Recombinant Mouse Homeobox protein SIX1 (Six1)
-
货号:CSB-YP737073MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP737073MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP737073MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP737073MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP737073MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Six1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Six1; Homeobox protein SIX1; Sine oculis homeobox homolog 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-284
-
氨基酸序列MSMLPSFGFT QEQVACVCEV LQQGGNLERL GRFLWSLPAC DHLHKNESVL KAKAVVAFHR GNFRELYKIL ESHQFSPHNH PKLQQLWLKA HYVEAEKLRG RPLGAVGKYR VRRKFPLPRT IWDGEETSYC FKEKSRGVLR EWYAHNPYPS PREKRELAEA TGLTTTQVSN WFKNRRQRDR AAEAKERENT ENNNSSSNKQ NQLSPLEGGK PLMSSSEEEF SPPQSPDQNS VLLLQSNMGH ARSSNYSLPG LTASQPSHGL QAHQHQLQDS LLGPLTSSLV DLGS
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis and embryonic development. Plays an important role in the development of several organs, including kidney, muscle and inner ear. Depending on context, functions as transcriptional repressor or activator. Lacks an activation domain, and requires interaction with EYA family members for transcription activation. Mediates nuclear translocation of EYA1 and EYA2. Binds the 5'-TCA[AG][AG]TTNC-3' motif present in the MEF3 element in the MYOG promoter and CIDEA enhancer. Regulates the expression of numerous genes, including MYC, CCNA1, CCND1 and EZR. Acts as activator of the IGFBP5 promoter, probably coactivated by EYA2. Repression of precursor cell proliferation in myoblasts is switched to activation through recruitment of EYA3 to the SIX1-DACH1 complex. During myogenesis, seems to act together with EYA2 and DACH2. Regulates the expression of CCNA1. Promotes brown adipocyte differentiation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- the continuous and complex expression pattern of Six1 during sensory organ formation is pieced together by separate enhancers PMID: 29106072
- Six1 is required for the expression of numerous genes encoding fast-type sarcomeric proteins, glycolytic enzymes and controlling intracellular calcium homeostasis. PMID: 27597886
