Recombinant Human Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS)
-
货号:CSB-YP013493HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013493HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013493HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP013493HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP013493HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:80 kDa protein; 80K L; 80K L protein; 80K-L protein; 80KL; 81 kDa protein; light chain; light chain; MACS; MARCKS; MARCS; MARCS_HUMAN; MGC52672; myristoylated alanine rich C kinase substrate; Myristoylated alanine rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS; 80K L); Myristoylated alanine rich protein kinase C substrate; Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate; Phosphomyristin; PKCSL; PRKCSL; protein kinase C substrate 80 kDa protein light chain; Protein kinase C substrate
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-332
-
氨基酸序列GAQFSKTAA KGEAAAERPG EAAVASSPSK ANGQENGHVK VNGDASPAAA ESGAKEELQA NGSAPAADKE EPAAAGSGAA SPSAAEKGEP AAAAAPEAGA SPVEKEAPAE GEAAEPGSPT AAEGEAASAA SSTSSPKAED GATPSPSNET PKKKKKRFSF KKSFKLSGFS FKKNKKEAGE GGEAEAPAAE GGKDEAAGGA AAAAAEAGAA SGEQAAAPGE EAAAGEEGAA GGDPQEAKPQ EAAVAPEKPP ASDETKAAEE PSKVEEKKAE EAGASAAACE APSAAGPGAP PEQEAAPAEE PAAAAASSAC AAPSQEAQPE CSPEAPPAEA AE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:MARCKS is the most prominent cellular substrate for protein kinase C. This protein binds calmodulin, actin, and synapsin. MARCKS is a filamentous (F) actin cross-linking protein.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Raman spectra show vibrational bands of Phenylalanine and Lysine residues specific for the protein effector domain, and evidence the presence of alpha helix structure in both configurations. PMID: 28866462
- tromal MARCKS overexpression in tumors might contribute to cancer-associated fibroblasts activation and to the poor prognosis of Epithelial ovarian cancer. PMID: 29295532
- Study identifies MARCKS phosphorylation at Ser46 is a hallmark of neurite degeneration, the classical hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. MARCKS phosphorylation is induced by HMGB1 via TLR4. PMID: 27557632
- we propose a role for MARCKS in a novel mechanism of BTZ resistance via exocytosis of ubiquitinated proteins in BTZ-resistant cells leading to quenching of proteolytic stress. PMID: 27542283
- MARCKS overexpression might in part explain the poor prognosis of inflammatory breast cancer. PMID: 28009981
- s determined that myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) was highly expressed in ovarian stroma, and was required for the differentiation and tumor promoting function of CAFs. PMID: 27081703
