Recombinant Mouse Forkhead box protein N1 (Foxn1)
-
货号:CSB-YP730743MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP730743MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP730743MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP730743MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP730743MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Foxn1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Foxn1; Fkh19; Hfh11; WhnForkhead box protein N1; Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 forkhead homolog 11; HFH-11; HNF-3/forkhead homolog 11; Winged-helix transcription factor nude
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-648
-
氨基酸序列MVSLLPPQSD VTLPGSTRLE GEPQGDLMQA PGLPDSPAPQ NKHANFSCSS FVPDGPPERT PSLPPHSPSI ASPDPEQIQG HCTAGPGPGS FRLSPSEKYP GFGFEEGPAG SPGRFLKGNH MPFHPYKRHF HEDIFSEAQT AMALDGHSFK TQGALEAFEE IPVDMGDAEA FLPSFPAEAW CNKLPYPSQE HNQILQGSEV KVKPQALDSG PGMYCYQPPL QHMYCSSQPA FHQYSPGGGS YPVPYLGSPH YPYQRIAPQA NAEGHQPLFP KPIYSYSILI FMALKNSKTG SLPVSEIYNF MTEHFPYFKT APDGWKNSVR HNLSLNKCFE KVENKSGSSS RKGCLWALNP SKIDKMQEEL QKWKRKDPIA VRKSMAKPEE LDSLIGDKRE KLGSPLLGCP PPGLAGPGPI RPMAPSAGLS QPLHPMHPAP GPMPGKNPLQ DLLGGHAPSC YGQTYPHLSP SLAPSGHQQP LFPQPDGHLE LQAQPGTPQD SPLPAHTPPS HGAKLMAEPS SARTMHDTLL PDGDLGTDLD AINPSLTDFD FQGNLWEQLK DDSLALDPLV LVTSSPTSSS MLPPPPAAHC FPPGPCLAET GNEAGELAPP GSGGSGALGD MHLSTLYSAF VELESTPSSA AAGPAVYLSP GSKPLALA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional regulator which regulates the development, differentiation, and function of thymic epithelial cells (TECs) both in the prenatal and postnatal thymus. Acts as a master regulator of the TECs lineage development and is required from the onset of differentiation in progenitor TECs in the developing fetus to the final differentiation steps through which TECs mature to acquire their full functionality. Regulates, either directly or indirectly the expression of a variety of genes that mediate diverse aspects of thymus development and function, including MHC Class II, DLL4, CCL25, CTSL, CD40 and PAX1. Regulates the differentiation of the immature TECs into functional cortical TECs (cTECs) and medullary TECs (mTECs). Essential for maintenance of mTECs population in the postnatal thymus. Involved in the morphogenesis and maintenance of the three-dimensional thymic microstructure which is necessary for a fully functional thymus. Plays an important role in the maintenance of hematopoiesis and particularly T lineage progenitors within the bone marrow niche with age. Essential for the vascularization of the thymus anlage. Promotes the terminal differentiation of epithelial cells in the epidermis and hair follicles, partly by negatively regulating the activity of protein kinase C.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study report the identification of a highly conserved Foxn1-binding sequence that is located proximal to the beta5t-coding sequence in the mouse genome. This cis-regulatory element is indeed essential for the optimal expression of beta5t in cortical thymic epithelial cells and the optimal production of CD8+ T cells. PMID: 28176764
- data identify the transcription factor Foxn1 as a potential key epidermal regulator modifying both epidermal and dermal healing processes after cutaneous wounding PMID: 28371152
- MicroRNA-205 maintains T cell development following stress by regulating Foxn1 and its two regulated targets, stem cell factor and ccl25, following stress. PMID: 27646003
- results show that Foxn1, and alleles under its control, are expressed in the pre-meiotic male germline, revealing a new tool for germline targeting of genes, and raising important concerns for gender selection when using Foxn1 regulatory elements. PMID: 27880796
- this study shows that critical events in thymic lympho-stromal cross-talk and T cell selection are regulated by Foxn1 PMID: 27548434
