Recombinant Human Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 1 (VIPR1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP025859HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP025859HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP025859HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP025859HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP025859HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:VIPR1; Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 1; VIP-R-1; Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type II receptor; PACAP type II receptor; PACAP-R-2; PACAP-R2; VPAC1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:This is a receptor for VIP. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase. The affinity is VIP = PACAP-27 > PACAP-38.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- In vitro-polarized macrophages by GM-CSF (GM-MO), with a proinflammatory profile, expressed higher levels of VIP receptors, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors 1 and 2 (VPAC1 and VPAC2, respectively), than macrophages polarized by M-CSF (M-MO) with anti-inflammatory activities. RA synovial macrophages, according to their GM-CSF-like polarization state, expressed both VPAC1 and VPAC2. PMID: 27381006
- VPAC1 rs9677 CC genotype could be correlated with a reduced response to statin therapy and seems to be involved in diabetes cardiomyopathy in female patients with type 2 diabetes. PMID: 26712708
- The results reveal that more severe inflammation, based on high levels of IL-6, is associated with lower expression of VPAC1 and, conversely, with increased expression of VPAC2. PMID: 26881970
- variations at the 3'UTR of the VPAC-1 gene act synergistically to affect the expression of the luciferase as well as of the GFP reporter genes expressed in HEK293T cells. PMID: 25390694
- These data suggest that VPAC1 overexpression is associated with poorer differentiation of colon cancer, which is likely caused by subsequent EGFR activation in cancer cells. PMID: 24671823
- VPAC1 receptor has a role in endotoxemia in peripheral blood mononuclear cells PMID: 23651810
- The overexpression of VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors and COX-2 in cancer tissue gives them a potential role as targets for diagnosis of prostate cancer. PMID: 22763881
- hree residues play an important role in VPAC1 interaction with the first histidine residue of VIP. These data demonstrate that VIP and PG97-269 bind to distinct domains of VPAC1 PMID: 22291440
- The genetic association reported here indicates that VIP/VPAC1 signaling can be a relevant pathway in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in females PMID: 22166542
- silencing of VPAC1 receptor inhibits vasoactive intestinal peptide effects on both EGF receptor and HER2 transactivation and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human breast cancer cells PMID: 21896307
- mRNA expression of the VPAC1 receptor was detected in 51% of the tumor specimens, while the incidence of mRNA expression for VPAC2 was 46%. PMID: 21769421
- increased expression in patients with allergic rhinitis PMID: 21711977
- The VIPR1 polymorphism, previously linked to gastrointestinal dysmotility disorders, does not represent a common risk factor for gallstones in the general or in an elderly population. PMID: 20922191
