Recombinant Mouse Insulin receptor (Insr), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP011753MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011753MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011753MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP011753MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP011753MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Insr; Insulin receptor; IR; CD antigen CD220
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates the pleiotropic actions of insulin. Binding of insulin leads to phosphorylation of several intracellular substrates, including, insulin receptor substrates (IRS1, 2, 3, 4), SHC, GAB1, CBL and other signaling intermediates. Each of these phosphorylated proteins serve as docking proteins for other signaling proteins that contain Src-homology-2 domains (SH2 domain) that specifically recognize different phosphotyrosine residues, including the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K and SHP2. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway, which is responsible for most of the metabolic actions of insulin, and the Ras-MAPK pathway, which regulates expression of some genes and cooperates with the PI3K pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of the SH2 domains of PI3K to phosphotyrosines on IRS1 leads to the activation of PI3K and the generation of phosphatidylinositol-(3, 4, 5)-triphosphate (PIP3), a lipid second messenger, which activates several PIP3-dependent serine/threonine kinases, such as PDPK1 and subsequently AKT/PKB. The net effect of this pathway is to produce a translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 from cytoplasmic vesicles to the cell membrane to facilitate glucose transport. Moreover, upon insulin stimulation, activated AKT/PKB is responsible for: anti-apoptotic effect of insulin by inducing phosphorylation of BAD; regulates the expression of gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes by controlling the activity of the winged helix or forkhead (FOX) class of transcription factors. Another pathway regulated by PI3K-AKT/PKB activation is mTORC1 signaling pathway which regulates cell growth and metabolism and integrates signals from insulin. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 thereby activating mTORC1 pathway. The Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway is mainly involved in mediating cell growth, survival and cellular differentiation of insulin. Phosphorylated IRS1 recruits GRB2/SOS complex, which triggers the activation of the Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway. In addition to binding insulin, the insulin receptor can bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFI and IGFII). When present in a hybrid receptor with IGF1R, binds IGF1. In adipocytes, inhibits lipolysis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Loss of Endothelial IR Impairs Barrier Function in the Brain. PMID: 28923931
- in beta cells, INSR-B has a protective role, while INSR-A expression sensitizes beta cells to programmed cell death. PMID: 27526875
- we show that glucagon receptor (GCGR) inhibition with a monoclonal antibody normalized blood glucose and beta-hydroxybutyrate levels. Insulin receptor antagonism increased pancreatic beta-cell mass threefold. Normalization of blood glucose levels with GCGR-blocking antibody unexpectedly doubled beta-cell mass relative to that observed with S961 alone and 5.8-fold over control PMID: 28115707
