-
货号:CSB-EP009369MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
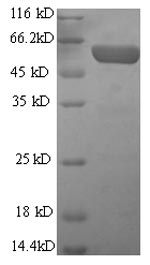
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-
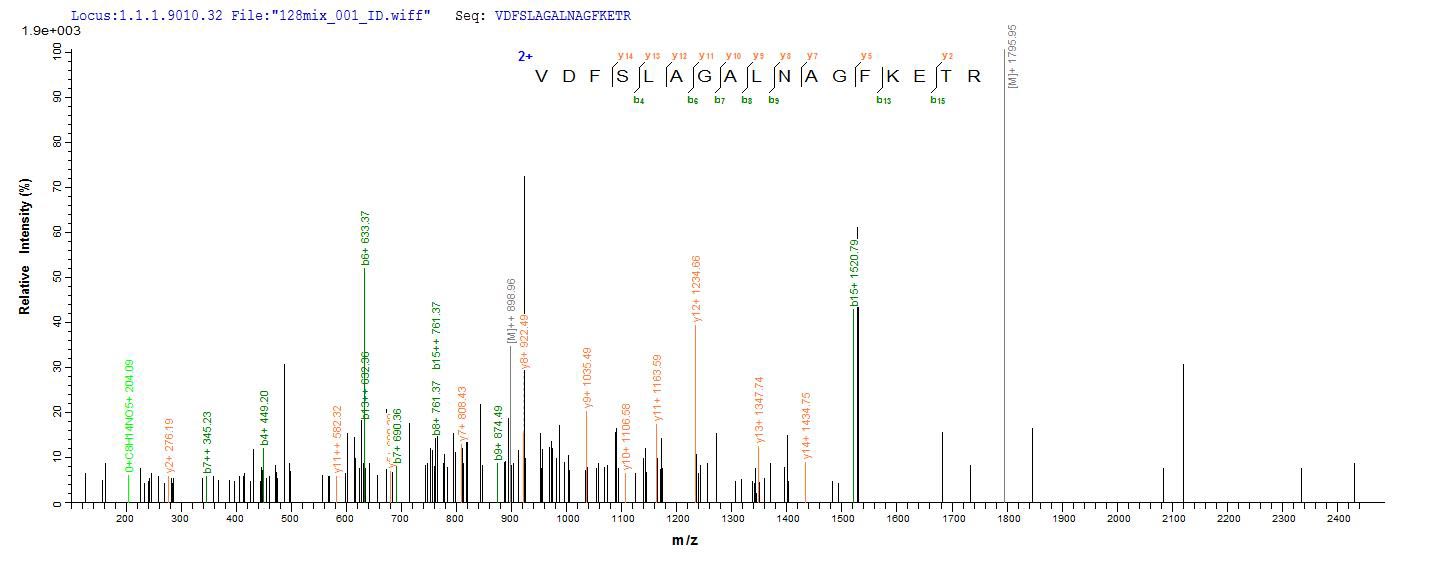
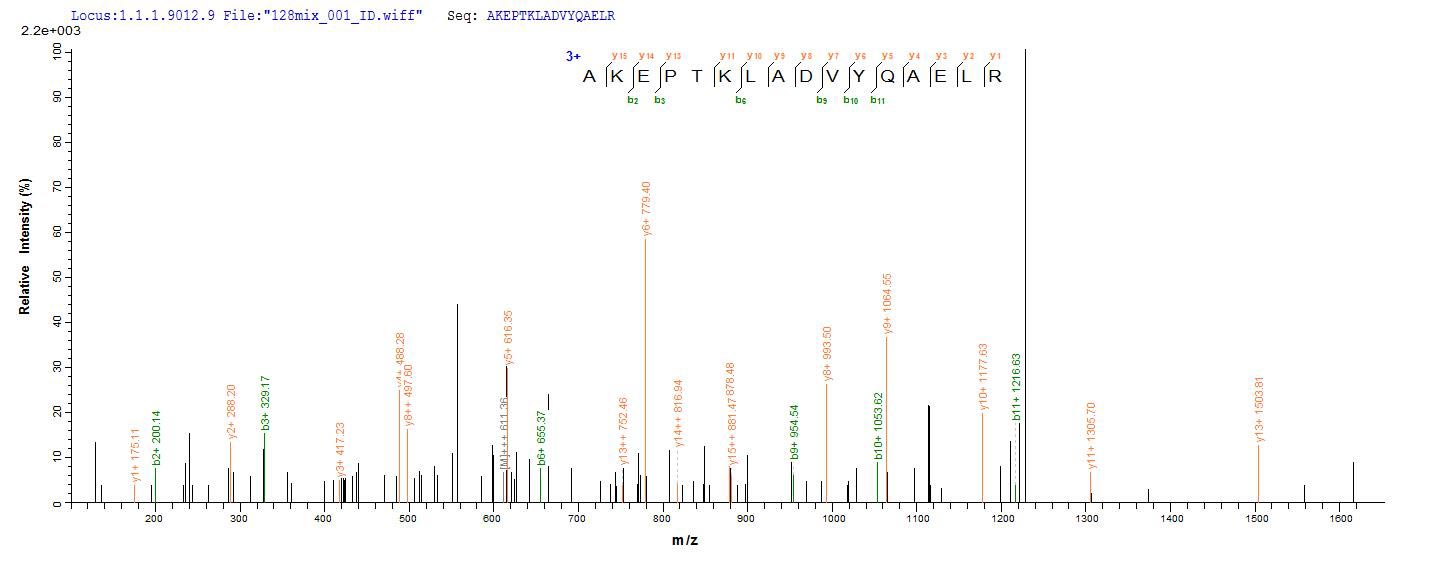
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP009369MO could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) GFAP.
-
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP009369MO could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) GFAP.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:GfapGlial fibrillary acidic protein; GFAP
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:65.9kDa
-
表达区域:1-430aa
-
氨基酸序列MERRRITSARRSYASETVVRGLGPSRQLGTMPRFSLSRMTPPLPARVDFSLAGALNAGFKETRASERAEMMELNDRFASYIEKVRFLEQQNKALAAELNQLRAKEPTKLADVYQAELRELRLRLDQLTANSARLEVERDNFAQDLGTLRQKLQDETNLRLEAENNLAAYRQEADEATLARVDLERKVESLEEEIQFLRKIYEEEVRELREQLAQQQVHVEMDVAKPDLTAALREIRTQYEAVATSNMQETEEWYRSKFADLTDAASRNAELLRQAKHEANDYRRQLQALTCDLESLRGTNESLERQMREQEERHARESASYQEALARLEEEGQSLKEEMARHLQEYQDLLNVKLALDIEIATYRKLLEGEENRITIPVQTFSNLQIRETSLDTKSVSEGHLKRNIVVKTVEMRDGEVIKDSKQEHKDVVM
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:Gfap是一种细胞骨架蛋白,它与微管和微丝一起构成大多数真核细胞的细胞骨架,为其他细胞或细胞外基质接触的质膜提供机械支持,具有维护星形胶质细胞形态稳定、参与血脑屏障形成、调节突触功能等多种生物学功能,还参与细胞迁移、运动和有丝分裂。这种蛋白质在中枢神经系统的星形胶质细胞中特异性表达,因此被认为是星形胶质细胞的特异性标志物。在实验室研究中,Gfap经常被用作研究工具,因为它的表达模式和功能使其成为研究星形胶质细胞及其功能的理想选择。j9九游会登录入口首页生物提供大肠杆菌表达的全长重组小鼠胶质纤维酸性蛋白(Gfap),由重组DNA技术制备而成,可作为研究各种生理和病理状态下细胞行为的重要工具。
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
引用文献
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a novel biomarker for the prediction of autoimmune diabetes Pang Z.et al,FASEB J,2017
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-specific marker that, during the development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- This report the successful prediction and validation of Gfap as an miR-3099 target gene using a combination of bioinformatics resources with enrichment of annotations based on functional ontologies and a spatio-temporal expression dataset. PMID: 28597341