- Moreover, we report the markedly nuclear localization of VPAC(1) receptors in estrogen-dependent (T47D) and independent (MDA-MB-468) human breast cancer cell lines PMID: 20691743
- role of in MicroRNA 525-5p down-modulating VPAC1 expressio PMID: 20706588
- Results indicate that VPAC1, but not VPAC2 or PAC1, up-regulation in macrophages is a common mechanism in response to acute and chronic pro-inflammatory stimuli. PMID: 20026142
- We describe significant upregulation of the SPP1 gene, downregulation of VIPR1, and losses of the VIPR1 gene. PMID: 20014941
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) is a novel gene target of the hemolymphopoietic transcription factor Ikaros. PMID: 11812772
- VPAC1 is a cellular neuroendocrine receptor expressed on T cells that actively facilitates productive HIV-1 infection. PMID: 11834941
- Thus, the highly diverged chemical properties of the hydrophobic "YL" motif and charged "DR(Y)" motif could be a crucial difference between the Secretin Receptor Family and the Rhodopsin Family with respect to receptor activation and G-protein coupling. PMID: 11859928
- VPAC1 receptor mRNA is expressed in the trigeminal, otic and superior cervical ganglia (prejunctional) and cerebral arteries (postjunctional). PMID: 11930171
- a small sequence in the third intracellular loop of the VPAC(1) receptor is responsible for the efficient agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium concentration increase PMID: 11981043
- Genetic complexity of HVR1 quasispecies of hepatitis C virus in patients with cirrhosis. PMID: 12094871
- a selective filter; Identification of a critical domain for restricting secretin binding PMID: 12133828
- the role of charged residues in the intracellular loop 3 and the proximal C-terminal tail of hVPAC1 receptor for agonist-induced adenylyl cyclase activation PMID: 12690118
