-
货号:CSB-EP008627MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
促销:

-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
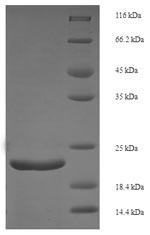
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Fgf21Fibroblast growth factor 21; FGF-21
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:23.9kDa
-
表达区域:29-210aa
-
氨基酸序列AYPIPDSSPLLQFGGQVRQRYLYTDDDQDTEAHLEIREDGTVVGAAHRSPESLLELKALKPGVIQILGVKASRFLCQQPDGALYGSPHFDPEACSFRELLLEDGYNVYQSEAHGLPLRLPQKDSPNQDATSWGPVRFLPMPGLLHEPQDQAGFLPPEPPDVGSSDPLSMVEPLQGRSPSYAS
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:
The preparation of Recombinant Mouse Fgf21 protein included 3 main steps: construct the expression vector, expression of protein of interest, and protein purification. Every step was performed under a strict QC system so that we got the premium protein. This Fgf21 was expressed in E.coli at and fused with N-terminal 6xHis tag. According to SDS-PAGE, the purity turns out to be 90%+.
FGF21 is a peptide hormone that is synthesized by several organs and regulates energy homeostasis. Excitement surrounding this relatively recently identified hormone is based on the documented metabolic beneficial effects of FGF21, which include weight loss and improved glycemia. The biology of FGF21 is intrinsically complicated owing to its diverse metabolic functions in multiple target organs and its ability to act as an autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine factor. In the liver, FGF21 plays an important role in the regulation of fatty acid oxidation both in the fasted state and in mice consuming a high-fat, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet. FGF21 also regulates fatty acid metabolism in mice consuming a diet that promotes hepatic lipotoxicity. In white adipose tissue (WAT), FGF21 regulates aspects of glucose metabolism, and in susceptible WAT depots, it can cause browning. This peptide is highly expressed in the pancreas, where it appears to play an anti-inflammatory role in experimental pancreatitis. It also has an anti-inflammatory role in cardiac muscle. Although typically not expressed in skeletal muscle, FGF21 is induced in situations of muscle stress, particularly mitochondrial myopathies. FGF21 has been proposed as a novel therapeutic for metabolic complications such as diabetes and fatty liver disease.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
引用文献
- Recombinant FGF21 Attenuates Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Induced NAFLD/NASH by Modulating Hepatic Lipocalin-2 Expression HY Kim,International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022
- Hepatic STAMP2 mediates recombinant FGF21‐induced improvement of hepatic iron overload in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease HY Kim,FASEB J.,2020
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Stimulates glucose uptake in differentiated adipocytes via the induction of glucose transporter SLC2A1/GLUT1 expression (but not SLC2A4/GLUT4 expression). Activity probably requires the presence of KLB. Regulates systemic glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- FGF21 alleviated atherosclerosis by ameliorating Fas-mediated apoptosis in apoE-/- mice. PMID: 30157856
- results demonstrate that fibroblast growth factor 21 reduces the increased expression of a subset of genes in the liver in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress PMID: 29962431
- Lack of FGF21 enhances the susceptibility to the development of obesity-related cardiomyopathy. PMID: 29519677
- The acute increase in circulating FGF21 following fructose gavage was absent in ChREBP knockout mice. Induction of ChREBP-beta and its glycolytic, fructolytic, and lipogenic gene targets were attenuated in FGF21 knockout mice fed high-fructose diets. PMID: 28123933
- Data, including data from studies using knockout mice, suggest that control of whole-body energy expenditure by Gcgr agonism requires intact Fxr signaling and Fgf21 secretion in liver. (Gcgr = glucagon receptor glucagon; Fxr = farnesoid X receptor; Fgf21 = fibroblast growth factor-21) PMID: 29925501
- FGF-21 has anti-inflammatory effects in Type 2 diabetes mellitus PMID: 29414665
- These data suggest that Fgf21 acts as one of intrathymic cytokines in the neonatal and juvenile thymus, involving thymocyte development in a beta-Klotho-independent manner. PMID: 28336912
- During pregnancy, both systemic and cardiac-produced Fgf21 act on the heart, leading to the normal physiological cardiac changes that are associated with pregnancy. PMID: 28472473
