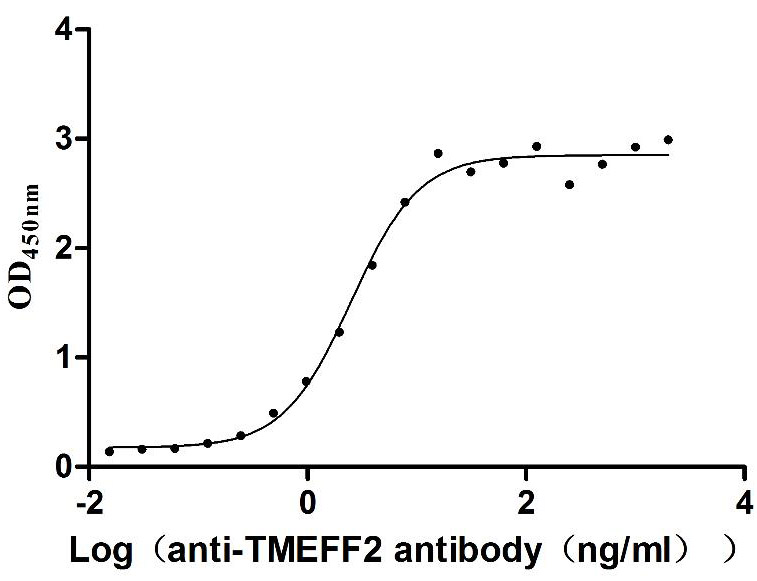
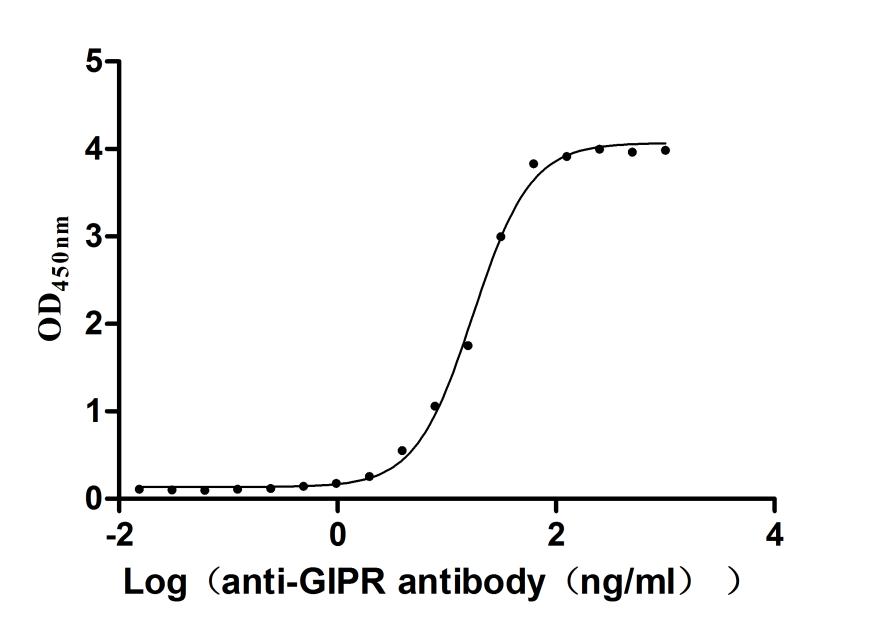
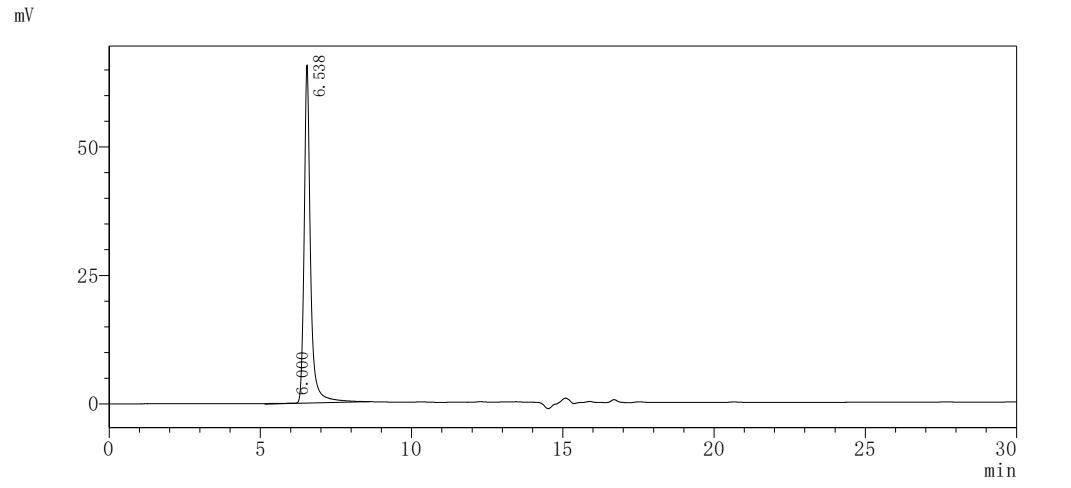
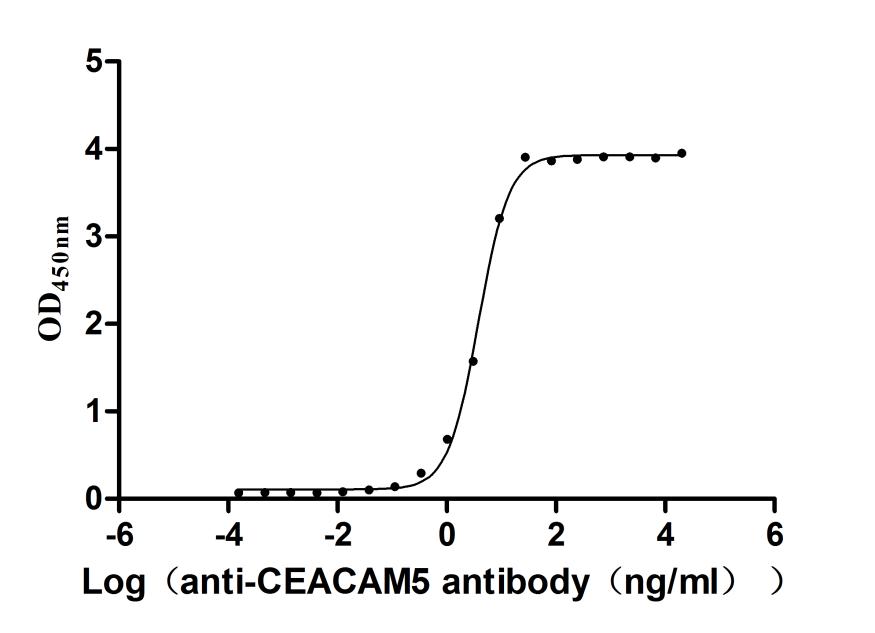
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP878942HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP878942HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP878942HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP878942HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:B7 H; B7 H1; B7 homolog 1; B7-H1; B7H; B7H1; CD 274; CD274; CD274 antigen; CD274 molecule; MGC142294; MGC142296; OTTHUMP00000021029 ; PD L1; PD-L1; PD1L1_HUMAN; PDCD1 ligand 1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1LG1; PDL 1; PDL1; Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1; Programmed death ligand 1; RGD1566211
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
表达区域:19-238
-
氨基酸序列FT VTVPKDLYVV EYGSNMTIEC KFPVEKQLDL AALIVYWEME DKNIIQFVHG EEDLKVQHSS YRQRARLLKD QLSLGNAALQ ITDVKLQDAG VYRCMISYGG ADYKRITVKV NAPYNKINQR ILVVDPVTSE HELTCQAEGY PKAEVIWTSS DHQVLSGKTT TTNSKREEKL FNVTSTLRIN TTTNEIFYCT FRRLDPEENH TAELVIPELP LAHPPNER
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response. Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10).; The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and escape destruction by the immune system, thereby facilitating tumor survival. The interaction with PDCD1/PD-1 inh...显示更多
-
基因功能参考文献:
- an HBV-pSTAT3-SALL4-miR-200c axis regulates PD-L1 causing T cell exhaustion PMID: 29593314
- hypothesized that an oncolytic poxvirus would attract T cells into the tumour, and induce PD-L1 expression in cancer and immune cells, leading to more susceptible targets for anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy PMID: 28345650
- multivariate Cox hazards regression analysis identified ALCAM and PD-L1 (both P < 0.01) as potential independent risk factors for primary diffuse pleural mesotheliomas PMID: 28811252
- miR-191-5p was identified to have negative correlation with PD-L1 expression and acted as an independent prognostic factor of OS in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. PMID: 30045644
- our findings suggest a regulatory mechanism of PD-L1 through data analysis, in vitro and vivo experiments, which is an important factor of immune evasion in GC cells, and CXCL9/10/11-CXCR3 could regulate PD-L1 expression through STAT and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways in GC cells. PMID: 29690901
- CD163(+)CD204(+) Tumor-associated macrophages possibly play a key role in the invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by T-cell regulation via IL-10 and PD-L1 production. PMID: 28496107
- Results demonstrated that the expression of PDL1 in colorectal carcinoma tissue was significantly increased compared with the paracancerous tissue. Blocking PDL1 can inhibit tumor growth by activating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells involved in the immune response. PMID: 30272332