- cloning and sequencing of 5' flanking region; VPAC1 may play a functional role in development of both cerebellum and adrenal medulla PMID: 14599709
- Data suggest that vasoactive intestinal peptide directly stimulates cortisol secretion from H295 cells via activation of the VPAC1 receptor subtype. PMID: 15171718
- the hVPAC1 receptor binds to vasoactive intestinal peptide at its N-terminal ectodomain PMID: 15247290
- Interaction of different G proteins with the recombinant VPAC1 receptor involves different receptor sub-domains. PMID: 15451021
- the VPAC1 receptor carboxyl terminus has a role in agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, internalization, and recycling PMID: 15932876
- Farnesoid X receptor agonists may increase gallbladder fluid secretion through transcriptional activation of VPAC1. PMID: 16037943
- analysis of the two-step activation mechanism of VPAC receptor and of class II G protein-coupled receptors PMID: 16520374
- Thr429 phosphorylation has a role in activation of human VPAC1 PMID: 16554109
- 125I-[Bpa28-vasoactive intestinal peptide] was covalently bonded to the 121-133 fragment within the N-terminal ectodomain of the receptor PMID: 16888162
- Photoaffinity experiments clearly indicated that the 6-28 part of VIP physically interacts with the N-terminal ectodomain of VPAC1 receptor PMID: 16888167
- MCF-7 cells have VPAC1 receptors that bound the VIP chemotherapeutic conjugate PMID: 16888206
- observations provide additional evidence for a role of proapoptotic caspase adaptor protein and PAC1 R in the events determining the outcome of prostate cancer PMID: 16888207
