Recombinant Mouse Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (Ifnar1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP011046MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011046MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011046MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP011046MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP011046MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Ifnar1; Ifar; Ifnar; Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1; IFN-R-1; IFN-alpha/beta receptor 1; Type I interferon receptor 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Component of the receptor for type I interferons, including interferons alpha, IFNB1 and IFNW1. Functions in general as heterodimer with IFNAR2. Type I interferon binding activates the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, and triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of proteins including JAKs, TYK2, STAT proteins and the IFNR alpha- and beta-subunits themselves. Can form an active IFNB1 receptor by itself and activate a signaling cascade that does not involve activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Contributes to modulate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Only type-I interferon restricts viral replication of attenuated Measles virus (MV) Schwarz strain in mice, independently of the presence of hCD46 receptor. PMID: 30199752
- A key role of the IL7 and Interferon type I receptor axis in the regulation of intratumoral t-cell functions and in the development of primary breast tumor growth and metastasis. PMID: 29070614
- Data, including data from studies in knockout and double-knockout mice, suggest complex and sex-specific roles of Ifnar1 and Ifnar2 in type 1 diabetes (T1D); female NOD mice develop T1D in absence of both Ifnar1 and Ifnar2, whereas male mice do not. PMID: 30084830
- we uncovered that IFNAR1 expression in stromal benign cells functions to protect against progression of leukemia. PMID: 28503979
- Concurrent ablation of Ifnar1 led to a modest attenuation of the CK1alpha-null phenotype indicating that, although other CK1alpha targets are likely to be important, IFNAR1 downregulation can contribute to the maintenance of the HSCs function. PMID: 28678581
- Central nervous system signaling through IFNAR1 is a factor that is critical to neural injury after stroke. PMID: 28647375
- a deleterious role for the type-1 IFNs as key modulators of the early neuroinflammatory response and therefore the neuronal cell death in Parkinson's disease PMID: 27404846
- results clearly demonstrate that: (i) MHV-68, MHV-72 and MHV-4556 differentially interact with intracellular signaling and dysregulate IFN signal transduction; (ii) MHV-68, MHV-72 and MHV-4556 degrade type I IFN receptor in very early stages of infection (2-4hpi), but not type III IFN receptor PMID: 27152708
- Results show that removal of type-1 IFN signalling in the APPSWE/PS1DeltaE9 mouse model of AD confers a predominantly anti-inflammatory glial response and protects from cognitive decline. However this phenotype does not correlate with alterations in amyloid deposition and only a modest reduction in Abeta monomer levels. PMID: 27400725
- transfusion-induced differentiation of IFNAR1(-/-) B cells into germinal center B cells and plasma cells was significantly reduced, compared to WT B cells. This study demonstrates that B cells require signaling from IFN-alpha/beta to produce alloantibodies to the human KEL glycoprotein in mice. PMID: 28836263
- study provides evidence of STING activation in T cells, in which STING agonists not only provoke type I IFN production and IFN-stimulated gene expression, mirroring the response of innate cells, but are also capable of activating cell stress and death pathways. PMID: 28615418
- These data suggest that plasmacytoid dendritic cells producing IFN-alpha and IL-33 play a pivotal role in the chronic fibro-inflammatory responses underlying murine autoimmune pancreatitis and human IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. PMID: 28373582
- type I interferons, besides their known antiviral properties, can initiate the recruitment and activation of leukocytes via induction of chemokine expression including CCL2. PMID: 26992431
- these studies demonstrate an important role for type I IFN in skin fibrosis, and they provide a rationale for IFNAR1 inhibition in scleroderma PMID: 27226090
- These results identify a key interface created by IFNAR1 residues Tyr(240) and Tyr(274) interacting with IFN-beta residues Phe(63), Leu(64), Glu(77), Thr(78), Val(81), and Arg(82) that underlie IFN-beta-IFNAR1-mediated signaling and biological processes. PMID: 28289093
- IFNAR1-deficiency accelerated humoral immune responses and parasite control by boosting ICOS-signalling in two non-lethal murine models of malaria PMID: 27812214
- reduced type I interferon production in obesity is caused by SOCS3 overexpression as well as tolerance induced by leptin PMID: 27704310
- These identify A129 mice as being highly susceptible to ZIKV and thus A129 mice represent a suitable, and urgently required, small animal model for the testing of vaccines and antivirals. PMID: 27149521
- Downregulation of IFNAR1 promotes melanoma development and progression. IFNAR1 mutation, which is partially resistant to downregulation, delays melanoma development. PMID: 27052162
- Data demonstrate that Type-1 interferons signaling is a critical pathway in the progression of neuroinflammation and presents a viable therapeutic target for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. PMID: 27022620
