Recombinant Human Phosphate-regulating neutral endopeptidase (PHEX), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP017896HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP017896HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP017896HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP017896HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP017896HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PHEX
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:PHEX; PEX; Phosphate-regulating neutral endopeptidase PHEX; Metalloendopeptidase homolog PEX; Vitamin D-resistant hypophosphatemic rickets protein; X-linked hypophosphatemia protein; HYP
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Peptidase that cleaves SIBLING (small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoprotein)-derived ASARM peptides, thus regulating their biological activity. Cleaves ASARM peptides between Ser and Glu or Asp residues. Regulates osteogenic cell differentiation and bone mineralization through the cleavage of the MEPE-derived ASARM peptide. Promotes dentin mineralization and renal phosphate reabsorption by cleaving DMP1- and MEPE-derived ASARM peptides. Inhibits the cleavage of MEPE by CTSB/cathepsin B thus preventing MEPE degradation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Nonsense mutation (p.E145*) in PHEX is involved in X-linked dominant hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 29858904
- Two novel variants of the PHEX gene were identified in two unrelated families with Xlinked dominant hypophosphatemic rickets by directly sequencing all 22 exon regions and intron/exon boundaries of the PHEX gene. PMID: 29393334
- genetic characteristics of 15 families with hereditary hypophosphatemia: Novel Mutations in PHEX and SLC34A3 PMID: 29505567
