Recombinant Mouse Dystroglycan (Dag1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP737069MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP737069MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP737069MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP737069MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP737069MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dag1; Dag-1Dystroglycan; Dystrophin-associated glycoprotein 1) [Cleaved into: Alpha-dystroglycan; Alpha-DG); Beta-dystroglycan; Beta-DG)]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:The dystroglycan complex is involved in a number of processes including laminin and basement membrane assembly, sarcolemmal stability, cell survival, peripheral nerve myelination, nodal structure, cell migration, and epithelial polarization.; Extracellular peripheral glycoprotein that acts as a receptor for extracellular matrix proteins containing laminin-G domains, and for certain adenoviruses. Receptor for laminin-2 (LAMA2) and agrin in peripheral nerve Schwann cells. Also acts as a receptor for laminin LAMA5.; Transmembrane protein that plays important roles in connecting the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton. Acts as a cell adhesion receptor in both muscle and non-muscle tissues. Receptor for both DMD and UTRN and, through these interactions, scaffolds axin to the cytoskeleton. Also functions in cell adhesion-mediated signaling and implicated in cell polarity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- alpha-DG hypoglycosylation, together with an increased protein instability, reduces the membrane dynamics of the beta-subunit and its clustering within the actin-rich domains, influencing cell migration and spontaneous cell movement. PMID: 28572004
- Utrn KO mdx mice but not mdx mice show decreased expression of serum N-terminal alpha Dystroglycan compared to normal mice. PMID: 27854211
- Loss of dystroglycan glycosylation is associated with dystroglycanopathies leading to a breakdown of muscle cell membrane integrity and eventual degeneration. PMID: 29320543
- These results reveal a role for DG in maintaining the stability of the sarcomeric cytoskeleton during contraction. PMID: 27625424
- Integrin beta1 and dystroglycan compensate each other to mediate laminin-dependent basement membrane assembly and epiblast polarization. PMID: 27449702
- Cleavage of beta-DG still occurred when both MMP-2 and MMP-9 were knocked out in gamma - sarcoglycan-deficient mice. The study found that up-regulation of MMP-14 is capable of cleaving beta-DG, and it may be involved in the pathogenesis of sarcoglycanopathy. PMID: 28821434
- The extracellular environment plays a critical role in coordinating neuronal migration and neurite outgrowth during neural circuit development. PMID: 28760865
- we provide evidence that a subset of GABAergic interneurons requires dystroglycan for formation and maintenance of axonal terminals on pyramidal cells PMID: 27707967
- These findings reveal a role for dystroglycan in orchestrating both the assembly and function of the subventricular zone neural stem cell niche PMID: 27569418
- Fktn deficient mice express moderate to severe muscular dystrophy; glycosylated alpha-dystroglycan has a unique role in muscle regeneration in these mice PMID: 26751696
- A glucuronic acid beta1,4-xylose disaccharide synthesized by B4GAT1 acts as an acceptor primer that can be elongated by LARGE with the ligand-binding heteropolysaccharide. PMID: 25279699
- This study demonstrated that the Postnatal development of the molecular complex underlying astrocyte polarization. PMID: 24777283
- The X-ray crystal structure of the missense variant T190M of the murine N-terminal domain of alpha-dystroglycan (50-313) has been determined. PMID: 25932631
- 5-amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside treatment increases utrophin A and beta-dystroglycan expression in mdx mouse muscle. PMID: 25324540
- Phosphorylation within the cysteine-rich region of dystrophin enhances its association with beta-dystroglycan and identifies a potential novel therapeutic target for skeletal muscle wasting. PMID: 25082828
- Results suggest that by interfering in the cross-talk between the transmembrane form of the laminin receptor dystroglycan and F-actin, AHNAK1 influences the cytoskeleton organization of Schwann cells PMID: 24796807
- We evaluate the key characteristics of the mdx in comparison with other mouse mutants with inactivations in DAPC components, along with key modifiers of the disease phenotype. PMID: 25270874
- results indicate a novel role for laminin-dystroglycan interactions in the cooperative integration of astrocytes, endothelial cells, and pericytes in regulating the Blood Brain Barrier. PMID: 25392494
- Endogenous glucuronyltransferase activity of LARGE or LARGE2 required for functional modification of alpha-dystroglycan in cells and tissues. PMID: 25138275
- Beta-dystroglycan can respond to ezrin driven cytoskeletal and cell morphology changes,by translocating from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. PMID: 24599031
- Down-regulation of beta-dystroglycan leads to dysfunctions of astrocytic endfeet in the epileptic cerebral cortex. PMID: 25228692
- Alpha dystroglycan is a perlecan receptor that specifically functions in the stellate reticulum of the embryonic stage. PMID: 23722005
- The study provides evidence for at least three separate pools of dystroglycan complexes within myofibers that differ in composition and are differentially affected by loss of dystrophin. PMID: 23951345