- The study provides evidence for the importance of brain endothelial and epithelial cells in the communication between the Central Nervous System and the immune system, and demonstrates tissue specific IFNAR1 engagement during sickness behavior. PMID: 27096319
- Data show that both NF-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and tonic interferon signals are involved in the final maturation of thymocytes into naive T cells. PMID: 27043411
- role in megakaryo- and thrombopoiesis PMID: 26134179
- ablation of Ifnar1 partially protected mice from caerulein-induced pancreatitis, as demonstrated by reduced tissue damage and macrophage recruitment. PMID: 26618925
- IFNAR signaling directly modulates T lymphocyte activity, resulting in milder experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis development PMID: 26232452
- IFN-I receptor 1 deficient mice (IFNAR1(-/-)) displayed significantly attenuated poly I:C-induced hypothermia, hypoactivity and weight loss compared to WT C57BL/6 mice. PMID: 25900439
- Data suggest MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response protein) is redundant for Ifnar1/IFN-I (interferon type I) responses and overall defense/innate immunity against systemic mouse Cytomegalovirus infection; this is consistent with human data. PMID: 25954804
- IFNAR1 signaling in microglia is essential for ischemic preconditioning in white matter. PMID: 26609155
- Lack of IFNB or IFNAR was associated with reduced neurogenesis in the hippocampus; dentate gyrus PMID: 26451483
- Taken together, our studies provide novel insights on how type I IFN receptor signaling regulates NK cell development and functions PMID: 25333658
- IFN-alpha/beta is able to drive the formation of a Stat2 and IRF-9 complex that drives the expression of a subset of IFN-stimulated genes, but with substantially delayed kinetics. PMID: 26019270
- our findings describe a novel role for IFN during metastasis development and suggest that new treatment strategies should be considered for prevention of metastasis formation in patients. PMID: 25604426
- TNFR1- and IFNAR1-deficient mice showed partial protection toward Aldara-induced inflammation compared with control groups. Double knockout mice lacking both receptors showed superior protection to Aldara in comparison with the single knockout mice. PMID: 25911755
- Impaired clearance of the high pathogenicity H1N1 influenza A virus prolonged IFN expression, leading to CCR2+ inflammatory monocytes amplifying their own recruitment via an interferon-alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1)-triggered chemokine loop. PMID: 25407417
- IFN-alpha/beta receptor signaling promotes regulatory T cell development and function under stress conditions. PMID: 25795758
- enhances cytotoxic activities of NK and CD8+ T cells but suppresses IFN-gamma production by these cells via the induction of IL-10 PMID: 24435166
- IRF7 suppresses antiparasitic immunity in the spleen, while IFNAR1-mediated, but IRF7-independent, signaling contributes to pathology in the brain during experimental blood-stage malaria. PMID: 25319247
- The C5a anaphylatoxin receptor (C5aR1) protects against Listeria monocytogenes infection by inhibiting interferon-alpha and interferon-beta expression. PMID: 25297874
- IFNAR1 joins several other genetic risk factors of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases whose products profoundly affect the intestinal microbiota and or Paneth cell function. PMID: 24555997
- Deficient IFN signaling by myeloid cells leads to MAVS-dependent virus-induced sepsis. PMID: 24743949
- Trigger IFNAR1 ubiquitination for limiting the inflammation-induced tissue damage can be purposely mimicked for therapeutic benefits. PMID: 24480543
- Collectively, persistent HBV replication IFNAR(-/-) mouse model that we established is a useful and convenient tool to detect the function of the type I interferon and IFNAR in HBV infection and anti-HBV treatments. PMID: 23771666
- TLR7-deficient and IFNAR1-deficient mice were more susceptible to liver fibrosis than wild type mice, indicating that TLR7-type I IFN signaling exerts a protective effect against liver fibrosis. PMID: 24375615
- Interferon-alpha but not MDA5/TLR3 activation of dendritic cells is required for maturation and metabolic shift to glycolysis after poly IC stimulation. PMID: 24409099
- Type I IFN receptor signaling acts as a central driver of early proinflammatory responses in the lung. PMID: 24648449
- Mice lacking the IFN-alpha/beta receptor succumbed to the infection, with vesicular stomatitis virus spreading from the olfactory bulb throughout the brain. PMID: 24429359
- IFNAR-/- mice were highly susceptible to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection, and all mice died within 3 to 4 days after inoculation. PMID: 24257618
- This study provided evidence for the production of IFNbeta from glia and using mice deficient in the type I IFN receptor alpha 1 (IFNAR1), demonstrate that its subsequent activation is likely to underlie the TLR3-mediated modulation of hippocampal excitability. PMID: 23554175
- Type I interferon signaling and responses limit HIV-1 infection and pathogenesis in brain. PMID: 24335529
- Data suggest Ifnar1 plays critical role in regulation of innate immunity; Oasl1 knockout mice mount better virus-specific CD8-positive T-cell response to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and this response is blocked if Ifnar1 signaling is blocked. PMID: 23874199
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Late endosome. Lysosome.
