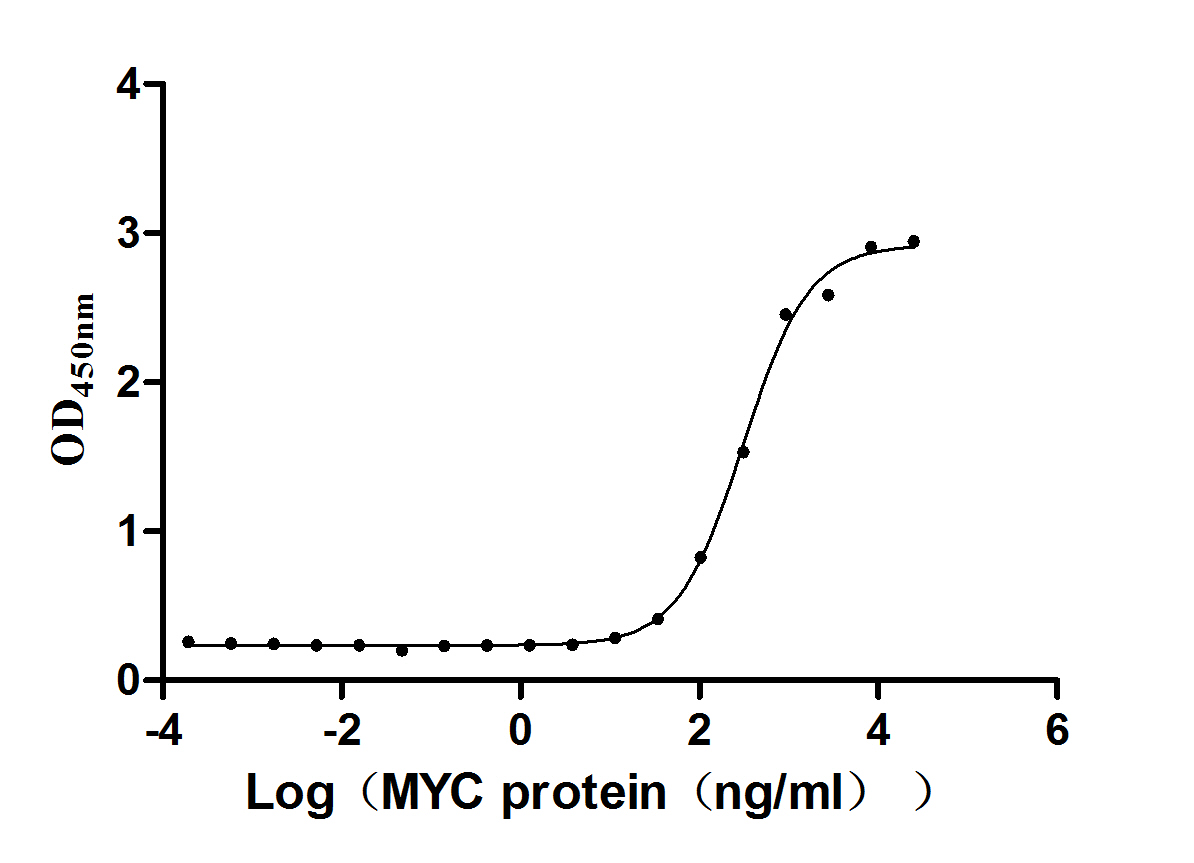
Recombinant Human THAP domain-containing protein 1 (THAP1)
-
中文名称:人THAP1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP885741HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人THAP1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP885741HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人THAP1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP885741HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人THAP1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP885741HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人THAP1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP885741HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:THAP1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:4833431A01Rik; DYT6; FLJ10477; MGC33014; Nuclear proapoptotic factor; THAP 1; THAP domain containing 1; THAP domain containing apoptosis associated protein 1; THAP domain containing protein 1; THAP domain protein 1; THAP domain-containing protein 1; Thap1; THAP1_HUMAN
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-213
-
氨基酸序列MVQSCSAYGC KNRYDKDKPV SFHKFPLTRP SLCKEWEAAV RRKNFKPTKY SSICSEHFTP DCFKRECNNK LLKENAVPTI FLCTEPHDKK EDLLEPQEQL PPPPLPPPVS QVDAAIGLLM PPLQTPVNLS VFCDHNYTVE DTMHQRKRIH QLEQQVEKLR KKLKTAQQRC RRQERQLEKL KEVVHFQKEK DDVSERGYVI LPNDYFEIVE VPA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:DNA-binding transcription regulator that regulates endothelial cell proliferation and G1/S cell-cycle progression. Specifically binds the 5'-[AT]NTNN[GT]GGCA[AGT]-3' core DNA sequence and acts by modulating expression of pRB-E2F cell-cycle target genes, including RRM1. Component of a THAP1/THAP3-HCFC1-OGT complex that is required for the regulation of the transcriptional activity of RRM1. May also have pro-apoptotic activity by potentiating both serum-withdrawal and TNF-induced apoptosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Dysfunction in similar pathways occurring with mutations in THAP1 as well as diverse dystonia genes highlight a point of convergence in the pathophysiology of several forms of inherited dystonia. PMID: 29364887
- The region of amino acids 139-185 is involved in formation of THAP1 homodimers. PMID: 28299530
- We functionally characterized for the first time three dystonia-causing missense variants (p.N136K, p.N136S and p.Y137C) within the HBM in the C-terminal region of THAP1. Dystonia-causing mutations affecting the residues N136 and Y137 in THAP1 significantly reduced HCFC1 recruitment to all four tested promoter regions. PMID: 28486698
- that the THAP1 is likely to have a causative role in the pathogenesis of Indian primary pure dystonia patients PMID: 27913194
- This study demonstrated that whole-exome sequencing show reveled THAP1 mutation with early-onset generalized dystonia. PMID: 27666935
- Genetic screening targeted at currently known disease-causing mutations in TOR1A, THAP1, and TUBB4 appears to have low diagnostic yield in sporadic spasmodic dysphonia. In our cohort, only 2 patients tested positive for novel/rare variants in THAP1. PMID: 27188707
- A deleterious THAP1 mutation was identified in patients with idiopathic isolated dystonia. PMID: 26940431
- there might not be an association between TOR1A or THAP1 and patients with adult-onset primary focal dystonia PMID: 26803725