- PHEX mutations are still the most common genetic defects in the Turkish population and were found in 12 of 14 patients with hypophosphataemic rickets PMID: 28383812
- dentification of the PHEX mutation by whole exome sequencing has facilitated genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis for the family affected with hypophosphatemic rickets PMID: 28981921
- Expression and inactivation of osteopontin-degrading PHEX enzyme in squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 27270332
- The novel splicing mutation IVS21+2T>G of the PHEX geneis associated with X-linked hypophosphatemia. PMID: 28397222
- c.931dupC and IVS14+1G>A are two novel mutations of the PHEX gene and might be the new pathogenic mutations of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets PMID: 28506344
- Herpes simplex virus 1 blocks MAVS-Pex mediated early interferon-stimulated gene activation through VP16 to dampen the immediate early antiviral innate immunity signaling from peroxisomes. PMID: 28222744
- Mutation in the PHEX gene is associated with type 1 diabetes. PMID: 26894575
- the findings of this study provide new insight into the spectrum of PHEX mutations and provide potential evidence of a critical domain in PHEX protein. PMID: 27840894
- This report that mutations in PHEX are the most frequent cause of hypophosphatemic rickets PMID: 26051471
- Downregulation of PHEX may constitute an important early component of bone loss and joint damage in leprosy PMID: 26362198
- A new splice acceptor mutation was seen in intron 9 (c.1080-3C>A) in a family with hypophosphatemic rickets. This transcript skipped exons 10-14. A sporadic case had a new exon 11 mutation (c.1211_1215delACAAAinsTTTACAT, p.Asp404Valfs*5, de novo). PMID: 26107949
