Recombinant Mouse Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1)
-
货号:CSB-YP319999MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP319999MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP319999MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP319999MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP319999MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cdk1; Cdc2; Cdc2a; Cdkn1Cyclin-dependent kinase 1; CDK1; EC 2.7.11.22; EC 2.7.11.23; Cell division control protein 2 homolog; Cell division protein kinase 1; p34 protein kinase
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-297
-
氨基酸序列MEDYIKIEKI GEGTYGVVYK GRHRVTGQIV AMKKIRLESE EEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELRH PNIVSLQDVL MQDSRLYLIF EFLSMDLKKY LDSIPPGQFM DSSLVKSYLH QILQGIVFCH SRRVLHRDLK PQNLLIDDKG TIKLADFGLA RAFGIPIRVY THEVVTLWYR SPEVLLGSAR YSTPVDIWSI GTIFAELATK KPLFHGDSEI DQLFRIFRAL GTPNNEVWPE VESLQDYKNT FPKWKPGSLA SHVKNLDENG LDLLSKMLVY DPAKRISGKM ALKHPYFDDL DNQIKKM
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays a key role in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle by modulating the centrosome cycle as well as mitotic onset; promotes G2-M transition, and regulates G1 progress and G1-S transition via association with multiple interphase cyclins. Required in higher cells for entry into S-phase and mitosis. Phosphorylates PARVA/actopaxin, APC, AMPH, APC, BARD1, Bcl-xL/BCL2L1, BRCA2, CALD1, CASP8, CDC7, CDC20, CDC25A, CDC25C, CC2D1A, CENPA, CSNK2 proteins/CKII, FZR1/CDH1, CDK7, CEBPB, CHAMP1, DMD/dystrophin, EEF1 proteins/EF-1, EZH2, KIF11/EG5, EGFR, FANCG, FOS, GFAP, GOLGA2/GM130, GRASP1, UBE2A/hHR6A, HIST1H1 proteins/histone H1, HMGA1, HIVEP3/KRC, LMNA, LMNB, LMNC, LBR, LATS1, MAP1B, MAP4, MARCKS, MCM2, MCM4, MKLP1, MYB, NEFH, NFIC, NPC/nuclear pore complex, PITPNM1/NIR2, NPM1, NCL, NUCKS1, NPM1/numatrin, ORC1, PRKAR2A, EEF1E1/p18, EIF3F/p47, p53/TP53, NONO/p54NRB, PAPOLA, PLEC/plectin, RB1, TPPP, UL40/R2, RAB4A, RAP1GAP, RCC1, RPS6KB1/S6K1, KHDRBS1/SAM68, ESPL1, SKI, BIRC5/survivin, STIP1, TEX14, beta-tubulins, MAPT/TAU, NEDD1, VIM/vimentin, TK1, FOXO1, RUNX1/AML1, SAMHD1, SIRT2 and RUNX2. CDK1/CDC2-cyclin-B controls pronuclear union in interphase fertilized eggs. Essential for early stages of embryonic development. During G2 and early mitosis, CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation activates CDK1/cyclin complexes which phosphorylate several substrates that trigger at least centrosome separation, Golgi dynamics, nuclear envelope breakdown and chromosome condensation. Once chromosomes are condensed and aligned at the metaphase plate, CDK1 activity is switched off by WEE1- and PKMYT1-mediated phosphorylation to allow sister chromatid separation, chromosome decondensation, reformation