Recombinant Mouse Insulin-like growth factor I (Igf1)
-
货号:CSB-YP011086MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011086MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011086MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP011086MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP011086MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Igf1; Igf-1Insulin-like growth factor I; IGF-I; Somatomedin
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:49-118
-
氨基酸序列GP ETLCGAELVD ALQFVCGPRG FYFNKPTGYG SSIRRAPQTG IVDECCFRSC DLRRLEMYCA PLKPTKAA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:The insulin-like growth factors, isolated from plasma, are structurally and functionally related to insulin but have a much higher growth-promoting activity. May be a physiological regulator of [1-14C]-2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) transport and glycogen synthesis in osteoblasts. Stimulates glucose transport in bone-derived osteoblastic (PyMS) cells and is effective at much lower concentrations than insulin, not only regarding glycogen and DNA synthesis but also with regard to enhancing glucose uptake. May play a role in synapse maturation. Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of IGF1 is required for sensory perception of smell in the olfactory bulb. Acts as a ligand for IGF1R. Binds to the alpha subunit of IGF1R, leading to the activation of the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity which autophosphorylates tyrosine residues in the beta subunit thus initiatiating a cascade of down-stream signaling events leading to activation of the PI3K-AKT/PKB and the Ras-MAPK pathways. Binds to integrins ITGAV:ITGB3 and ITGA6:ITGB4. Its binding to integrins and subsequent ternary complex formation with integrins and IGFR1 are essential for IGF1 signaling. Induces the phosphorylation and activation of IGFR1, MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK1/ERK2 and AKT1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- IGF-1 upregulated c-kit expression in c-kit-positive C-kit-positive cardiac stem cells (CSCs) resulting in enhanced CSC proliferation and migration by activating the PI3K/AKT/DNMT signaling pathway to epigenetically silence miR-193a, which negatively modifies the c-kit expression level. PMID: 29467020
- glucagon and/or IGF-1 production are additional key factors in food-induced entrainment. PMID: 29396301
- Combined treatment with electrical stimulation and insulin-like growth factor-1 promotes bone regeneration in vitro. PMID: 29746517
- Enteric neural stem cells expressing IGF1 has been proposed as a novel cellular therapy for Hirschsprung's Disease tested in a mouse model. PMID: 29792527
- Deficiency in the liver-derived IGF-I does not affect wound healing in mice, neither in normoglycemic conditions nor in diabetes. PMID: 29534073
- diabetic gastroparesis was an aggressive process due to the successive damages of myenteric cholinergic neurones and ICC by impairing the insulin/InsR and IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling. Insulin therapy in the early stage may delay diabetic gastroparesis PMID: 28931726
- these results indicate that IGF-I induces senescence of hepatic stellate cells, inactivates these cells and limits fibrosis in a p53-dependent manner and that IGF-I may be applied to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. PMID: 27721459
- IGF-1 is involved in hepatic mitochondrial protection, because it is able to reduce free radical production, oxidative damage and apoptosis. All these IGF-1 actions are mediated by the modulation of the expression of genes encoding citoprotective and antiapoptotic proteins. PMID: 28648804
- Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation using rapamycin restored Mb mRNA expression to control levels. Lipid supplementation had no effect on Mb gene expression. Thus, IGF-1-induced anabolic signaling can be a strategy to improve muscle size under mild hypoxia, but lowers Mb gene expression PMID: 28862673
- Macrophage subtypes enhanced the osteogenesis in transwell setting and the transition from M1 to M2 was associated with an increase in bone anabolic factors CCL2/MCP-1, CCL5/RANTES and IGF-1 in vitro. PMID: 28782174
