Recombinant Human Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NFKB1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP015759HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP015759HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP015759HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP015759HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:DKFZp686C01211; DNA binding factor KBF1; DNA binding factor KBF1 EBP1; DNA-binding factor KBF1; EBP 1; EBP-1; EBP1; KBF1; MGC54151; nf b; NF kappa B; NF kappaB; NF kappabeta; NF kB1; NF-kappaB; NFkappaB; NFKB 1; NFKB p105; NFKB p50; NFKB-p105; Nfkb1; NFKB1_HUMAN; Nuclear factor kappa B DNA binding subunit; Nuclear factor kappa-B; Nuclear factor kappa-B, subunit 1; Nuclear factor NF kappa B p105 subunit; Nuclear factor NF kappa B p50 subunit; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit; Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells 1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1; p105; p50; p84/NF-kappa-B1 p98; Transcription factor NFKB1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- NF-kappaB signaling contributes to prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration via androgen receptor and estrogen receptor beta. PMID: 30236540
- PKC-delta isoform plays a crucial role in Tat-TLR4 signaling pathway to activate NF-kappaB and CXCL8 production. PMID: 28539656
- Knockdown of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (p16INK4A) in cardiac stem/progenitor cell (hCPC) reverses the senescent phenotype and has an antioxidant effect on aging hCPCs via NF-KAPPA B (NF-kB) signaling. PMID: 29675777
- Chandipura virus infection triggered the activation of signalling pathways mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases, including p38, JNK 1 and 2, and nuclear factor kappaB. PMID: 30001342
- TSPAN15 interacts with BTRC to promote oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via activating NF-kappaB signaling. PMID: 29650964
- FABP5 promotes lipolysis of lipid droplets, de novo fatty acid synthesis and activation of NF-kappaB signaling in cancer cells. PMID: 29906613
- Prognostic significance of NF-kappaB expression in non-small cell lung cancer PMID: 29813121
- LMP1 functions to constitutively activate NF-kappaB signalling during nasopharynx cancer pathogenesis. PMID: 28098136
- NF-kappaB signalling may repress ANT1 gene transcription and impair mitochondrial functions. PMID: 28317877
- High NFKB expression is associated with chemotherapeutic resistance in gastric cancer. PMID: 30106453
- PGF promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like changes in retinal pigment epithelium cells under hypoxia by activating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PMID: 29769799
- Data indicated that nestin regulated NF-kappa B (NF-kappaB) activity in foetal spinal cord tissues. PMID: 29697001
- NF-kappaB p50 and NF-kappaB p65 in thyroid carcinoma were positively associated with tumour diameter and the presence of lymph node metastasis PMID: 30014762
- This study establishes PML as an important regulator of NF-kappaB and demonstrates that PML-RARalpha dysregulates NF-kappaB. PMID: 28317833
- Notch signaling can initiate Asb2 transcription and NF-kappa B activation in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. PMID: 30116272
- High NFKB expression is associated with colorectal cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis PMID: 30015978
- These findings indicated that microRNA-98 could promote apoptosis of glioma cells via inhibiting inhibitor of kappa B kinase epsilon/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling and presented a novel regulatory pathway of microRNA-98 by direct suppression of inhibitor of kappa B kinase epsilon/nuclear factor-kappa B expression in glioma cells. PMID: 29333957
- Anti-rotavirus effect of TNF-alpha was achieved by NFkappaB-regulated genes via the activation of classical nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling. PMID: 29859235
- Knockdown of REG-GAMMA (REGgamma) may inhibit the proliferation and migration, and promote the apoptosis of plasma cell myeloma RPMI-8226 cells possibly by downregulating NF-kappa-B (NF-kappaB) signal pathway. PMID: 29020881
- L5-LDL, a naturally occurring mild oxidized LDL, induced G-CSF and GM-CSF production in human macrophages through LOX-1, ERK2, and NF-kappaB dependent pathways PMID: 29078142
- Priming cells with IFNbeta synergistically enhances IL6 induction in response to treatments that activate NF-kappaB, in a process that depends upon the recruitment of STAT2, IRF9. PMID: 29581268
- HMGB1 promoted lung cancer invasion and metastasis by upregulating the expression and activity of MMP-2 in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. PMID: 29850505
- NF-kappaB activation in breast cancer cells depends on the presence of the CHORDC1 gene product Morgana. PMID: 29158506
- Data suggest the angiopoietin-like 8 (ANGPTL8)/p62-IKKgamma axis as a negative feedback loop that regulates NF-kappaB activation, and extends the role of selective autophagy in fine-tuned inflammatory responses. PMID: 29255244
