Recombinant Mouse Growth hormone receptor (Ghr), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP009411MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009411MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009411MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP009411MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP009411MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
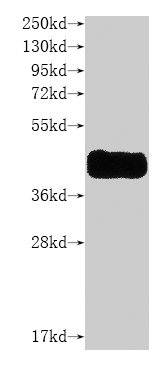
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Ghr; Growth hormone receptor; GH receptor; Somatotropin receptor
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for pituitary gland growth hormone involved in regulating postnatal body growth. On ligand binding, couples to, and activates the JAK2/STAT5 pathway.; The soluble form (GHBP) acts as a reservoir of growth hormone in plasma and may be a modulator/inhibitor of GH signaling.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- GHR -/- mice had decreased body weight but increased percent fat mass. Serum FGF21 levels were unchanged in GHR -/- mice. Expression of Fgf21, Fgfr1, and Klb mRNA in white AT and liver were downregulated or unchanged inGHR -/- mice. The only exception was Fgf21 expression in brown AT of GHR -/-, which trended toward increased expression. PMID: 27585733
- A role for GH in influencing hormone signaling in adipose tissue in a depot-dependent manner in GHR-/- knock-out mice. PMID: 28323915
- disruption of cardiomyocyte GH-induced signaling in adult GhrKO mice does not affect cardiac function, but it does play a role in systemic glucose homeostasis, in part through modulation of circulating IGF-1. PMID: 27035649
- Snell, GHKRO, and PAPPA-KO mice express high levels of two proteins involved in DNA repair, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) and N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1). PMID: 27618784