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest double knockout (DKO) mice lacking Insr and Igf1r exhibit obesity with insulin resistance and increased adiposity; on high-fat diet, DKO mice exhibit metabolic syndrome. (Insr = insulin receptor; Igf1r = insulin-like growth factor I receptor) PMID: 29040448
- The data in this paper demonstrate that IR knockdown in primary tumors partially reverses the growth-promoting effects of hyperinsulinemia as well as highlighting the importance of the insulin receptor signaling pathway in cancer progression, and more specifically in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PMID: 27435064
- long-term hepatic expression of IRA could be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 27562101
- the overlap of IR and IGF1R signaling is critical to the regulation of muscle protein turnover, and this regulation depends on suppression of FoxO-regulated, autophagy-mediated protein degradation PMID: 27525440
- These data reveal a critical pathophysiological role for INSR Thr1160 phosphorylation and provide further mechanistic links between PKCepsilon and INSR in mediating Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease -induced hepatic insulin resistance. PMID: 27760050
- Insr was downregulated in the arcuate nucleus of type 2 diabetic mice. PMID: 28456145
- Mice lacking the insulin receptor in AgRP neurons (AgRP IR KO) exhibited impaired hepatic insulin action because the ability of insulin to suppress hepatic glucose production (hGP) was reduced, but the ability of insulin to suppress lipolysis was unaltered. To the contrary, in POMC IR KO mice, insulin lowered hGP but failed to suppress adipose tissue lipolysis. PMID: 28385803
- Intracellular retention of the insulin receptor is caused by elevated amounts of alpha-taxilin, a free syntaxin binding protein, in HBV expressing hepatocytes preventing proper targeting of the insulin receptor to the cell surface. PMID: 27155659
- Results found that glioblastoma tumors resistant to PDGFR inhibition required the expression and activation of the insulin receptor (IR)/insulin growth-like factor receptor (IGF1R) for tumor cell proliferation and survival. PMID: 28138037
- IR is critical in adipocyte maintenance. PMID: 28065828
- The IR in the intestinal epithelium plays important roles in intestinal gene expression, glucose uptake, and GIP production, which may contribute to pathophysiological changes in individuals with diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and other insulin-resistant states. PMID: 28096258
- In conclusion, we have identified that ARL15 acts as an insulin-sensitizing effector molecule to upregulate the phosphorylation of members of the canonical IR/IRS1/PDPK1/AKT insulin pathway by interacting with its GAP ASAP2 and activating PDPK1. This research may provide new insights into GTPase-mediated insulin signalling regulation and facilitate the development of new pharmacotherapeutic targets for insulin sensitizati PMID: 28322786
- Data suggest IGT10 mice, diabetes type 2 model, exhibit 2 genetic defects: haploinsufficiency (heterozygosity for null allele) of insulin receptor (Insr); splice-site mutation in protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B alpha (Ppp2r2a). Inheritance of either allele results in insulin resistance but not overt diabetes. Double heterozygosity leads to insulin resistance and diabetes type 2 without increase in body weight. PMID: 26868295