- Studied role of bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST2) in gastric cancer (GC); results show BST2 is overexpressed in GC tissues and BST2 silencing inhibits cell proliferation and migration, partly by regulating NF-kappaB signaling. PMID: 29774441
- vaspin decreased miR-33a levels, which in turn increased ABCA1 expression and cholesteorl efflux. PMID: 29653102
- these results define a tumor-supportive role for CDCA3. PMID: 29627567
- NFKB1 variants were significantly associated with type 2 diabetes PMID: 29601852
- NF-kappaB has been identified as the main transcription factor regulating the induction of inflammation-related genes in intracranial aneurysms lesions. This transcription factor has also been related to intracranial aneurysms rupture and resulting Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. [review] PMID: 29671828
- miR-150 predicts survival in patients with sepsis and inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory factors and apoptosis by targeting NF-kappaB1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PMID: 29689269
- These results illustrate an alternative mechanism of HIV-1 Vpr regulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) latency and aberrant cytokines through the miR-711/Notch/NF-kappaB axis. Our novel findings further demonstrate the role of an HIV-1-secreted regulatory protein in the KSHV life cycle and KSHV-related malignancies. PMID: 29976660
- In conclusion, HSP70 modulates NF-kappaB activation in alveolar macrophages of TB patients, through inhibiting IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation or acting as a chaperon molecule to prevent NF-kappaB binding to the target genes by facilitating degradation. The upregulated HSP70 may suppress the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines during active pulmonary tuberculosis infection, and prevent overwhelming tissue damage. PMID: 28450725
- Gene expression analyses show strong correlation between the cellular dynamic response and NF-kappaB-dependent target gene activation. PMID: 27381163
- NF-kappaB served as a positive transcriptional regulator of WIP1 to activate its expression and affect its function in colorectal cancer cells. PMID: 29367109
- Data do not support a role for the NFKB1 and HIF1A polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of bowel disease. PMID: 29307990
- a few seconds of exposure to TNF is sufficient to activate the NF-kappaB pathway in HeLa cells and induce apoptotic cell death in both HeLa and Kym-1 cells PMID: 28004761
- HMGB1 mediates fibroblast activity via RAGE-MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling in keloid scar formation. PMID: 29283384
- High NFKB expression is associated with glioma. PMID: 28534933
- NFkappaB1-94ins/ins genotype was associated with the risk of developing colorectal cancer in Egyptian subjects. PMID: 28389768
- miR-146 exerted protective functions might be via up-regulation of Sirt1 thereby blocking NF-kappaB and Notch pathways. PMID: 29229881
- Data suggest that environmental carcinogen PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) stimulates ovarian cancer cell migration, invasion, and MMP2/MMP9 expression by up-regulating ERK/NFkappaB signaling pathway. (MMP = matrix metallopeptidase; NFkappaB = nuclear factor kappa B) PMID: 29753068
- High NFKB expression is associated with KSHV infection. PMID: 29698475
- Significantly elevated blood levels of NFkappaB in myelodysplastic syndrome patients. PMID: 28856536
- These data indicate a process of NF-kappaB-induced miR-506 suppression and JAG1 upregulation upon IL-1beta induction. PMID: 28926924
- High Expressions of NFkappaB is associated with degenerative knee osteoarthritis. PMID: 28418842
- Inflammatory factors suppress microRNA-1275 transcription in human adipocytes through NF-kappaB. PMID: 28901460
- GSK-3beta is critically important for ordered NF-kappaB signalling through modulation of NEMO phosphorylation. PMID: 27929056
- results establish a role for the linear Ubiquitin coat around cytosolic S. Typhimurium as the local NF-kappaB signalling platform and provide insights into the function of OTULIN in NF-kappaB activation during bacterial pathogenesis PMID: 28481361
- the lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTbetaR) to elicit the fast release of NF-kappaB inducing kinase (NIK) from the receptor complex leading to non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling. PMID: 29329668
- Data demonstrate that S. Typhimurium attenuates NF-kappaB signaling in fibroblasts; this tune-down in a central host defense might be instrumental for S. Typhimurium to establish intracellular persistent infections PMID: 27575017
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Immunodeficiency, common variable, 12 (CVID12)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B).
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 7794
OMIM: 164011
KEGG: hsa:4790
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000226574
UniGene: Hs.618430
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
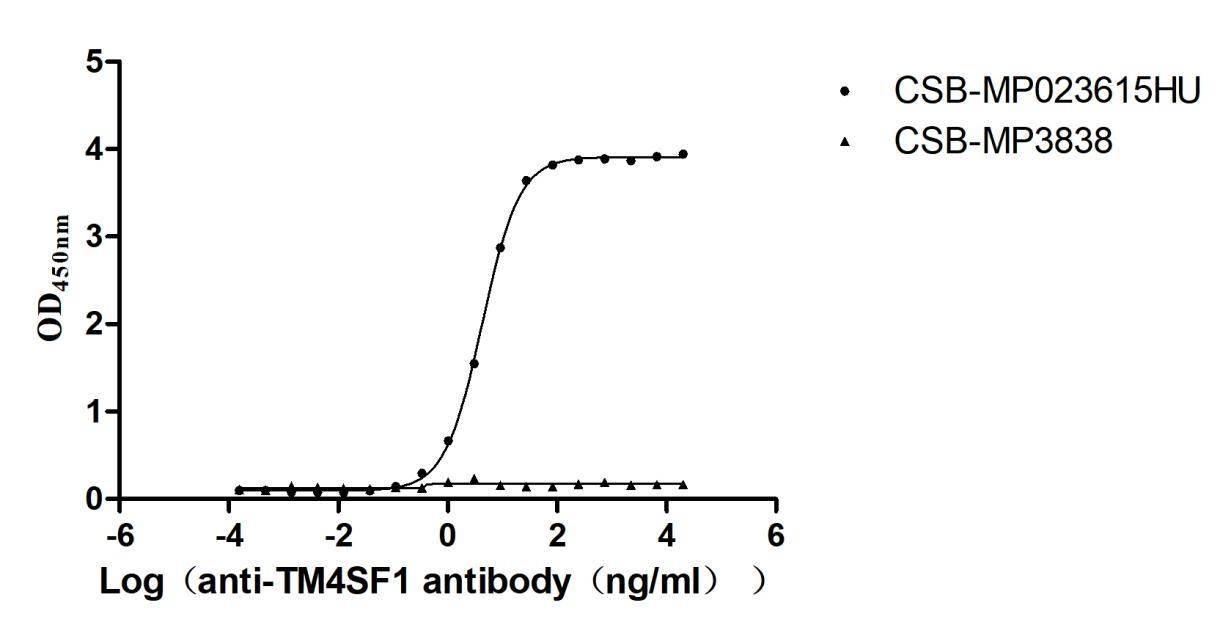
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)