Recombinant Human Replication protein A 70 kDa DNA-binding subunit (RPA1)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP020088HU
-
规格:¥1344
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dmrpa1; Drosophila Replication Protein A; DRPA; HSSB; Human single stranded DNA binding protein ; MST075; MSTP075; p70; REPA1; Replication factor A; Replication factor A protein 1; Replication protein A 70 kDa DNA-binding subunit; Replication protein A 70kDa DNA binding subunit; Replication protein A1 70kDa; Replication protein A1; RF A; RF-A protein 1; RFA; RFA1_HUMAN; RP A; RP-A p70; RPA 70; RPA; rpa1; Single stranded binding protein 70; Single-stranded DNA-binding protein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:84.0kDa
-
表达区域:2-616aa
-
氨基酸序列VGQLSEGAIAAIMQKGDTNIKPILQVINIRPITTGNSPPRYRLLMSDGLNTLSSFMLATQLNPLVEEEQLSSNCVCQIHRFIVNTLKDGRRVVILMELEVLKSAEAVGVKIGNPVPYNEGLGQPQVAPPAPAASPAASSRPQPQNGSSGMGSTVSKAYGASKTFGKAAGPSLSHTSGGTQSKVVPIASLTPYQSKWTICARVTNKSQIRTWSNSRGEGKLFSLELVDESGEIRATAFNEQVDKFFPLIEVNKVYYFSKGTLKIANKQFTAVKNDYEMTFNNETSVMPCEDDHHLPTVQFDFTGIDDLENKSKDSLVDIIGICKSYEDATKITVRSNNREVAKRNIYLMDTSGKVVTATLWGEDADKFDGSRQPVLAIKGARVSDFGGRSLSVLSSSTIIANPDIPEAYKLRGWFDAEGQALDGVSISDLKSGGVGGSNTNWKTLYEVKSENLGQGDKPDYFSSVATVVYLRKENCMYQACPTQDCNKKVIDQQNGLYRCEKCDTEFPNFKYRMILSVNIADFQENQWVTCFQESAEAILGQNAAYLGELKDKNEQAFEEVFQNANFRSFIFRVRVKVETYNDESRIKATVMDVKPVDYREYGRRLVMSIRRSALM
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:
Recombinant Human RPA1 expression in E.coli requires the insertion of the target DNA fragment into an E.coli expression vector, routinely a plasmid vector, and the transferral of this vector into E.coli cells. The cells are then cultured and induced to express this RPA1 protein. The cells are harvested by centrifugation, samples prepared and proteins detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subsequent staining of the gel with Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver stain or by immunoblotting. The RPA1 protein expression in E.coli is highly scalable and can be adjusted from the bacterial colony to conical flasks for liquid cultures, to fermentation reaction chambers.
RPA1 is a protein coding gene that encodes Replication protein A 70 kDa DNA-binding subunit. According to some studies, RPA1 may have the following features.