- adipocyte IR function is crucial to systemic energy metabolism and has profound effects on adiposity, hepatic homeostasis and lifespan PMID: 27246738
- ZIP14-mediated zinc transport contributes to regulation of endosomal insulin receptor activity and glucose homeostasis in hepatocytes. PMID: 27703010
- Suggest that overexpression of IGF-IR or IRA isoform, as homodimers or as part of IRA/IGF-IR hybrid receptors, confers a stronger migratory capability to vascular smooth muscle cells and might occur in early stages of atherosclerotic process. PMID: 27905925
- Acute knockdown of Insr or both Irs1 and Irs2 in adipocytes increased Adipoq mRNA expression but reduced adiponectin secretion. PMID: 26888756
- unsuppressed lipolysis in adipocytes elicited by HFD feeding is linked with enhanced gluconeogenesis from glycerol and with alterations in BA physiology in Insr(P1195L/+)/HFD liver. PMID: 26615883
- NF-kappaB-miR-195/497-Igf1r/Insr-Ccnd2/Ccne1 plays important roles in myogenesis. PMID: 26567220
- Therefore, overexpression of insulin receptor improves obese and diabetic phenotypes in db/db mice, with consequences on growth. PMID: 26096452
- only Ptprj was co-expressed with the IR in major insulin target tissues : the skeletal muscle, liver and adipose tissue. the activation of IR and Akt by insulin was enhanced, and glucose and insulin tolerance was improved in Ptprj-deficient mice PMID: 26063811
- Data reports that IRA in beta cells confers a stronger proliferation capability favoring the mitogenic effects of IGF-I and also increasing glucose uptake of these cells, a key factor in pancreatic beta cell proliferation. PMID: 25797178
- Our results indicate that the insulin receptor may have some role in controlling the rate of rod response decay, but they exclude a major role of the insulin receptor pathway in phototransduction. PMID: 25598343
- Mutation in the insulin receptor attenuated the oxidative stress and apoptosis in beta-cells. PMID: 25295420
- Our results highlight the mitogenic role of the IR in mammary tumor progression with a direct link to CD24 expression PMID: 25694511
- Deletion of the insulin receptor alone or in combination with the IGF-1 receptor or treatment with rapamycin prevented hyperphosphorylation of S6RP without affecting the mitochondrial structural defect in PHB2-deficient animals. PMID: 25643582
- Data suggest that insulin/insulin receptor-stimulated GLUT4 (facilitated glucose transporter member 4) translocation to plasma membrane in adipocytes may require assembly of SNARE protein complexes. [REVIEW] PMID: 25233421
- Data indicate that insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors (IR and IGF1R) signals that regulating expression of imprinted genes and miRNAs through transcriptional mechanisms distinct from classical imprinting control. PMID: 25246545
- Leptin knockouts are hyperphagic and obese, whereas insulin receptor knockouts are similar to controls but double knockouts exihibit higher body weight and adiposity solely due to reduced energy expenditure. PMID: 25125486
- insulin receptor expression in osteoblasts is critically important for proper bone development and maintenance of structural integrity PMID: 24963495
- Male insulin receptor knock-out mice exhibited significantly augmented LH concentration and a trend toward reduced seminal vesicle weight compared with control mice, which may be indicative of primary hypogonadism. PMID: 25116708