of the nuclear envelope and cytokinesis. Inactivated by PKR/EIF2AK2- and WEE1-mediated phosphorylation upon DNA damage to stop cell cycle and genome replication at the G2 checkpoint thus facilitating DNA repair. Reactivated after successful DNA repair through WIP1-dependent signaling leading to CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation and restoring cell cycle progression. In proliferating cells, CDK1-mediated FOXO1 phosphorylation at the G2-M phase represses FOXO1 interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and thereby promotes FOXO1 nuclear accumulation and transcription factor activity, leading to cell death of postmitotic neurons. The phosphorylation of beta-tubulins regulates microtubule dynamics during mitosis. NEDD1 phosphorylation promotes PLK1-mediated NEDD1 phosphorylation and subsequent targeting of the gamma-tubulin ring complex (gTuRC) to the centrosome, an important step for spindle formation. In addition, CC2D1A phosphorylation regulates CC2D1A spindle pole localization and association with SCC1/RAD21 and centriole cohesion during mitosis. The phosphorylation of Bcl-xL/BCL2L1 after prolongated G2 arrest upon DNA damage triggers apoptosis. In contrast, CASP8 phosphorylation during mitosis prevents its activation by proteolysis and subsequent apoptosis. This phosphorylation occurs in cancer cell lines, as well as in primary breast tissues and lymphocytes. EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing. CALD1 phosphorylation promotes Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration. CDK1-cyclin-B complex phosphorylates NCKAP5L and mediates its dissociation from centrosomes during mitosis. Regulates the amplitude of the cyclic expression of the core clock gene ARNTL/BMAL1 by phosphorylating its transcriptional repressor NR1D1, and this phosphorylation is necessary for SCF(FBXW7)-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NR1D1. Phosphorylates EML3 at 'Thr-881' which is essential for its interaction with HAUS augmin-like complex and TUBG1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results provide evidence that cdc2/cyclin B1 kinase activation was synchronous with the initial appearance of cytoskeletal lesions in mouse with Niemann-Pick disease type C. PMID: 29058287
- CDK1, Aurora-B, and Rho-kinase phosphorylate keratin 5/14. PMID: 29518391
- the ability of oocytes to mature, as well as oocyte CDK1 levels, were dependent on follicle size, but CDK1 expression in oocytes from preantral follicles was not acutely altered by the activity of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). PMID: 29274320
- our results show that the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 promotes translation at the onset of meiosis to support the spindle assembly and suggest an important role of CDK1 and mTOR kinases in this process PMID: 28272965