- These data indicate that KSR2 functions in a cell non-autonomous fashion to regulate GH-stimulated IGF-1 expression in the liver of neonatal mice, which plays a key role in the development of body length. PMID: 27561547
- The data demonstrate that miR-206 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to irradiation by targeting IGF1, highlighting the therapeutic potential of miR-206 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitization. PMID: 28865599
- These results indicated that the proproliferative effects of IGF1 are mediated in response to the PI3K/protein kinase B signaling pathway. PMID: 28627605
- These results suggest that Dexras1 is a critical mediator of the IGF-1 signal to activate MAPK, linking glucocorticoid signaling to IGF-1 signaling in adipogenesis. PMID: 27345868
- In inflamed experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) spinal cord, study found a significant increased number of IGF-I expressing neurons versus a reduced number of IGFBP-1 positive neurons. Moreover, while nearly all IGF-I neurons expressed GSK3beta, some expressed it more intensely. PMID: 28617951
- MGF overexpression increases the number of neural progenitor cells and promotes neurogenesis. PMID: 28683812
- RIP3 and phosphorylated MLKL expressions were relatively decreased in the IGF-1 receptor monoclonal antibody group compared to the non-treated group. IGF-1 may be associated with RIP3-mediated necroptosis in vitro, while blocking of the IGF-1 pathway may reduce LPS-induced lung injuries in vivo. PMID: 29545181
- The down-regulation of IGF-I signaling, as observed in old mice, leads to increasing the activity of FoxO factors that may be important for the neuroprotective effects seen with dietary restriction. PMID: 27718093
- Data suggest that gut resident bacteria-derived short-chain fatty acids mediate microbiota induced changes in host IGF-1 levels and contribute to the effects of colonization on bone turnover. PMID: 27821775
- High IGF1 expression is sensitive to initial injury intensity induced by freeze damage. PMID: 27647425
- IGF-1 signaling in involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of B16-F10 cells and in the control of the stem cell phenotype. PMID: 27764776
- Findings provided morphological evidence that T-type Cav3.2 channel, at least partially, mediates the pain facilitation of insulin-like growth factor-1/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling in chronic inflammatory pain condition. PMID: 27213932
- Conditional deletion of IGF-1 in osteocytes enhanced bony union of the fracture gap in a tibial fracture model. PMID: 27519969
- IGF-I stimulated IRS-1 phosphorylation and recruitment of PKCzeta and vimentin to phospho-IRS-1. PMID: 26773517
- local IGF-I plays critical roles during postnatal/adult hippocampal neurogenesis. PMID: 27144663
- miR-199a-3p appears to be involved in the estrogen regulatory networks that mediate bone cell autophagy, potentially by targeting IGF-1 and mTOR. PMID: 28708244
- IGF-1 deficiency during a critical period during early in life results in persistent changes in post-transcriptional miRNA-mediated control of genes critical targets for vascular health, which likely contribute to the deleterious late-life cardiovascular effects known to occur with developmental IGF-1 deficiency. PMID: 27566308
- this study provides new evidence in a mouse model of IGF-1 deficiency that autophagy is an adaptive response that might confer protection against persistent inflammation in the retina during ageing. PMID: 27483352
- IGF1 deficiency exacerbates hypertension-induced cerebral microhemorrhages in mice, mimicking the aging phenotype. PMID: 28295976
- the dipeptide Pro-Asp promoted IGF-1 secretion and expression in hepatocytes. PMID: 27473671
- miR-18a suppresses the expression of Igf1 in a 3'UTR-dependent manner PMID: 28782600
- down-regulation of IGF-1 expression and signaling is involved in FD-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-22 hippocampal neuron cells PMID: 27592453
- Study demonstrates that GH/IGF-I, somatostatin/cortistatin and ghrelin systems expression is altered in mammary gland during fasting, suggesting a relevant role in coordinating its response to metabolic stress, wherein endogenous cortistatin might be essential for an appropriate response. PMID: 27291340
