Recombinant Human Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22 (USP22)
-
货号:CSB-YP891982HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP891982HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP891982HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP891982HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP891982HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:USP22
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Deubiquitinating enzyme 22; KIAA1063; Ubiquitin carboxyl terminal hydrolase 22; Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 22; Ubiquitin specific peptidase 22; Ubiquitin specific peptidase 3 like; Ubiquitin specific processing protease 22; Ubiquitin specific protease 22; Ubiquitin thioesterase 22; Ubiquitin thiolesterase 22; Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 22; UBP22_HUMAN; USP 22; Usp22; USP3L
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-525
-
氨基酸序列MVSRPEPEGE AMDAELAVAP PGCSHLGSFK VDNWKQNLRA IYQCFVWSGT AEARKRKAKS CICHVCGVHL NRLHSCLYCV FFGCFTKKHI HEHAKAKRHN LAIDLMYGGI YCFLCQDYIY DKDMEIIAKE EQRKAWKMQG VGEKFSTWEP TKRELELLKH NPKRRKITSN CTIGLRGLIN LGNTCFMNCI VQALTHTPLL RDFFLSDRHR CEMQSPSSCL VCEMSSLFQE FYSGHRSPHI PYKLLHLVWT HARHLAGYEQ QDAHEFLIAA LDVLHRHCKG DDNGKKANNP NHCNCIIDQI FTGGLQSDVT CQVCHGVSTT IDPFWDISLD LPGSSTPFWP LSPGSEGNVV NGESHVSGTT TLTDCLRRFT RPEHLGSSAK IKCSGCHSYQ ESTKQLTMKK LPIVACFHLK RFEHSAKLRR KITTYVSFPL ELDMTPFMAS SKESRMNGQY QQPTDSLNND NKYSLFAVVN HQGTLESGHY TSFIRQHKDQ WFKCDDAIIT KASIKDVLDS EGYLLFYHKQ FLEYE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Histone deubiquitinating component of the transcription regulatory histone acetylation (HAT) complex SAGA. Catalyzes the deubiquitination of both histones H2A and H2B, thereby acting as a coactivator. Recruited to specific gene promoters by activators such as MYC, where it is required for transcription. Required for nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation and cell cycle progression.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- USP22 and CCND1 levels correlate in patient lung and colorectal cancer samples and our preclinical studies indicate that targeting USP22 in combination with CDK inhibitors may offer an approach for treating cancer patients whose tumors exhibit elevated CCND1. PMID: 30224477