- adult-onset growth hormone receptor knockout mice (aGHRKO mice), like GHRKO animals, displayed retarded growth and high adiposity with improved insulin sensitivity. Importantly, female aGHRKO animals showed an increase in their maximal lifespan, whereas the lifespan of male aGHRKO mice was not different from controls. PMID: 27732088
- Similar to other mice with decreased GH action, female GHA mice display reduced age-related lipid redistribution and improved insulin sensitivity, but no change in cellular senescence. PMID: 26372907
- The dwarf phenotype was partially corrected via plasmid containing the growth hormone gene administrated intramuscularly, depending on age at treatment. PMID: 26774398
- GHR-dependent downregulation of NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages is linked to pro-longevity effects that maintain immune system homeostasis in aging. PMID: 26876170
- both brown adipose tissue (BAT) and white adipose tissue (WAT) contribute in different ways to phenotypes in GHRKO mice, with Ghr ablation blunting inflammation in BAT as well as cellular metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis in WAT PMID: 26436954
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest Socs2 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 2) regulates liver regeneration rate after partial hepatectomy, Ghr level via ubiquitination/proteolysis, and serum Igf1 (insulin-like growth factor-1). PMID: 26703468
- removal of GHR in muscle of male MuGHRKO mice replicates some of the health benefits seen in global GHR-/- mice including improvements to glucose homeostasis and smaller body weight in males PMID: 26233957
- GHR knockdown caused increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL) as well as increased glucokinase mRNA and protein levels as well as fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels. PMID: 26015548
- deletion in liver affects regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis PMID: 25855408