- findings strongly suggest the role of other genetic factors or environmental triggers in the pathogenesis of dystonia related to mutations in THAP1 gene. PMID: 25385508
- The aim of this study was to assess the presence of DYT6 mutations in Polish patients with isolated dystonia. It shows known and novel substitutions. PMID: 26087139
- THAP1 variants are an important cause of dystonia among individuals with an early-onset disease and a positive family history. PMID: 24976531
- This study demonistrated that Combined occurrence of a novel TOR1A and a THAP1 mutation in primary dystonia. PMID: 24862462
- this study identified a feedback-loop in the regulation of THAP1 expression and demonstrated that mutant THAP1 leads to higher THAP1 expression levels. PMID: 25088175
- Primary dystonia in the Amish-Mennonites is genetically diverse and includes not only the THAP1 indel founder mutation but also different mutations in THAP1 and GNAL as well as the TOR1A GAG deletion. PMID: 24500857
- This study suggest that the clinical disease course in dystonia patients with mutation of THAP1 in Japanese' PMID: 24227593
- Our results indicate that certain mutations in the THAP1 gene may lead to primary dystonia with remarkable intrafamilial clinical variability. PMID: 25168324
- deletion of SLC20A2 and THAP1 may have a role in familial basal ganglia calcification with dystonia [case report and family study] PMID: 24135862
- Current known dystonia genes include those related to dopamine metabolism, transcription factor, cytoskeleton, transport of glucose and sodium ion, etc. PMID: 23782819
- Par-4/THAP1 complex and Notch3 competitively regulated pre-mRNA splicing of CCAR1 and affected inversely the survival of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. PMID: 23975424
- The genotypic spectrum of THAP1 and strengthen the association with upper body involvement, including the cranial and cervical regions that are usually spared in DYT1-primary dystonia. PMID: 23180184
- Our findings indicate that THAP1 mutations are very rare in blepharospasm PMID: 23036512
- Truncated THAP1 mutations (F22fs71X and F25fs53X) can alter subcellular distributions in DYT6 dystonia, while some missense mutations (C54F and L180S) cannot. PMID: 22652465
- in dystonia DYT1 and DYT6 gene mutation carriers, diffusion tensor imaging detected fewer fibers in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways PMID: 22987473
- This study supported that THAP1 mutations are an important cause of dystonia. PMID: 22903657
- this study demonstrated marked intrafamilial variations of dystonia in a single Japanese family with DYT6 and limited efficiency of deep brain stimulation. PMID: 22821615
- Evaluation of the effect of missense mutations, within the THAP domain, on the structure, stability and DNA binding. PMID: 22844099
- The role of THAP1 as a major genetic modifier in DYT1 dystonia and suggest the presence of other genetic or environmental factors that may influence the manifestation of DYT1 dystonia. PMID: 22508326
- THAP domain of THAP1 tend to manifest at an earlier age and exhibit more extensive anatomical distributions than mutations localized to other regions of THAP1. PMID: 22377579
- THAP1 mutations do not seem to play a major role in primary focal/segmental dystonia in this sample of southern German origin. PMID: 21782490
- Mutation frequency of the THAP1 gene is 0.87% in Chinese patients with primary pure dystonia, similar to the mutation frequency found in other ethnic groups. PMID: 21839475