- these findings suggest that miR-30e-5p suppresses non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis by downregulating USP22-mediated Sirt1/JAK/STAT3 signaling. PMID: 29174979
- USP22 played an important role in retinoblastoma cell proliferation/aging and apoptosis. PMID: 28682440
- indicate USP22 as a novel deubiquitinase of BMI1 in glioma PMID: 29788550
- USP22 mediates CRC cell chemoresistance through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and that reducing USP22 in CRC cells diminishes chemoresistance. PMID: 29689565
- Data provided evidence that USP22, an up-stream molecule of AP4, exhibits strong potential to promote colorectal cancer (CRC) metastasis, particularly CRC migration and invasion capacities, both in vitro and in vivo, by inducing EMT via AP4 activating. Moreover, USP22 and AP4 overexpression may stimulate tumor metastasis and adversely affect overall survival in CRC patients. PMID: 28427243
- Cancer stem cells marker USP22 influences drug sensitivity via regulating SIRT1, which will shed new insights into the mechanisms of multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma . PMID: 28417539
- our study demonstrates that USP22 is indispensable for gastric cancer stem cell self-renewal through stabilization of BMI1. PMID: 28415621
- Downregulation of USP22 in ATC cells impeded tumor growth and lung metastasis in vivo. PMID: 27145278
- Studies indicate that aberrant expression of the Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 22 (USP22) has been associated with poor cancer prognosis. PMID: 27057639
- we demonstrated that USP22 was highly expressed in OS tissues and cells lines. Downregulation of USP22 inhibited OS cell proliferation, invasion, and EMT in vitro. In addition, downregulation of USP22 suppressed OS tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. PMID: 27983930
- In breast cancer cell lines USP22 increases c-Myc stability through c-Myc deubiquitination, which is closely correlated with breast cancer progression. PMID: 28160502
- findings suggest that USP22 may be involved in hepatocellular carcinoma progression in cooperation with survivin. PMID: 26497847