- our analyses uncover essential roles of Six1 in hair cell differentiation and formation of the organ of Corti in the mammalian cochlea PMID: 28892484
- SIX1 regulates dorsal arch development not only by inducing dorsal Jag1 expression but also by inhibiting endothelin 1 (Edn1) expression in the pharyngeal endoderm of the dorsal arch, thus preventing dorsal EDNRA signaling. PMID: 28455376
- significant co-localization of binding sites for MyoD and Six proteins on over a thousand mouse genomic DNA regions, were found. PMID: 27302134
- we show that SIX1 binds to adipogenic and brown marker genes and interacts with C/EBPa, C/EBPb and EBF2, suggesting their functional cooperation during adipogenesis. PMID: 27923061
- Studies strongly suggest that Six1 overexpression promotes CRC growth and metastasis and remodels tumor stroma by stimulating angiogenesis and recruiting TAM. MAPK activation may be a pivotal event in Six1-associated tumor progression. PMID: 28199476
- Downregulation of Six1 effectively inhibited airway inflammation and reversed airway remodeling, which suggest that Six1 represents a promising therapeutic strategy for human allergic asthma. PMID: 27847210
- results suggest that SIX1 is a key proliferation regulator in mouse DFCs and human PDLCs, which provides novel insight into Six family gene function in mammals. PMID: 27241908
- Our findings imply that SIX1 may play a role as an important regulator to orchestrate the dynamic of uterine endometrium in response to estrogen level during the estrous cycle. PMID: 26940739
- These data suggest differential SIX-factor regulation might have contributed to species differences in nephron progenitor programs such as the duration of nephrogenesis and the final nephron count PMID: 26884396
- Activation of Six1 Expression in Vertebrate Sensory Neurons. PMID: 26313368
- data support a model where Eya-Six may form a complex to regulate nephron progenitor cell development before metanephric specification and are critical mesenchymal factors for inducing nephric duct development. PMID: 25903664
- Six1 knockdown caused a fast-to-slow shift in myosin heavy chain isoform PMID: 24102895