- Global GHR deletion induces beneficial changes in apoptotic factors, whereas liver-specific GHR disruption does not. Sexual dimorphism may play a role in regulating apoptosis during liver-specific suppression of the somatotrophic signaling. PMID: 24550353
- loss of Ghr signaling may slow the progression from fibrosis/cirrhosis to cancer in the liver PMID: 25179284
- Mice in which GHR has been disrupted only in the liver do not show extended lifespan and also fail to show the decline in mTORC1 and increase in mTORC2 seen in mice with global loss of GHR. PMID: 25456069
- Hematopoietic-specific genetic deletion of Ghr neither impacted steady-state hematopoiesis nor serial transplantation potential. PMID: 25274507
- GHRs occur as approximately 500-kDa complexes that dimerize into active approximately 900-kDa complexes upon GH binding. The dimerized complexes act as platforms for transient interaction with JAK2 and ubiquitin ligases. PMID: 24280222
- Data from mutant/knockout mice suggest that Ghr in liver (not muscle or adipose tissue) is involved in regulation of expression of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes. PMID: 23941873
- Data from knockout/transgenic mice suggest that neither Ghr nor Igf1r (insulin-like growth factor I receptor) signaling is required for postnatal skeletal muscle development or for regeneration in response to cardiotoxin injury. PMID: 23861377
- Serum IGF-1 is insufficient to restore skeletal size in the total absence of the growth hormone receptor. PMID: 23456957
- Results suggest that GH sensitivity is rapidly impaired after acute injury and that trauma combined with hemorrhage results in a more severe form of GH resistance resulting from alteration or inactivation of hepatic GHR. PMID: 23417424
- Upregulation of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis in the heart and the kidney of growth hormone receptor knock-out mice PMID: 22947377