- identification and characterization of novel five-transmembrane(5TM) isoforms of VPAC1 PMID: 16934434
- expression of VIP receptor-1 (VPAC1) and VPAC2 in CD4+ T cells changed reciprocally in the context of the activation state PMID: 17077178
- The differential expression of VIPR1 in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease mucosa suggests that the VIP system plays different roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. PMID: 17611633
- Both intra- and extracellular Ca2+ play a role in controlling pro-inflammatory functions stimulated by PACAP which acts through a VPAC-1, FPRL1/Galphai/PI3K/ERK pathway and a VPAC-1/Galphas/PKA/p38 pathway to fully activate monocytes PMID: 17651798
- analysis of VIP 16gamma-glutamyl diamino derivative positive charges on hVPAC1 and hVPAC2 receptor function PMID: 17883247
- VPAC1 signaling tempers normal megakaryopoiesis, and inhibition of this pathway stimulates megakaryocyte differentiation. PMID: 18000164
- Proinflammatory effect of VIP is mediated via the specific G protein-coupled receptor VIP/pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating protein (VPAC1) receptor as well as via FPRL1. PMID: 18174366
- deficient expression of VPAC1 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1) in immune cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis was associated with the predominant proinflammatory Th1 mileu; reduced VPAC1 expression in RA is associated with genetic polymorphism PMID: 18383379
- Results indicate that the N-terminal part of VIP physically interacts with the N-ted in the continuity of 6-28 VIP sequence; and the N-terminal part of VIP and its antagonist (PG97-269) have different sites of interaction with the VPAC1 receptor N-ted. PMID: 18597186