- These findings provide evidence that high USP22 expression might be important in tumor progression and serves as an independent molecular marker for poor hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis PMID: 25909224
- USP22 attenuated the invasion capacity of colon cancer cells by inhibiting the STAT3/MMP9 signaling pathway. PMID: 25902005
- Our data indicated that USP22 may promote lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion by the induction of EMT. PMID: 25907317
- Data show that the aggregates formed by polyQ-expanded ataxin 7 sequester ubiquitin-specific protease (USP22) through specific interactions. PMID: 26195632
- the deubiquitinating enzyme activity of USP22 is necessary for regulating HeLa cell growth, and it promotes cell proliferation via the c-Myc/cyclin D2, BMI-1 and p53 pathways in HeLa cells PMID: 26143114
- ShRNA-mediated silencing of the ubiquitin-specific protease 22 gene restrained cell progression and affected the Akt pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PMID: 25482932
- Data indicate that ubiquitin specific peptidase 22 (USP22)-mediated sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) deubiquitination inhibits STAT3 transcription factor acetylation and its transcriptional activation. PMID: 24969755
- USP22 is overexpressed in human NSCLC tissues and cell lines. USP22 silencing downregulates MDMX protein expression and activates the p53 pathway. PMID: 25547493
- Increased USP22 expression in colon cancer correlated with reduced uH2B expression, and this expression pattern may contribute to tumor progression. PMID: 25971547
- findings of the present study suggest a potential mechanism underlying the oncogenic role of USP22 mediated by the modulation of the stability and activity of COX-2 PMID: 25817787
- USP22 may accelerate ovarian cancer cell cycle progression via synergizing with TGFB1 to regulate the TGFB1 downstream cell cycle pathway. PMID: 25369910
- Collectively, the present study demonstrated a new function of USP22 that induces autophagy, thus leading to the poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. PMID: 25241857
- Results show that USP22 and FoxM1 are overexpressed in patients with pancreatic cancer and jointly involved in the development and progression of pancreatic cancerthe disease. PMID: 24993031
