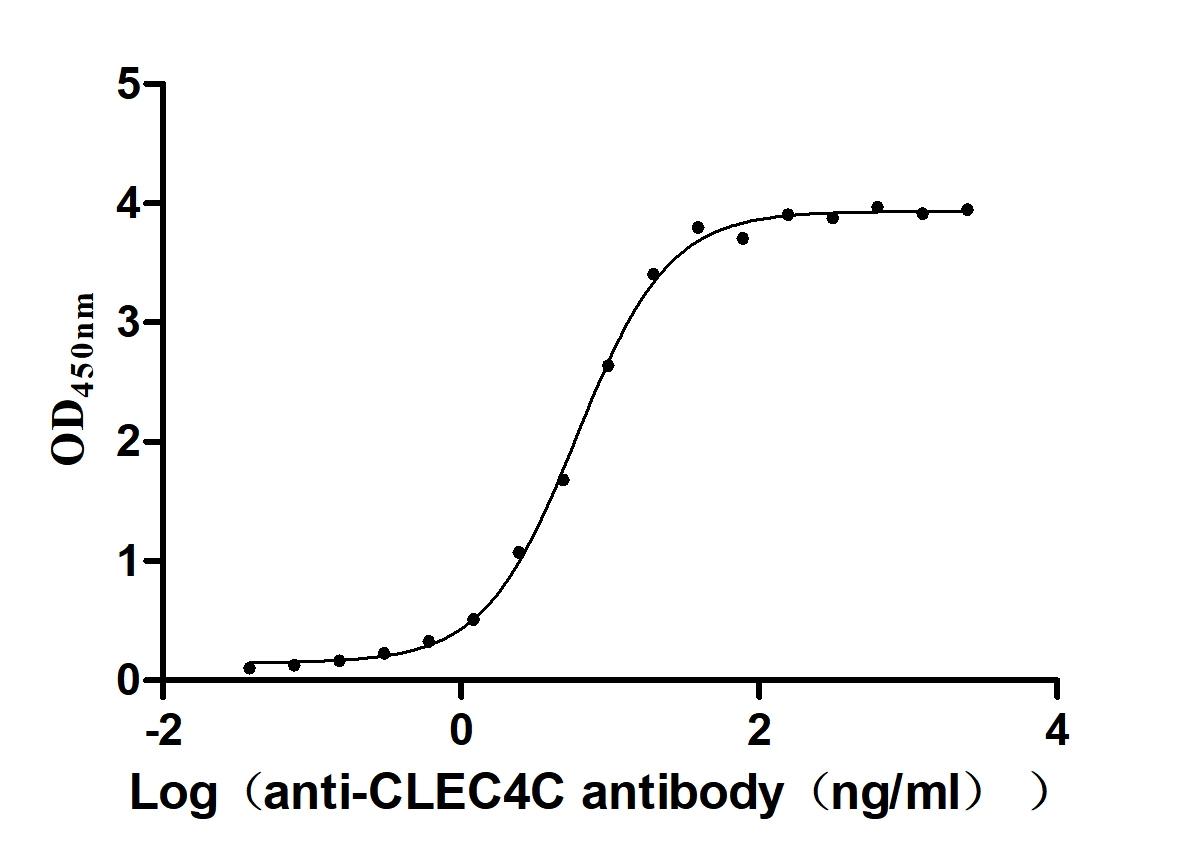
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
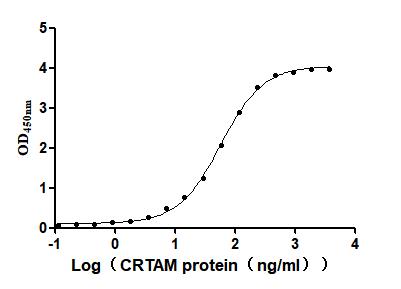
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