- Study shows that Cdk1 phosphorylates Ska3 to promote its direct binding to the Ndc80 complex (Ndc80C), a core outer kinetochore component, also show that this phosphorylation occurs specifically during mitosis and is required for the kinetochore localization of the Ska complex. PMID: 28479321
- loss of LAR activity resulted in reduced activity of CDK1. PMID: 27352860
- CDK1 is a positive regulator of the IFN signaling pathway. The overexpression of CDK1 might contribute to the abnormally amplified type I IFN signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus. PMID: 26663909
- Cdk1-induced desmin phosphorylation is required for efficient separation of desmin-IFs and generally detected in muscular mitotic cells in vivo. PMID: 27565725
- using in vitro dephosphorylation assays, we demonstrate that Mastl promotes persistent MPS1 phosphorylation by inhibiting PP2A/B55-mediated MPS1 dephosphorylation rather than affecting Cdk1 kinase activity. Our findings establish a key regulatory function of the Greatwall kinase/Mastl - PP2A/B55 pathway in preventing premature SAC silencing PMID: 27631493
- CDK1 is required upstream of a checkpoint-associated cell death as well as meiotic metaphase progression in mouse spermatocytes. PMID: 26490841
- CDK1 is a synthetic lethal target for KRAS mutant tumors. PMID: 26881434
- Our data demonstrate that ES cells are uniquely sensitive to CDK1 inhibition via a p53/NOXA/MCL1 pathway. PMID: 25733019
- Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of GATA 2 is promoted by Fbw7, is cyclin B-CDK1-mediated Thr176 phosphorylation-dependent, and influences hematopoietic cell differentiation. PMID: 25670854
- HDAC3 controls G2/M phase progression mainly through posttranslational stabilization of the G2/M cyclin-dependent kinase 1. PMID: 25161285
- Our findings reveal the following novel molecular mechanisms controlling mitochondrial fission during A/R injury of cardiomyocytes resulted from both increased activation Drp1 through Cdk1, PKCdelta, and calcineurin-mediated pathways, respectively PMID: 25445585
- CDK1 activation proceeds with concomitant inhibition by CDC6, which tunes the timing of the M-phase entry during the embryonic cell cycle PMID: 25264619
- FlnB loss reduced Cdk1 phosphorylation (an inhibitor of G2/M phase progression) and Cdk1 inhibition in chondrocytes mimicked the null FlnB, premature differentiation phenotype, through a beta1-integrin receptor- Pi3k/Akt mediated pathway. PMID: 24551245
- CDK1-dependent phosphorylations required for the initiation of nuclear membrane disassembly during mitosis are adapted for removal of nuclei during fiber cell differentiation. PMID: 25139855