The function of Rpa1 in DNA metabolism is critical for maintaining chromosomal stability and suppressing tumors. Binding of RPA1 to NRF2 switches ARE-dependent transcriptional activation to ARE-NRE-dependent repression. The acetylation state of RPA1 plays a critical role in repairing DNA damage through NER. RPA1 has multiple roles in the body, playing a role in DNA replication, repair and recombination. The physical interaction between Rfc4 and Rpa1N is required for both effects. K163 acetylation of RPA1 plays a key role in repairing UV-induced DNA damage. -
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:As part of the heterotrimeric replication protein A complex (RPA/RP-A), binds and stabilizes single-stranded DNA intermediates, that form during DNA replication or upon DNA stress. It prevents their reannealing and in parallel, recruits and activates different proteins and complexes involved in DNA metabolism. Thereby, it plays an essential role both in DNA replication and the cellular response to DNA damage. In the cellular response to DNA damage, the RPA complex controls DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint activation. Through recruitment of ATRIP activates the ATR kinase a master regulator of the DNA damage response. It is required for the recruitment of the DNA double-strand break repair factors RAD51 and RAD52 to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Also recruits to sites of DNA damage proteins like XPA and XPG that are involved in nucleotide excision repair and is required for this mechanism of DNA repair. Plays also a role in base excision repair (BER) probably through interaction with UNG. Also recruits SMARCAL1/HARP, which is involved in replication fork restart, to sites of DNA