- Two novel mutations were detected unrelated families with hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 24836714
- PHEX c.*231A > G can masquerade as sporadic or X-linked recessive HR. PMID: 25042154
- A novel de novo nonsense mutation of the PHEX gene has been identified in Chinese family expanding the mutation spectrum of PHEX leading to X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 25839938
- exon 22 is the mutation hot spot and missense mutation is the most common type of mutation in the PHEX gene in Chinese X-link dominate hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH) patients PMID: 24857004
- 15 PHEX mutations have been reported in Chinese populations with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets PMID: 23813354
- The c.732+1G>T mutation of PHEX is associated with hypophosphatasia pedigree. PMID: 24078575
- study shows that PHEX mutation is a common cause of either familial or sporadic hypophosphatemic rickets in Turkish population PMID: 23079138
- Mutations in PHEX and DMP1 play a role in causing hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 22695891
- PHEX gene mutations were responsible for X-linked hypophosphatemia in these Chinese families. PMID: 22713460
- Analysis of PHEX mRNA from peripheral blood would be appropriate for the first screening step in determining the etiology of FGF23-related hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 22577109
- PTHrP(1-34)-mediated repression of the PHEX gene in osteoblastic cells involves the transcriptional repressor E4BP4. PMID: 21826652
- Hypophosphatemic rickets (HR) is a rare hereditary disease in which dental problems in terms of spontaneous periapical infections are frequently reported PMID: 21902707