- necessary for maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) PMID: 24583015
- Loss of 4.1/NuMA interaction results in spindle orientation defects and inhibition of Cdk1 causes increase in cortical NuMA localization PMID: 24109598
- Cyclin B1/Cdk1-mediated phosphorylation of mitochondrial substrates allows cells to sense and respond to increased energy demand for G2/M transition and, subsequently, to upregulate mitochondrial respiration for successful cell-cycle progression. PMID: 24746669
- these results raise an exciting possibility that targeting CDK1 or NF-Y in the diseased heart may inhibit fibrosis and subsequently confer cardioprotection. PMID: 24477232
- Meiotic CDK1 activity controls the timing of stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. PMID: 23857768
- UCH-L1 physically interacts with CDK1, CDK4, and CDK5, enhancing their kinase activity. PMID: 23543736
- These results identified the mechanisms by which CDK1 inactivation affects the first meiotic division in oocytes, manifested by extrusion of the first polar body. PMID: 22859367
- Data found that Cdk1 enhances the binding of Oct4 on the trophectoderm marker Cdx2 and promotes Cdx2 repression. PMID: 23108051
- Cdk1 is the sole Cdk that is essential and sufficient to drive resumption of meiosis in mouse oocytes PMID: 22367880
- a novel function for CDK1-mediated Ezh2 phosphorylation and provide a mechanism by which Ezh2 protein levels can be regulated in cells. PMID: 21659531
- Unlike other Cdks, loss of Cdk1 in the liver confers complete resistance against tumorigenesis induced by activated Ras and silencing of p53 PMID: 22355113
- c-erbB(2) and c-myb may induce oocyte maturation through mediating a pathway involving the activation of MPF. PMID: 21793718
- CDK1-mediated phosphorylation of Abi1 attenuates Bcr-Abl-induced F-actin assembly and tyrosine phosphorylation of WAVE complex during mitosis PMID: 21900237
- Cdk1 is required for the self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells PMID: 21328468
- cdk1 phosphorylates p62 in vitro and in vivo at T269 and S272, which is necessary for the maintenance of appropriate cyclin B1 levels and the levels of cdk1 activity necessary to allow cells to properly enter and exit mitosis. PMID: 20974803
- The mechanisms by which estrogens influence the cell cycle machinery in IRS-1 knockout mice, including the role of cdk1 and IGF1, are reported. PMID: 20798132
- the hyperphosphorylation of CUX1 by cyclin B/CDK1 inhibits its DNA binding activity in mitosis and interferes with its nuclear localization following cell division and formation of the nuclear membrane PMID: 20729212
- Cdk1 activity is required for mitotic activation of aurora A during G2/M transition PMID: 20444701
