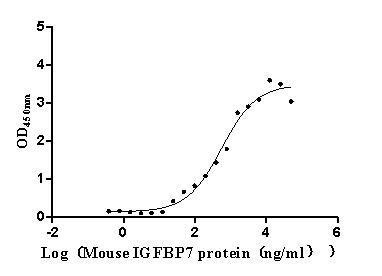
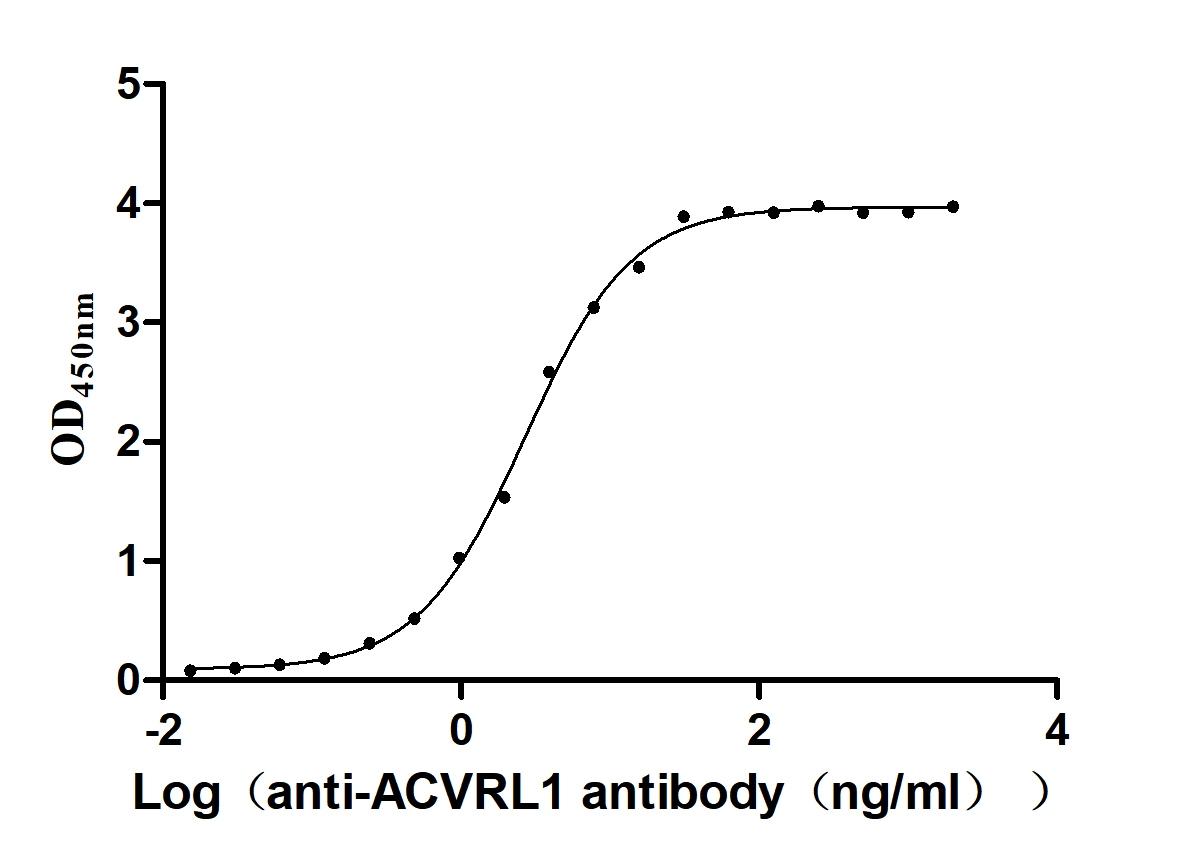
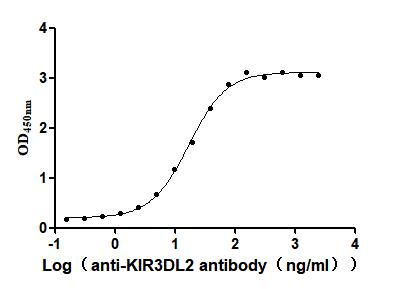
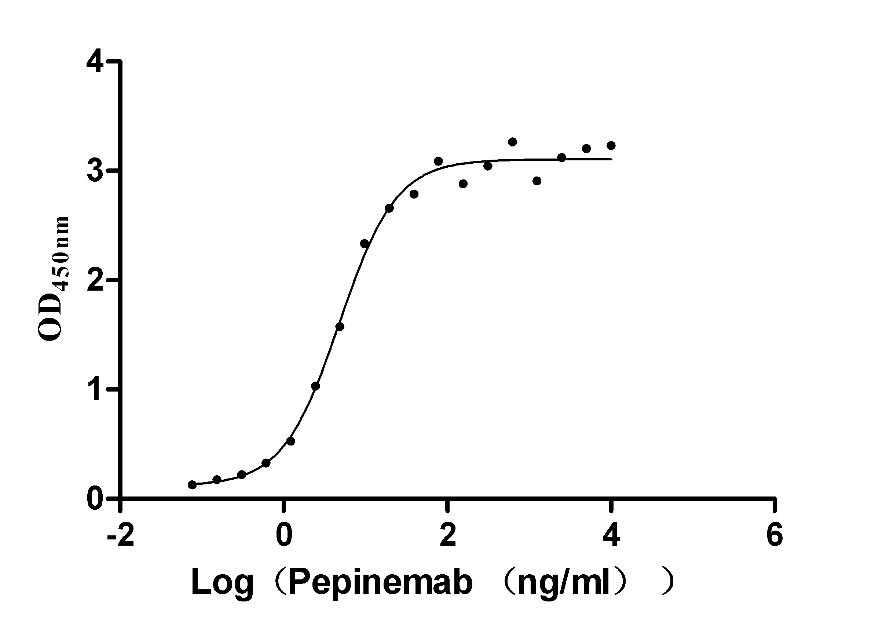
Recombinant Mouse Fibroblast growth factor 10 (Fgf10)
-
货号:CSB-YP008616MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP008616MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP008616MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP008616MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP008616MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Fgf10Fibroblast growth factor 10; FGF-10; Keratinocyte growth factor 2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:37-209
-
氨基酸序列QALG QDMVSQEATN CSSSSSSFSS PSSAGRHVRS YNHLQGDVRW RRLFSFTKYF LTIEKNGKVS GTKNEDCPYS VLEITSVEIG VVAVKAINSN YYLAMNKKGK LYGSKEFNND CKLKERIEEN GYNTYASFNW QHNGRQMYVA LNGKGAPRRG QKTRRKNTSA HFLPMTIQT
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Required for normal branching morphogenesis. May play a role in wound healing.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- It is concluded that during early pseudoglandular stage of lung development Ptch1 patterns Fgf10 and regulates Foxf1 expression in the lung mesenchyme to direct branch formation and this is essential for proper lobe formation and lung function. PMID: 28939119
- small interfering RNA knockdown of FGFR2 suppressed PI3K/Akt pathway activation by FGF10 and abolished its anti-apoptotic and neurite repair effects in vitro. PMID: 28981091
- the response of FGF10(+) progenitors and differentiated Airway smooth muscle cells to growth factor treatment in real time using lineage tracing in the background of an air-liquid interface (ALI) culture system. PMID: 28387977
- Inactivation of ALX4/Alx4 causes lacrimal gland aplasia in both human and mouse. These results reveal a key role of Alx4 in mediating FGF-Shp2-FGF signaling in the neural crest for lacrimal gland development. PMID: 29028795
- show that during homeostasis, basal stem/progenitor cells in cartilaginous airways maintain their stem cell state by downregulating the Hippo pathway (resulting in increased nuclear Yap), which generates a localized Fgf10-expressing stromal niche PMID: 29017029
- that miR-205 in the surface ectoderm functions to ensure robust activation of pathways associated with Fgf10 signaling. PMID: 28511845
- Mesenchymal FGF10 controls the size of the taste bud papillary area, while overall patterning remains unchanged. Results show that FGF signaling negatively affects the extent of canonical Wnt signaling, which is the main activation pathway during fungiform papillae development; however, this effect does not occur at the level of gene transcription. PMID: 28506989