-
蛋白家族:Type II cytokine receptor family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:15975
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000023689
UniGene: Mm.502
Most popular with customers
-
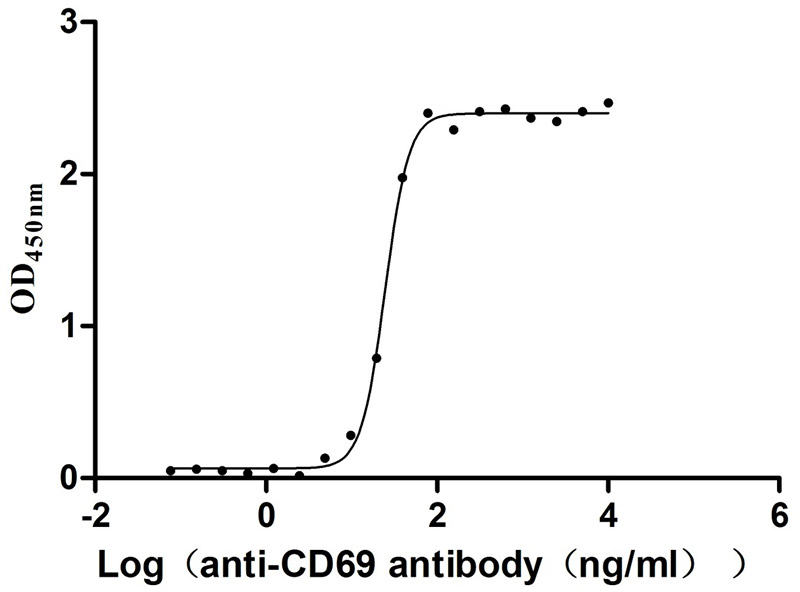
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
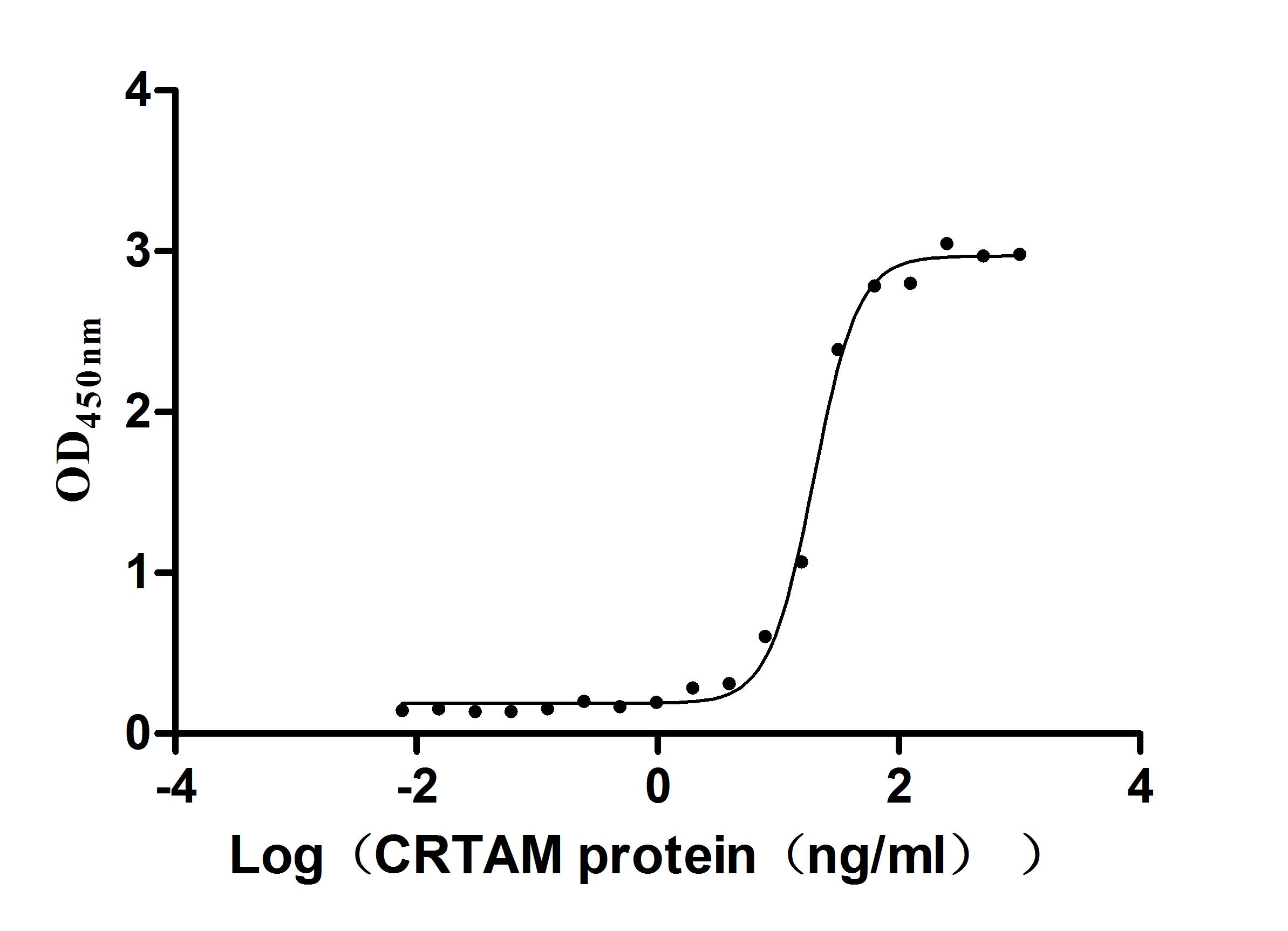
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