- findings show that in the regenerating liver the circadian clock controls the expression of cell cycle-related genes that in turn modulate the expression of active Cyclin B1-Cdc2 kinase, a key regulator of mitosis PMID: 12934012
- PKA regulates cell cycle progression of fertilized eggs by modulating the activity of Cdc2. PMID: 15580572
- cyclin B1, phosphorylated cyclin B1 and p34cdc2 have similar distributions at some stages but different localizations at other stages during oocyte meiotic maturation and fertilization PMID: 15984162
- Cdc2 may compensate the loss of Cdk2 function in p27/cdk2 double knock-out mice. PMID: 16007079
- CDP/Cux p110 is differentially regulated by cyclin A/Cdk2 and cyclin A/Cdk1 PMID: 16081423
- Chk1 deficiency resulted in a premature onset of mitosis because of abnormal activation of cyclin B-Cdc2 and led to the activation of caspases 3 and 9 triggered by cytoplasmic release of cytochrome c. PMID: 16159883
- Cdk1 regulated mitotic vimentin phosphorylation via not only a direct enzyme reaction but also Plk1 recruitment to vimentin. PMID: 16260496
- These results suggest that endogenous necdin attenuates neuronal apoptosis by suppressing the E2F1-Cdc2 system. PMID: 17108174
- DEDD acts as a novel inhibitor of the mitotic Cdk1/cyclin B1 complex and is an impeder of cell mitosis, and its absence critically influences cell and body size via modulation of rRNA synthesis PMID: 17283331
- results indicate that Cdk1 is the only essential cell cycle Cdk; in the absence of interphase Cdks, Cdk1 can execute all the events that are required to drive cell division PMID: 17700700
- cell-cycle effects in early embryos under normal conditions and after irradiation are strictly paralleled by changes in the activity of the central cell-cycle driving enzyme complex PMID: 17708348
- G1/S DNA damage checkpoint is intact in the absence of Cdk2, but Cdk2 is important for proper repair of the damaged DNA. PMID: 17942597
- findings define a conserved signaling link between Cdk1 and FOXO1 that may have a key role in diverse biological processes, including the degeneration of postmitotic neurons PMID: 18356527
- lack of Cdc2 might induce spermatocyte apoptosis after transient heat stress PMID: 18374969
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:12534
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000020099
UniGene: Mm.281367
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
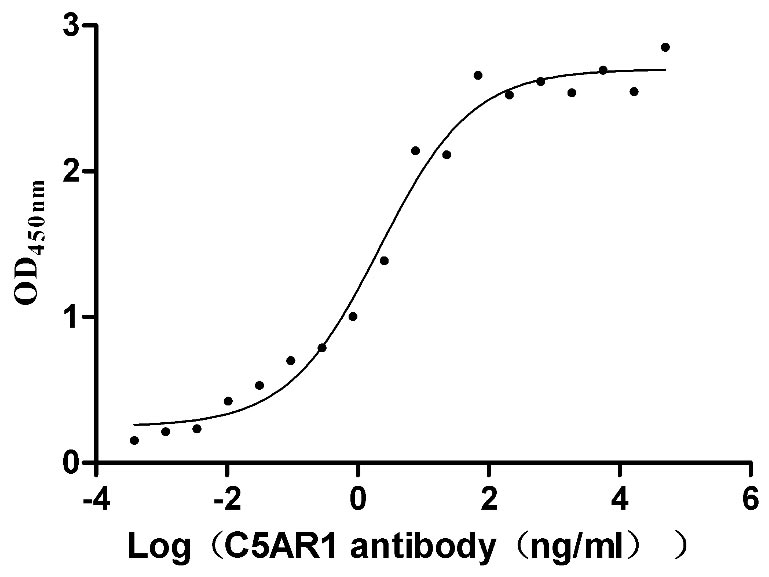
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
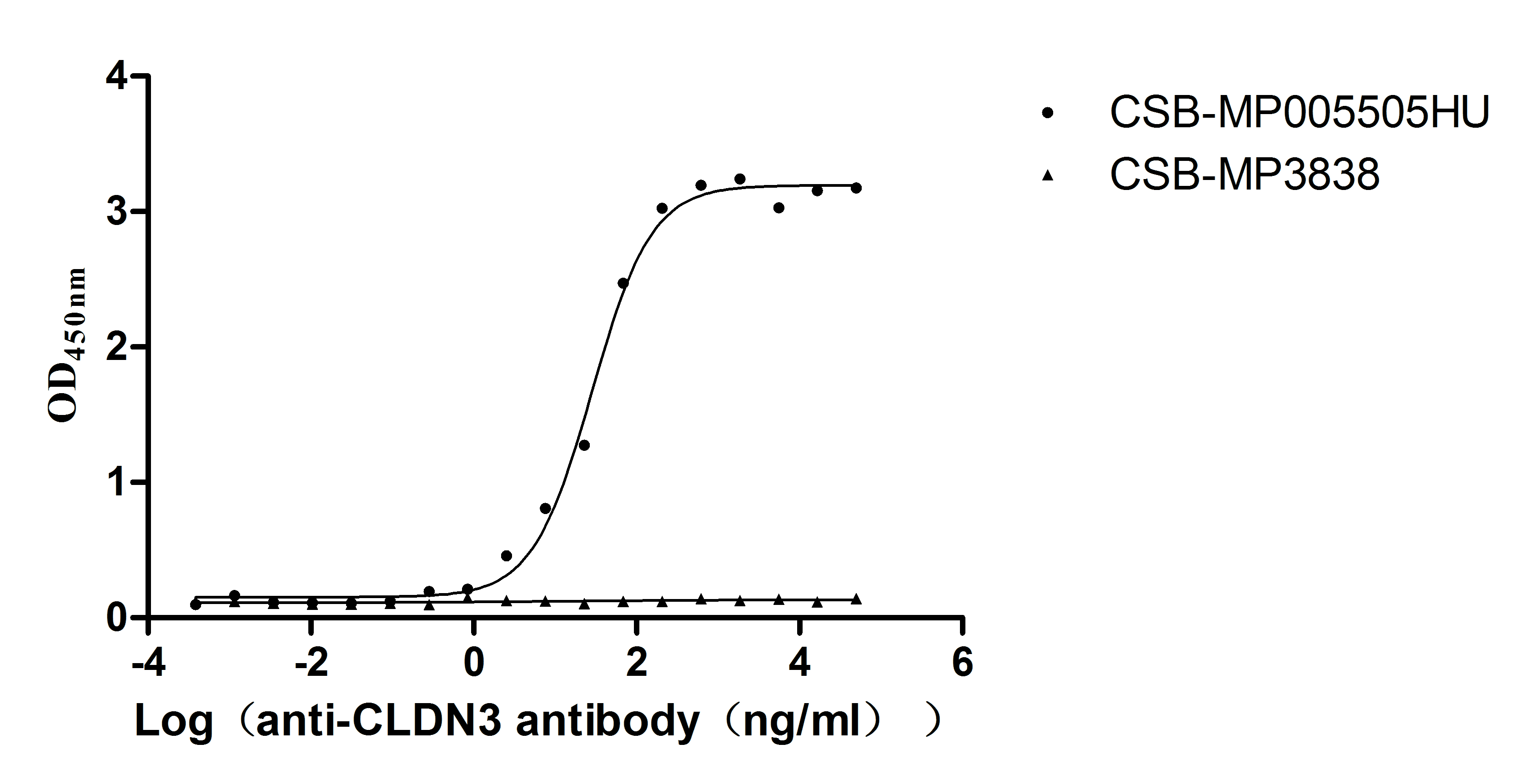
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
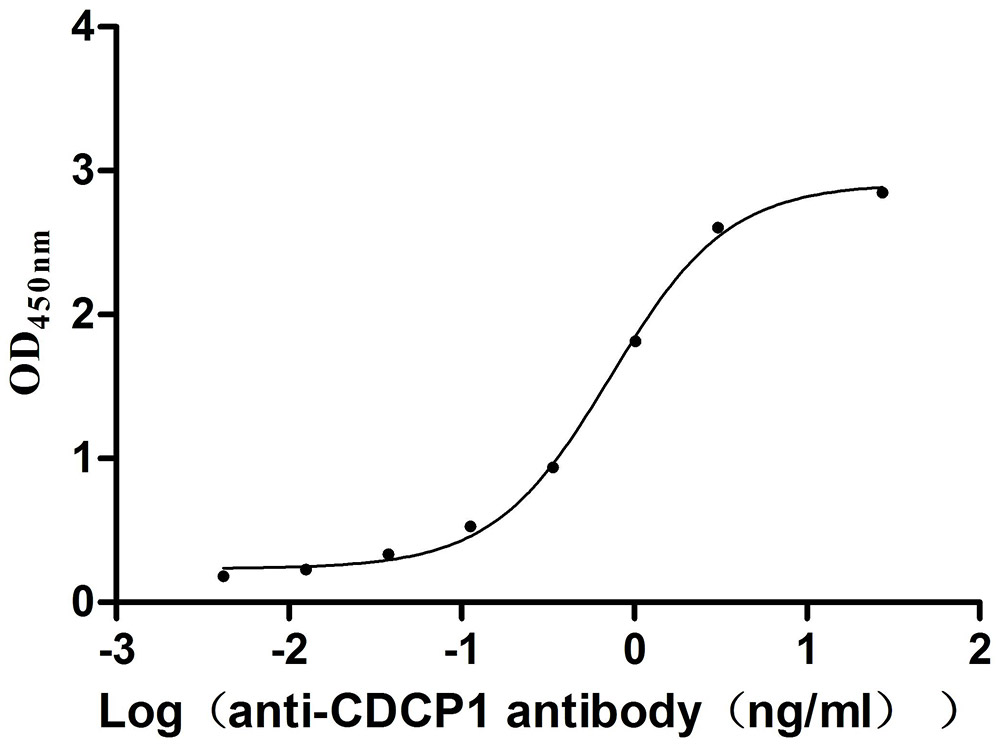
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
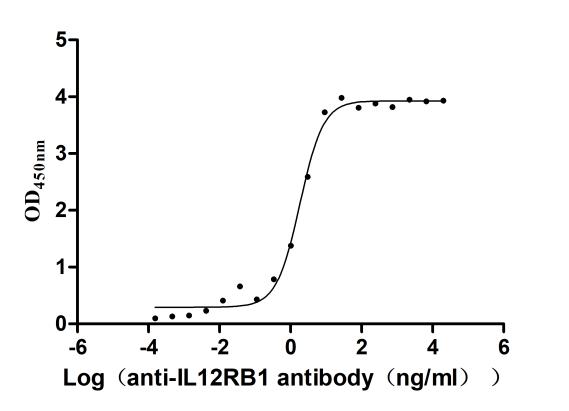
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)