- Results suggest that the increase of SIX1 expression could promote tumorigenesis, progression and invasive growth of cervical cancer by promoting DNA replication. PMID: 24970368
- Fast myosin heavy chain (MYH) genes and linc-MYH share a common enhancer, located in the fast MYH gene locus and regulated by Six1 homeoproteins PMID: 24852826
- The results indicated the critical role of Six1 in transition of Rohon-Beard cells to dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons during Xenopus development and establishment of exclusive DRG system of mice. PMID: 24885223
- Six1 is required for the proper chromatin structure at the Core Enhancer Region, as well as for MyoD binding at its own enhancer. PMID: 23840772
- Results indicated that sine oculis homeobox 1 (Six1) overexpression could significantly promote the expression of fast-type muscle genes Atp2a1, Srl, and Mylpf. PMID: 23613228
- These findings uncover novel functions for Six1-Eya1-SHH pathway during the saccular phase of lung morphogenesis. PMID: 23895934
- the transcription factors Six1 and Six4 are required for male gonadal differentiation. PMID: 23987514
- Six1 and Six2 are complementarily but asymmetrically expressed in the peri-cloacal mesenchymal progenitors and are critical for correct genitor-urinary and digestive organs body patterning. PMID: 23390542
- Direct molecular regulation of the myogenic determination gene Myf5 by Pax3, with modulation by Six1/4 factors, is exemplified by the -111 kb-Myf5 enhancer PMID: 23384562
- Six1 regulated the expression of the myogenic regulatory factors MyoD. PMID: 22945933
- The data showed that Six1 and Six1 co-factor expression is responsive to muscle overload in both fast and slow muscles. PMID: 22700049
- Studies indicate that the Six1 enhancers provide valuable tools to understand the mechanism of Six1 regulation and to manipulate gene expression in the developing embryo, particularly in the sensory organs. PMID: 22659139
- EYA1 and SIX1 drive the neuronal developmental program in cooperation with the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex and SOX2 in the mammalian inner ear. PMID: 22513373
- Ezh2-mediated repression of Six1 in differentiating cardiac progenitors is essential for stable gene expression and homeostasis in the postnatal heart. PMID: 22267199
