Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein (Ddit4)
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(Ddit4),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP863508MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(Ddit4),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP863508MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(Ddit4),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP863508MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(Ddit4),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP863508MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(Ddit4),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP863508MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Ddit4; Dig2; Redd1; Rtp801DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein; Dexamethasone-induced gene 2 protein; HIF-1 responsive protein RTP801; Protein regulated in development and DNA damage response 1; REDD-1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-229
-
氨基酸序列MPSLWDRFSS SSSSSSSSRT PAADRPPRSA WGSAAREEGL DRCASLESSD CESLDSSNSG FGPEEDSSYL DGVSLPDFEL LSDPEDEHLC ANLMQLLQES LSQARLGSRR PARLLMPSQL VSQVGKELLR LAYSEPCGLR GALLDVCVEQ GKSCHSVAQL ALDPSLVPTF QLTLVLRLDS RLWPKIQGLL SSANSSLVPG YSQSLTLSTG FRVIKKKLYS SEQLLIEEC
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Regulates cell growth, proliferation and survival via inhibition of the activity of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Inhibition of mTORC1 is mediated by a pathway that involves DDIT4/REDD1, AKT1, the TSC1-TSC2 complex and the GTPase RHEB. Plays an important role in responses to cellular energy levels and cellular stress, including responses to hypoxia and DNA damage. Regulates p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis in response to DNA damage via its effect on mTORC1 activity. Its role in the response to hypoxia depends on the cell type; it mediates mTORC1 inhibition in fibroblasts and thymocytes, but not in hepatocytes. Inhibits neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth mediated by NGF via its effect on mTORC1 activity. Required for normal neuron migration during embryonic brain development. Plays a role in neuronal cell death. Required for mTORC1-mediated defense against viral protein synthesis and virus replication.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- RTP801 plays a essential role in the progression of restraint stress induced neurodegenerative disease. PMID: 29130486
- Findings suggest that REDD1 in cacna1c heterozygous mice may influence depression-related behavior via regulation of the FoxO3a pathway. Study identified the prefrontal cortex as a key brain region in which cacna1c mechanisms through previously unidentified, novel molecular pathways contribute to depression-related behavior. PMID: 27922594
- Diabetic wild-type mice exhibited functional deficiencies in visual acuity and contrast sensitivity, whereas diabetic REDD1-deficient mice had no visual dysfunction. The results support a role for REDD1 in diabetes-induced retinal neurodegeneration. PMID: 29074598
- these data show that REDD1 induction regulates the exercise-mediated change in a distinct set of genes within skeletal muscle. PMID: 28899858