- the THAP1 gene to colligate all reported patients with a specific THAP1 mutation and the associated clinical signs in order to describe the broad phenotypic continuum of DYT6 dystonia ( THAP1 ) PMID: 21793105
- One silent mutation (c.267G>A) was shown to affect THAP1 expression. PMID: 21800139
- THAP1 mutations are rare in unselected dystonia patients and functional analysis is necessary to distinguish between benign variants and pathogenic mutations. PMID: 21847143
- This study demonistrated that THAP1 mutations are infrequent in spasmodic dysphonia in Dutch patient. PMID: 21538522
- This study demonistrated that Truncating mutations in THAP1 define the nuclear localization signal. PMID: 21495072
- The results of this study suggested that No evidence for THAP1/DYT6 variants as disease modifiers in DYT1 dystonia. PMID: 21638323
- Genetic analysis of the entire genomic region of THAP1 revealed a novel variant that was specific for African-Americans PMID: 21601506
- this study presented that the DYT6 phenotypes in association with new THAP1 frameshift mutations. PMID: 21520283
- These observations offer additional insight into the role of the coiled-coil domain in THAP1, which may facilitate future analyses of DYT6 mutations in this region PMID: 21752024
- The data of this study suggested that homozygous THAP1 mutations cause dystonia and may be associated with a less severe dysfunction of the encoded protein compared with heterozygous disease-causing mutations. PMID: 21425335
- This study indicated that the c.-237_236GA>TT THAP1 sequence variant does not increase risk for adult-onset primary dystonia in Caucasians. PMID: 21370264
- Three subjects were found to have the GAG deletion in the TOR1A gene, and two patients were detected with THAP1 gene mutations/variations PMID: 20825472
- found five heterozygous mutations in THAP1 in autosomal dominant primary torsion dystonia 6 PMID: 21110056
- Mutations in these two known primary torsion dystonia (PTD) genes, TOR1A and THAP1, are responsible for about 10% of the PTD cases in our Brazilian cohort suggesting genetic heterogeneity and supporting the role of other genes in PTD. PMID: 20925076
- The variant of THAP1( c.71+9C>A) in intron 19 was found in 3 late onset dystonia patients (0.6%) and one control subject (0.5%). PMID: 20687191
- These findings suggest that THAP1 sequence variations in primary dystonia seem to be associated with different ages of onset and distribution of symptoms PMID: 20669277
- This study demonstrated a physical interaction between THAP1 and the TOR1A promoter that is abolished by pathophysiologic mutations. PMID: 20865765
- The THAP zinc finger uses its double-stranded beta-sheet to fill the DNA major groove and provides a unique combination of contacts from the beta-sheet, the N-terminal tail and surrounding loops toward the five invariant base pairs of the THABS sequence PMID: 20144952
- THAP1 mediates the recruitment of HCF-1 to the RRM1 promoter during endothelial cell proliferation and that HCF-1 is essential for transcriptional activation of RRM1. PMID: 20200153
- These data suggest that early-onset dystonia that includes the involvement of the larynx or face is frequently associated with THAP1 mutations. PMID: 20211909
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Dystonia 6, torsion (DYT6)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus, PML body.