damage. May also play a role in telomere maintenance. As part of the alternative replication protein A complex, aRPA, binds single-stranded DNA and probably plays a role in DNA repair. Compared to the RPA2-containing, canonical RPA complex, may not support chromosomal DNA replication and cell cycle progression through S-phase. The aRPA may not promote efficient priming by DNA polymerase alpha but could support DNA synthesis by polymerase delta in presence of PCNA and replication factor C (RFC), the dual incision/excision reaction of nucleotide excision repair and RAD51-dependent strand exchange.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- RPA serves to stimulate the primase activity of PrimPol. PMID: 28534480
- These new findings supports the existence of a functional PrimPol/RPA association that allows repriming at the exposed ssDNA regions formed in the leading strand upon replicase stalling. PMID: 28396594
- regulatory pathway based on casein kinase 2-G9a-RPA permits homologous recombination in cancer cells PMID: 28698370
- RPA1 serves as an oncogene during gastrointestinal cancers progression PMID: 29601890
- RPA1 is significantly up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with poor prognosis. RPA1 influences cell cycle through CDK4/Cyclin-D pathway. PMID: 29477843
- PCAF/GCN5-mediated lysine 163 acetylation of RPA1 is crucial for nucleotide excision repair. PMID: 28854354
- the acetylation status of RPA1 played a crucial role in repair of DNA damage via nucleotide excision repair. PMID: 28854355
- data obtained allow us to suggest that XPA can be involved in the post-incision NER stages via its interaction with RPA PMID: 29320546