- Data indicate MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate) as a target of miR-21. PMID: 27050372
- data suggest a major contribution of MARCKS to kidney cancer growth and provide an alternative therapeutic strategy of improving the efficacy of multikinase inhibitors. PMID: 28166200
- These data suggested that miR34c3p acts as a tumor suppressor via regulation of MARCKS expression in OS progression PMID: 28075441
- Ca(2+)-PKC-MARCKS-PIP2-PI3K-PIP3 system functions as an activation module in vitro PMID: 27119641
- Findings show that calmodulin (CaM) stimulates phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) lipid kinase activity by binding MARCKS and displacing it from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) headgroups, thereby releasing free PIP2 that recruits active PI3K to the membrane and serves as the substrate for the generation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). PMID: 27933776
- Findings suggest that MIR429 modulates mucin secretion in human colorectal cells and mouse colitis tissues by up-regulating of MARCKS expression. PMID: 26818658
- Knockdown of MARCKS in HepG2 cells reduced cell migration and invasion, but not cell proliferation. PMID: 26722462
- MARCKS upregulation increases vascular smooth muscle cell motility by activation of Rac1 and Cdc42, promoting neointima formation. PMID: 26450120
- A novel role for MARCKS in regulating nuclear functions such as gene expression. PMID: 26470026
- MARCKS knockdown arrested VSMC cell cycle by decreasing KIS expression. Decreased KIS expression resulted in nuclear trapping of p27kip1 in VSMCs. PMID: 26528715
- unresponsiveness of breast cancer to paclitaxel treatment is, at least in part, mediated by phospho-MARCKS PMID: 26015406
- MARCKS and PPP1R9A might contribute to spine loss in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder through their interactions. PMID: 25757715
- isotype delta-PKC is responsible for myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) phosphorylation in human neutrophils following f-Met-Leu-Phe stimulation and MARCKS phosphorylation is essential for neutrophil migration and adhesion. PMID: 25515270
- A key role of the effector domain of MARCKS in terms of cellular response, particularly to radiation: the importance of MARCKS phosphorylation status for its subcellular localization in lung cancer. PMID: 25524703
- MARCKS overexpression was observed in several drug-resistant human myeloma cell lines and in drug-resistant primary multiple myeloma samples. PMID: 25179733