- our results demonstrated that FGF21 promotes cell cycle exit and enhances myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. This study provided new evidence that FGF21 promotes myogenic differentiation, which could be useful for better understanding the roles of FGF21 in myogenesis. PMID: 29109955
- We will clarify the positive and negative signaling mechanisms which control the stress-related expression of FGF21 through the ISR pathway. Moreover, we will examine the role of FGF21 as an interorgan coordinator of survival functions in metabolic and stress disorders. We conclude that FGF21 can be viewed as a cell non-autonomous enhancer of longevity in mammals. PMID: 28844867
- under nutrient-limiting conditions that stimulate ATF4 activity, TRIB3 is implicated in the regulation of metabolic adaptation by restraining the transcription of Fgf21. PMID: 29378327
- alcohol-induced FGF21 expression is a hepatic adaptive response to lipid dysregulation. PMID: 27498701
- the adipose-derived FGF21-CCL11 axis triggers cold-induced beiging and thermogenesis by coupling sympathetic nervous system to activation of type 2 immunity in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. PMID: 28844880
- These results uncover a negative feedback loop in which CREBH regulates nonesterified fatty acid flux from adipose tissue to the liver via FGF21. PMID: 27301791
- Chronic high-sucrose diet does not lead to obesity in mice. Data suggest that high-sucrose diet leads to up-regulation of Fgf21 expression in liver and brown adipose tissue plus high levels of Fgf21 in plasma which eventually lead to increased energy expenditure and, thus, does not cause obesity in this species. PMID: 28886439
- plasma levels of Fgf21 reflect liver fat accumulation and dysregulation of metabolic pathways in the liver. PMID: 27470139
- atheroprotective effect of brown adipose transplantation is BAT-specific and independent of lipid-lowering effect, accompanied by adrenergic receptor-mediated activation of the FGF-21-adiponectin axis. PMID: 29496444
- the suppression of Nrf2 attenuates adipogenesis and decreases FGF21 expression through PPARgamma in 3T3-L1 cells. PMID: 28131830
- these findings elucidate the involvement of abnormal FGF21 expression in early APAP-induced liver impairment. Interestingly, FGF21 may be a promising biomarker of APAP-exposed livers. PMID: 28591702
- Reduced DNA methylation is associated with enhanced induction of hepatic FGF21 expression after PPARalpha activation, which may partly explain the attenuation of diet-induced obesity in adulthood. PMID: 29434210
- These results suggest that FGF21 deficiency slow gastric emptying rate and indirectly influence initial alcohol metabolism in mice exposed to acute alcohol. Our findings provide additional information for understanding the gastrointestinal mechanism of alcoholic liver disease and other alcohol use disorders. PMID: 29448103
- Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) levels positively correlate with the subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) area in insulin-sensitive obese mice. PMID: 29348470
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest that dietary manipulations that induce ketosis also lead to increased HPA axis tone; FGF21 knockout mice exhibit blunted HPA response to ketogenic diet relative to wild-type mice; thus, the hepatokine FGF21 appears to play important role in response to ketogenic diet. (HPA axis = hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis) PMID: 29077838
- These results suggest that berberine-induced activation of AMPK may contribute to hepatic FGF21 expression via NUR77. PMID: 29247651
- our results demonstrate that Sp1 positively regulates the basal transcription of FGF21 in the liver and adipose tissue and contributes to the obesity-induced FGF21 upregulation in mouse adipose tissue and hepatic FGF21 upregulation in hepatocarcinogenesis. PMID: 28466020
- FGF21 deletion aggravates aortic remodeling and cell death probably via exacerbation of aortic inflammation and oxidative stress in type 1 diabetes. PMID: 27391008
- This study demonstrates that FGF21 action is necessary to achieve the full metabolic benefits of exercise during chronic HF feeding. PMID: 27445299
- cholestasis could induce FGF21 expression in FXR dependent manner PMID: 27003131
- FGF21 appears to act in a paracrine manner to increase glucose uptake under low insulin conditions, but it does not contribute to the resistance to diet-induced obesity. PMID: 27184848