- The results suggest that RPA phosphorylation enhances the recruitment of PRP19 to RPA-ssDNA and stimulates RPA ubiquitylation through a process requiring both PRP19 and RFWD3, thereby triggering a phosphorylation-ubiquitylation circuitry that promotes ATR activation and homologous recombination. PMID: 28666352
- RPA recruits HIRA to promoters and enhancers and regulates deposition of newly synthesized H3.3 to these regulatory elements for gene regulation. PMID: 28107649
- RPA is a sensor of R loops and a regulator of RNaseH1, extending the versatile role of RPA in suppression of genomic instability. PMID: 28257700
- Results suggest that the UNG2 N-terminus may serve as a flexible scaffold to tether PCNA and RPA at the replication fork, and that post-translational modifications on the UNG2 N-terminus disrupt formation of the PCNA-UNG2-RPA protein complex. PMID: 28746850
- Data suggest that, during human DNA replication, restricting PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) to the vicinity of its DNA target site is important; PCNA can be maintained at or near primer/template junctions during DNA synthesis by RPA (replication protein A) or SSB (single-stranded DNA-binding protein); here, the SSB used was from Escherichia coli. PMID: 28590137
- Strikingly, the addition of the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding replication protein A (RPA) selectively restores XPF-ERCC1 endonuclease activity on this structure. The 5'-3' exonuclease SNM1A can load from the XPF-ERCC1-RPA-induced incisions and digest past the crosslink to quantitatively complete the unhooking reaction. PMID: 28607004
- RPA deficiency induces activation of the Fanconi anemia pathway in an ATR-dependent manner, which may play a role in the genome maintenance. PMID: 27398742