- muscle growth hormone receptor signaling regulates basal lipid oxidation, but not the induction of lipid oxidation in response to fasting. PMID: 23024761
- These results suggest that diabetes induces an imbalance in the GH/IGF-1 system leading to altered activity in the PFC and associated cognitive deficiencies. PMID: 22750159
- insulin-like growth factor I receptor may serve as a proximal component of growth hormone/growth hormone receptor signaling, contributing to enhancement of pancreatic beta-cell mass and function PMID: 22034225
- Skeletal muscle GHR signaling mediates insulin resistance in obesity and, more importantly, has a role in facilitating cross-talk between muscle and other metabolic tissues. PMID: 22187377
- The renal levels of PGC-1alpha, AMPKalpha, p-AMPKalpha, SIRT-3, eNOS, p-eNOS and MFN-2 were increased in growth hormone receptor knockout. PMID: 21755522
- Data suggest that GHR signaling plays a major role in liver regeneration and that GHR acts through activation of both epidermal growth factor receptor and Erk1/2 pathways. Liver regeneration is severely delayed in mutant GHR knockout mice. PMID: 21540290
- Data indicate a role for GH in establishing pubertal skeletal and body size that is independent of hepatic IGF-1 production. PMID: 20928887
- GH receptor plays critical roles in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and beta cell compensation in response to a high-fat diet. PMID: 21555853
- The decreased renal levels of pro-apoptotic proteins could contribute to the extended life-span caused by targeted disruption of the GH receptor gene but are apparently not involved in mediating the effects of visceral fat removal. PMID: 21391871
- These results identify distinct signaling pathways through which the growth hormone receptor regulates skeletal muscle development and modulates nutrient metabolism. PMID: 20921627