- sphingolipids and fatty acids associated with a decrease in glycerolipids suggest that the lipidome in mice skin is regulated by the Foxn1 gene PMID: 26427556
- Foxn1 transcription factor regulates wound healing of skin through promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PMID: 26938103
- early differentiation and maturation of cortical and medullary thymic epithelial cells coincides with precise sub-lineage-specific regulation of Foxn1 expression levels. PMID: 26983083
- upregulated expression in thymus epithelial cells upon challenges PMID: 26538393
- Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay using RarB as the immunoprecipitation target suggests retinoic acid regulation of Aldh1a3 and Foxn1 in mice. PMID: 26352270
- The maturation and distribution of thymic epithelial cells in the Foxn1(-/-) thymic rudiment and the thymopoiesis of this newly developed rudiment, were examined. PMID: 24561455
- Expression of FoxN1 in early life adversely influence immature epithelial cells T and B cell, and skin epithelial development. PMID: 25299782
- this study presents the characterization of the adult thymic epithelial stem cells and demonstrates the dispensability of FoxN1 function for their stemness. PMID: 25148026
- Enforced Foxn1 expression is sufficient to reprogramme fibroblasts into functional thymic epithelial cells. PMID: 25150981
- TAp63 levels are positively correlated with TEC senescence but inversely correlated with expression of FoxN1 and FoxN1-regulated thymic epithelial cell differentiation. PMID: 24263106
- Upregulation of a single transcription factor can substantially reverse age-related thymic involution, identifying FOXN1 as a specific target for improving thymus function. PMID: 24715454
- The similar characteristics between IL-22 and Foxn1 leads to a speculation that Foxn1 is probably involved in thymic regeneration driven by IL-22. PMID: 24333537
- skews multipotent progenitors development toward T lineage PMID: 24184560
- Increased Foxn1 expression is required for the thymic expansion observed in Rb family mutant mice. PMID: 23669396
- Findings provide the first evidence that K14-mediated FoxN1 deletion causes changes in T-cell function that mimic those in aging during an immune response to challenge with an infectious agent. PMID: 22514652
- regulation by Foxn1 of a suite of genes with diverse roles in thymus development and/or function, suggests it acts as a master regulator of the core thymic epithelial programme. PMID: 22072979
- Manipulation of Foxn1 expression in the thymus ameliorates thymopoiesis in aged mice and offer a strategy to combat the age-associated decline in naive T-cell production and CD4 naive/memory ratios in the elderly. PMID: 21908422
- Msx2 and Foxn1 regulate differentiation of the keratogenous zone, proliferation of distal nail matrix cells, and organization of the nail bed. PMID: 21387539
- The findings provide new insights into FoxN1 regulation of 3D thymic epithelial morphogenesis and maintenance, the distinct impacts of FoxN1 in the K14 epithelial subset of the thymus and skin, and its postnatal requirement. PMID: 21109991
- data support a regulatory model of keratinocyte differentiation in which HOXC13-dependent activation of Foxn1 is part of a regulatory cascade controlling the expression of hair and nail terminal differentiation markers PMID: 21191399
- Data show that the capacity for positive and negative selection of both CD4 and CD8 SP thymocytes was reduced in Foxn1(Delta/Delta) mutants. PMID: 21079757
- Foxn1 is the essential transcription factor regulating the differentiation of thymic epithelial cells PMID: 20823228
- results support the notion that decline of a single epithelial cell-autonomous gene FoxN1 levels with age causes primary deterioration in thymic epithelial cells PMID: 20156205
- Notch/CSL signaling plays a unique function in control of hair follicle differentiation by the underlying mesenchyme, with Wnt5a signaling and FoxN1 as mediators. PMID: 20634318
