Recombinant Human Transmembrane protein 106B (TMEM106B), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP023674HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP023674HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP023674HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP023674HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP023674HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:TMEM106B
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:2310036D22Rik; 5830455K21Rik; 6430519M21Rik; AI428776; AI661344; FLJ11273; LRRGT00101; MGC33727; MGC94135; T106B_HUMAN; Tmem106b; Transmembrane protein 106B
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in dendrite morphogenesis and maintenance by regulating lysosomal trafficking via its interaction with MAP6. May act by inhibiting retrograde transport of lysosomes along dendrites. Required for dendrite branching.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- TMEM106B drives lung cancer metastasis by inducing TFEB-dependent lysosome synthesis and secretion of cathepsins. PMID: 30013069
- These findings illustrate the profound effect of TMEM106B haplotypes on brain health and highlight the importance to better understand TMEM106B's function and dysfunction in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. PMID: 29970152
- This study demonstrated that in Chinese patient minor alleles of rs1990622 and rs3173615 in TMEM106B may be associated with PD patients with initial symptom of rigidity/bradykinesia. PMID: 28477711
- Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the TMEM106B gene have been identified as a risk factor in frontotemporal dementia (FTD). PMID: 28888721
- A common causal variant underlying both association with disease and association with TMEM106B expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. PMID: 29056226
- Study developed a TMEM106B transgenic mouse model that recapitulates the interaction between progranulin and TMEM106B in human patients and supports a regulation of TMEM106B by progranulin in the aged brain and a role of TMEM106B in frontotemporal lobar degeneration-progranulin disease progression. PMID: 28126008
- This review revealed TMEM106B variants as significant contributors to one's risk of developing various TDP-43 proteinopathies, both in patients harboring disease-causing mutations and in subjects with TDP-43 pathology of unknown cause. PMID: 27543298
- TMEM106B enhances the benefit of cognitive reserve on brain structure in fronto-temporal dementia. PMID: 28460069
- we expanded our understanding of the TMEM106B haplotype that is protective against TDP-43 proteinopathy. PMID: 28441426
- These findings suggest that the up-regulation of TMEM106B may increase the risk of frontotemporal lobar degeneration by directly causing neurotoxicity and a pathological phenotype linked to FTLD-TDP. PMID: 27563066
- Endogenous TMEM106B was partly sequestered in CHMP2B-positive structures. The roles of SNPs T185, S185, or S134N in endosomal sorting complexes required for transport were studied. T185 is a risk factor in neurodegeneration with endolysosomal defects. PMID: 26651479
- Study suggests that TMEM106B is associated with frontotemporal dementia, although the extent of this effect is difficult to be estimated by using clinical frontotemporal dementia series PMID: 25096617