- These results indicate that autoantibodies against GFAP could serve as a predictive marker for the development of overt autoimmune diabetes. PMID: 28546444
- GFAP is specifically expressed in the auricular chondrocytes, and assumes a pivotal role in resistance against mechanical stress. PMID: 28063220
- compared open-skull and thinned-skull imaging methods for two-photon laser microscopy of live astrocytes in neocortex of GFAP-GFP transgenic mice PMID: 28107381
- work reveals that an Alexander disease-causing mutation alters GFAP turnover kinetics in vivo and provides an essential foundation for future studies aimed at preventing or reducing the accumulation of GFAP. PMID: 28223355
- Tat expression or GFAP expression led to formation of GFAP aggregates and induction of unfolded protein response (UPR) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in astrocytes. PMID: 27609520
- Study provides evidence that transcription of one of the astrocyte-specific genes, Gfap, is cooperatively regulated by co-expressed genes and their regulatory factors. PMID: 27041678
- This study demonstrated the GFAP-ApoE4 mice exhibited motor impairments when compared to GFAP-ApoE3 and wild-type mice. PMID: 26892275
- PINK1 deficiency causes defects in GFAP-positive astrogliogenesis during brain development. PMID: 26746235
- Gnasxl deficiency does not directly affect glial development in the hypothalamus, since it is expressed in neurons, and Gfap-positive astrocytes and tanycytes appear normal during early postnatal stages. PMID: 27080240
- Induction of glial cytokine expression was sequential, aligned with active sickness behavior, and preceded increased Iba-1 or GFAP immunoreactivity after lipopolysaccharide challenge PMID: 26470014
- Study provides a mechanistic link between the GFAP mutations/overexpression and the symptoms in those affected with Type II Alexander disease PMID: 26190408