- MsrA and protein oxidation play a role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis; data support a novel hypothesis that obesity-induced insulin resistance is caused in part by reduced function of insulin signaling proteins arising from protein oxidation PMID: 23089224
- Nox2-derived ROS played a key role in damaging insulin receptor and endothelial function in dietary obesity after middle-age. PMID: 23957783
- GM3 supplementation or inhibition of IGF-1R or PI3K reverses the increased migration of GM3S(-/-) keratinocytes, whereas IR knockdown only partially suppresses migration. PMID: 24326453
- GH signaling in mouse calvarial cells depends on insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), but not insulin receptor (IR) PMID: 24302626
- IGF-II promotes stemness of neural stem cells via the IR-A and not through activation of either the IGF-1R or the IGF-2R. PMID: 24398690
- SIRP-alpha is part of a novel mechanism for inflammation-mediated insulin resistance in muscle and muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. PMID: 23515050
- LMBD1 plays an imperative role in mediating and regulating the endocytosis of the IR. PMID: 24078630
- The insulin/IGF signaling pathway is required for FSH-mediated Sertoli cell proliferation. PMID: 23518924
- We conclude that insulin interacting with IR is essential for mammary differentiation during murine pregnancy PMID: 23982156
- these results support a role for insulin receptor in the proximal tubule in the modulation of systemic glucose levels. PMID: 23723425
- Data indicate that insulin receptor (InsR) is important for epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity. PMID: 23558339
- Insulin receptor signaling in cones. PMID: 23673657
- These results suggest that insulin stimulates the association of insulin receptor with syndecan-1 and the complex formation of syndecan-1 and integrin could play an important role in ERK I/II-ALP signaling pathway in osteoblast cells. PMID: 23252577
- Data from knockout mice and cocultured hepatocytes/sinusoidal endothelial cells suggest that up-regulation (not down-regulation) of insulin/Insr/insulin receptor substrate 1 signaling in liver sinusoidal endothelium leads mice to insulin resistance. PMID: 23349480
- These findings indicate that prior to sex determination somatic progenitors in Insr;Igf1r mutant gonads are not lineage primed and thus incapable of upregulating/repressing the male and female genetic programs required for cell fate restriction. PMID: 23300479
- Data indicate that insulin receptors in pro-opiomelanocortin neurons (IR/LepR(POMC) mice may serve as a new mouse model to clarify the involvement of adipose and liver tissue in the pathogenesis and etiology of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PMID: 23119079
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane. Late endosome. Lysosome.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Insulin receptor subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16337
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000088837
UniGene: Mm.268003
Most popular with customers
-
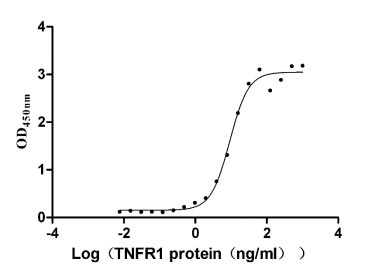
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
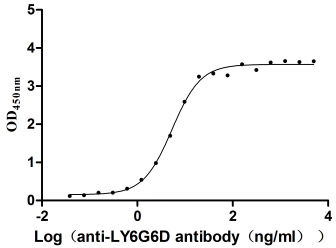
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
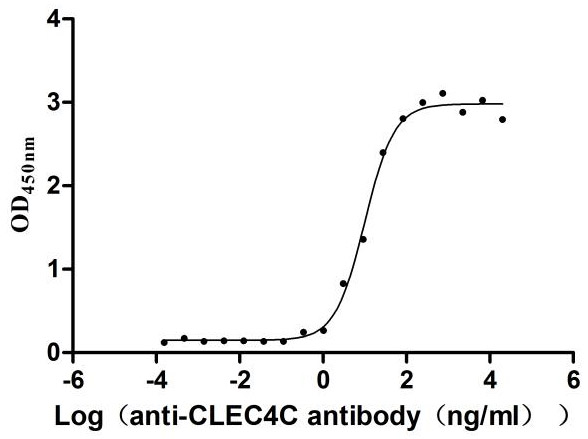
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
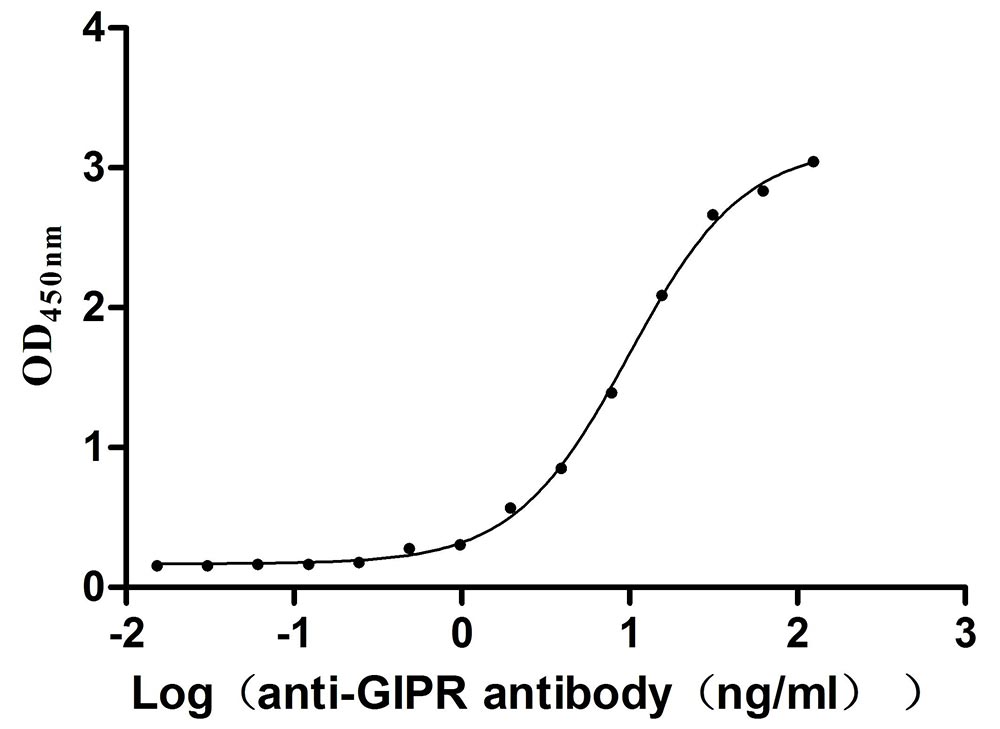
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)