- Sox9 is positively regulated by mesenchymal Fgf10, a process that requires active Erk signaling during salivary gland development PMID: 28506998
- Fgf10 is expressed in the mesenchyme around developing submucosal glands. All nasal glands require FGF10 for branching morphogenesis. FGF10 is required for gland budding and ductal morphogenesis of the Steno's gland and the maxillary sinus glands. PMID: 27590203
- FGFR2c signaling regulates branching morphogenesis through the activation of FGFR2b signaling via increased FGF10 autocrine. These results provide new insight into the mechanisms by which crosstalk between FGFR2b and FGFR2c results in efficient branching morphogenesis. PMID: 27206683
- Decreased Fgf10 mRNA levels lead to congenital lung defects, which are compatible with postnatal survival, but which compromise the ability of the lungs to cope with sub-lethal hyperoxic injury. PMID: 27770432
- Fgf10 enhances the formation of tissue-engineered small intestine. PMID: 23468377
- Lhx9 expression overlapped markedly with FGF10 expression cells in the limb mesenchyme and was associated with proliferative cells of the progress zone. PMID: 26220830
- Hypoplasia of the salivary glands led to a significant reduction in saliva production in Fgf10 heterozygous adult mice PMID: 26321752
- Fgf10 signaling has an essential role in the formation of lipofibroblasts during late lung development PMID: 26511927
- novel allele of Alx4 results in reduced Fgf10 expression and failure of eyelid fusion in mice PMID: 25673119
- regulates regional cardiomyocyte proliferation in the foetal heart through a FOXO3/p27(kip1) pathway PMID: 25344367
- Fgf10 alters epithelial cell differentiation in the small intestinal mucosa. PMID: 25721301
- Fgf10 plays a dual role in cochlear development: to regulate outgrowth of the duct and subsequently as a bidirectional signal that sequentially specifies Reissners membrane and outer sulcus non-sensory domains. PMID: 25624266
- FGF10 has a role in protecting neuron against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury through inducing heme oxygenase-1 PMID: 25446127
- A signaling mechanism based on FGF10 and SHH directs outgrowth of the lung bud via a ligand-receptor-based Turing mechanism and a geometry effect in the embryonic mouse. PMID: 25359721
- Results thus show how Pbx1 controls Fgf10 in the developing lung. PMID: 24591256
- Data identify autocrine activation of FGF signaling as an essential mechanism in promoting Pten-deficient skin tumors. PMID: 24582960