- model confirms dystroglycan phosphorylation as an important pathway in the aetiology of Duchenne muscular dystrophy PMID: 22810924
- This study demonistrated that the axonal guidance defects observed in dystroglycan mutant mice. PMID: 23217742
- This study verified that Dag1 mRNA is expressed by RG cells in the embryonic subventricular zone , whereas DG protein is localized to glia end feet in contact with the pial basement membrane. PMID: 23147502
- Our data provides novel evidence that functionally links the teneurin and dystroglycan systems and provides new insight into the molecular mechanisms by which TCAP-1 regulates cytoskeletal dynamics in hippocampal neurons PMID: 22698694
- Cajal band appositions contain a dystroglycan complex that includes periaxin and dystrophin-related protein (Drp)2. PMID: 22764250
- one form of glycosylation can influence another form of glycosylation in alpha-DG and suggest that in the absence of proper O-mannosylation, as is associated with certain forms of muscular dystrophy PMID: 22549772
- Data show that in Dp71-null mice, the levels of beta-dystroglycan (beta-DG) and alpha1-syntrophin (alpha1-Syn) were lower and utrophin expression did not change, and the neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) expression and activity were increased. PMID: 22493004
- alpha-DG prepared from lung- or testis-derived cells lacks the post-phosphoryl moiety and shows little laminin a1 and a2 binding activity. PMID: 22270369
- Differential glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan and proteins other than alpha-dystroglycan by like-glycosyltransferase. PMID: 21930648
- Age-related alterations in beta-dystroglycan are observed in the intrinsic laryngeal muscles of mdx mice. PMID: 22102469
- Cleavage of dystroglycan by matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 is regulated in normal nerves and modulates dystroglycan complex composition and the size of Schwann cell compartments. PMID: 21865464
- Dystroglycan is a functional laminin 211 receptor during axonal sorting and the key substrate relevant to the pathogenesis of glycosyltransferase congenital muscular dystrophies. PMID: 21862561
- DG is necessary for the formation of the glial endfoot architecture. PMID: 21501259
- results indicate that overexpression of LARGE catalyzes the glycosylation of at least one other glycoprotein in addition to alpha-DG, and that this glycosylation(s) promotes laminin binding activity PMID: 21533062
- classical beta1,2-elongation and beta1,6-GlcNAc branching of O-mannose glycan structures are dependent upon the POMGnT1 enzyme and O-mannosylation is not limited solely to alpha-DG in the brain PMID: 21460210
- LARGE has a role in inducing alpha-dystroglycan hyperglycosylation in skeletal and cardiac muscle PMID: 21203384
- required for the growth and function of a mammalian epithelial tissue; controls STAT5-dependent hormone signaling pathways PMID: 20940259
- These results indicate that pikachurin interactions with alpha-dystroglycan and its localization at the photoreceptor ribbon synapse require normal glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan. PMID: 21129441
- Results indicate that appropriate glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan has an important role in the maintenance of podocyte architecture. PMID: 20944549
- Dystroglycan does not contribute significantly to kidney development or function, in health or after injury. PMID: 21209007
- DG function is modulated by glycosylation during T cell development in vivo, and DG is essential for normal development and differentiation of T cells PMID: 20369005
- alpha-dystroglycan is necessary for neuregulin-, agrin-, and laminin-induced Egr3 expression during muscle spindle formation. PMID: 20213761
- Our findings provide genetic evidence that neuronal dystroglycan plays a role in synaptic plasticity and that glial dystroglycan is involved in forebrain development PMID: 20980614
- Post-translational maturation of dystroglycan is necessary for pikachurin binding and ribbon synaptic localization. PMID: 20682766
- cerebral hypoxia promotes first an endothelial response followed by astrocyte activation, proliferation, and reorganization of astrocyte end-feet, which correlates with increased expression of adhesion molecules alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and dystroglycan PMID: 20544851
- severe sepsis leads to a marked reduction in membrane localization of dystrophin and beta-dystroglycan in septic cardiomyocytes PMID: 20142806
- dystroglycan in luminal epithelial cells is not required for the maintenance of basement membranes, cell polarity or prostate regeneration. PMID: 20054819
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Alpha-dystroglycan]: Secreted, extracellular space.; [Beta-dystroglycan]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Cell membrane, sarcolemma. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane. Note=The monomeric form translocates to the nucleus via the action of importins and depends on RAN. Nuclear transport is inhibited by Tyr-892 phosphorylation. In skeletal muscle, this phosphorylated form locates to a vesicular internal membrane compartment. In muscle cells, sarcolemma localization requires the presence of ANK2, while localization to costameres requires the presence of ANK3. Localizes to neuromuscular junctions (NMJs). In adult muscle, NMJ localization depends upon ANK2 presence, but not in newborn animals. In peripheral nerves, localizes to the Schwann cell membrane. Colocalizes with ERM proteins in Schwann-cell microvilli.