- Data show that absence of Six1 and Six4 leads to the development of dorsal myofibers lacking expression of fast-type muscle genes, and mainly expressing a slow-type muscle program. PMID: 21884692
- Deletion of either or both Six1 and Eya1 genes results in genitourinary tract defects including persistent cloaca; hypospadias; and hypoplastic genitalia. PMID: 21968101
- findings suggest Six1 regulates production of functional apical and basal progenitors during olfactory epithelium development, through regulation of various genes, such as neuronal bHLH, neuronal repressor bHLH and genes involved in Notch signal pathway PMID: 21302255
- evidence for the requirement of Six1 in coordinating Shh-Fgf10 signaling in embryonic lung to ensure proper levels of proliferation and differentiation along the proximodistal axis of epithelial, mesenchymal and endothelial cells PMID: 21385574
- Six1 and Eya1 genetically interacted with Fgf8 and the Tbx1 pathway that is crucial for cardiovascular and craniofacial morphogenesis PMID: 21364285
- This study uncovers an essential function for Six1 in the metanephric mesenchyme as an upstream regulator of Grem1 in initiating branching morphogenesis. PMID: 21281623
- Six1-bound Regulatory Element 1 is a functionally conserved transcriptional enhancer regulated by Six1. PMID: 21041981
- These results suggest that Six1 and Six4 genes are expressed in the taste bud cells, in newly formed or surviving type-II cells. PMID: 20668922
- mouse Six1 is expressed in the pre-placodal region (PPR) and regulated by an enhancer for the rostral PPR PMID: 20471971
- The expression patterns of Six1 and its role in the morphogenesis of taste bud-bearing lingual papillae during mouse embryonic development, was analyzed. PMID: 20143239
- Six1 is not critical for normal mammary gland development, since neither loss nor inappropriate overexpression of Six1 adversely affects normal mammary gland development or function. PMID: 20074369
- Six1 and Six4 expression is required to specifically activate fast-type muscle genes PMID: 19962975