- Finding that MARCKS acts as a mediator of apoptosis in microsatellite stable colorectal cancer cells adds a novel tumor-suppressing function to the established roles of MARCKS in cell motility and proliferation. PMID: 24662837
- results suggest a key role for MARCKS PSD in cancer disease and provide a unique strategy for inhibiting the activity of MARCKS PSD as a treatment for lung cancer. PMID: 25318062
- decreased MARCKS and pMARCKS in the frontal cortex in schizophrenia was found; results suggest a mechanism other than myristoylation was responsible for decreased MARCKS expression in schizophrenia PMID: 24568864
- MARCKS may represent a potential biomarker for the prognosis of primary lung SCC. PMID: 24240590
- Phospho-MARCKS, a post-translational modification, is associated with cell motility, and has a role in the regulation of cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis. PMID: 24735036
- MARCKS is a negative modulator of the acrosomal exocytosis. PMID: 23704996
- High MARCKS expression is associated with therapeutic responsiveness in breast cancer. PMID: 23876235
- MARCKS plays an articulated role in the progression of colorectal cancer PMID: 23376641
- heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and cysteine string protein (CSP), associate with MARCKS in the secretory mechanism in bronchial epithelial cells PMID: 23377348
- Cleavage ofMARCKS by Calpain may have an important role in regulation of the PKC/MARCKS pathway regulating airway mucin secretion PMID: 22710197
- These findings implicate that MARCKS is essential for proper cytokinesis and that MARCKS and its partner actin are key mitotic regulators during cell cycle in human hepatic stellate cells. PMID: 22555845
- a critical role for H(2)O(2) in angiotensin-II signaling to the endothelial cytoskeleton in a novel pathway that is critically dependent on MARCKS, Rac1, and c-Abl. PMID: 22773836
- Relative mRNA expression of MARCKS in white blood cells of O. viverrini-infected patients was higher than in healthy subjects; thus, MARCKS is expressed in macrophages and plays a role in inflammation-related cholangiocarcinoma induced by O. viverrini. PMID: 21763456
- BK promotes neurite outgrowth through transient MARCKS phosphorylation involving the PKC-dependent RhoA/ROCK pathway and PP2A in a neuroblastoma cell line. PMID: 21448919
- MARCKS and related chaperones bind to unconventional myosin V isoforms in airway epithelial cells PMID: 20203291
- reducing MRP expression promotes formation of adherens junctions in EpRas cells, allowing collective cell migration, but interferes with oncogenic beta-catenin signaling and tumorigenesis PMID: 19924305