- Postnatal ubiquitous deletion of FoxN1 caused dramatic thymic atrophy in 5 days PMID: 19955175
- Foxn1 gene knockout associated with male odor in mice might be jointly affected by the level of inbreeding and immunodeficiency. PMID: 20019156
- Results indicate that Foxn1 dependent epithelial development is essential for vascularization of the thymus anlagen. PMID: 19853842
- Role of the nude gene in epithelial terminal differentiation PMID: 11841548
- In Pax9 null mice, the thymic anlage develops as an ectopic polyp-like structure in the larynx. It expresses Whn/Foxn1, a marker of thymic epithelium. PMID: 11932925
- Secreted Wnt glycoproteins, expressed by thymic epithelial cells and thymocytes, regulate epithelial Foxn1 expression in both autocrine and paracrine fashions. PMID: 12379851
- pattern-forming phenomenon that occurs in the skin of mutant mice with a defect in splicing of the Foxn1 gene PMID: 12893877
- Foxn1(nu) mutated gene has effects beyond downregulating keratin expression, including changes in filaggrin expression, and is critical for normal onycholemmal differentiation PMID: 15610506
- the nude mutation of Foxn1 in mice retards the early growth of development of muscle but not of the matrix tissue in limb muscles PMID: 15694130
- foxn1 may be involved in directing lineage choices of multi-potential progenitor epithelial cells PMID: 15986478
- Mechanisms and signaling pathways by which Foxn1 modulates keratinocyte differentiation in hair follicle and nail apparatus. Molecular and functional consequences of loss of function of Foxn1 protein in skin. Review. PMID: 16232301
- Modulates stage-specific markers by modulating protein kinase C activity, providing control over the timing of steps in the keratinocyte differentiation program. PMID: 17459087
- Gene targeting into the 3' untranlated region of the Foxn1 locus is an efficient method to express any gene of interest in thymus epithelial cells from the earliest stage of thymus organogenesis. PMID: 17577402
- lack of thymopoiesis in Foxn1-deficient mice is caused by multiple functional defects PMID: 17683113
- These results suggest that the phenotype of peripheral T cells in Foxn1Delta/Delta mutant mice is the result of atypical progenitor cells developing in an abnormal thymic microenvironment with a deficient TCR and IL7 signaling system. PMID: 18056358
- Thymopoiesis in the Foxn1Delta/Delta adult thymus proceeds from CD117- atypical progenitors, while CD117+ DN1a cells are absent or blocked in their ability to differentiate to the T lineage. PMID: 18178831
- an evolutionarily conserved role of BMP signaling in the maintenance of Foxn1 expression. PMID: 18832682
- Foxn1 is required to maintain the postnatal thymus PMID: 18978204
- Results position Msx2 and Foxn1 upstream of Notch1 within the hair matrix and demonstrate that together these factors play a pivotal role in hair inner root sheath, cortex and medulla differentiation. PMID: 19103190
- FoxN1 expression per se is not a signature for the thymic lineage. FoxN1 expression, whereas necessary for thymic epithelium, development, is not sufficient for this process to occur. PMID: 19786540
- may control important regulating genes of lympho-epithelial interactions PMID: 11500834
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Defects in FOXN1 are the cause of the nude/severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) phenotype which is characterized by athymia and hairlessness. Mice develop largely normal hair follicles and produce hair shafts. However, presumably because of a lack of certain hair keratins, the hair shafts that are generated twist and coil in the hair follicle infundibulum, which becomes dilated. Since hair shafts fail to penetrate the epidermis, macroscopic nudity results and generates the grossly misleading impression that nude mice are hairless.