- An essential role for Six1 in establishing a functionally normal ureter and new insights into the molecular basis of urinary tract malformations in branchio-oto-renal syndrome patients. PMID: 20110314
- Data show that Six1 plays a specific role in hypaxial muscle differentiation, distinct from those of other hypaxial determinants such as Pax3, cMet, Lbx1 or Mox2. PMID: 12668636
- Six1 has a role in the initial inductive step for metanephric development PMID: 12783782
- Six1 was expressed in tendon clone cells. PMID: 12837285
- The phosphatase function of Eya switches the function of Six1-Dach from repression to activation, causing transcriptional activation through recruitment of co-activators PMID: 14628042
- Data show that ezrin and the homeodomain-containing transcription factor Six-1 had essential roles in determining the metastatic fate of rhabdomyosarcoma cells. PMID: 14704789
- Data identify Six1 and Eya1 as the first transcriptional complex that is able to reprogram adult slow-twitch oxidative fibers toward a fast-twitch glycolytic phenotype. PMID: 15226428
- During the development of epibranchial placode-derived distal cranial sensory ganglia, while the phenotype appears less severe in Six1 than in Eya1 mutants PMID: 15496442
- Early syndetomal expression of scleraxis is reduced in the Six1Six4 embryo PMID: 15788460
- Sonic hedgehog is necessary and sufficient for Six1 expression in posterior limb regions PMID: 15804569
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:SIX/Sine oculis homeobox family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in phalangeal tendons and in skeletal muscle and in head and body mesenchyme.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20471
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000059026
UniGene: Mm.4645
Most popular with customers
-
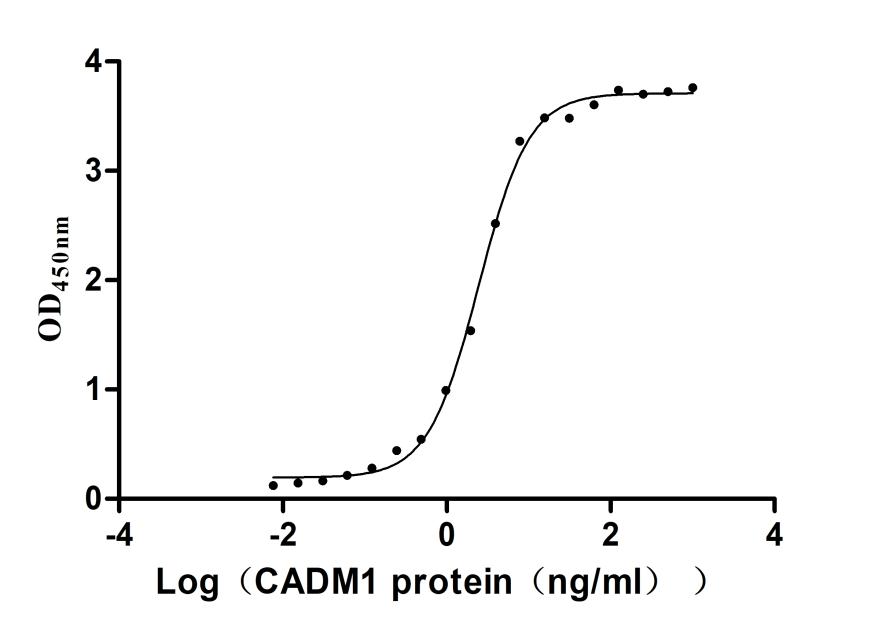
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse Claudin-18 (Cldn18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
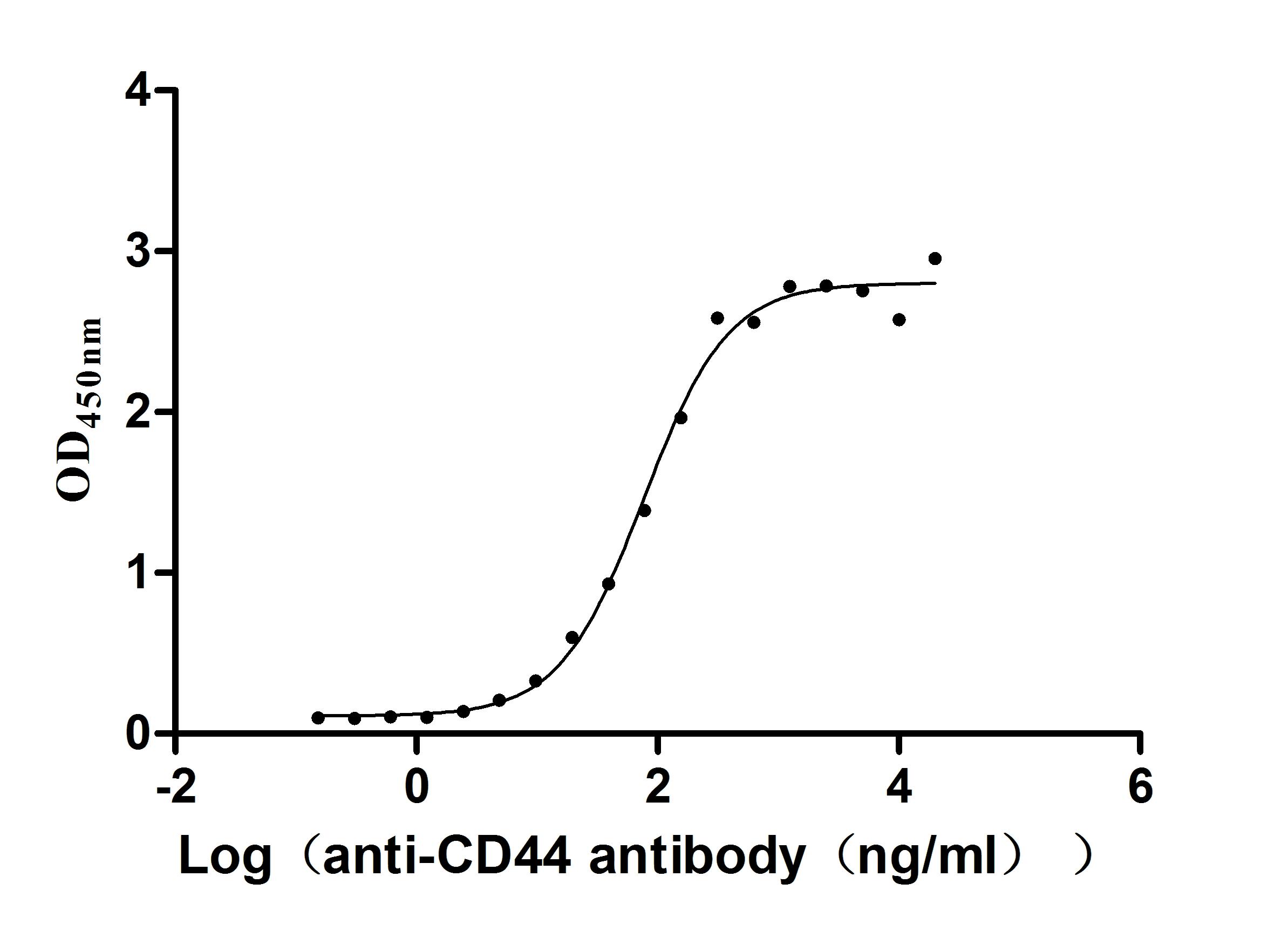
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
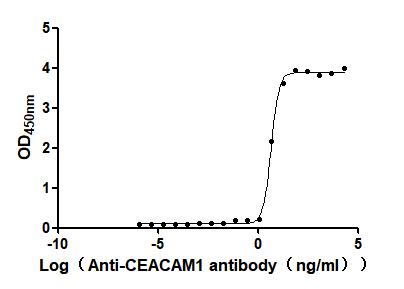
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
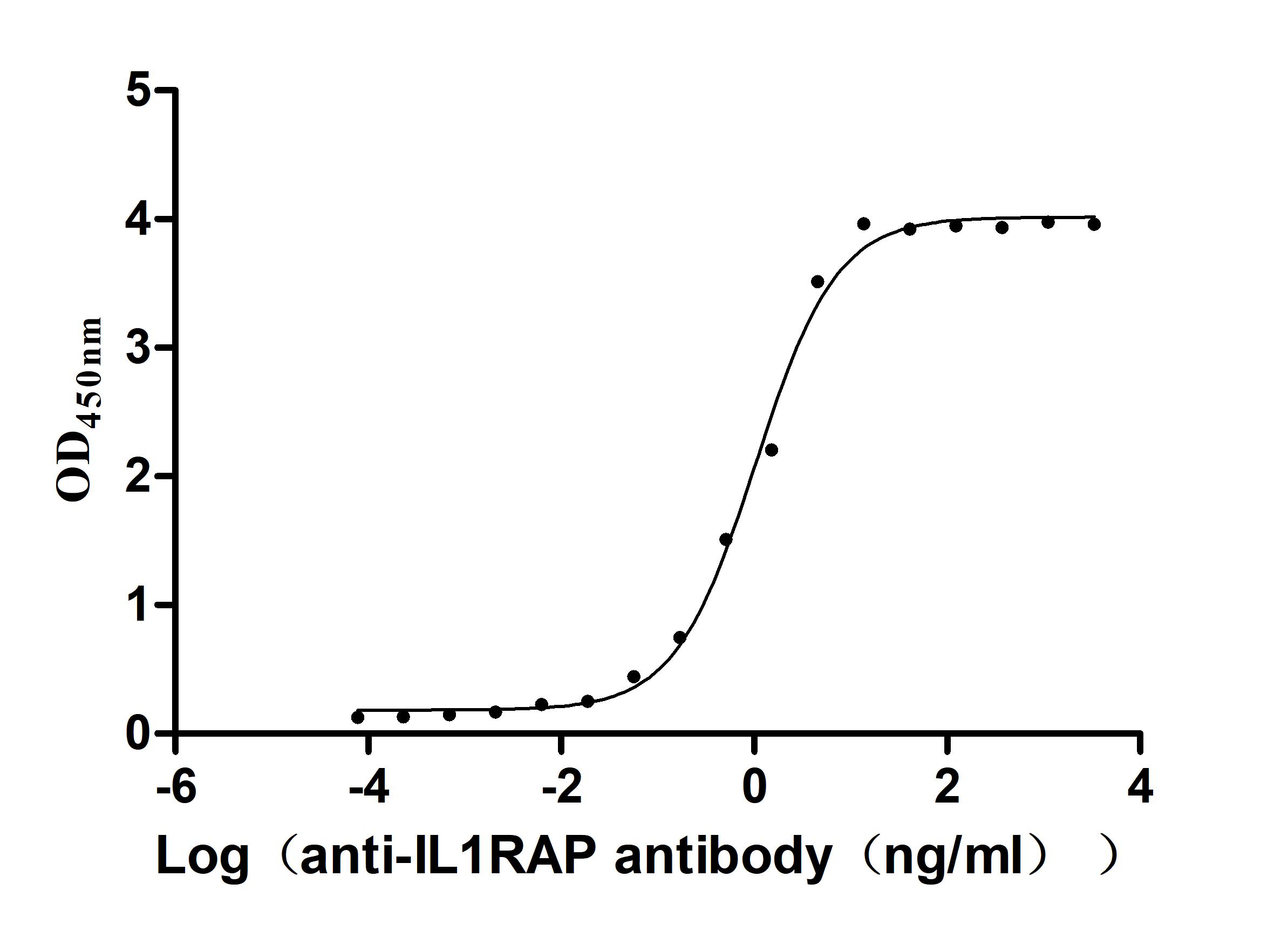
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)