- Force regulated dynamics of RPA1 on a DNA fork during DNA replication has been reported. PMID: 27016742
- By monitoring DNA double-strand breaks mis-repair using a sensitive bioassay, it was found that depletion of homologous recombination proteins, including BRCA2, BRCA1 or RPA1, resulted in a distinct mutational signature associated with significant increases in break-induced mutation frequencies. PMID: 27131361
- results reveal that ETAA1 is a novel RPA-interacting protein that promotes restart of stalled replication forks. PMID: 27601467
- miR-30a targets the DNA replication protein RPA1, hinders the replication of DNA and induces DNA fragmentation. PMID: 27208176
- show that RPA can bind on each side of the G-quadruplex but it unwinds the G4 only from 5' toward 3'. PMID: 27440048
- Replication protein A binds tightly to the single-stranded DNA adjacent to a blocked primer/template junction and restricts PCNA to the upstream duplex region by physically blocking diffusion of PCNA along ssDNA. PMID: 28177605
- CTF18 forms a complex with RPA when replication stress is elicited by hydroxyurea treatment or UV exposure during S phase. The interaction kinetics between CTF18 and RPA is positively associated with the phosphorylation status of Chk1. PMID: 27175616
- ATRIP deacetylation by SIRT2 promotes ATR-ATRIP binding to replication protein A-single-stranded DNA to drive ATR activation and thus facilitate recovery from replication stress. PMID: 26854234
- radiation induced the excessive expression RPA1 in TE-1 cells, and the radiosensitivity of TE-1R cells was less than that of TE-1 cells PMID: 26824734
- Our study predicted that UBC and RPA had potential as target genes for the diagnosis and treatment of osteosarcoma PMID: 26782416