- USP22 is involved in the carcinogenesis of human pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 25241842
- The overexpression of USP22 was observed to attenuate TSAinduced apoptosis in HeLa cells. PMID: 25323692
- These results suggest that USP22 positively regulates RCAN1 levels, which would consequently affect diverse RCAN1-linked cellular processes. PMID: 25546086
- Overexpression of USP22 in pancreatic cancer promoted cytoskeletal remodeling, upregulated expression of transcription factors to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and increased cellular invasion and migration. PMID: 25070659
- USP22 expression may play an important role in gastric carcinoma tissue. PMID: 25445209
- Genetic studies indicate that Gcn5 and USP22 have important roles during development, which may presage important functions for these proteins in human diseases. [review] PMID: 25111486
- USP22 overexpression may be associated with poor prognosis in patients with glioma PMID: 24573640
- High expression of USP22 was associated with Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. PMID: 24466336
- In the present study, a functional NLS and the minimal sequences required for the active targeting of USP22 to the nucleus were identified. PMID: 24802393
- Findings define USP22 as a critical effector of tumor progression, which drives lethal phenotypes. PMID: 24197134
- USP22 deubiquitinates and stabilizes NFATc2 protein levels thereby promoting IL2 expression. PMID: 24561192
- In this study, we investigated the protein expression of USP22 in different cervical tissues by immunohistochemical staining and analyze the correlation between USP22 level and clinicopathologic features including patient outco PMID: 23979981
- Overexpression of USP22 may contribute to the progression of SDC and thus may serve as a new molecular marker to predict the prognosis of SDC patients PMID: 23664741
- USP22 plays an important role in NSCLC progression at the early stage, and that overexpression of USP22 in tumor tissues could be used as a potential prognostic marker for patients with early clinical stage of NSCLC PMID: 23361242
- High USP22 expression is associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma. PMID: 23412977
- Sp1 is a crucial regulator of USP22 transcription. PMID: 23300749