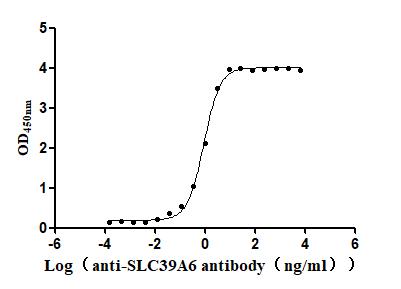
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
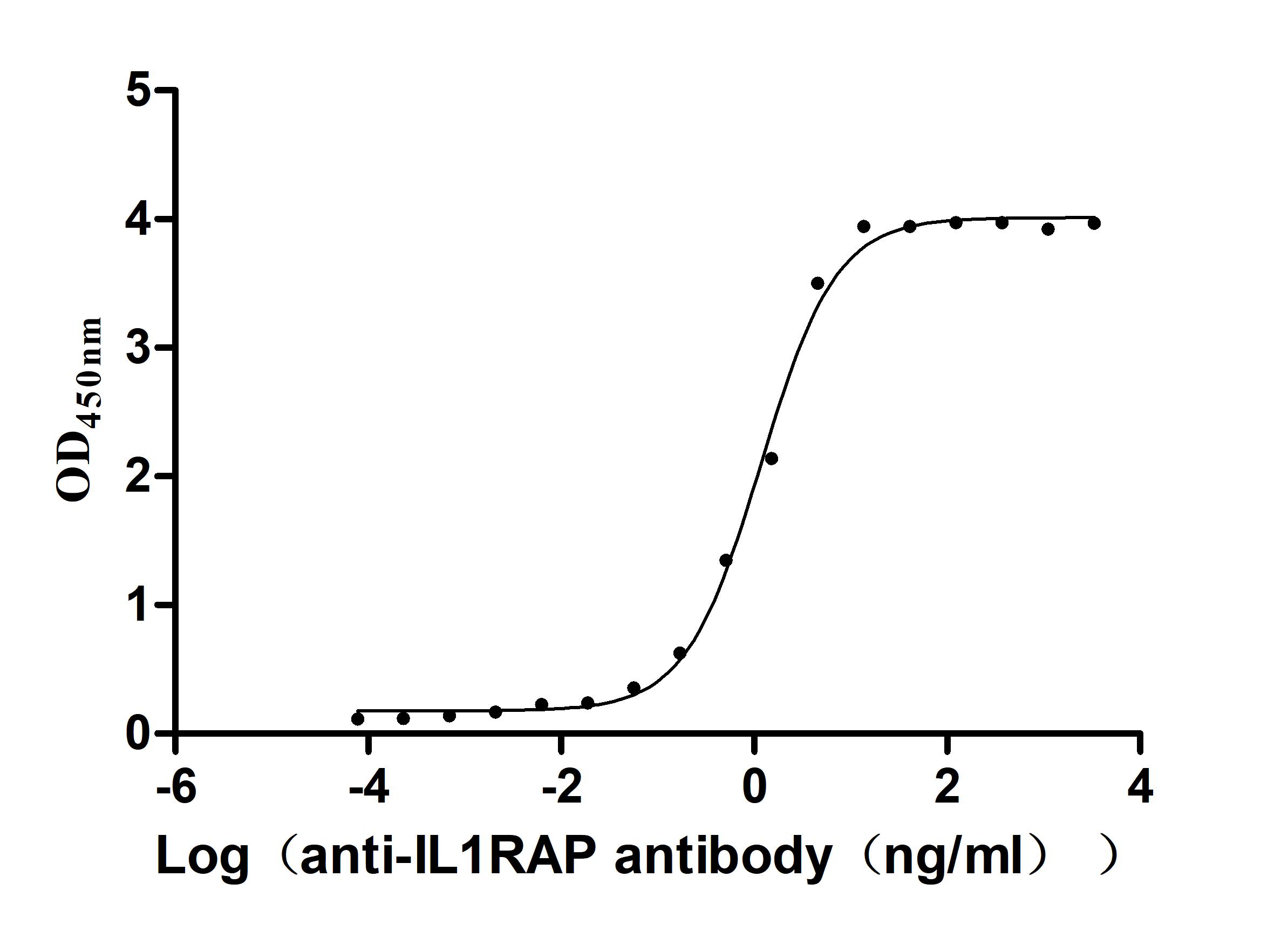
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)