-
蛋白家族:THAP1 family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in heart, skeletal muscle, kidney and liver. Weaker expression in brain and placenta.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 20856
OMIM: 602629
KEGG: hsa:55145
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000254250
UniGene: Hs.7432
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-18.2 (CLDN18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
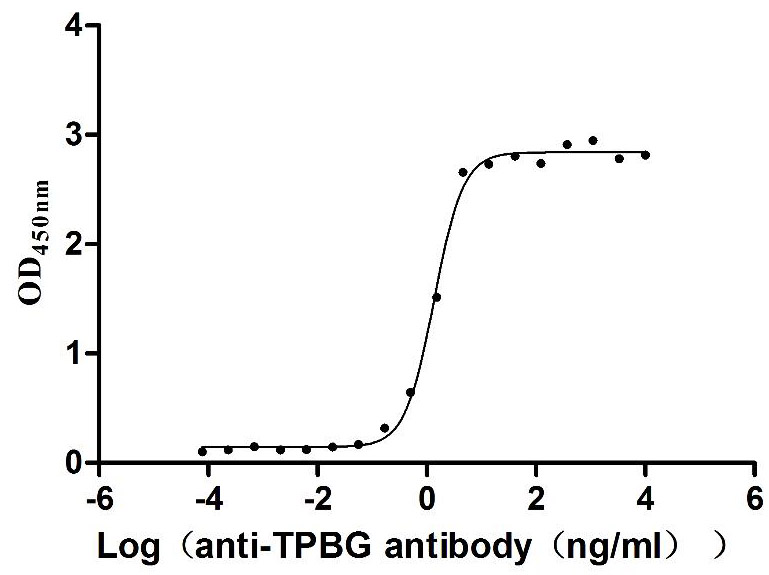
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
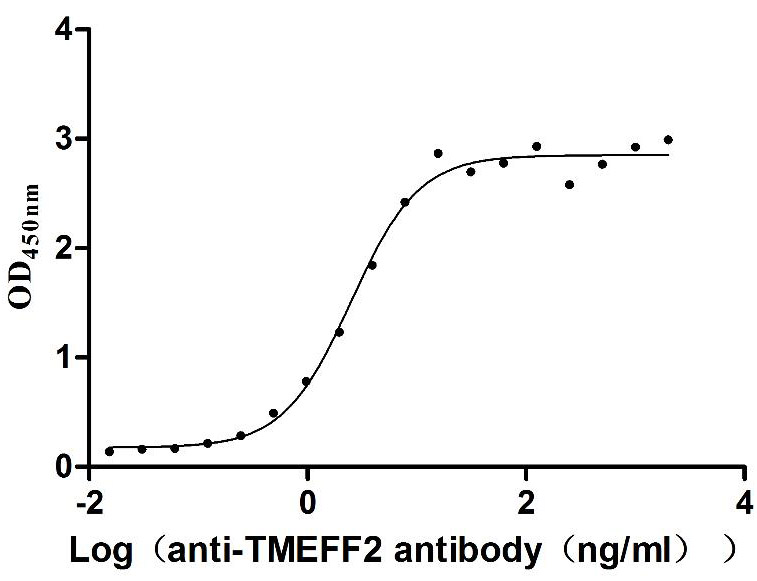
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
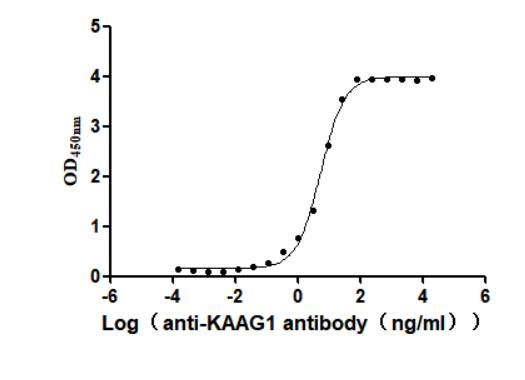
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
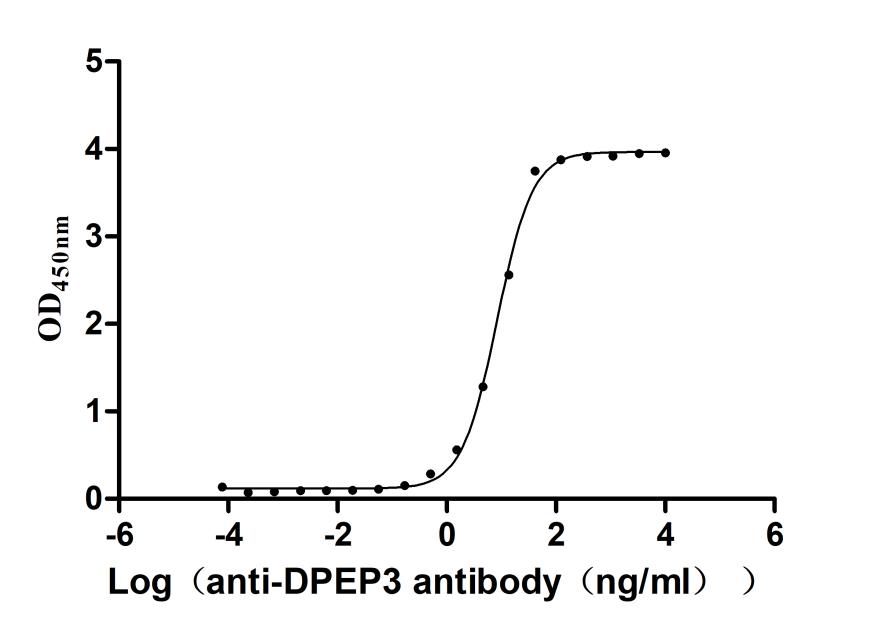
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
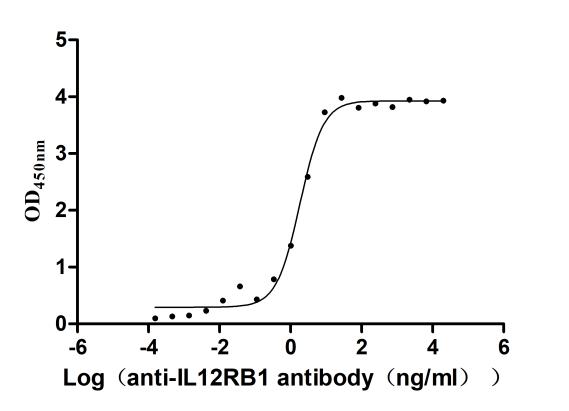
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)