- study identified the deubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 22 (USP22), a component of the deubiquitinating module (DUBm) of the SAGA transcriptional coactivating complex, as a SIRT1-interacting partner PMID: 23382074
- The USP22 regulates the cell cycle via the c--Myc/cyclin D2 pathway and down--regulating p15 and p21 expression in HepG2 cell. PMID: 23217440
- This is the first study that determines the relationship between USP22 expression and prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 22880026
- Data show that USP22 protein plays an essential role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and has clinical potentials as a biomarker and as an attractively therapeutic target for ESCC. PMID: 22447106
- USP22 may act as an oncogene in CRC as it positively regulates cell cycle via both BMI-1-mediated INK4a/ARF pathway and Akt signaling pathway. PMID: 21928107
- USP22 plays a crucial role in tumor formation and growth by regulating cell proliferation with USP22-dependent signaling pathway. PMID: 21773699
- RNAi-mediated knockdown of the ubiquitin hydrolase, USP22, results in 2-fold higher ubH2B, and 2-fold lower transcriptional elongation at IRF1. USP22 depletion also diminishes 3'-end cleavage/polyadenylation by 2- to 3-fold. PMID: 22067483
- simultaneous activation of USP22 and BMI-1 may associate with GC progression and therapy failure PMID: 21735131
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Peptidase C19 family, UBP8 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Moderately expressed in various tissues including heart and skeletal muscle, and weakly expressed in lung and liver.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 12621
OMIM: 612116
KEGG: hsa:23326
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000261497
UniGene: Hs.462492
Most popular with customers
-
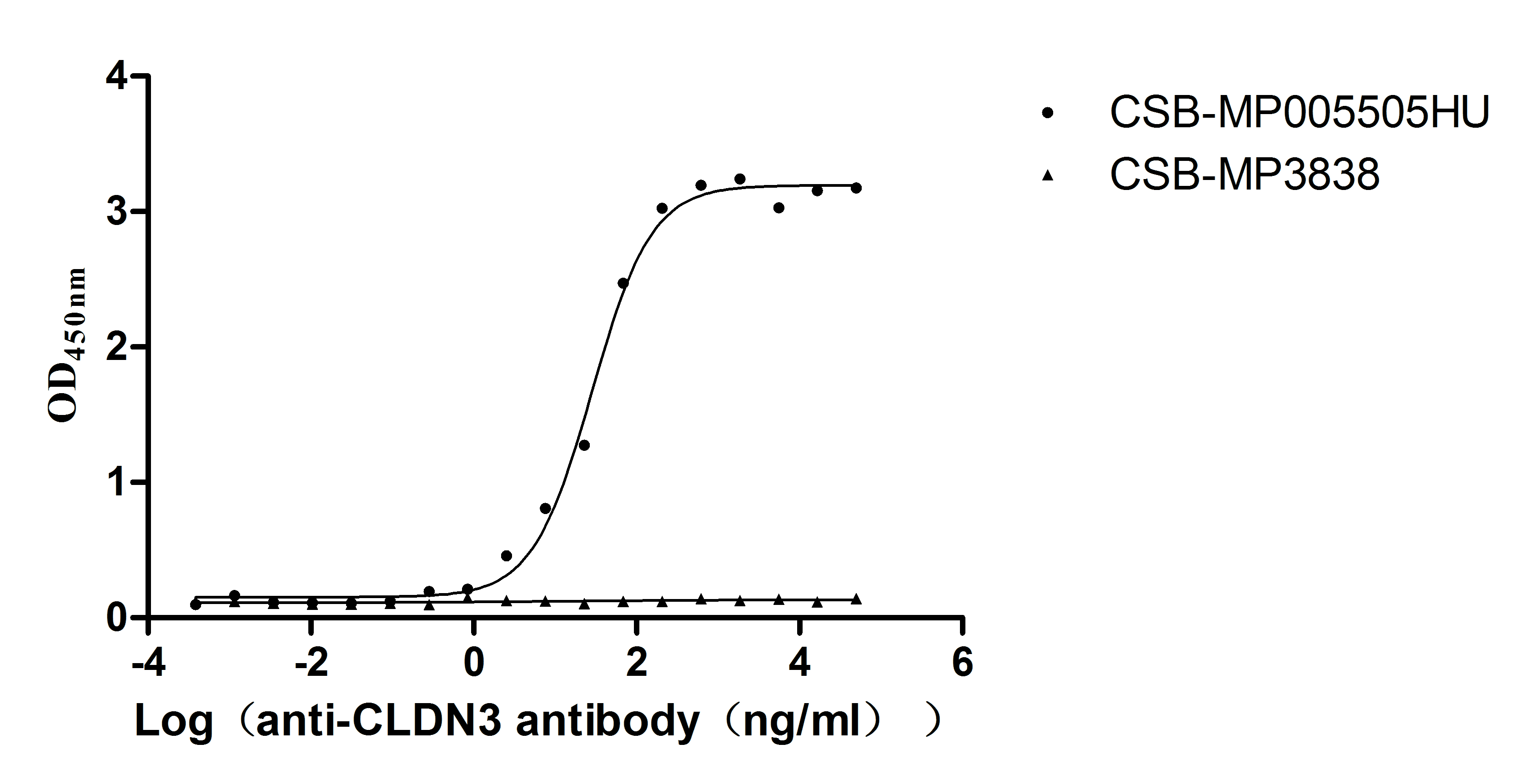
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
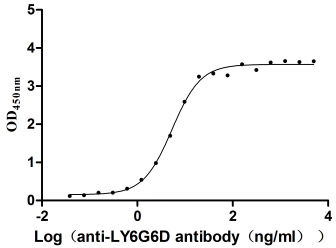
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
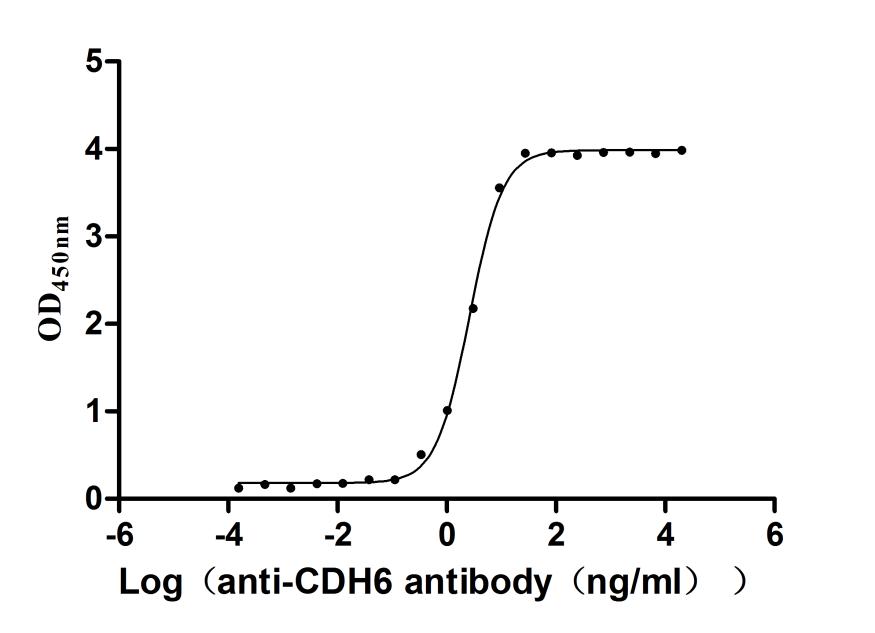
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
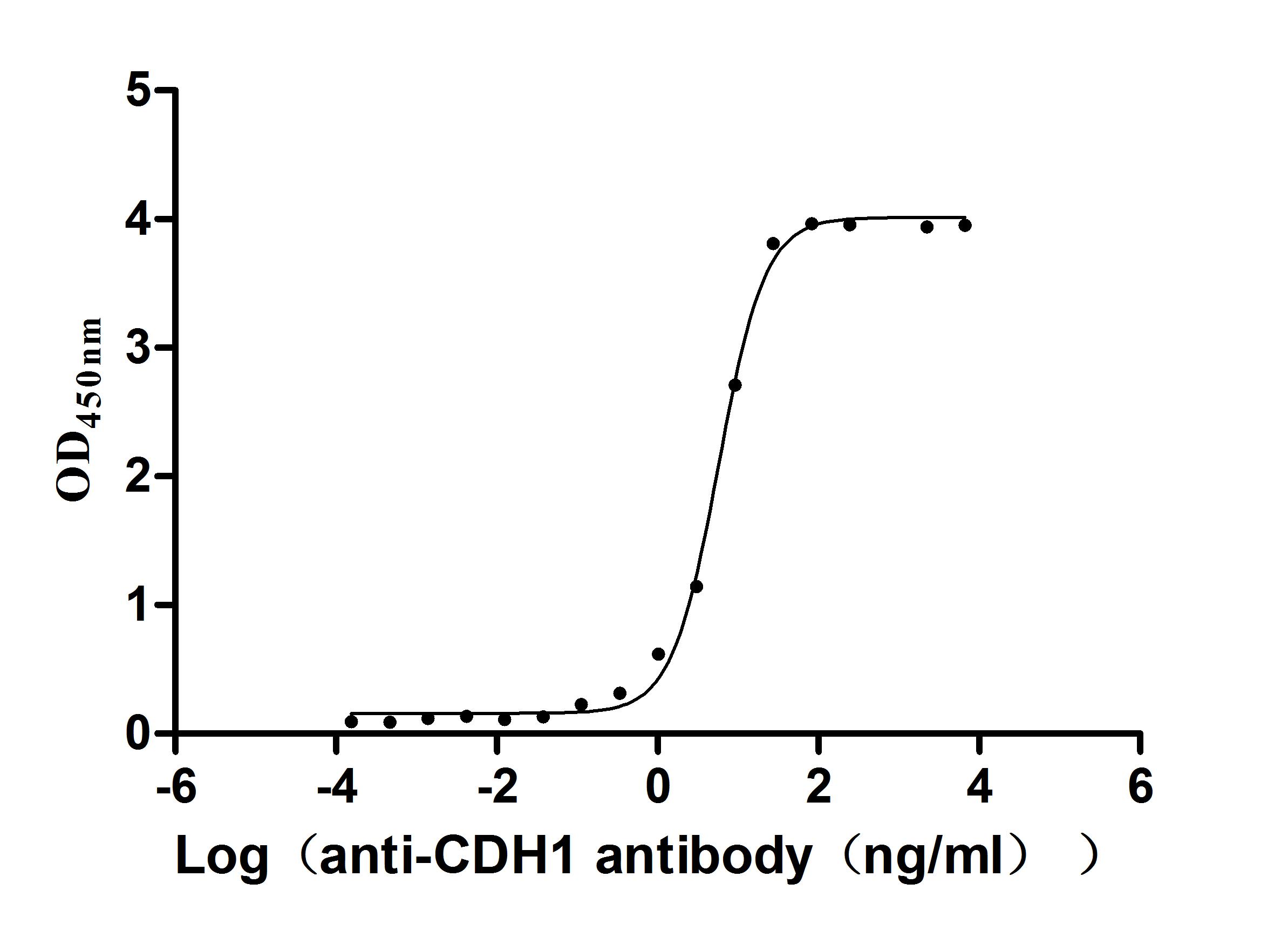
Recombinant Human Cadherin-1(CDH1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)