- FAN1 efficiently promoted DNA incision at the proper site of RPA-coated 5'-flapped DNA. Therefore, FAN1 possesses the ability to promote the ICL repair of 5'-flapped DNA covered by RPA. PMID: 25922199
- a significant increase in DKC1, RAD50, MRE11 and RPA1 expression in MM cases with high bone marrow infiltration (p
- Here, we introduce a number of key characteristics and concepts, including the modularity of the proteins, linkage of weak binding sites, direct competition between sites, and allostery, using the protein replication protein A (RPA). [review] PMID: 25542993
- RFWD3-dependent ubiquitination of RPA regulates repair at stalled replication forks. PMID: 26474068
- RPA70 is an intrinsically highly dynamic single-stranded DNA-binding complex during both replication and distinct steps of nucleotide excision repair. PMID: 25453469
- by targeting RPA and mimicking DNA, DSS1 functions with BRCA2 in a two-component homologous recombination mediator complex in genome maintenance and tumor suppression PMID: 26145171
- The D228Y mutation in human RPA1 affects its DNA-binding activity to telomeric DNA. PMID: 26041456
- RPA plays an important maintaining genome integrity. [Review] PMID: 25400143
- RPA by itself does not affect pol eta dependent lesion bypass fidelity when copying either 8-oxoG or T-T CPD lesions. PMID: 24824831
- Both human RPA and hepatitis C virus NS5A(S25-C447), but not NS5A(S25-K215), enabled the NS5BDelta21-NS3 helicase complex to be stably associated with the template and synthesize RNA product in a highly processive manner in vitro. PMID: 25320291
- In addition to its annealing helicase activity, which eliminates the natural binding substrate for RPA, HARP blocks the phosphorylation of RPA by DNA-PK. PMID: 24565939