- Compared to wild type controls, the GHR -/- mice were smaller, consumed more food, and had greater energy expenditure. PMID: 19747867
- In studies using targeted knock-in mice with mutation in the Ghr Box1 motif (disabling Jak2 activation by Ghr), data indicate Ghr activation of Src and Erk1/2 is independent of Jak2. PMID: 19884384
- intermittent fasting diet increased the survivorship and improved insulin sensitivity of normal males, but failed to affect either parameter in GHR-KO mice. PMID: 19747233
- although growth hormone receptor knockout female mice are fertile, they exhibit quantitative deficits in various parameters of reproductive function PMID: 12297526
- in the kidney diabetes mellitus is associated with enhanced GHR expression and lack of alteration in the assembly of the repressosome complex PMID: 12529387
- the degree of blockade of growth hormone receptor signaling can lead to dramatically different phenotypes. PMID: 12933651
- Data suggest that expression of truncated growth hormone receptors (GHRs) is regulated in a different manner from that of the full-length GHR, thereby modulating growth hormone action in murine adipocytes. PMID: 14615057
- Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates suppression of Ghr. PMID: 14759523
- Located on caveolae and lipid rafts of 3t3 cells. PMID: 15010456
- serum igf-i levels and body weights of mature Ghsr-null mice are modestly reduced compared to wild-type littermates. PMID: 15070777
- Average size of islets found in GHR(-/-) mice was only one-third of that in wild-type littermates. Total beta-cell mass was reduced 4.5-fold in GHR(-/-) mice, significantly more than their body size reduction. PMID: 15138153
- Two truncated isoforms of GHR mRNAs were detected in liver, skeletal muscle, and subcutaneous fat of mice. The ratio of GHR-truncated to GHR-full length mRNA was tissue specific and not affected by chronic excess or deficiency of GH. PMID: 15165994