- tubular reabsorption of phosphate and 1,25(OH)2D serum levels are associated with PHEX mutation type in X-linked dominant Hypophosphatemic Rickets PMID: 21902834
- Novel PHEX nonsense mutation in a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets and review of current therapeutic regimens. PMID: 21553362
- Three novel mutations in the PHEX gene in Chinese subjects with hypophosphatemic rickets extends genotypic variability. PMID: 21293852
- Data show the wide spectrum of genetic variation that can be seen in PHEX, FGF23 and DMP1 when screening a large cohort with hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 21050253
- M. leprae is capable of inhibiting PHEX expression in osteoblasts in a very similar manner as that observed in Schwann cells, indicating that the bacillus modulates PHEX in both osteogenic and non-osteogenic cells. PMID: 20835608
- Case Report: describe a novel nonsense mutation in exon 3 of the PHEX gene (Glu(96)X (c.286G>T) causing X linked hypophosphatemic rickets in a mother and daughter of Indian ancestry. PMID: 20664300
- Cooperative role of NF-{kappa}B and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) in the TNF-induced inhibition of PHEX expression in osteoblasts. PMID: 20817730
- fibroblast growth factor-23 and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein sequences are potential PHEX substrates PMID: 12678920
- There is evidence for a hormone/enzyme/extracellular matrix protein cascade involving fibroblastic growth factor 23 (FGF23), a phosphate-regulating gene with homologies to (PHEX) and (MEPE)--REVIEW PMID: 12791601
- regulates fgf23 expression as part of a potential hormonal axis between bone and kidney that controls systemic phosphate homeostasis and mineralization PMID: 12874285