- Study described GFAP-expressing non-myelinating Schwann cells in the lung, validated a transgenic mouse line that drives expression of cre under a GFAP promoter PMID: 26442852
- findings thus show that the inability to produce GFAP and Vim affects normal retinal physiology and that the effect of IF deficiency on retinal cell survival differs, depending on the underlying pathologic condition PMID: 26251181
- CUL4B as a negative regulator of GFAP expression during neural development. PMID: 26025376
- Astrocytes deficient of GFAP and vimentin showed decreased Notch signal sending competence and altered expression of Notch signaling pathway-related genes PMID: 26118771
- Absence of GFAP, or both GFAP and vimentin, alters Alzheimer's disease-induced changes in gene expression profile of astrocytes, showing a compensation of the decrease of neuronal support genes and a trend for a higher inflammatory expression profile PMID: 25731615
- Data indicate that glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was up-regulated in satellite glial cells (SGCs) in dorsal root ganglia 14 days after streptozotocin injection. PMID: 25312986
- Findings demonstrate that ENT1 regulates GFAP expression and possibly astrocyte function PMID: 25365803
- Data suggest that prenatal alterations in expression of various fetal brain proteins (including down-regulation of Gfap) are associated with aberrant behavioral characteristics of transgenic mice that model autism-like behavior. PMID: 25849768
- Study shows that increased levels of astrocytic GFAP can contribute to increases on inter-ictal spikes but do not represent a risk factor for appearance of post-traumatic seizures, even when there is increase in reactive gliosis PMID: 25069089
- The Phactr4 signals were not associated with F-actin fibers but were closely associated with intermediate filaments such as nestin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) fibers. PMID: 24748504