- miR-574-3p was identified to potentially regulate PD-L1 expression in chordoma, which inversely correlated with PD-L1. Positive PD-L1 expression on tumor cells was associated with advanced stages and TILs infiltration, whereas decreased miR-574-3p level correlated with higher muscle invasion, more severe tumor necrosis and poor patient survival. PMID: 29051990
- PD-L1 expression was detected in 69% of cases of primary melanoma of the vulva PMID: 28914674
- PD-L1 tumor cell expression is strongly associated with increased HIF-2alpha expression and presence of dense lymphocytic infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PMID: 30144808
- Different Signaling Pathways in Regulating PD-L1 Expression in EGFR Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma PMID: 30454551
- PD-L1, Ki-67, and p53 staining individually had significant prognostic value for patients with stage II and III colorectal cancer PMID: 28782638
- Challenging PD-L1 expressing cytotoxic T cells as a predictor for response to immunotherapy in melanoma PMID: 30050132
- Our results confirm and extend prior studies of PD-L1 and provide new data of PD-L2 expression in lymphomas PMID: 29122656
- Positive PD-L1 expression is indicative of worse clinical outcome in Xp11.2 renal cell carcinoma. PMID: 28522811
- PD-L1 expression in cancer cells is upregulated in response to DNA double-strand break. PMID: 29170499
- Targeting PD-L1 Protein is an efficient anti-cancer immunotherapy strategy. (Review) PMID: 30264678
- Suggest that PD-L1 may play a relevant role in metastatic spread and may be a candidate prognostic biomarker in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 29742559
- PD-L1 immunostaining scoring for non-small cell lung cancer based on immunosurveillance parameters. PMID: 29874226
- SLC18A1 might complement other biomarkers currently under study in relation to programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death protein ligand 1 inhibition PMID: 30194079
- Low PDL1 expression is associated with mammary and extra-mammary Paget disease. PMID: 29943071
- Low PDL1 mRNA expression is associated with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. PMID: 29150702
- we found that in advanced stage NSCLC patients who received nivolumab, the C allele of PD-L1 rs4143815 and the G allele of rs2282055 were significantly associated with better ORR and PFS. This is the first report that PD-L1 SNP, which was thought to increase PD-L1 expression, is associated with a response to nivolumab. PMID: 28332580
- PD-L1 expression differs between the two components of lung ASCs. Given the complexity of lung ASCs, their treatment outcomes may be improved by administration of both EGFR TKIs and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in cases where EGFR mutations are present and PD-L1 is overexpressed. PMID: 28387300