- FGF21 has a role in promoting remyelination in the central nervous system PMID: 28825598
- Data suggest that expression of Fgf21 in liver responds acutely to dietary protein intake; low-protein high-carbohydrate diet induces Fgf21 expression; high-protein low-carbohydrate diet reduces Fgf21 expression; Fgf21 expression/secretion in cultured hepatocytes appears to be controlled by glucose but not amino acids. PMID: 27574977
- These findings reveal a previously unappreciated anti-inflammatory role for FGF21 in adipose tissue, but do not support that FGF21 is necessary for exercise-mediated anti-inflammatory effects. PMID: 28765264
- OPA1 mutant mice are resistant to age- and diet-induced weight gain and insulin resistance, by mechanisms that involve activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and secretion of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) from skeletal muscle, resulting in increased metabolic rates and improved whole-body insulin sensitivity. PMID: 28607005
- FGF21 is not critical for bone homeostasis or actions of PPARalpha and PPARgamma. PMID: 27505721
- inhibitor of mTORC1 to control hepatic insulin action and maintain glucose homeostasis PMID: 26926384
- the acute and chronic effects of FGF21 can be dissociated through adipose-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PMID: 28380381
- pancreatic FGF21 is a digestive enzyme secretagogue. PMID: 28089565
- These findings reveal an iNKT cell-FGF21 axis that defines a new immune-mediated pathway that could be targeted for glycemic control and weight regulation. PMID: 27593966
- the metabolic outcomes associated with elevated FGF21 depend on the nutritional context, differing according to whether the animal is in a state of under- or overfeeding. PMID: 27693377
- These findings indicate that FGF21 is crucial for the fenofibrate-mediated improvement of whole body glucose metabolism in obese mice via the amelioration of WAT dysfunctions. PMID: 28404815
- These new findings reveal that the FGF21-betaKlotho-FGFR1 signaling axis plays roles in maintaining phospholipid homeostasis and the dynamic functions of the lipid droplet, whereas protecting against ER stress, and suggest a potential link of phospholipid biosynthesis, lipid droplet dynamics, ER stress, and energy homeostasis in adipose tissue coordinated by this signaling axis. PMID: 27690692
- CYP2A5 protects against the development of alcoholic fatty liver disease, and the PPARalpha-FGF21 axis contributes to the protective effects of CYP2A5 on alcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 28131861
- Heme-Regulated eIF2alpha Kinase Modulates Hepatic FGF21 and Is Activated by PPARbeta/delta Deficiency. Findings suggest that HRI is a potential target for regulating hepatic FGF21 levels. PMID: 27486236
- FGF21 promotes myoblast differentiation and serves as a switch of molecular transformation from anaerobic myofibers to aerobic myofibers via the FGF21-SIRT1-AMPK-PGC1alpha axis. PMID: 27966786
- FGF21-PXR signaling pathway may be involved in decreased hepatic CYP3A4 metabolic activity in Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 27482056
- data show that AHR contributes to hepatic energy homeostasis, partly through the regulation of FGF21 expression and signaling. PMID: 27226639
- this study shows that FGF21 exerts an anti-inflammatory effect mainly via enhancing Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidant capacity and suppressing NF-kappaB signaling pathway PMID: 27276443
- FGF21 corrects multiple metabolic parameters on NAFLD in vitro and in vivo by inducing autophagy. PMID: 27435856
- these data reveal a previously unidentified role for FGF21 on bile acid metabolism and may be relevant to understand the effects of FGF21 analogs in clinical studies. PMID: 28041926
- These results suggest for the first time that FF prevents the development of diabetic nephropathy via up-regulating FGF21 and stimulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3b/Fyn-mediated activation of the Nrf2 pathway. PMID: 26849944
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Heparin-binding growth factors family
-
组织特异性:Most abundantly expressed in the liver, also expressed in the thymus at lower levels. Expressed in skeletal muscle (at protein level). Secreted in plasma (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:56636
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000033099
UniGene: Mm.143736
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)