- Report increasing glial fibrillary acidic protein expression and electron microscopic features of brain edema in rodent cerebral malaria. PMID: 24966914
- absence of GFAP and vimentin in glial cells does not seem to affect the outcome after peripheral motoneuron injury but may have an important effect on the response dynamics PMID: 24223940
- the astrocyte became activated, exhibiting significantly increased levels of GFAP expression directly related to the level of HIV/VSV replication PMID: 24254728
- traumatic scratch injury to astrocytes triggered a calcium influx from the extracellular compartment and activated the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway to switch on GFAP PMID: 24123203
- Data show that CD8 T cells reactive to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a protein expressed in astrocytes, drive unique aspects of inflammatory central nervous system autoimmunity. PMID: 24591371
- Brain levels of GFAP and Tau proteins decreased significantly at 6 h and increased considerably at 24 h after repeated blast exposures. Plasma samples showed a similar initial decrease and later increase over this timeframe. PMID: 23933206
- Data indicate that Gfapdelta is expressed in the in developing mouse brain sub-ventricular zones in accordance with the described localization in the developing and adult human brain. PMID: 23991052
- GFAP was found to be downregulated in HSV-1 acute infection in cornea and upregulated in late stage, suggesting that GFAP might play some role during HSV-1 infection in cornea. PMID: 23758602
- Data show that neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-inactivation results in a cell-autonomous increase in glial fibrillary acidic protein+ (GFAP+), but not in NG2 proteoglycan NG2+, cell proliferation in vitro. PMID: 23318450
- this study demonistrated that mouse models of Alexander disease exhibit significant pathology in GFAP-positive radial glia-like cells in the dentate gyrus, and suffer from deficits in adult neurogenesis. PMID: 24259590