- apical ectodermal ridge-Fibroblast growth factors activate sub-apical ectodermal ridge mesenchymal Fgf10 transcription via the downstream Mek-Erk pathway, Etv1, and Ewsr1 in an AGAAAR cluster-dependent manner. PMID: 25109552
- FGF10 and FGF2 were identified as stromal ligands that control distinct aspects of mammary ductal branching. PMID: 25078648
- FGF10, which was produced from tumor cells, was essential for the proliferation of tumor cell itself and also supports proliferation of endothelial cells. PMID: 24320134
- Fgf10-expressing cells represent a pool of mesenchymal progenitors in the embryonic and postnatal lung. PMID: 24353064
- Fgf-10 and Fgf-18 are expressed specifically within ventral tanycyte subpopulations. PMID: 23804023
- Fgf10 prevents ciliated cell differentiation and promotes basal cell differentiation. PMID: 23924632
- inhibition of FGF-10 by inflammatory signaling involves the NF-kappaB-dependent interactions between RELA, SP3, and the Fgf-10 promoter. PMID: 23558680
- The sclera of myopic eyes had higher FGF10 levels. The risk G allele of SNP rs339501 was associated with extreme myopia in human and caused a higher gene expression in the luciferase assay. PMID: 23599340
- These studies provide direct evidence in support of hypothalamic neurogenesis during late postnatal and adult life, and identify Fgf10(+) tanycytes as a source of parenchymal neurons with putative roles in appetite and energy balance. PMID: 23554498
- the FGF10-FGFR2b signaling pathway is not required for epithelial proliferation and differentiation during adult glandular stomach homeostasis PMID: 23133671
- Gata3 directly activates Fgf10 in the early inner ear, and does so through a single binding site PMID: 23220102
- Fibroblast growth factor 10 gene regulation in the second heart field by Tbx1, Nkx2-5, and Islet1 reveals a genetic switch for down-regulation in the myocardium PMID: 23093675
- show that the Fgf10(iCre) line can be used for conditional gene inactivation in an inducible fashion during early developmental stages PMID: 22719891
- Results demonstrate that organ fate commitment and progenitor cell expansion are coordinately controlled by the activity of a Sox9/Fgf10/Fgfr2b feed-forward loop in the pancreatic niche. PMID: 22874919
- Using tissue specific Fgf9 versus Pitx2 loss of function approaches in the gut epithelium and/or mesenchyme, we determined that FGF9 signals to the mesenchyme via Pitx2 to induce mesenchymal Fgf10 expression, which leads to epithelial cecal bud formation. PMID: 22819677