- Fanconi anemia group J (FANCJ) helicase partners with the single-stranded DNA-binding protein replication protein A (RPA) to displace BamHI-E111A bound to duplex DNA in a specific manner. PMID: 24895130
- LT prevents recruitment of RPA to nuclear foci after DNA damage. This leads to failure to recruit repair proteins such as Rad51 or Rad9, explaining why LT prevents repair of double strand DNA breaks by homologous recombination. PMID: 24204272
- these results suggest that the PSO4 complex functionally interacts with RPA and plays an important role in the DNA damage response. PMID: 24443570
- the current understanding of RPA's roles in replication by reviewing the available structural data, DNA-binding properties, interactions with various replication proteins, and interactions with DNA repair proteins when DNA replication is stalled. PMID: 22918586
- ATR-mediated suppression of dormant origins shields active forks against irreversible breakage via preventing exhaustion of nuclear RPA. This study elucidates how replicating genomes avoid destabilizing DNA damage. PMID: 24267891
- Data suggest that replication protein A (RPA) brings a complex of SMARCAL1 and WRN to stalled forks, but that they may act in different pathways to promote fork repair and restart. PMID: 23671665
- Results reveal a mechanism for the crosstalk between HR repair and NHEJ through the co-regulation of p53-RPA interaction by DNA-PK, ATM and ATR. PMID: 22797063
- RPA is a cofactor of the BLM-Topo IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex in double holliday junction dissolution PMID: 23543748
- Depletion of RPA1 abolishes HSF1 access to the promoter of HSP70 in unstressed condition and delays its rapid activation in response to heat shock. PMID: 22940245