- These studies demonstrate that transactivation of the Gfap promoter is an early and sustained indicator of the disease process in the mouse. PMID: 23432455
- These data suggest that all astroglia cells in the developing and adolescent mouse brain express GFAPdelta, regardless of their neurogenic capabilities. PMID: 23285135
- The GFAP-stained intensity of the retinal area is increased in contralateral eyes and decreased in retinal ganglion cells of eyes with laser-induced ocular hypertension. PMID: 22583833
- Postulate that glial cells with increased Gfap expression support the elongation of new neurites from retinal ganglion cells possibly by providing a scaffold for outgrowth. PMID: 23259929
- GFAP expression is almost not affected by melatonin treatment in aged mice. PMID: 22200709
- differential regulation of GFAP isoforms is not involved in the reorganization of the intermediate filament network in reactive gliosis or in neurogenesis in the mouse brain. PMID: 22912745
- CD44-positive cells are APCs in the early postnatal cerebellum; surviving cells gradually express glial fibrillary acidic protein GFAP), a marker for mature astrocytes, indicating differentiation into mature astrocytes is the default for these cells. PMID: 21732075
- GFAP-negative astrocytes are fully inflammation-competent, displaying phenotypic heterogeneity as is commonly observed in brain astrocytes. PMID: 22072312
- In a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), GFAP is not necessary for the initiation of disease; instead, it plays some modulatory roles in the progression of ALS. PMID: 21453731
- Treadmill exercise training decreased the expression of GFAP in the striatum of chronic Parkinsonian mice, which can partially explain the beneficial neuroprotective role of exercise in patients with parkinson disease. PMID: 21725169
- The study shows opposing pattern of nestin and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in mouse hippocampus occuring in early postnatal development, suggesting that it is important for neural differentiation and positioning in the hippocampus. PMID: 21368556