- Findings suggest that REDD1 is a key mediator of cartilage homeostasis through regulation of autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis and that REDD1 deficiency exacerbates the severity of injury-induced osteoarthritis. PMID: 28334504
- These data suggest that loss of REDD1 augments the rate of the OV-induced increase in muscle mass by altering multiple protein balance pathways. PMID: 27465734
- The production of superoxide anion in nockout-Rtp801 mouse lung fibroblasts (MLF) was lower than that in Rtp801 Wt cells after cigarette smoke extract treatment, and it was inhibited in Wt MLF by silencing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-4 (Nox4) expression with small interfering Nox4 RNA. PMID: 27556956
- REDD1 is required for normal insulin-stimulated signaling, and a subtle balance exists between MEK1/2, REDD1, and mTOR PMID: 27913296
- study suggests that VDR regulates Ddit4 expression during epidermal homeostasis and the wound healing process, while elevated Ddit4 represents an early growth-arresting stress response within VDR(-/-) follicles. PMID: 27898044
- REDD1 knockout T cells exhibit a defect in proliferation and cell survival, although markers of activation appear normal. These findings demonstrate a previously unappreciated role for REDD1 in T cell function. PMID: 26301899
- Reactive oxygen species regulation through REDD1/TXNIP is physiological rheostat controlling stress-induced autophagy. PMID: 25916556
- LPS induces REDD1 expression by two distinct CREB-mediated mechanisms PMID: 26296313
- Glucocorticoids induce skin atrophy and activate REDD1 expression. PMID: 25504525
- REDD1 expression limits the nutrient-induced stimulation of protein synthesis and activation of mTORC1 signaling during periods of feed deprivation. PMID: 25716553
- REDD1 is necessary for hyperglycemia mediated effects on VEGF expression in the retina of diabetic mice. PMID: 25548280
- These data suggest that epithelial mTORC1 activity plays a protective role against lung injury, and its inhibition by Rtp801 exacerbates alveolar injury caused by endotoxin. PMID: 25016184
- The REDD1 KO mouse muscle displayed blunted mTORC1 signaling responses. PMID: 24876363
- the results demonstrate that REDD1 acts not only as a repressor of mTORC1 but also as a constant modulator of the phosphorylation of Akt in response to growth factors and nutrients. PMID: 25056877
- REDD1 is required for glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of protein synthesis via mTORC1 downregulation PMID: 25315696
- Collectively, these novel data suggest that REDD1 has a more distinct role in whole body and skeletal muscle metabolism and insulin action than previously thought. PMID: 25445588
- Data (including data from knockout mice) suggest REDD1 expression modulates mTORC1 (mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1) signaling in skeletal muscle; downregulation of REDD1 activates mTORC1 (in refeeding and electrically induced contraction). PMID: 25159324
- this study reports a novel pathway that increased REDD1 gene expression in macrophages. PMID: 24374096
- significant increases in Col1a1, serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, Ctnnb1, CSRNP1, Ddit4, Cyp2e1, and Krit1 expressions and great decreases inreceptor D2, Neu1, and Dhcr7 expressions following long-term exposure to TiO2 NPs PMID: 23533084
- P53, and its downstream target Ddit4, are novel components in the transcriptional response to food deprivation in mice. PMID: 24191950