- HLA-B (*)2705 and a functional polymorphism in VIPR1 gene, might be due to a founder effect or might be the result of a selective pressure. Consequent downregulation of this receptor in presence of a 'danger' signal might influence susceptibility to AS. PMID: 18668120
- Patients with idiopathic achalasia show a significant difference in allele, genotype and phenotype of VIPR1 distribution of snps PMID: 19309439
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 2 family
-
组织特异性:In lung, HT-29 colonic epithelial cells, Raji B-lymphoblasts. Lesser extent in brain, heart, kidney, liver and placenta. Not expressed in CD4+ or CD8+ T-cells. Expressed in the T-cell lines HARRIS, HuT 78, Jurkat and SUP-T1, but not in the T-cell lines Pe
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 12694
OMIM: 192321
KEGG: hsa:7433
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000327246
UniGene: Hs.348500
Most popular with customers
-
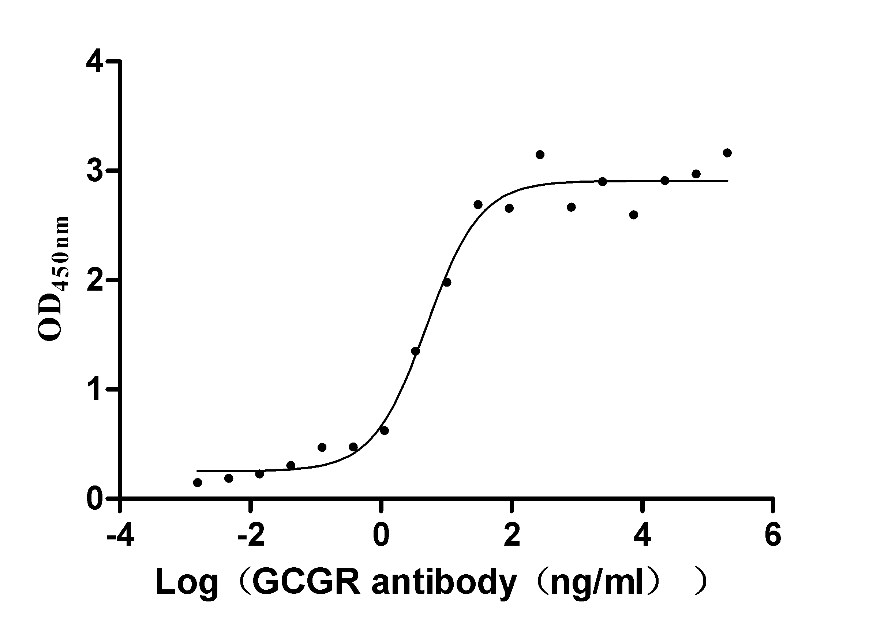
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
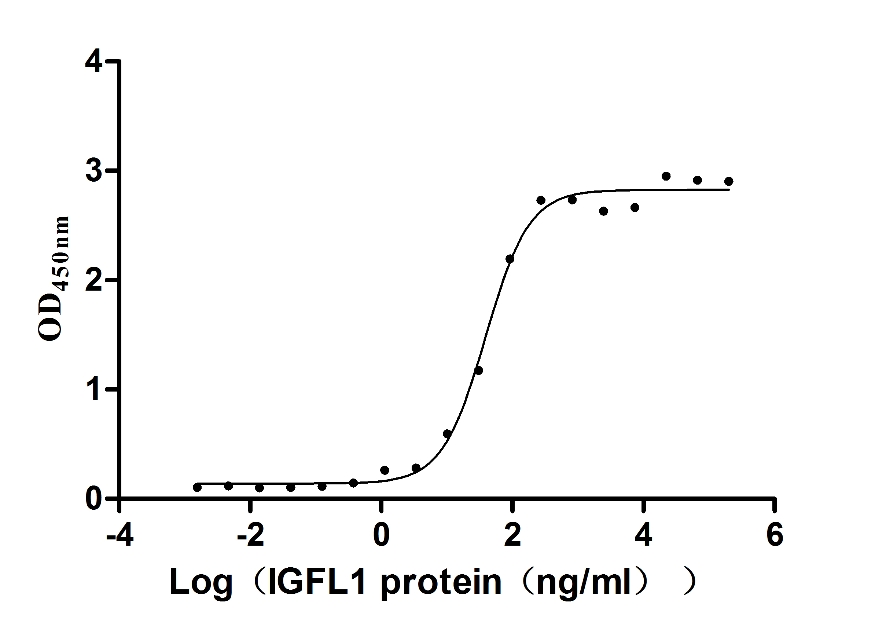
Recombinant Human Insulin growth factor-like family member 1 (IGFL1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
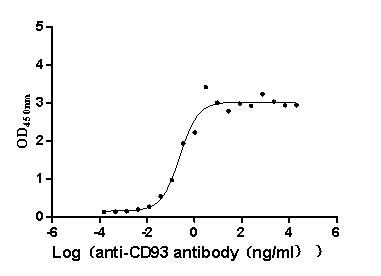
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
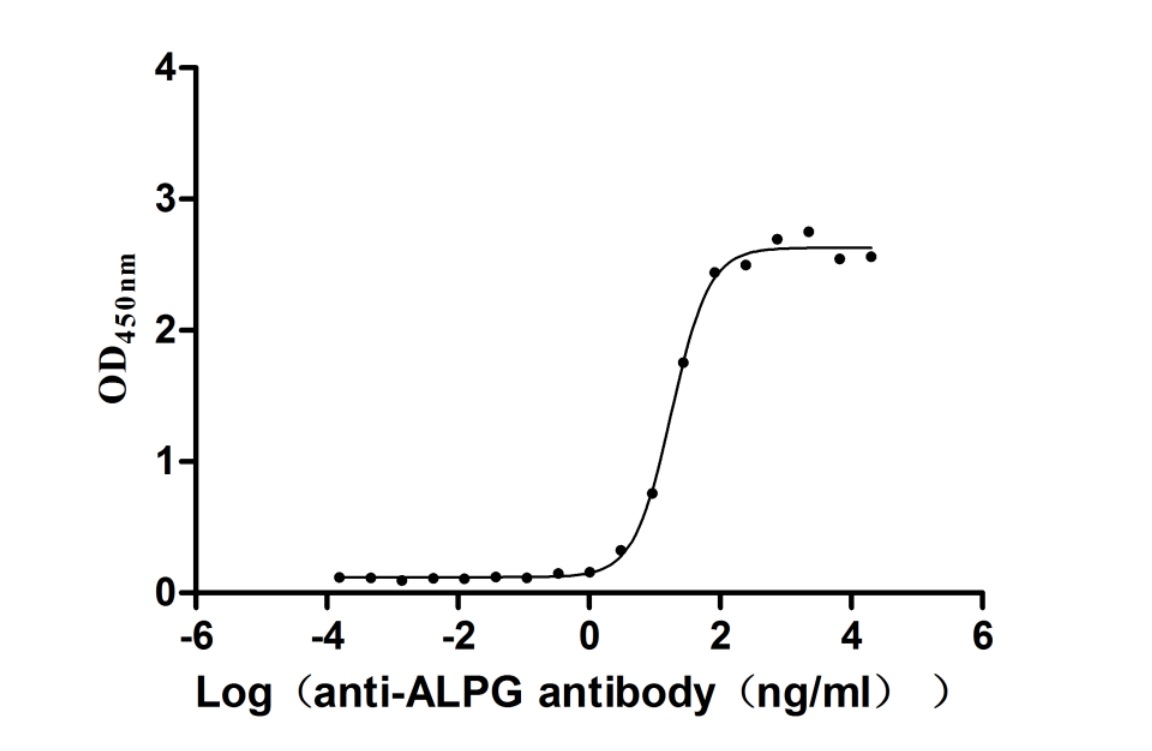
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
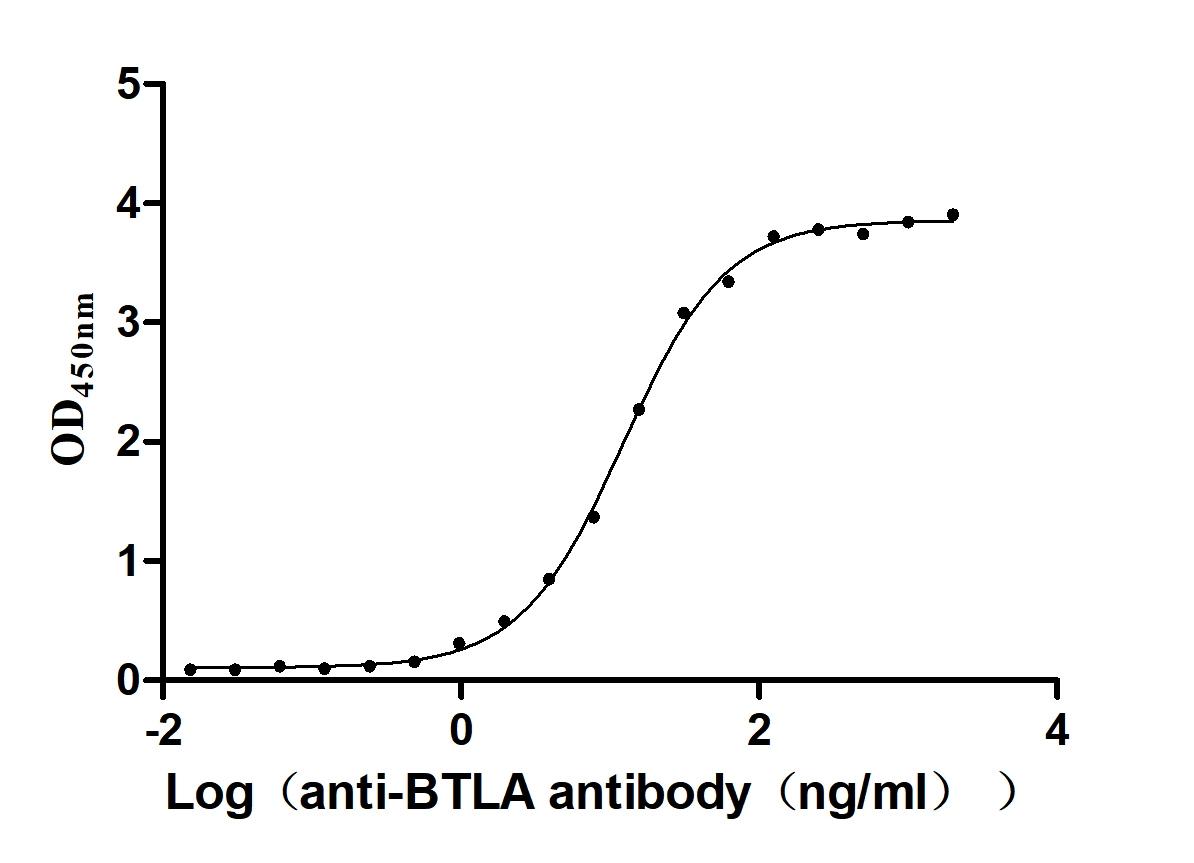
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
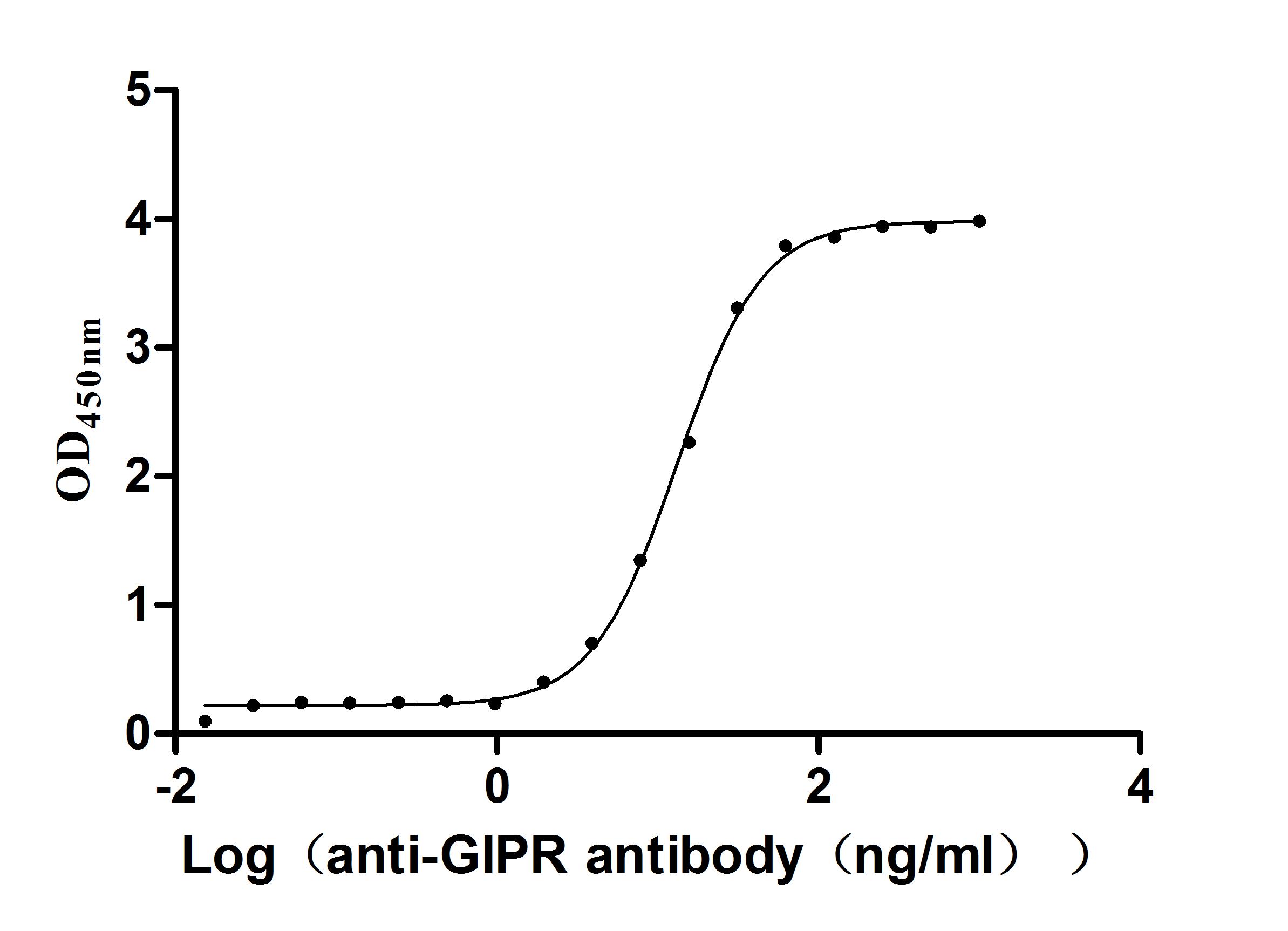
Recombinant Macaca Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
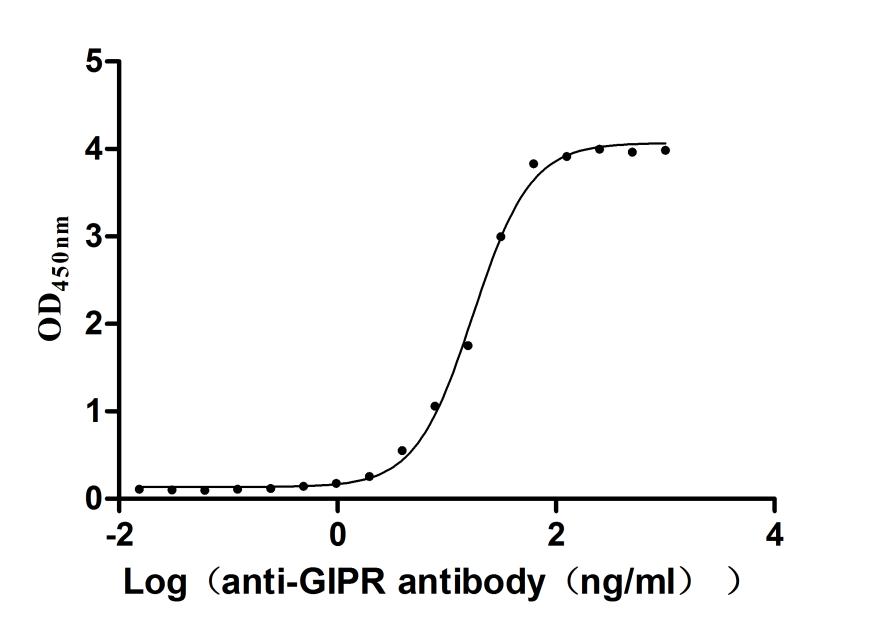
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)