- IDO and B7-H1 expressions were observed in patients with pancreatic carcinoma tissues and are important markers for PC malignant progression PMID: 30029936
- There was higher programmed cell death protein ligand-1(PD-L1) expression in post-treatment EBV DNA-positive patients. Post-treatment positive EBV DNA status maybe a useful biomarker of worse outcomes in early stage -stage extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma. PMID: 30116872
- PD-L1 is a critical TTP-regulated factor that contributes to inhibiting antitumor immunity. PMID: 29936792
- Structural and functional analyses unexpectedly reveal an N-terminal loop outside the IgV domain of PD-1. This loop is not involved in recognition of PD-L1 but dominates binding to nivolumab, whereas N-glycosylation is not involved in binding at all. PMID: 28165004
- While mutational analysis appeared similar to that of older patients with OCSCC who lack a smoking history, a comparatively high degree of PD-L1 expression and PD-1/L1 concordance (P=0.001) was found among young female OCSCC patients. PMID: 28969885
- PD-L1 expression is predictive of survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, irrespective of rituximab treatment. PMID: 29748856
- PD-L1 expression was augmented on CD8+ T cells in BALF of a patient with smoldering adult T-cell lymphoma and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. This suggested that the PD-1-PD-L1 system may suppress not only antitumor immunity but also host defense against pathogens and thereby allow establishment of chronic HTLV-1 infection and immunodeficiency. PMID: 28967040
- MUC1 drives PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer cells. PMID: 29263152
- Positive PD-L1 expression was found in 36.8% of inflammatory breast carcinoma (IBC) samples but was not significantly associated with the clinicopathologic variables examined. Worse overall survival (OS) was significantly associated with positive PD-L1, negative estrogen receptor, and triple-negative status. The 5-year OS rate was 36.4% for patients with PD-L1-positive IBC and 47.3% for those with PD-L1-negative. PMID: 29425258
- PD-L1 expression display a highly variable distribution in clear cell renal cell carcinomas and this particularity should be kept in mind when selecting the tumor samples to be tested for immunotherapy. PMID: 29661736
- Report relatively low level PD-L1 positivity in treatment-naive acinar prostatic adenocarcinoma. PMID: 30257853
- High PD-L1 expression is associated with pulmonary metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 29937180
- these data suggest that DNA-damage signaling is insufficient for upregulating PD-L1 in normal human dermal fibroblasts PMID: 29859207