- Anthropometric characteristics arising from mutations of PHEX were evaluated. PMID: 15057978
- a cis-element is required for PHEX gene transcription that participates in negative feedback control of PHEX expression and thereby modulates the actions of phosphatonin PMID: 15337762
- In our present study, we found that suppression of PHEX expression by PHEX antisense in human osteoblast cells caused an increase in cathepsin D expression at protein, but not mRNA, levels. PMID: 15896324
- Overexpression of human PHEX under the human beta-actin promoter in hypophosphatemia mice rescued the bone phenotype almost completely, but did not affect phosphate homeostasis. PMID: 15940367
- seven PHEX mutations were detected in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets patients: two missense mutations, two nonsense mutations, and three short deletions; no functional FGF23 mutation was detected in any patient PMID: 16055933
- XLH is caused by mutations in the PHEX (phosphate regulating gene with homology to endopeptidases) gene, which is located on Xp22.1. PMID: 16437029
- Our data support previous findings and therefore contribute to the decipherment of the pathogenetic pathways of XLH. PMID: 17406123
- The results suggest that PHEX gene mutations were responsible for XLH in these patients and these mutations may contribute to a higher serum fibroblast growth factor 23 level. PMID: 18046499
- Skeletal disease tended to be more severe in the group with a mutation in the C-terminal half of the PHEX gene, but no genotype-phenotype correlation was detected in other comparisons. PMID: 18162710