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Bone marrow (at protein level). Expressed in thymus and skin.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:15218
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000103929
UniGene: Mm.392151
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Paguma larvata Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Paguma larvata (Masked palm civet)
-
Recombinant Human Glypican-3 (GPC3) (G537R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-18.2 (CLDN18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
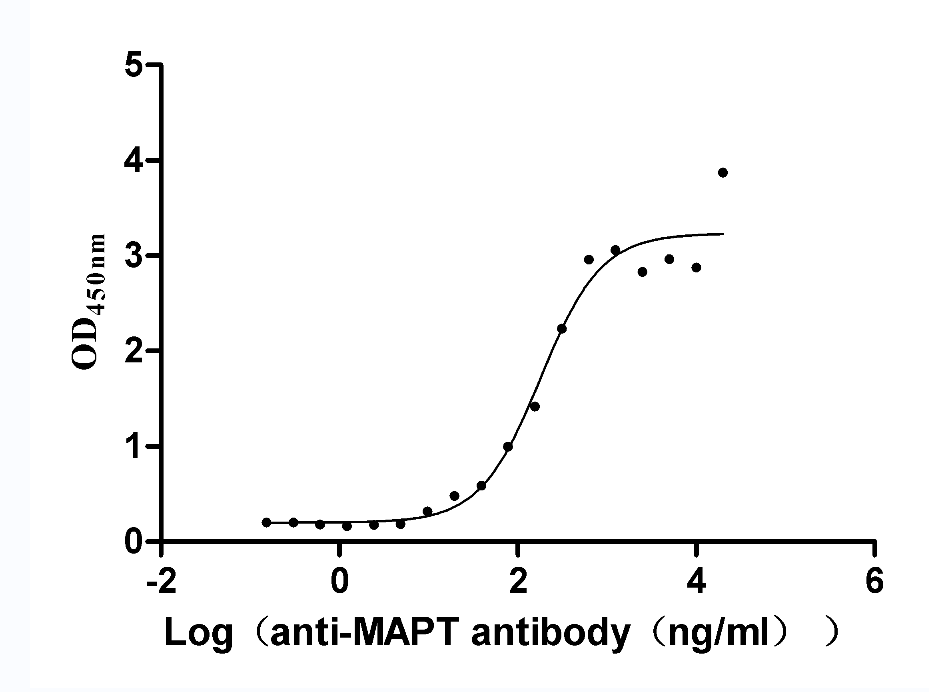
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
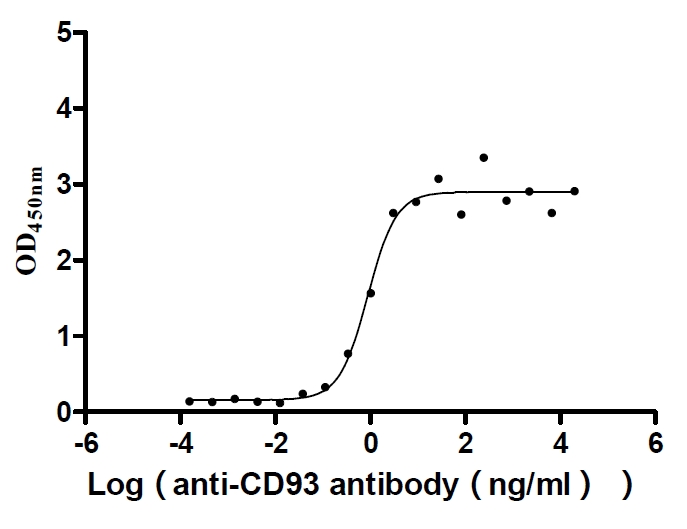
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
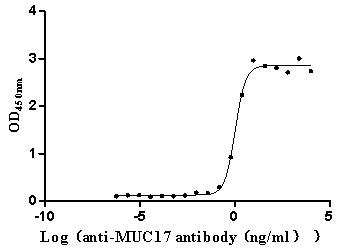
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
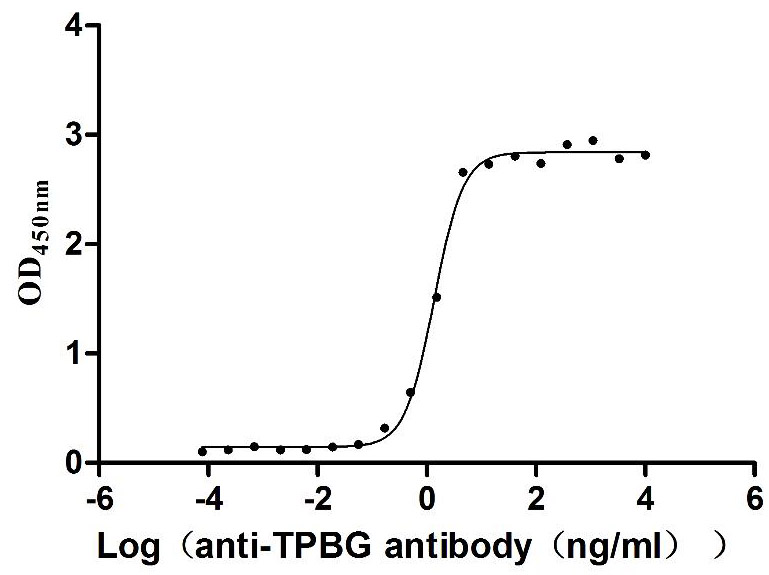
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)