- It is a risk factor for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. PMID: 25085782
- TMEM106b variability does not influence Alzheimer disease risk or plasma progranulin levels. PMID: 25114081
- Common variants in TMEM106B serve as a distinct risk factor for TDP-43 pathology in older persons without frontotemporal lobe dementia. PMID: 25653292
- The HpScl groups (Hippocampual Sclerosis and Hippocampual Sclerosis-AD) were more likely to exhibit genetic variants in TMEM106B that are associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration. PMID: 24899141
- results show that, in nondemented persons, TMEM106B influences the volume of temporal brain regions that are important for language processing. PMID: 24731779
- Neuronal TMEM106B plays a central role in regulating lysosomal size, motility and responsiveness to stress, highlighting the possible role of lysosomal biology in FTLD-TDP. PMID: 25066864
- Data provide an initial neuropathological characterization of the newly discovered frontotemporal lobar degeneration-associated protein TMEM106B PMID: 24252750
- This study confirmed that specific TMEM106B single-nucleotide polymorphisms is associated with HS-Aging pathology in the Alzheimer disease. PMID: 25470345
- Study identifies TMEM106B as the first genetic factor modifying disease presentation in C9ORF72 expansion carriers PMID: 24385136
- Study demonstrates that TMEM106B is the first reported genetic modifier in C9orf72 expansion-related frontotemporal lobar degeneration PMID: 24442578
- This study demonstrate that TMEM106B and APOE interact to increase late-onset Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese. PMID: 24166182
- Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration risk factor, TMEM106B, by signal peptide peptidase-like 2a (SPPL2a). PMID: 24872421
- These data show that TMEM106B/MAP6 interaction is crucial for controlling dendritic trafficking of lysosomes, presumably by acting as a molecular brake for retrograde transport. PMID: 24357581
- TMEM106B polymorphism modulates brain connectivity in granulin mutation carriers. PMID: 24343233
- These findings suggest that low TMEM106B levels might protect against frontotemporal lobar degeneration TAR DNA binding protein 43 in these patients PMID: 23742080
- TMEM106B is localized in the late endosome/lysosome compartments and TMEM106B levels are regulated by lysosomal activities. PMID: 23136129
- This study demonistrated that aberrant overexpression of TMEM106B affects the distribution and intracellular levels of progranulin, suggesting that the two proteins may act in the same pathogenic pathway in FTLD-TDP. PMID: 22895706
- Our data implicate TMEM106B in the pathological presentation of Alzheimer Disease. PMID: 22855871
- Endogenous as well as overexpressed TMEM106B localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes. Interestingly, the inhibition of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases significantly increased the levels of TMEM106B. PMID: 22511793
- Our results suggest that genetic variation in TMEM106B (rs1990622) may influence risk for frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TAR DNA-binding protein inclusions (FTLD-TDP) by modulating secreted levels of GRN. PMID: 21220649
- FTLD-TDP risk gene TMEM106B is involved in the development of cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 21104415