- These data provide evidence that aberrant Phex function in osteoblasts and/or osteocytes alone is sufficient to underlie the hyp-mouse phenotype. PMID: 18172553
- mRNA of PHEX involved in the pathogenesis of hypophosphataemic rickets is highly expressed in cells of the osteoblasts/osteocyte lineage. PMID: 18214537
- Normal growth and muscle dysfunction in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets associated with a novel mutation in the PHEX gene. PMID: 18252791
- U(2)OS cells transfected with wild-type TNAP and polymorphism TNAP cDNA showed PHEX (phosphate-regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X chromosome) induction as in SaOS-2 cells. PMID: 18455459
- Data indicate that there is no single predominant PHEX mutation responsible for X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. PMID: 18625346
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Hypophosphatemic rickets, X-linked dominant (XLHR)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Peptidase M13 family
-
组织特异性:Specifically expressed in ovary. Expressed at low levels in kidney.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 8918
OMIM: 300550
KEGG: hsa:5251
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000368682
UniGene: Hs.495834
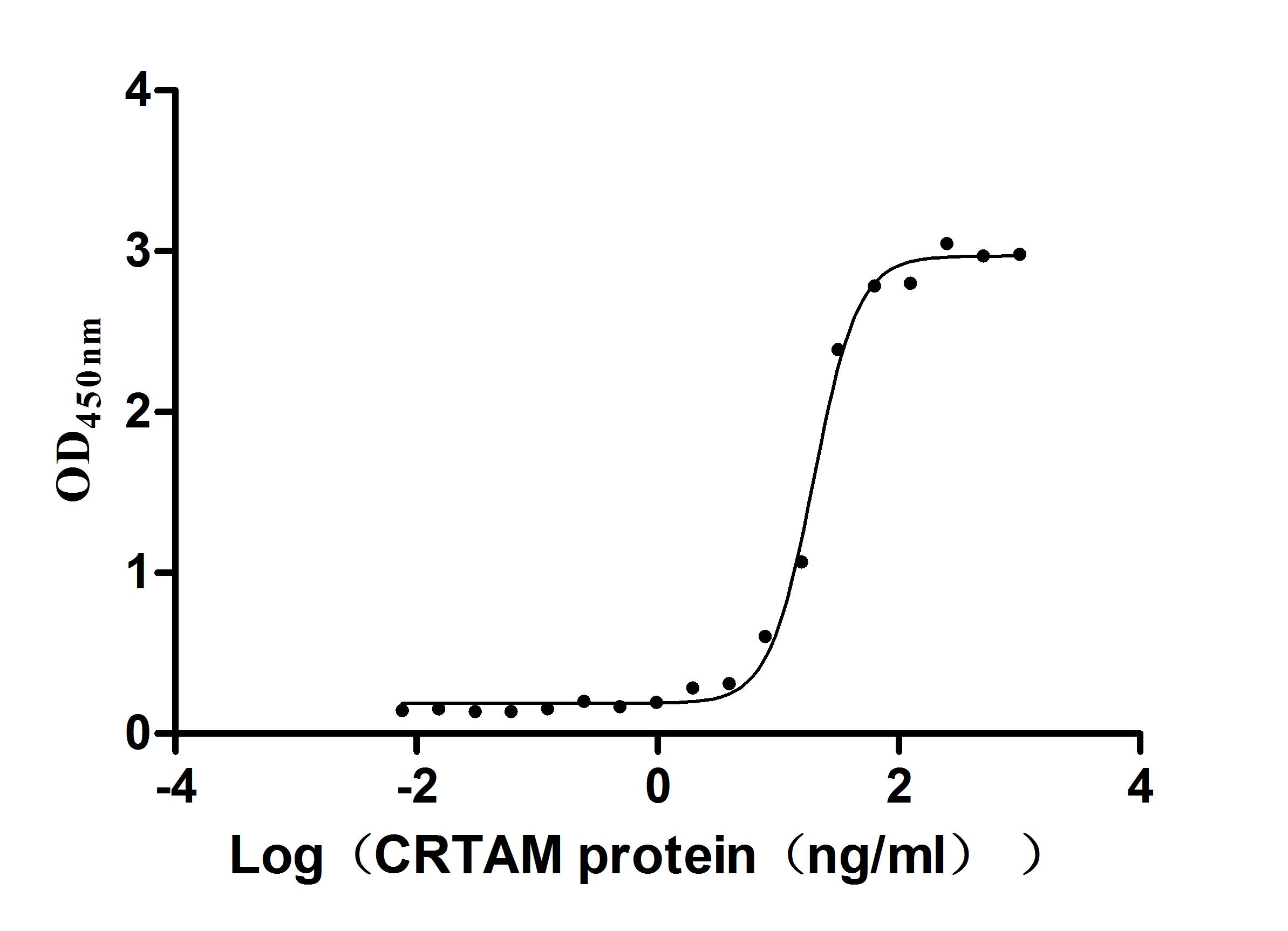
Most popular with customers
-
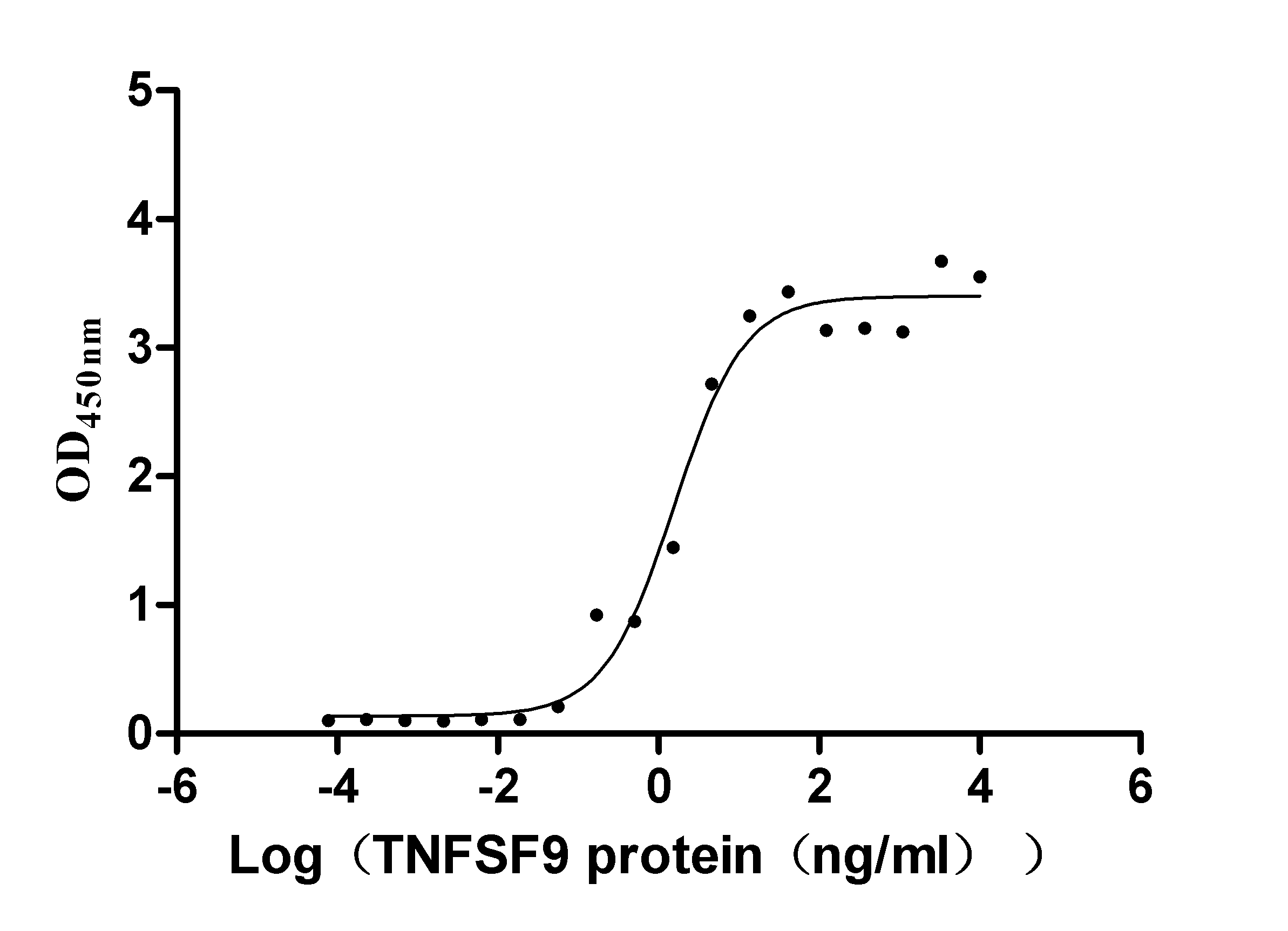
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
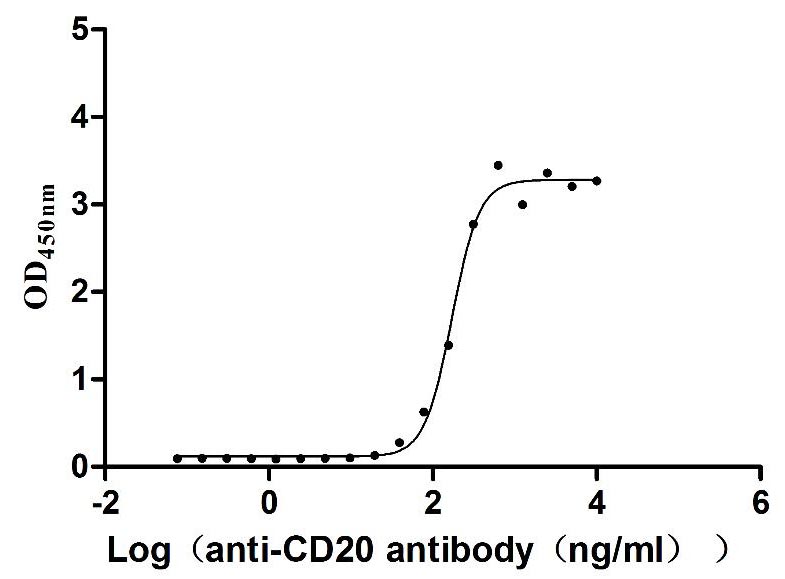
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
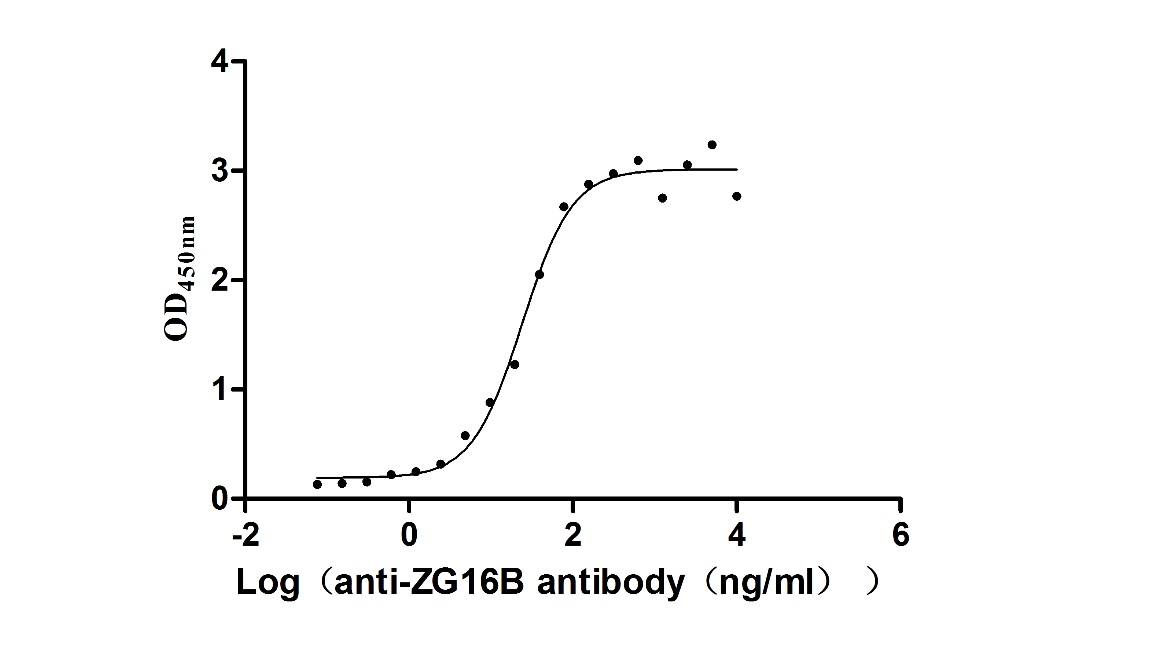
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
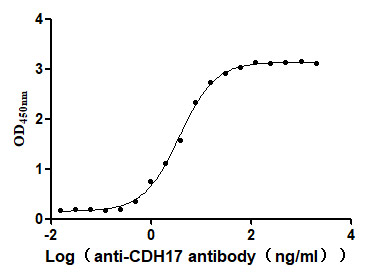
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
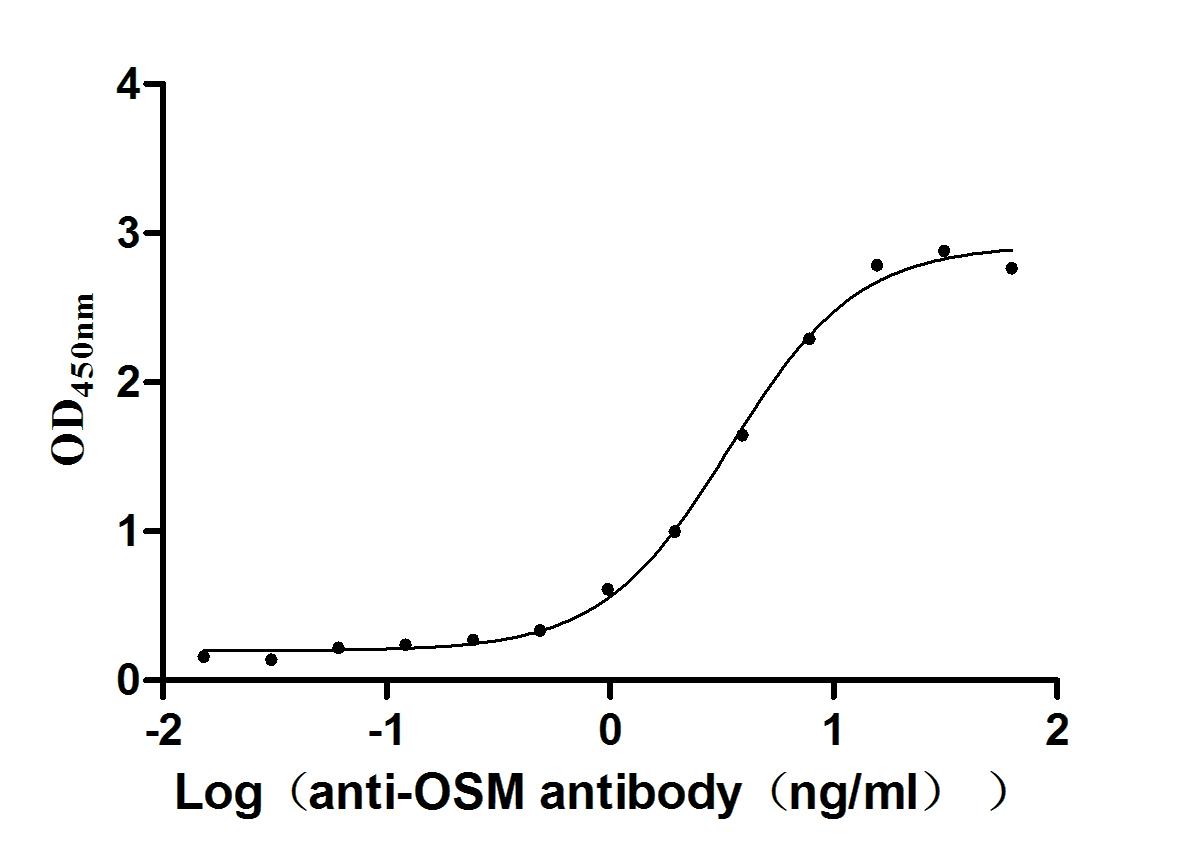
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)