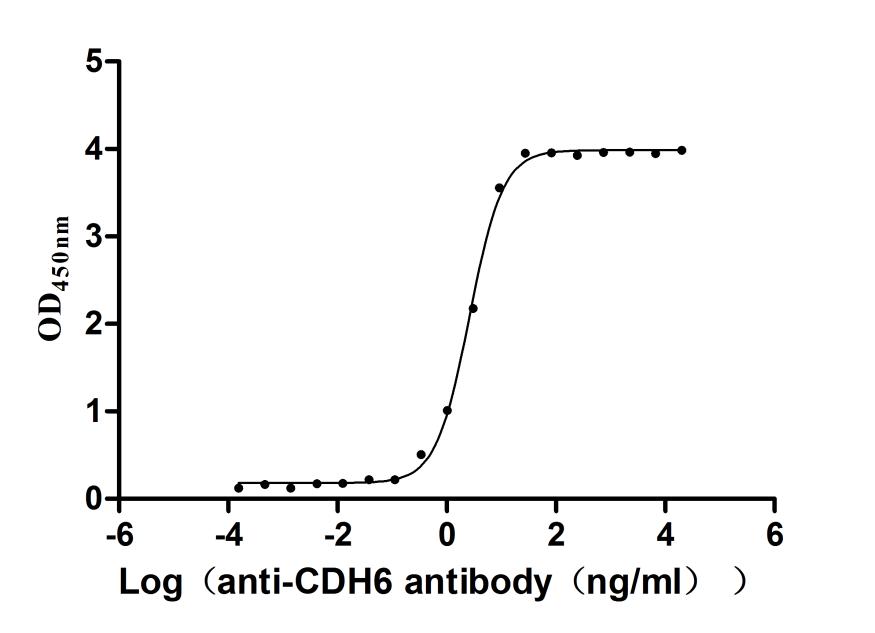
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
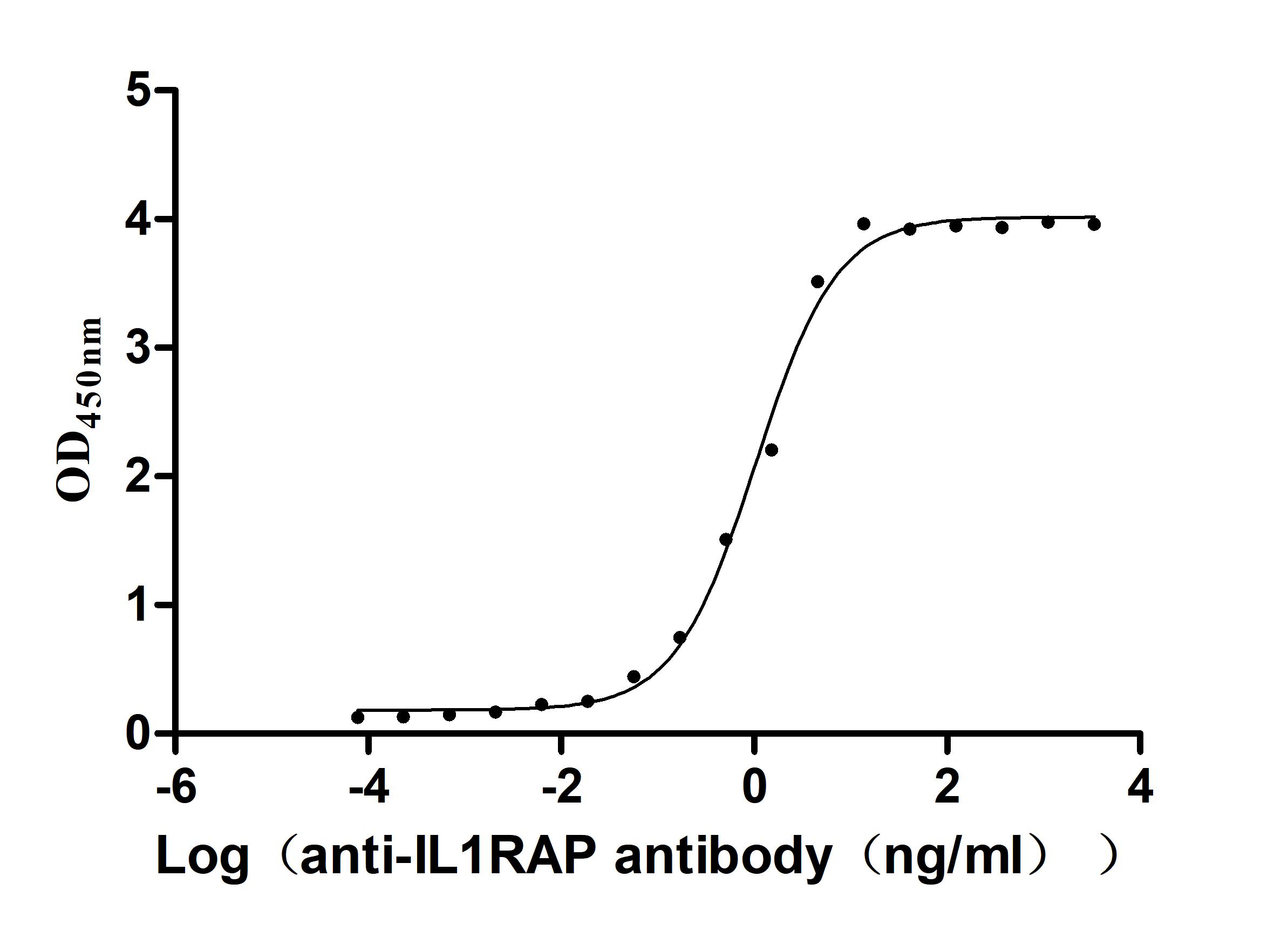
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)