- targeted disruption of the GH receptor/GH-binding protein gene and caloric restriction act via overlapping, but distinct, mechanisms. PMID: 15498882
- specific domains of the GHR regulate body growth and composition PMID: 15601831
- GHR is subject to sequential proteolysis by metalloprotease and gamma-secretases, including PS1 PMID: 15743767
- The lower fasting and postmeal plasma ghrelin levels in binge eaating disorder are consistent with lower ghrelin levels in obese compared to lean individuals. PMID: 15867334
- Retention of ubiquitin-dependent endocytosis motif in N-terminal cytoplasmic domain of growth hormone receptor permits turnover of these mutant receptors because no dominant-negative phenotype is seen. PMID: 16166215
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Secreted.; [Growth hormone-binding protein]: Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Type I cytokine receptor family, Type 1 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in all tissues tested including, liver, heart, adipose tissue, mammary gland, testes, ovary, brain, kidney and muscle. Highest levels in liver.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14600
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000069457
UniGene: Mm.3986
Most popular with customers
-
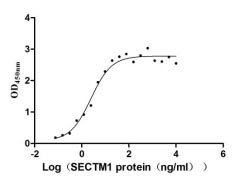
Recombinant Human Secreted and transmembrane protein 1 (SECTM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
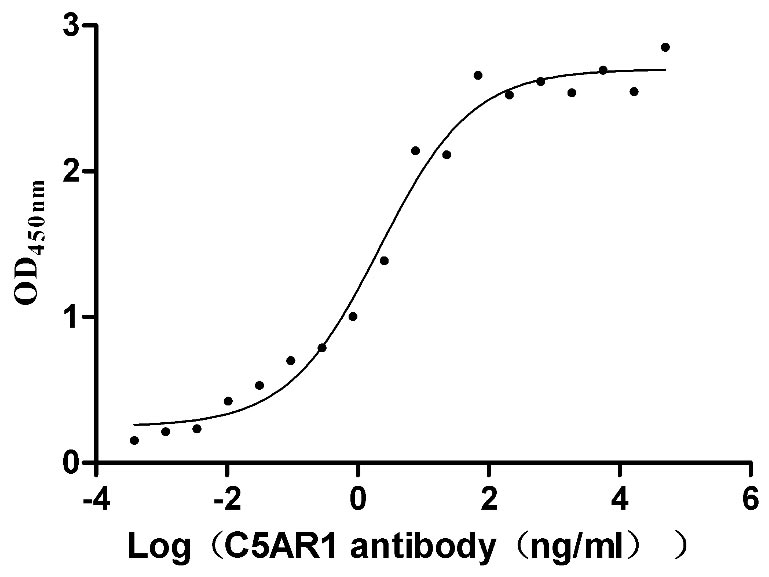
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
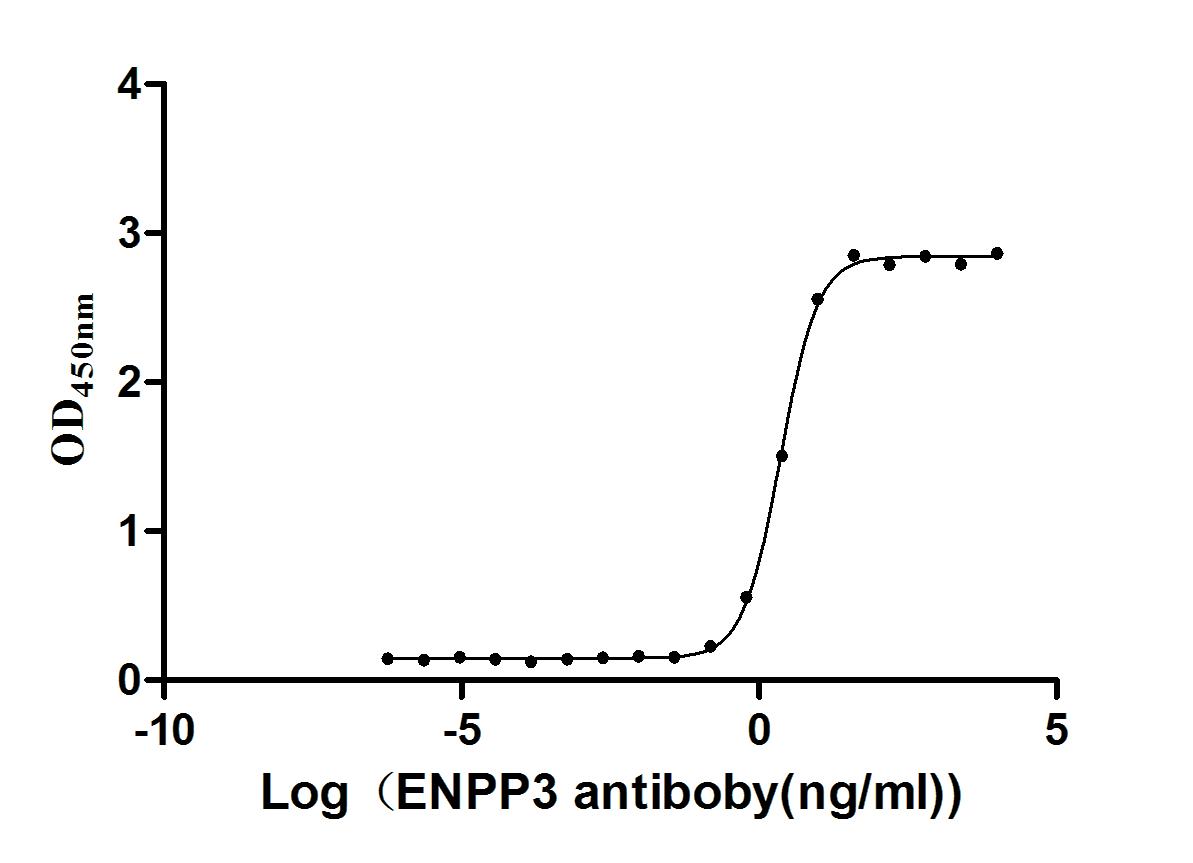
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
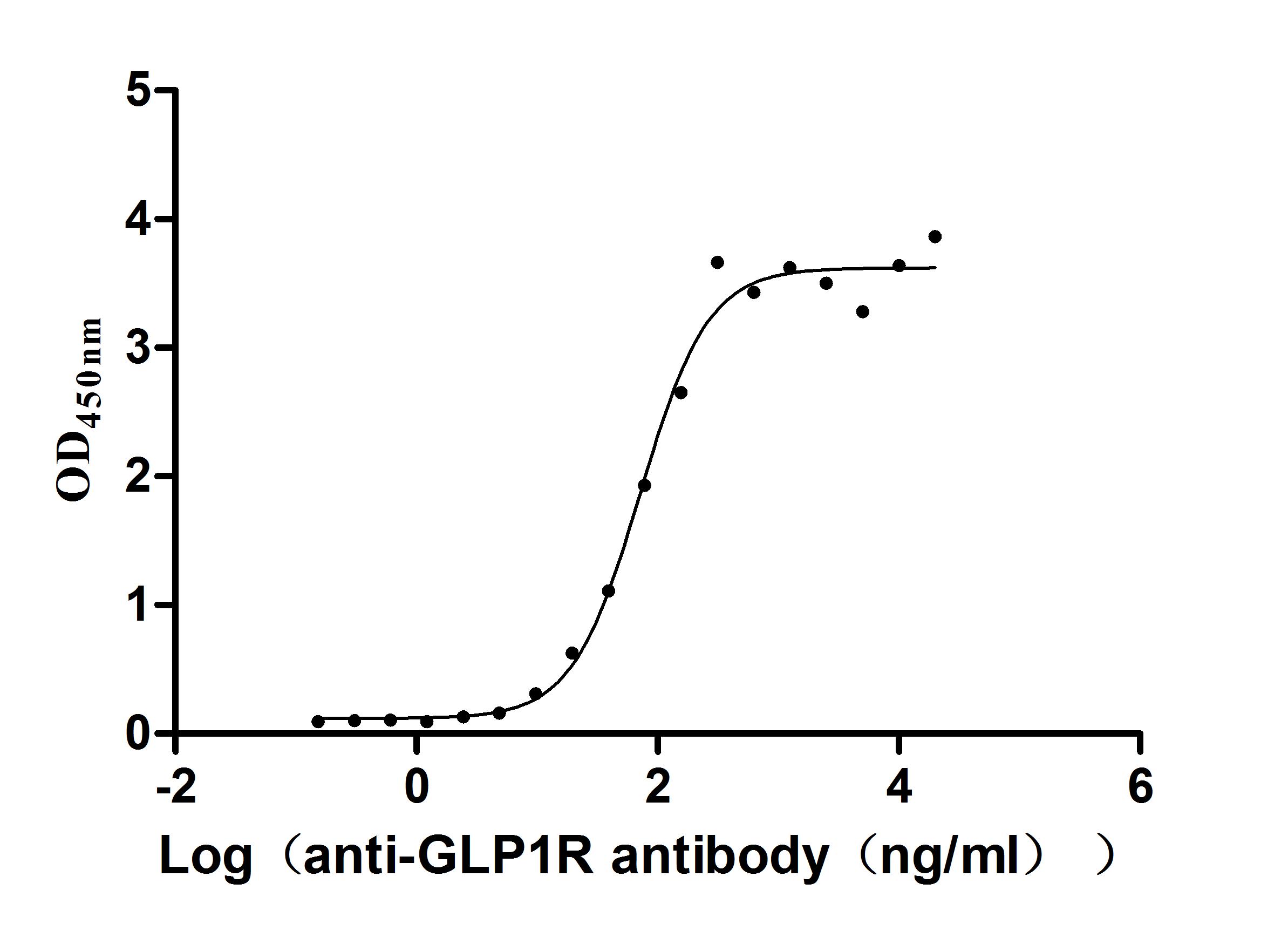
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
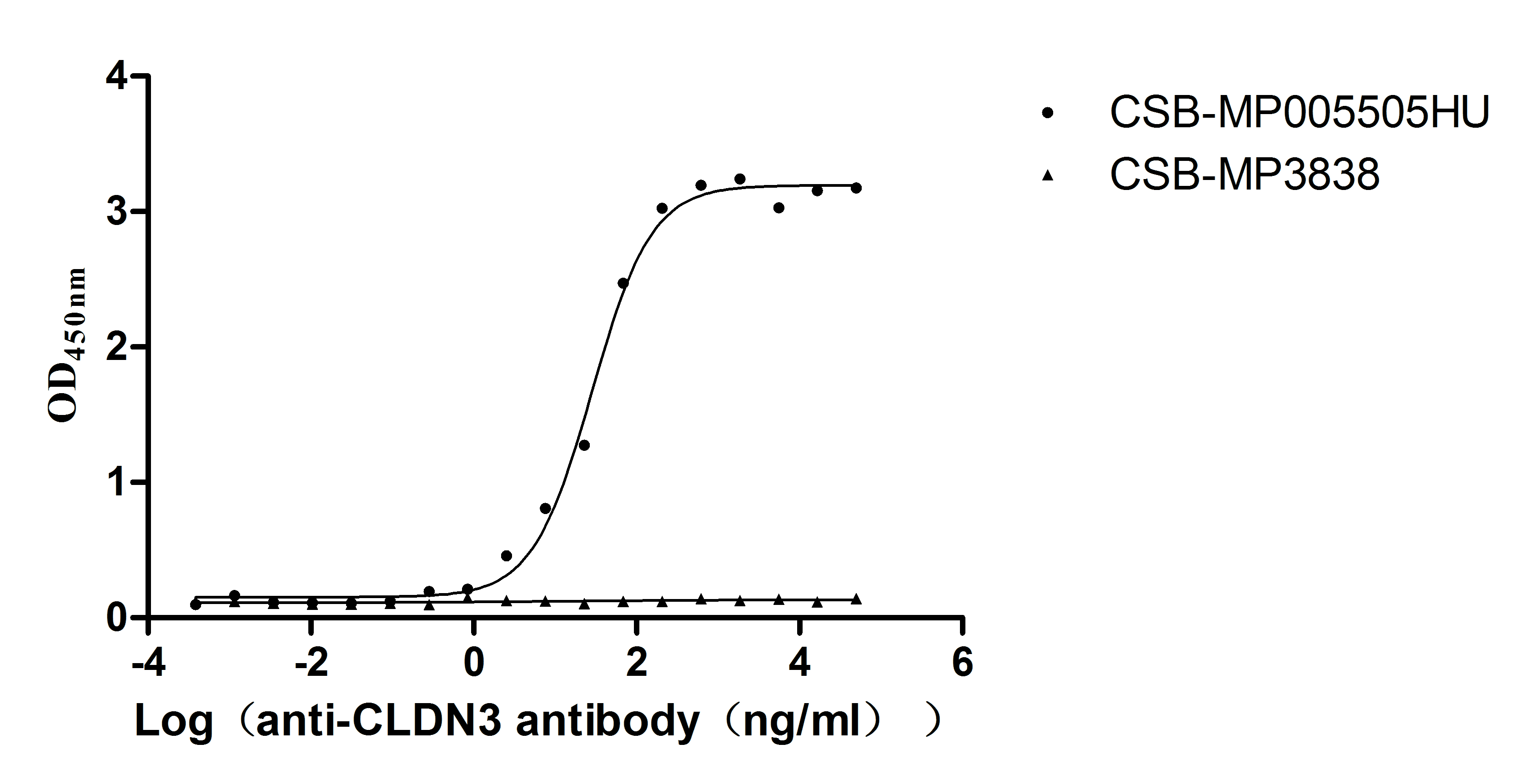
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
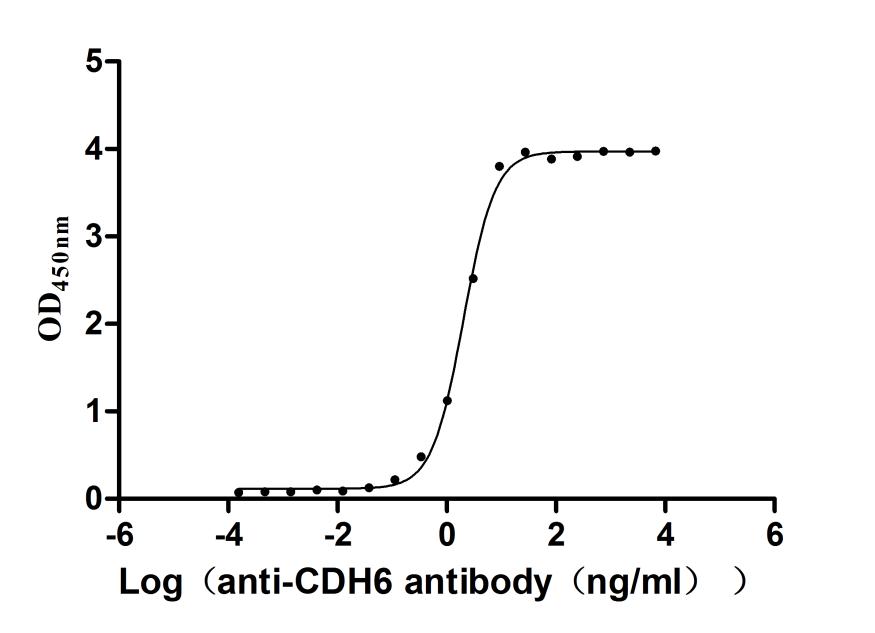
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)