- MARCKS, via its myristoylated aminoterminus, is a key regulator of neutrophil migration and adhesion. PMID: 19574534
- role for MARCKS as one of the key players in the migration of CCA cells and suggest that cycling between MARCKS and pMARCKS can regulate the metastasis of biliary cancer cells. PMID: 20047593
- Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) sequesters spin-labeled phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in lipid bilayers. PMID: 11825894
- role in interaction with calmodulin PMID: 14506265
- MARCKS proteolysis is necessary for the fusion of myoblasts. PMID: 15239673
- MARCKS-mediated neurotensin release occurs via protein kinase C-delta downstream of the Rho/ROK pathwaymediated neurotensin release occurs via protein kinase C-delta downstream of the Rho/ROK pathway PMID: 15623535
- elevations in MARCKS expression are detrimental to specific aspects of hippocampal function PMID: 15889447
- These findings suggest that some PDBu-induced MARCKS phosphorylation includes the RhoA/ROCK pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. PMID: 16677610
- Results suggest that unphosphorylated MARCKS is involved in neurite initiation, and highlight the important role played by MARCKS in organization of the actin cytoskeleton. PMID: 16941482
- We suggest that the downregulation of MRP by beta3 is not required for increased cell spreading but instead that MRP downregulation is a secondary effect of increased cell spreading. PMID: 17292354
- PKC delta plays an important role in mucin secretion by airway epithelium via regulation of MARCKS phosphorylation. PMID: 18055557
- First evidence that cysteine string protein and HSP70, and their interactions with MARCKS, are involved in mucin secretion from airway epithelium. PMID: 18314541
- The present study indicates that MARCKS play a major key role in PDGF-BB-induced chemotaxis in activated human hepatic stellate cells. PMID: 18329017
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:MARCKS family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6759
OMIM: 177061
KEGG: hsa:4082
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000357624
UniGene: Hs.519909
Most popular with customers
-
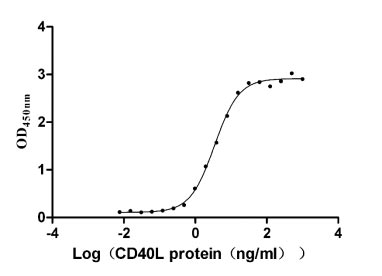
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Lymphotoxin-alpha (LTA) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
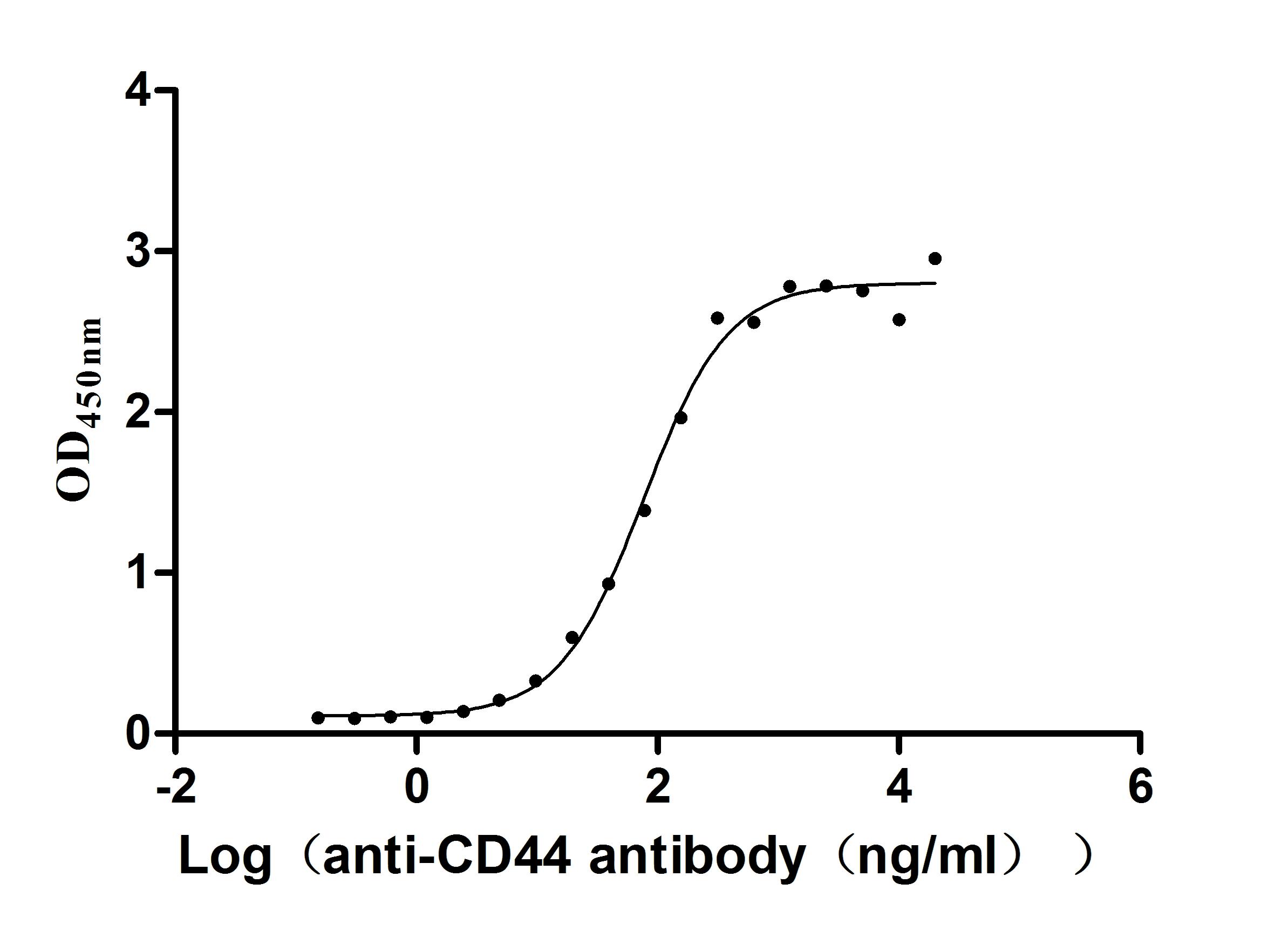
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
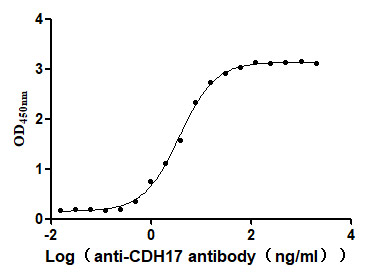
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
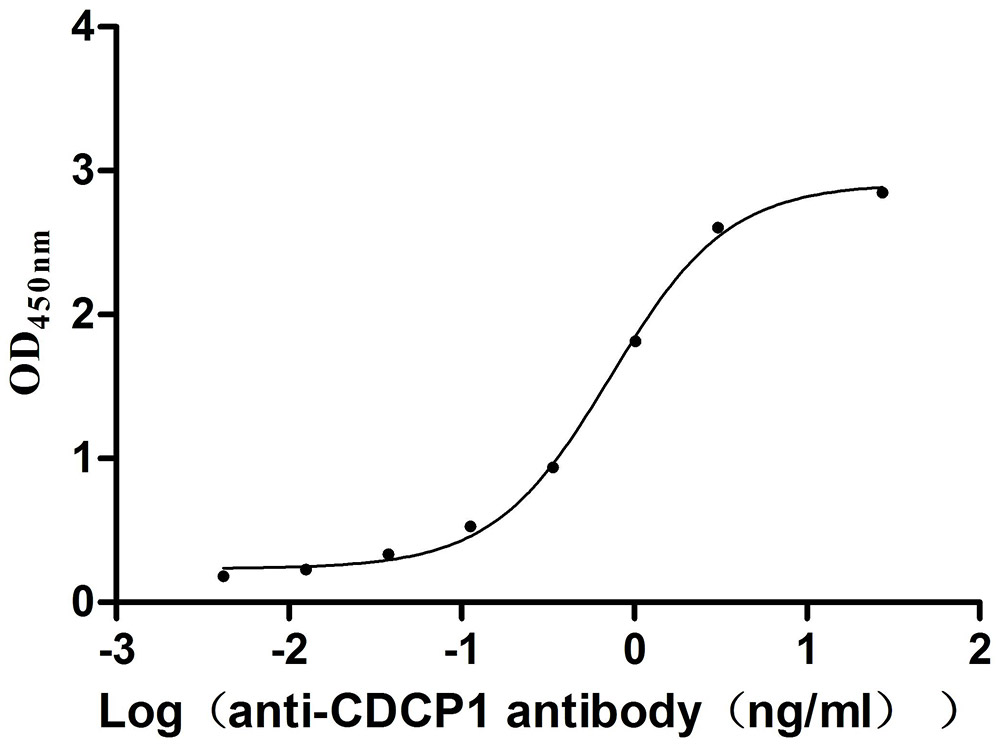
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)