- The results of this study supported a role for DDIT4 as a negative regulator of myelination, as its loss both in vitro and in vivo results in hypermyelination. PMID: 24048858
- Redd1 alone is not required for testis development or fertility in mice. PMID: 22797524
- the induction of REDD1 gene expression was shown to require the protein kinase PERK and enhanced phosphorylation of its substrate, the alpha-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. PMID: 23000413
- ceramide and RTP801 participate in alveolar cell apoptosis through a process of mutual up-regulation, which may result in self-amplification loops, leading to alveolar damage PMID: 23024063
- REDD1 is a new host defense factor, and chemical activation of REDD1 expression represents a potent antiviral intervention strategy PMID: 21909097
- REDD1-mediated suppression of mTORC1 activity exerts feedback control on p53, thereby limiting the apoptotic response and contributing to cellular survival following DNA damage. PMID: 21896779
- elevation of Dig2/RTP801/REDD1 contributes to the induction of autophagy. PMID: 21733849
- Redd1 induction by hypoxia is tissue dependent and hypoxia signals are relayed to Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 through different pathways in a tissue-specific manner. PMID: 21383064
- Data show that loss of REDD1 induces HIF-1 stabilization and tumorigenesis through a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. PMID: 20176937
- sertraline exerts antiproliferative activity by targeting the mTOR signaling pathway in a REDD1-dependent manner PMID: 20354178
- Insulin induces REDD1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation in adipocytes. PMID: 19996311
- REDD1 encodes a shared transcriptional target that implicates ROS in the p53-dependent DNA damage response and in p63-mediated regulation of epithelial differentiation [REDD1] PMID: 12453409
- dig2 appears to have a pro-survival function, as overexpression of dig2 reduces the sensitivity of WEHI7.2 cells to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. PMID: 12736248
- REDD1 overexpression is sufficient to down-regulate S6 kinase phosphorylation in a TSC1/TSC2-dependent manner PMID: 15545625
- RTP801 expression is induced by MPTP in the mouse model of Parkinson disease. PMID: 17005863
- analysis of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) repressor REDD1 and activation of mTORC1 signaling following inhibition of protein synthesis PMID: 18070882
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm, cytosol.
-
蛋白家族:DDIT4 family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitously expressed.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:74747
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000020308
UniGene: Mm.21697
Most popular with customers
-
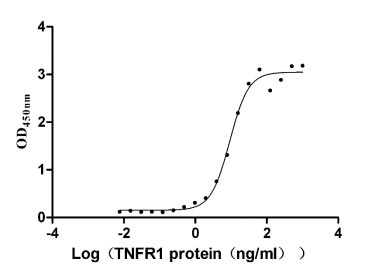
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
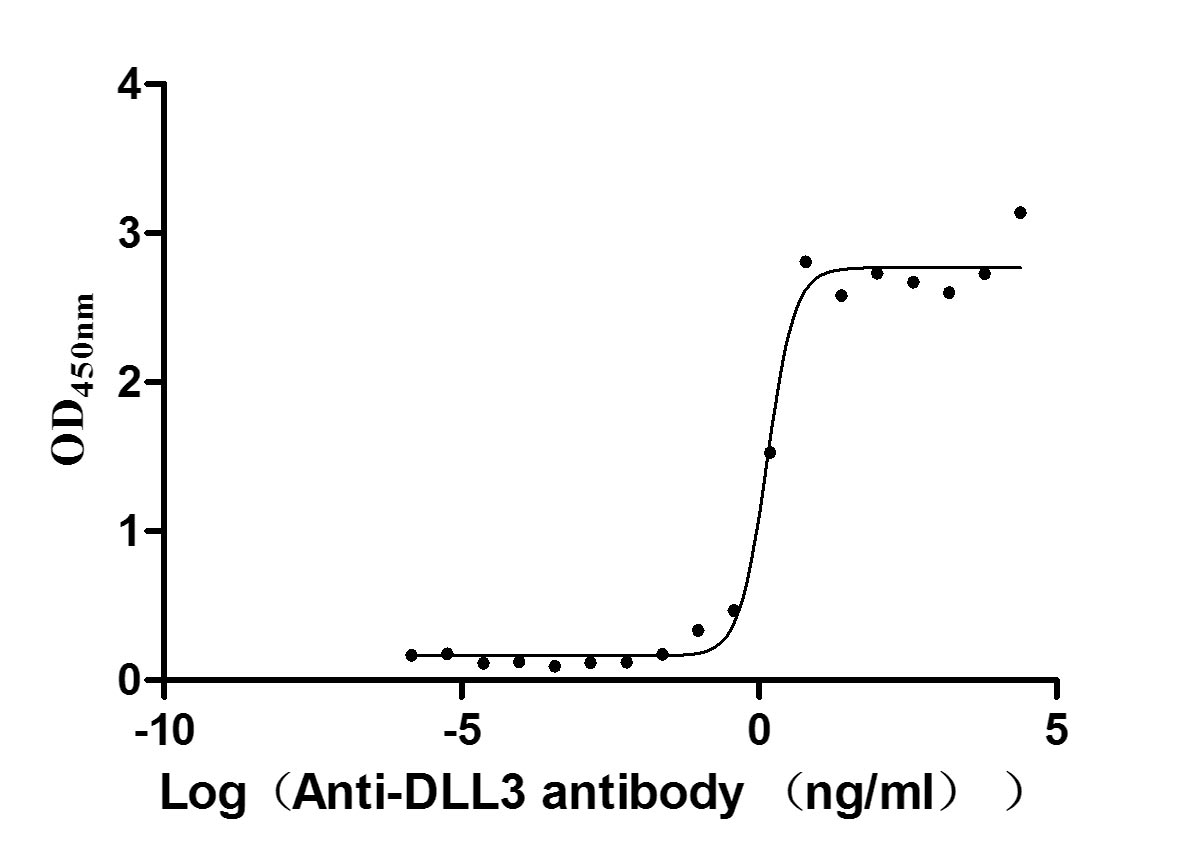
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
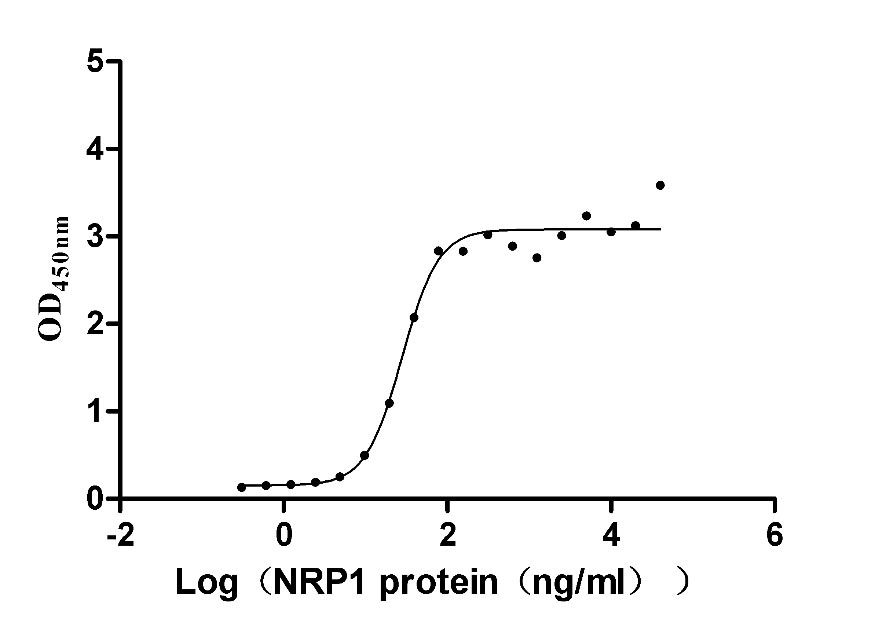
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human T-cell surface protein tactile (CD96), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
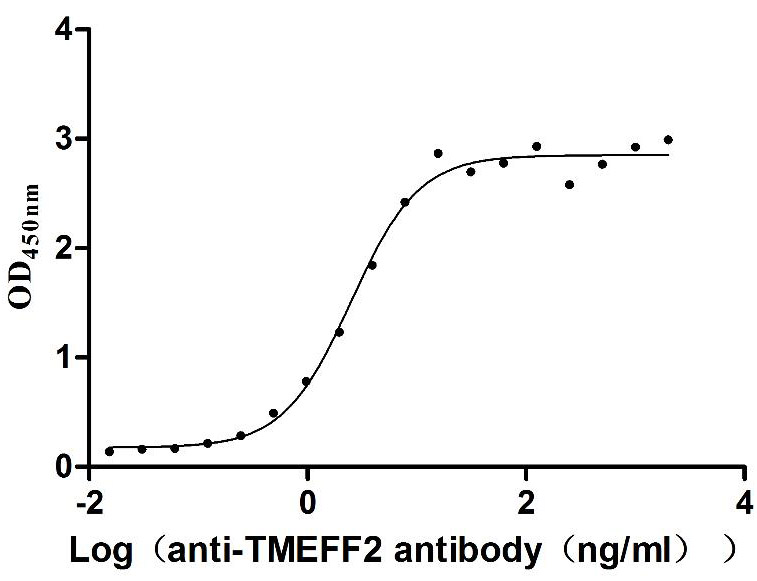
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)