- Enhanced study of the role of IIS pathway and epigenetic mechanisms that regulate aging may facilitate progressive prevention and treatment of human age-related diseases. PMID: 28101820
- The specific aim of the present work was to study whether the partial IGF-1 deficiency influences heart and/or coronary circulation, comparing vasoactive factors before and after of ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). PMID: 28806738
- Data (including data from studies using heterozygous transgenic mice) suggest that gene expression in liver is altered in a model of inflammation of liver due to partial deficiency of Igf1; this leads to over-expression of Igf1 receptor, inflammation mediators, and acute-phase proteins, but under-expression of cytoskeletal proteins, extracellular matrix proteins, and tight junction proteins. PMID: 28124277
- Findings indicate that the energy-sensing LKB1-AMPK pathway regulates IGF1 secretion in mouse primary hepatocytes, which in turn regulates activation of the IGF1R-PKB pathway. PMID: 28500773
- These results demonstrate that a greater than additive effect is observed on the growth of skeletal muscle and in the reduction of body fat when myostatin is absent and IGF1 is in excess, and that myostatin and IGF1 regulate skeletal muscle size, myofibre type and gonadal fat through distinct mechanisms. PMID: 28533420
- These results indicate that IGF-1 plays a critical role in spermatogenesis from SSCs. PMID: 28552527
- Exercise negatively regulates IGF-1 pathway in skin epidermis. PMID: 27509024
- A role for IGF-1 in axon elongation that appears to be cell selective and participates in the complex cellular mechanisms that link underfeeding during the early postnatal period with programming of the growth trajectory. PMID: 28076448
- These findings demonstrate that the AMPK-TBC1D1 signaling nexus interacts with the PKB-mTOR pathway via IGF1 secretion, which consequently controls expression of lipogenic genes in the adipose tissue PMID: 27307439
- Increased diet-induced fatty streak formation in female Liver derived-IGF-I(-/-) mice was associated with increased serum cholesterol and signs of systemic inflammation, endothelial activation, lipid deposition, and macrophage infiltration in the vascular wall. PMID: 26627099
- findings represent the first demonstration to our knowledge of tissue IGF-1 regulation through proteolytic degradation and suggest that chymase inhibition may be a viable therapeutic approach to enhance late cardioprotection in postischemic heart disease PMID: 27274047
- Experimental NAFLD is associated with sarcopenia, decreased muscle strength, and reduced IGF-1 serum levels. IGF-1 reduction may be involved in pathogenesis of NAFLD-associated sarcopenia. PMID: 27572941
- vascular smooth muscle-derived IGF-1 plays a critical role in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. PMID: 27438786
- Overexpression of IGF-I in the osteoblast lineage does not contribute to an increase in repair of erosions or syndesmophyte formation in mouse models for destructive and remodeling arthritis. PMID: 27695067
- Under nonpathological conditions, IGF-1 regulates brain IGF-IR PMID: 27792405
- These findings highlight the sex-dependent and potentially detrimental effects of in utero smoke exposure on DNA methylation and Igf1 and Igf1r mRNA levels. PMID: 28130259
- Liver-derived IGF-I regulates cortical bone mass, cortical porosity, and mechanical strength under normal (nonloaded) conditions. However, despite an approximately 70% reduction in circulating IGF-I, the osteogenic response to mechanical loading was not attenuated in the LI-IGF-I(-/-) mice. PMID: 27221117
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Insulin family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16000
UniGene: Mm.268521
Most popular with customers
-
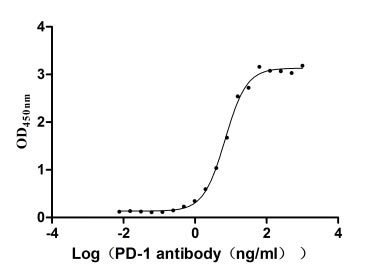
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death protein 1 (PDCD1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
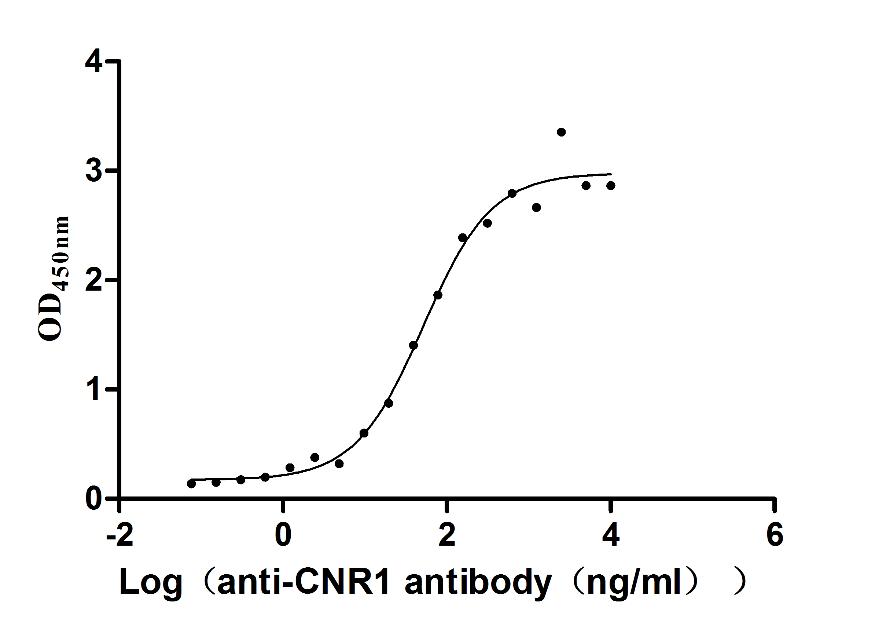
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
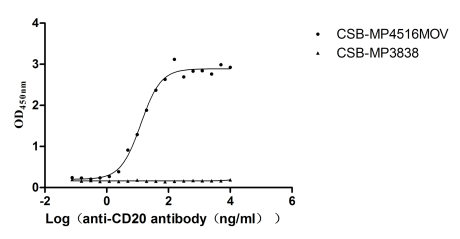
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
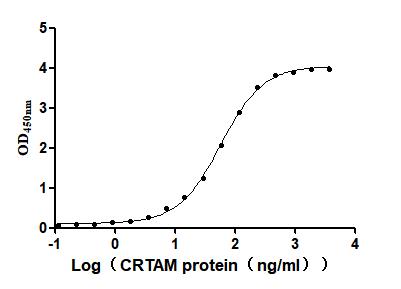
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)
f4-AC1.jpg)