- GAG controls lacrimal gland induction by restricting the diffusion of Fgf10 PMID: 22745308
- [review] Preadipocyte proliferation and adipogenesis are greatly impaired in Fgf10 knockout mouse embryos. PMID: 21696361
- Functional analysis of Fgf signaling revealed precise reciprocal interactions, which showed that mesenchymal Fgf10 rather than Fgf7 modulates tongue epithelial differentiation via Fgfr2b in a temporal- and spatial-specific manner. PMID: 21720756
- deletion of Fgf10 led to absence of the CVP, identifying FGF10 as the first inductive, mesenchyme-derived factor for taste papillae PMID: 21655085
- Fgf3 and Fgf10 are not required for specification of cardiovascular progenitors, but rather for their normal developmental coordination. PMID: 21664901
- show that Wnt2 signaling is necessary and sufficient for activation of a transcriptional and signaling network critical for smooth muscle specification and differentiation including myocardin/Mrtf-B and the signaling factor Fgf10 PMID: 21704027
- Results identify a myocardial to epicardial fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signal, mediated by FGF10 and FGFR2b, that is essential for movement of cardiac fibroblasts into the compact myocardium. PMID: 21750042
- FGF-10 induced cardiomyocyte differentiation from ES cells and iPS cells, which may have potential for translation into clinical applications PMID: 21203390
- study proposes that Alk5 functions upstream of Fgf10 to regulate transit-amplifying cell proliferation and stem cell maintenance and that this signaling mechanism is crucial for stem cell-mediated tooth regeneration PMID: 21402782
- Fgf10-Fgfr2b signaling and lacrimal gland development are controlled by 2-O- and 6-O-sulfated heparan sulfate PMID: 21357686
- role of two crucial morphogens, fibroblast growth factor 10 and sonic hedgehog, in the formation of periodically alternating cartilaginous and non-cartilaginous domains in the ventral mesenchyme PMID: 21148187
- demonstrate that FGF10-signaling targets include ETS-family transcription factors, which have previously been shown to regulate epithelial maturation and tumor progression PMID: 20883684
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Heparin-binding growth factors family
-
组织特异性:Expressed abundantly in embryos and the lung, and at much lower levels in brain and heart.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14165
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000022246
UniGene: Mm.317323


-AC1.jpg)
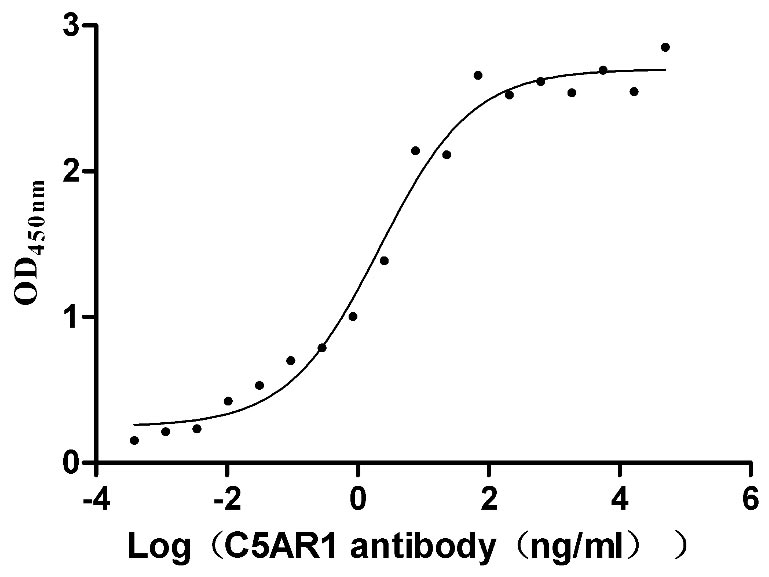
-AC1.jpg)