- In vitro analysis of the role of replication protein A (RPA) and RPA phosphorylation in ATR-mediated checkpoint signaling. PMID: 22948311
- The radiosensitizing effect of DPYD depletion plus CPT was the additive effect of DPYD depletion and CPT. PMID: 22510597
- Replication stress-induced recruitment of HDHB to chromatin is independent of checkpoint signaling but correlates with the level of replication protein A (RPA) recruited to chromatin. PMID: 22194613
- cells require different RPA functions in DNA replication and DNA repair. PMID: 22179778
- Study propose that RPA plays a role in the protection of the human genome cell from A3G and other deaminases when they are inadvertently diverged from their natural targets. PMID: 21935481
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Nucleus, PML body.
-
蛋白家族:Replication factor A protein 1 family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10289
OMIM: 179835
KEGG: hsa:6117
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000254719
UniGene: Hs.461925
Most popular with customers
-
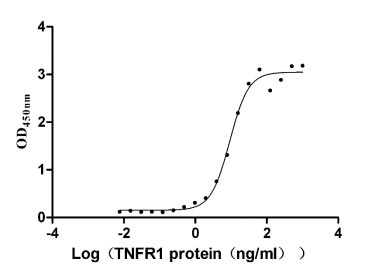
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
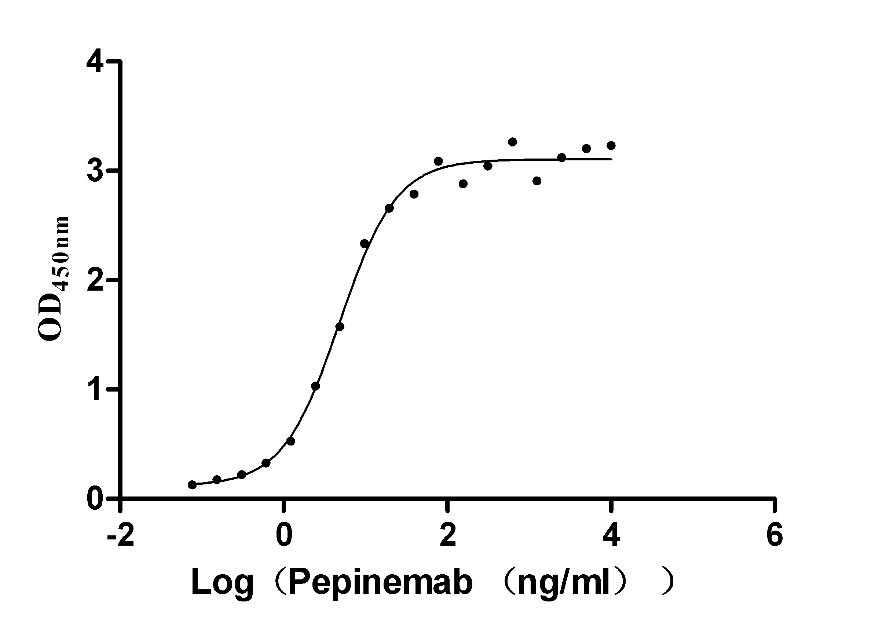
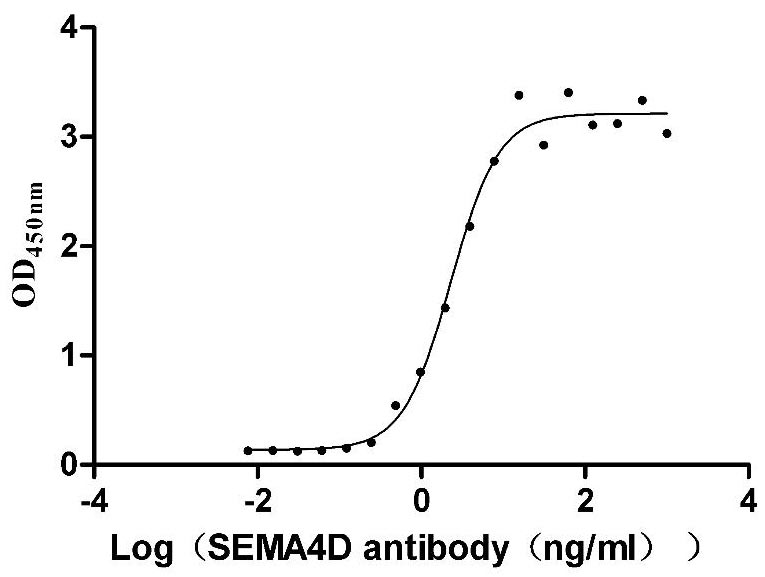
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
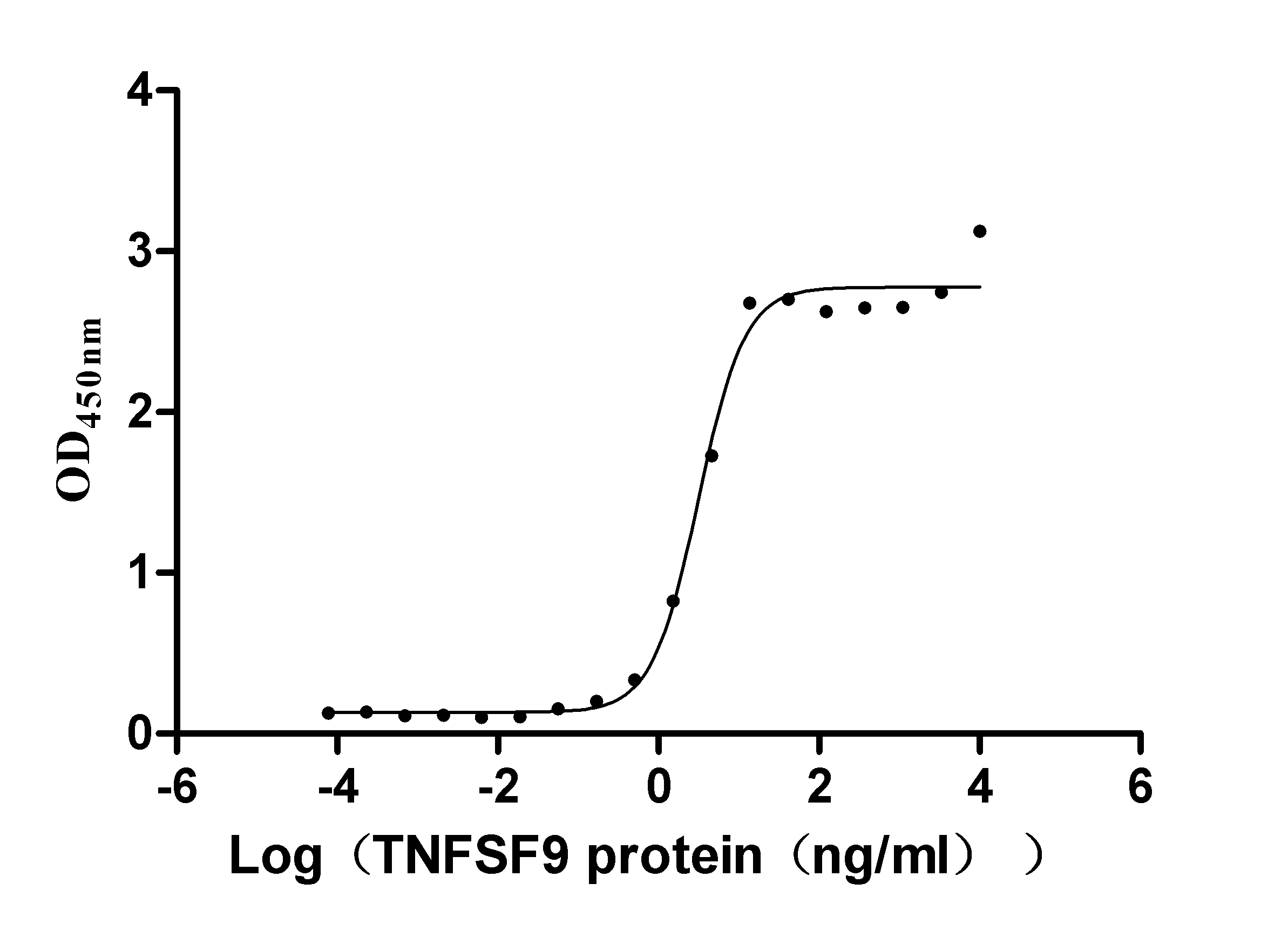
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
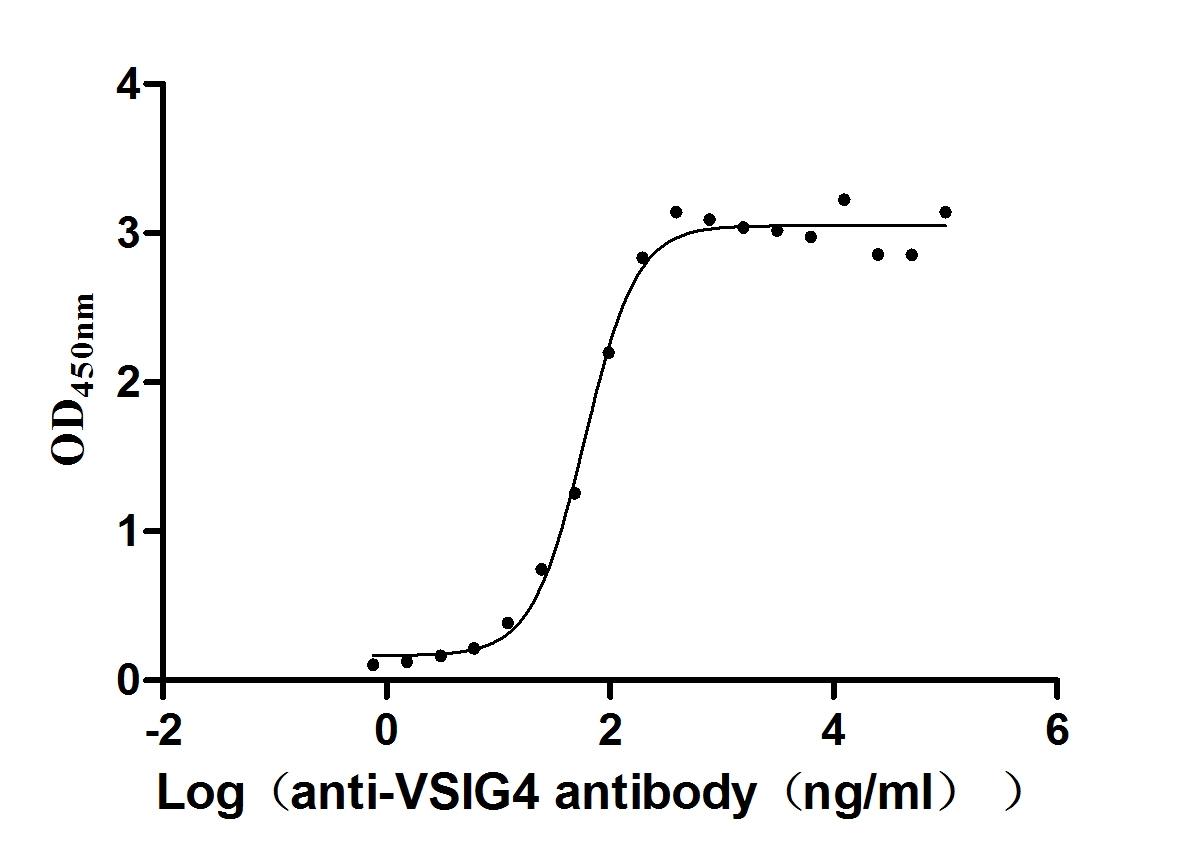
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
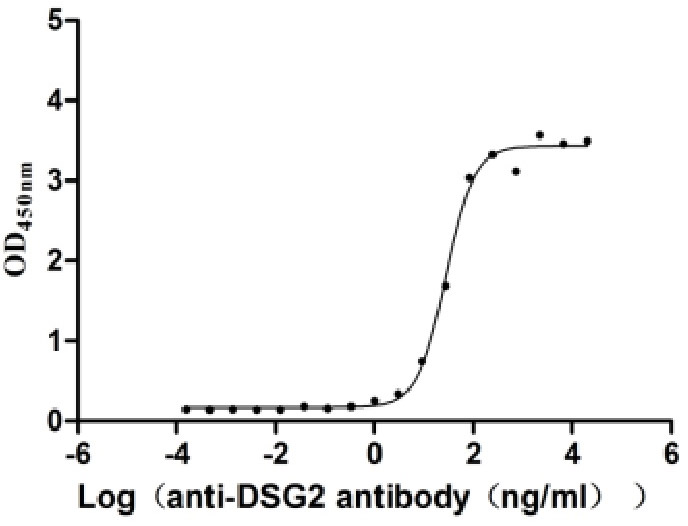
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
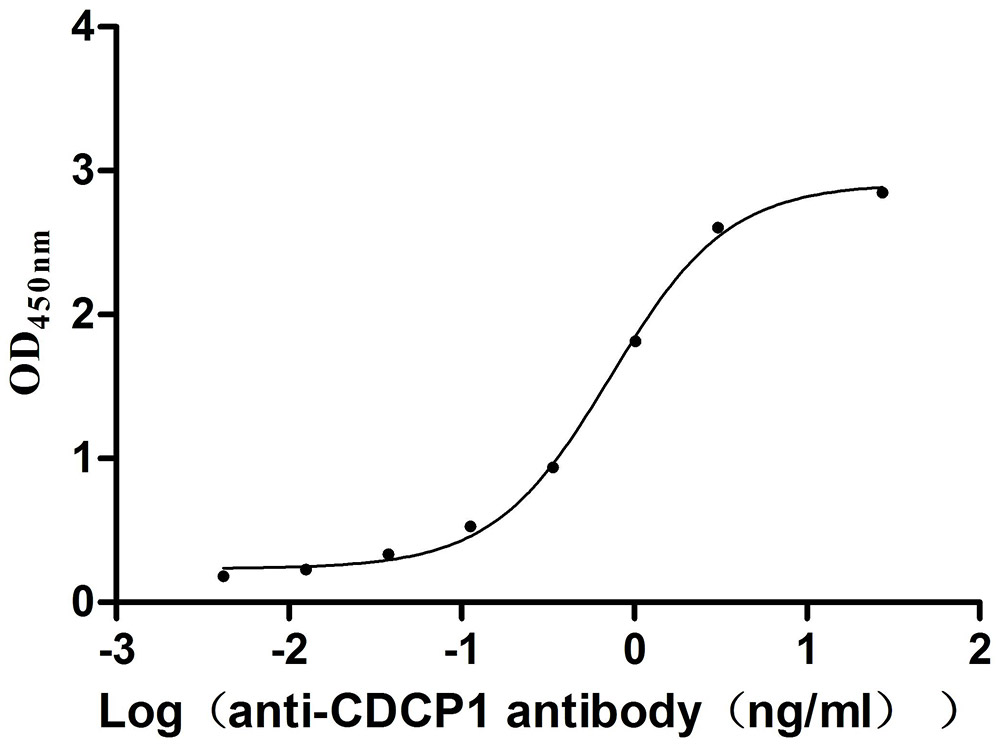
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
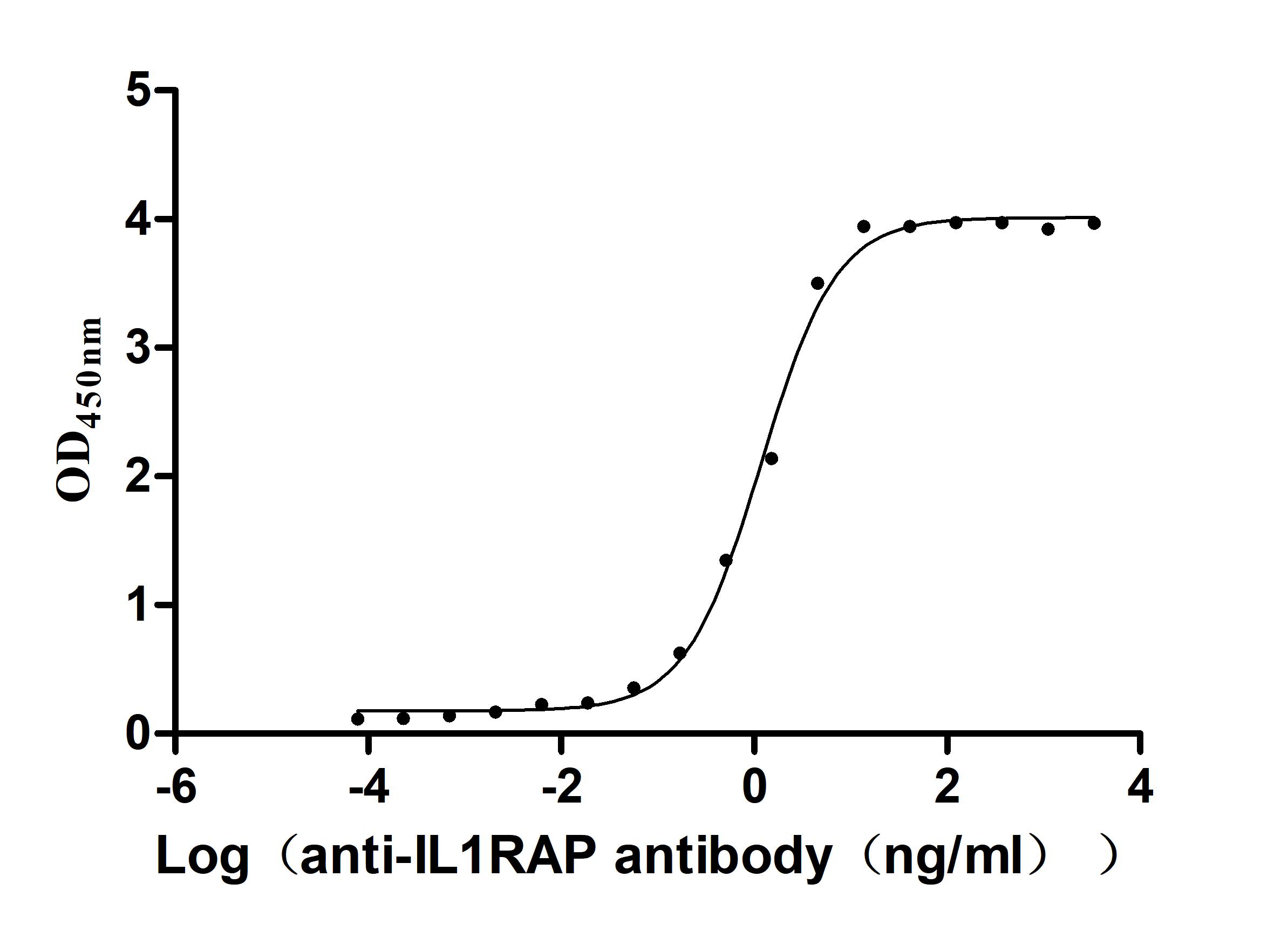
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)