- This study strongly supported TMEM106B as a risk gene for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. PMID: 21354975
- The genome-wide association study revealed a strong association between FTLD-TDP and several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that mapped in the region of the TMEM106B gene PMID: 20383883
- Variants in TMEM106B are strong risk factors for frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inculsions. PMID: 20154673
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia (UP-FTD); Frontotemporal dementia and/or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 1 (FTDALS1)
-
亚细胞定位:Late endosome membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Lysosome membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:TMEM106 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in frontal cortex.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 22407
OMIM: 105550
KEGG: hsa:54664
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000379901
UniGene: Hs.396358
Most popular with customers
-
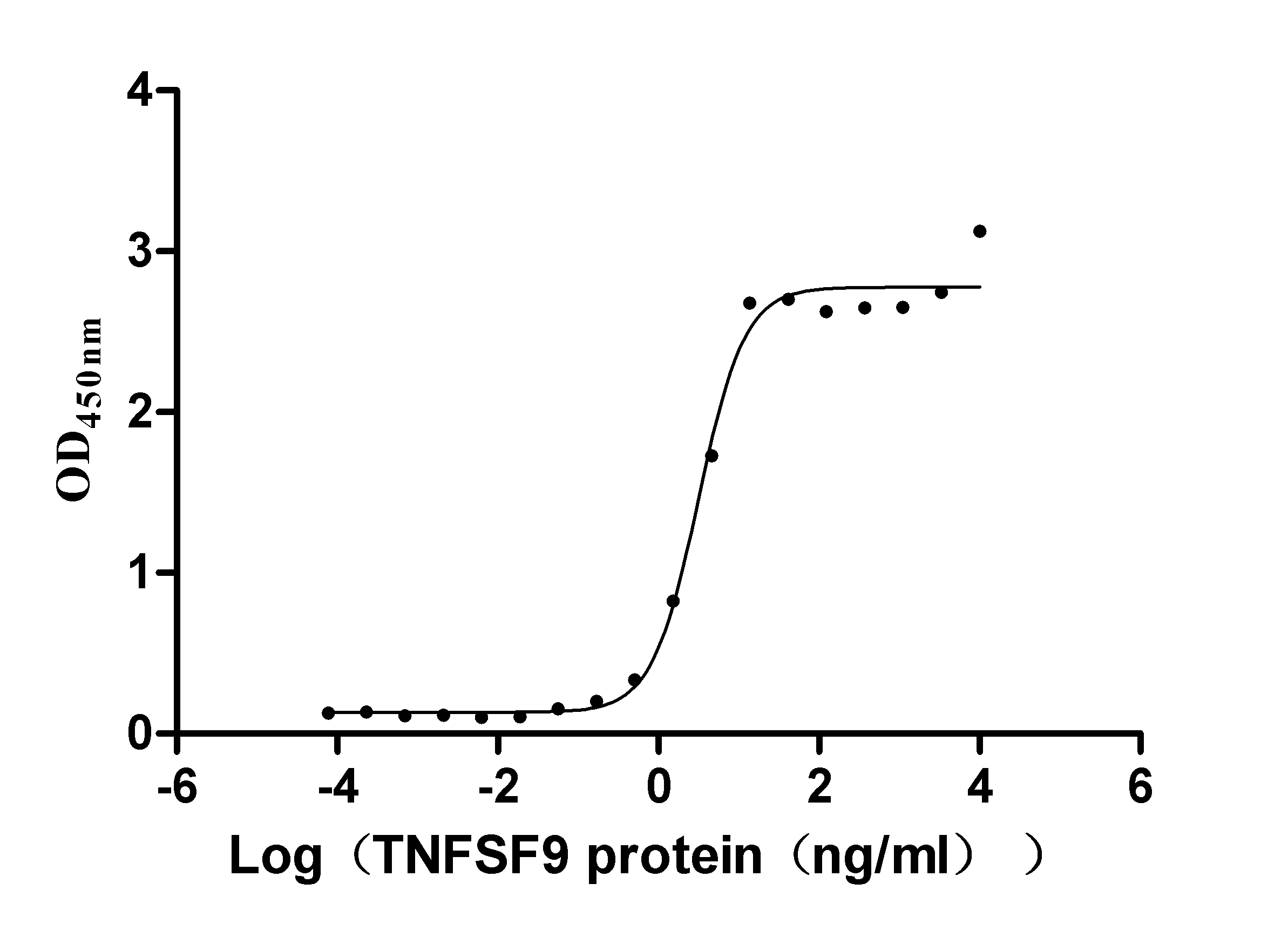
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
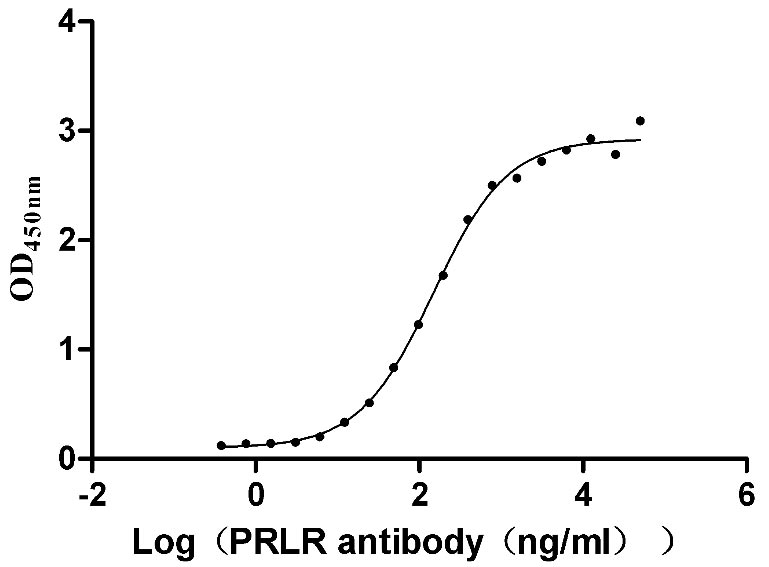
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
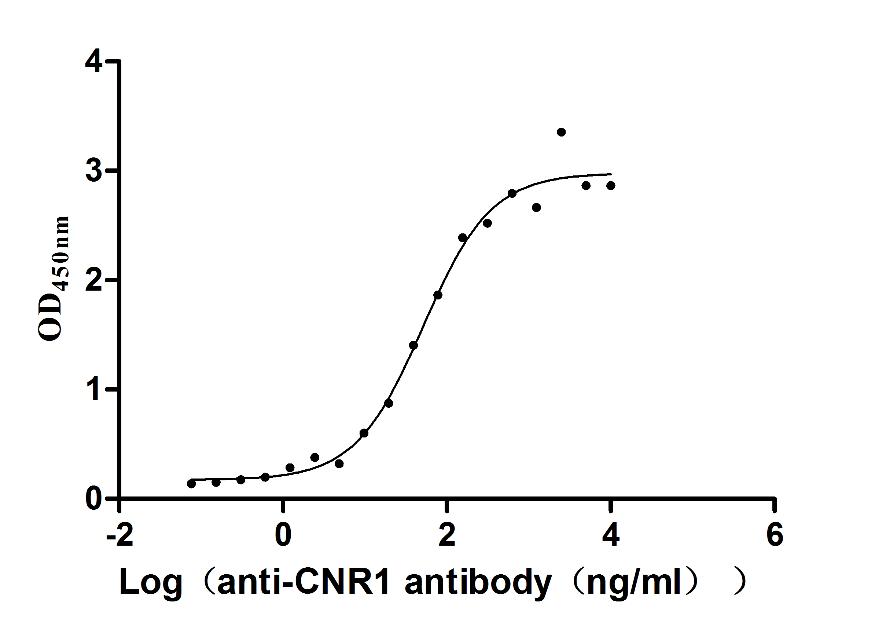
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
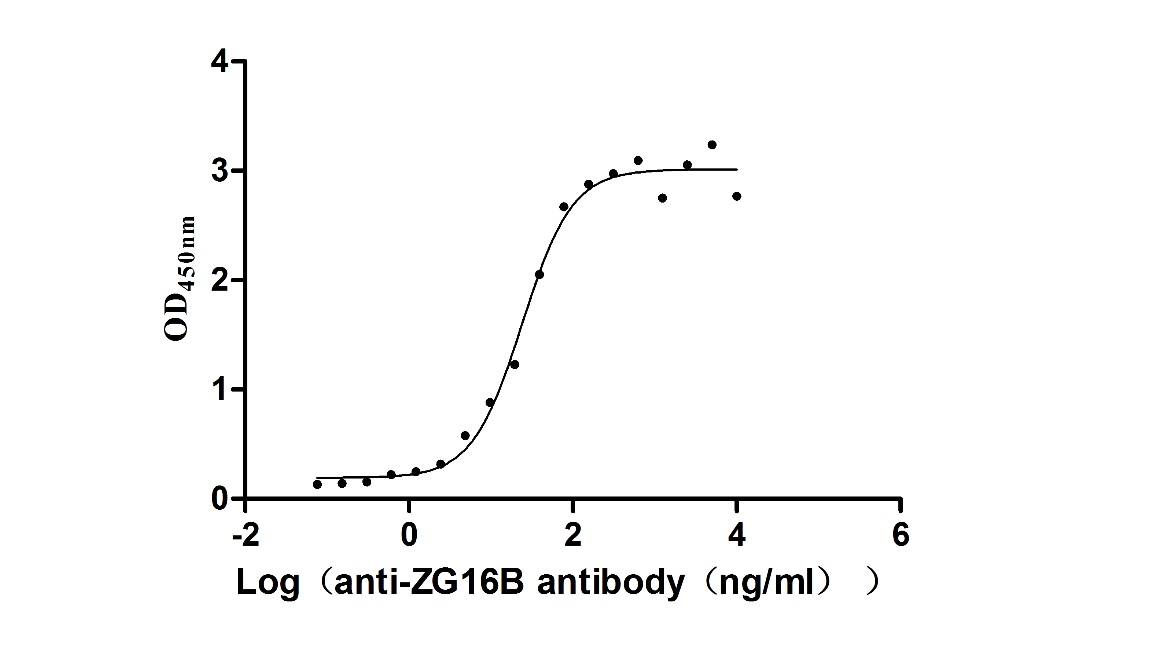
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
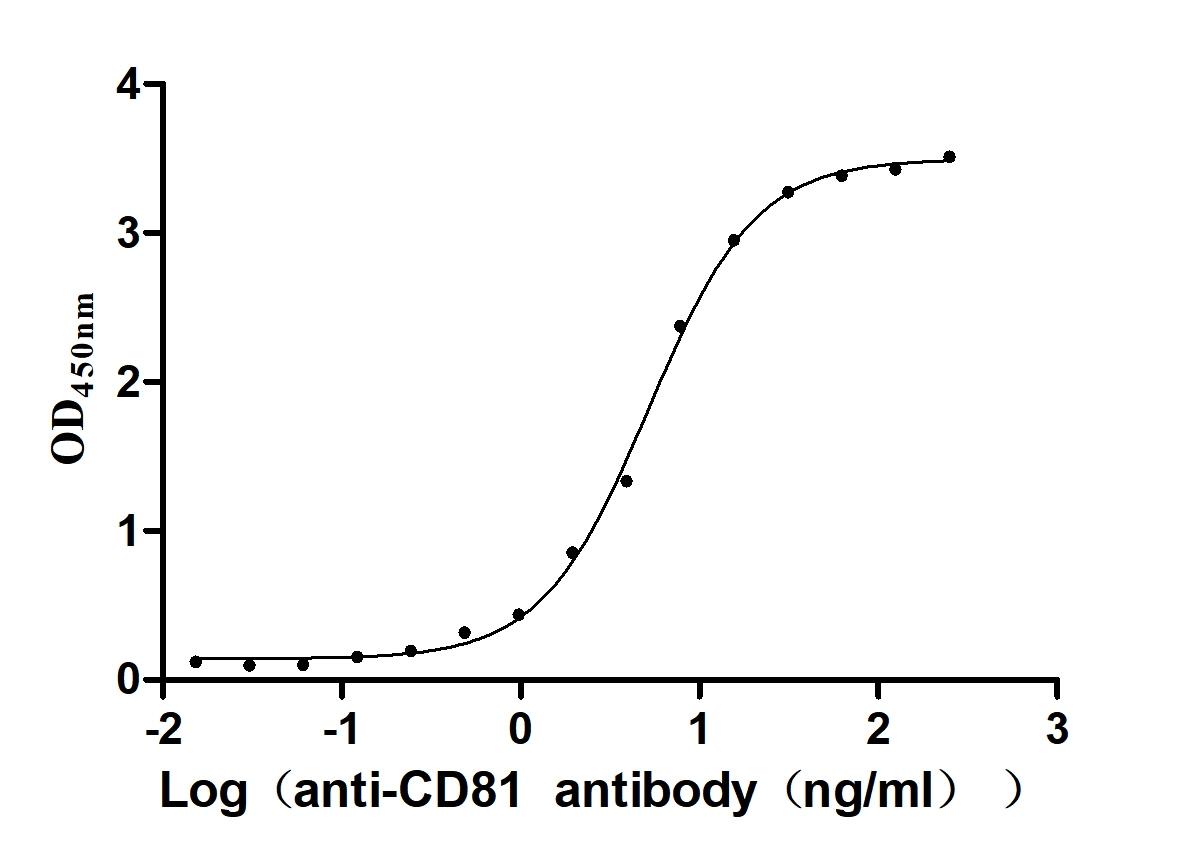
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
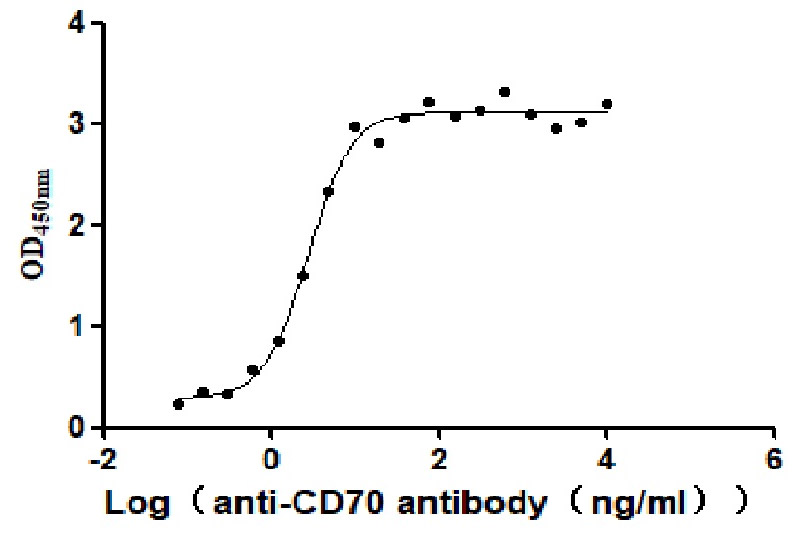
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)