- High CD274 expression is associated with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PMID: 28669079
- This study provides important evidence of higher levels of agreement of PD-L1 expression in pulmonary metastasis compared with in multiple primary lung cancer, and high positivity of PD-L1 expression in pulmonary metastatic lesions with wild-type EGFR in an Asian population. PMID: 29254651
- High PD-L1 expression is associated with Mycobacterium avium complex-induced lung disease. PMID: 28169347
- PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated immune cells may be associated with a higher probability of clinical response to avelumab in metastatic breast cancer PMID: 29063313
- The expression of PDL1 was significantly increased following treatment with gefitinib. PMID: 29901173
- These results demonstrated that the IFNGinduced immunosuppressive properties of B7H1 in human BM and WJMSCs were mediated by STAT1 signaling, and not by PI3K/RACalpha serine/threonineprotein kinase signaling PMID: 29901104
- PD-1/PD-L1 expression is a frequent occurrence in poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas of the digestive system. PMID: 29037958
- High CD274 expression is associated with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. PMID: 30275195
- Studied expression levels of CD274 molecule (PD-L1) in thymic epithelial tumors. Found PD-L1 expression level correlated with the degree of TET malignancy. PMID: 29850538
- s assessed PD-L1 expression in both tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells in the tumor specimens (complete histological sections, not tissue microarray). PMID: 28420659
- We conclude that a subgroup of advanced disease ovarian cancer patients with high grade tumors, expressing PD-L1, may be prime candidates for immunotherapy targeting PD-1 signaling PMID: 29843813
- PD-L1 expression is a prognostic factor related with poor survival among patients that developed non-small cell lung cancer. PMID: 29614306
- The inhibition of PTEN also reduced the cancer effects of CD4+ T cells on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines following miR-142-5p downregulation. Therefore, our study demonstrated that miR-142-5p regulated CD4+ T cells in human NSCLC through PD-L1 expression via the PTEN pathway. PMID: 29767245
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Early endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Endomembrane system; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Immunoglobulin superfamily, BTN/MOG family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung. Weakly expressed in the thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Expressed on activated T- and B-cells, dendritic cells, keratinocytes and monocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 17635
OMIM: 605402
KEGG: hsa:29126
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000370989
UniGene: Hs.521989