- In the mouse there is a slight increase in the number of GFAP positive cells in the white matter after 3 days of severe cerebral contusion trauma. PMID: 20479526
- Increased expression of GFAP in Muller cells of mer knockout mice occur at P20d in the peripheral retina and P4w in the central retina. GFAP expression in Muller cells appears to be a secondary response to the loss of retinal neurons. PMID: 20497693
- One protein, GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), was found to be elevated in the LINCL mice compared with normal controls in both isolated storage bodies and a lysosome-enriched subcellular fraction that contains storage material. PMID: 20370715
- The results of this study suggested that GFAP is necessary for morphological retention and distribution of reactive astrocytes during prion disease, and that there is a GFAP-dependent function of glial filaments in reactive astrocytes. PMID: 19931516
- Report demonstrated for the first time that GFAPdelta is specifically expressed in radial glia and SVZ neural progenitors during human brain development. PMID: 20040497
- The exact expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in trigeminal ganglion and dental pulp. PMID: 11838710
- Human influenza viral infection in utero alters GFAP immunoreactivity in the developing brains of neonatal mice. PMID: 12140787
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Intermediate filament family
-
组织特异性:Brain; isoform 2 expressed at 20-fold lower level than isoform 1.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14580
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000064691
UniGene: Mm.1239
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
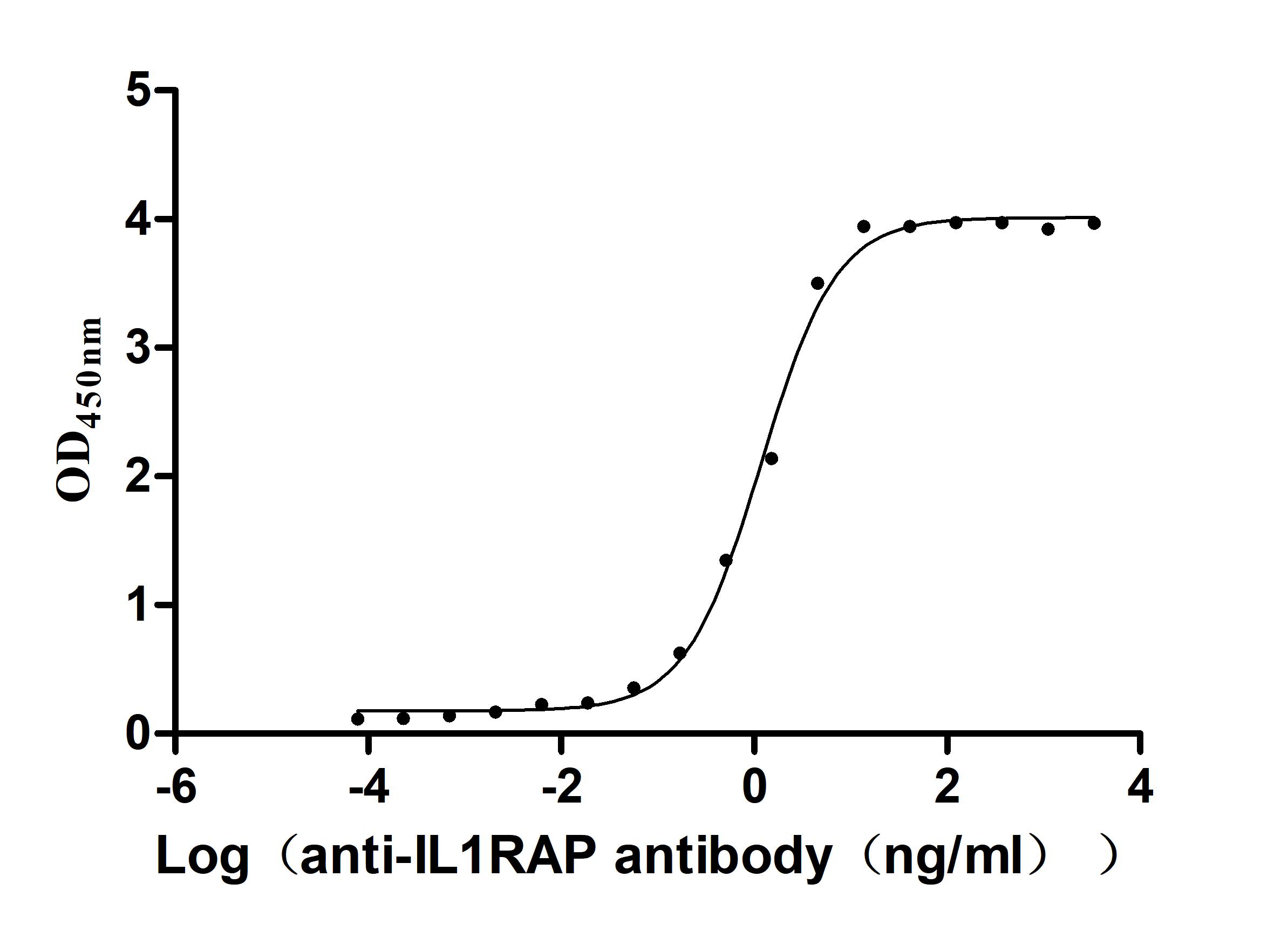
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
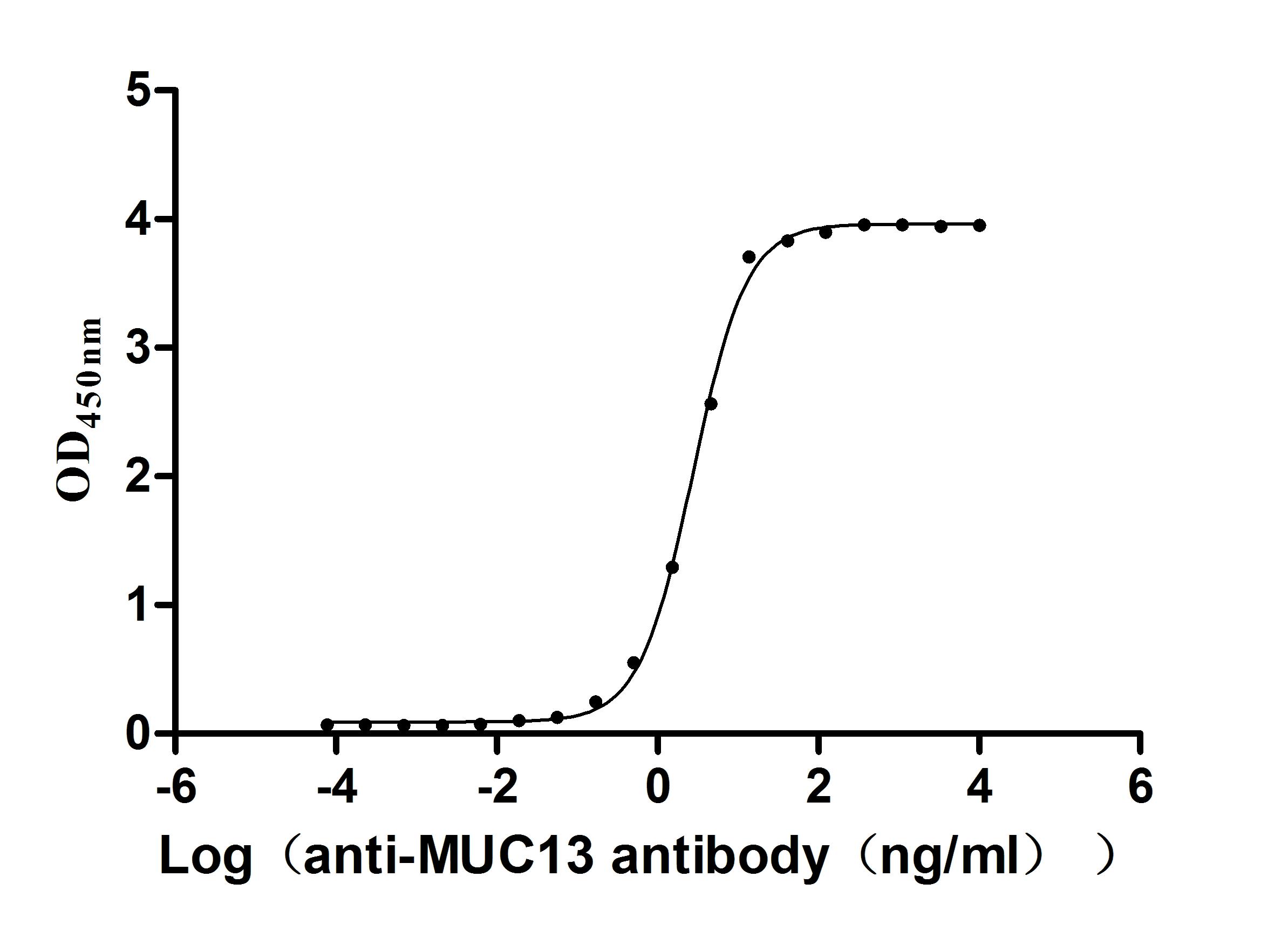
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)