-
组织特异性:Detected in brain and kidney (at protein level). Detected in sciatic nerve (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and muscle cells (at protein level). Expressed in a variety of tissues. In brain, expressed in the hippocampal formation, the olfactory bul
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:13138
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000079294
UniGene: Mm.491797
Most popular with customers
-
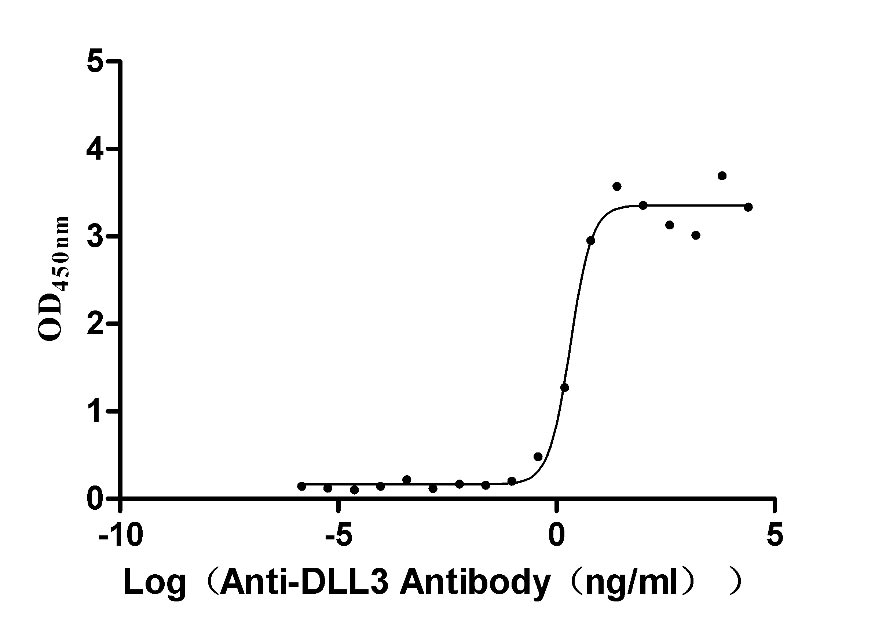
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
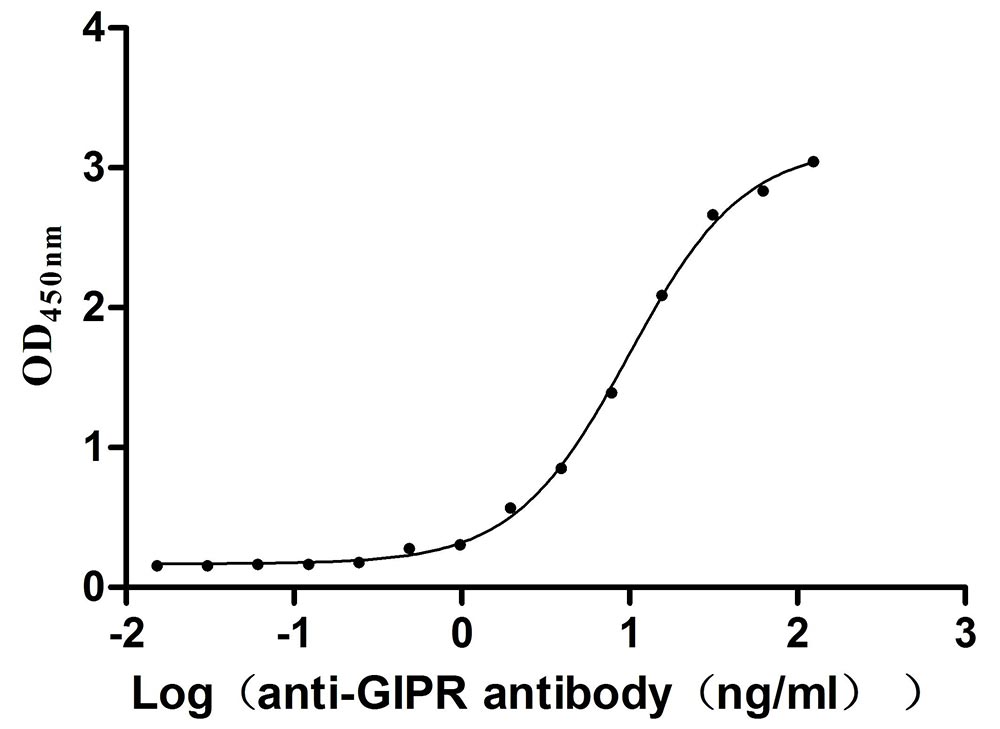
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
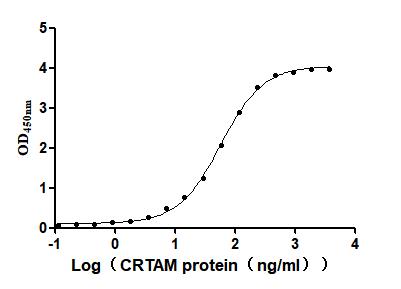
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


-AC1.jpg)