Recombinant Human Metallothionein-1A (MT1A)
-
货号:CSB-YP015107HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP015107HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP015107HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP015107HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP015107HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:MT1A
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:CES 1; CES1; Metallothionein 1A; Metallothionein 1S; Metallothionein 2; Metallothionein 2A; Metallothionein IA; Metallothionein II; Metallothionein-1A; Metallothionein-IA; Metallothionein2; MGC32848; MT 1A; MT 2; MT 2A; MT IA; MT II; MT-1A; MT-IA; MT1; MT1A; MT1A_HUMAN; MT1S; MT2; MT2A; MTC
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-61
-
氨基酸序列MDPNCSCATG GSCTCTGSCK CKECKCTSCK KSCCSCCPMS CAKCAQGCIC KGASEKCSCC A
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Metallothioneins have a high content of cysteine residues that bind various heavy metals; these proteins are transcriptionally regulated by both heavy metals and glucocorticoids.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Full-length recombinant MT isoform 1a and it's isolated domain fragments were alkylated, changing protein conformation. PMID: 29518586
- MT1A is aberrantly silenced by DNA methylation of 5' MT1A CpG island in melanoma. PMID: 28764861
- Using a combination of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), circular dichroism (CD), and emission spectroscopy, this study reports that the Cu(i) to human apo-MT1A binding mechanism is highly pH-dependent. PMID: 28466911
- Disruption of metallothionein I and II genes in mouse produced viable mice with increased susceptibility to cadmium poisoning. PMID: 8290567
- Selective cysteine modification of metal-free human metallothionein 1a and its isolated domain fragments: Solution structural properties revealed via ESI-MS. PMID: 28187517
- blockade of metallothioneins 1 and 2 constitutes a promising approach for the treatment of conditions which result in muscle atrophy. PMID: 27956698
- Neonatal phthalate ester exposure induced placental MTs, FATP1 and HFABP mRNA expression PMID: 26867681
- The present study was undertaken to explore further the interrelationship between p53 and metallothioneins. PMID: 27049123
- MTF1 heads a hierarchy of zinc sensors, and through controlling the expression of a raft of metallothioneins and other key proteins involved in controlling intracellular zinc levels (e.g. ZnT1) alters zinc buffering capacity and total cellular zinc content. PMID: 26824222
- These results clearly suggest that MT-1 may be involved in AD pathogenesis. PMID: 26836194
- Zn(ii) and Cd(ii) metalation of the human MT1a takes place through two distinct pathways. PMID: 26583802
- We report on the competitive zinc metalation of apo-carbonic anhydrase [CA; metal-free CA (apo-CA)] in the presence of apo-metallothionein 1A domain fragments to identify domain specific determinants of zinc binding and zinc donation PMID: 26475450
- The Zinc and Cadmium exchange kinetics between human MT1A and carbonic anhydrase were examined using time-dependent electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. PMID: 26401817
- Modeling of the reactions showed that at both physiological (7.4) and acidic (5.8) pHs, zinc binding and cadmium exchanges occur essentially randomly between two MT1A fragments. PMID: 26167879
- Data indicate the calculated equilibrium zinc binding constants of each of the 7 zinc metallothionein 1A species ranged from a high of (log(KF)) 12.5 to a low of 11.8. PMID: 25208334
- Low MT1A expression is associateed with lung carcinogenesis. PMID: 23947958
- The metal-free, apo-alpha-MT also adopts a folded structure in the presence of the As(3+) even though there is no As(3+) bound. PMID: 24140052
- Increased metallothionein expression reflects steroid resistance in renal allograft recipients. PMID: 23763497
- Polymorphisms in the MT1A gene may influence excretion of urine uric acid and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine in chronic lead-exposed workers. PMID: 23429061
- MT-1A is epigenetically regulated by PU.1 during monocytic differentiation. PMID: 23501100
- During the titration with Zn(2+), the electrospray ionization mass spectrometry data show that several metalated species coexist until the fully saturated proteins are formed. PMID: 23506369
- MT1A rs11076161 was associated with B-Cd concentrations and Cd-induced kidney toxicity at high exposure levels. PMID: 22995156
- A positive correlation between MT and Ki-67 expression was observed for all the studied cases but was even stronger in the metatypic subtype of basal cell carcinoma. PMID: 23042264
- Variations in the ability of LAT1/DMT1/MTF1/MT1a to process and transport Hg may not play a significant role in the etiology of autism. PMID: 21798283
- Possible role of MT as a marker of cell stress and homeostasis restoration in Graves'disease. PMID: 22090273
- The expression of metallothioneins MT1A and MT1X was significantly downregulated during differentiation of Caco-2 cells treated with high levels of zinc. PMID: 21103883
- MT-1A, -1F, -1G, -1X and -2A isoforms are significantly down-regulated in proliferating keloid fibroblasts. PMID: 20812968
- Data show that MT-I + II and megalin are significantly altered in CNS lymphoma relative to controls. PMID: 20038220
- Metallothionein, potential interaction partner for ECRG2, might be involved in regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis and in various physiological processes. PMID: 12970870
- metallothionein measured in renal specimens from cadaver kidneys was restricted to tubular cells with no differences between controls and patients with death due to chronic diseases PMID: 15812196
- The overexpression of human MT1A gene dynamically affected cell viability, and the effect was influenced by zinc and cadmium ions. PMID: 16087360
- MT-II mRNA expression may be involved in cell proliferation in the livers of patients with chronic HCV infection. PMID: 16107899
- +647 MT1a genetic polymorphism may be essential for longevity in women. PMID: 16955215
- analysis of glial fibrillary acidic protein, metallothionein, and MHC II expression in human, rat and mouse cells PMID: 17008879
- The findings define a pathway for cellular metal acquisition. The results suggest a function of MT in intercellular communication. PMID: 17111383
- One biomarker which has recently shown to be expressed in various human tumors but still less reported in carcinoma is metallothionein. PMID: 17373731
- The partially metallated and metal-free metallothionein-1a species are stable intermediates and thus may have a potential role in the currently undefined function of metallothionein. PMID: 17388808
- The goals of this study were to define the expression of the isoforms of MT 1, 2, 3 at both mRNA and protein levels, in normal prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and malignant PC-3 cells. PMID: 18208603
- the association of the +647 A/C MT1A polymorphism with diabetes mellitus 2 and cardiovascular complications PMID: 18249147
- the interleukin-6 and metallothionein 1a genes act in a concerted manner to control zinc-regulated gene expression PMID: 18316168
- Metal exchange in metallothioneins: a novel structurally significant Cd(5) species in the alpha domain of MT1A. PMID: 18429853
- This study provides the necessary data establishing unambiguously the noncooperative nature of cadmium binding to both isolated domains and the combined beta-domains (beta-rhMT) of human MT-1a. PMID: 18533113
- Lupus nephritis is associated with significant alterations in renal MT-I+II expression. Important prognostic information can be deduced from the renal MT-I+II expression profile in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with nephritis. PMID: 18601746
- MT-IA mRNA expression in HPBLs may be used as a biomarker for renal dysfunction in occupational cadmium exposure. PMID: 19359654
- HIF-1alpha expression qualified as an independent prognostic and characterised an aggressive cancer phenotype associated with an increased expression of MT. PMID: 19529947
显示更多
收起更多
-
蛋白家族:Metallothionein superfamily, Type 1 family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 7393
OMIM: 156350
KEGG: hsa:4489
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000290705
UniGene: Hs.655199
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Glypican-3 (GPC3) (G537R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
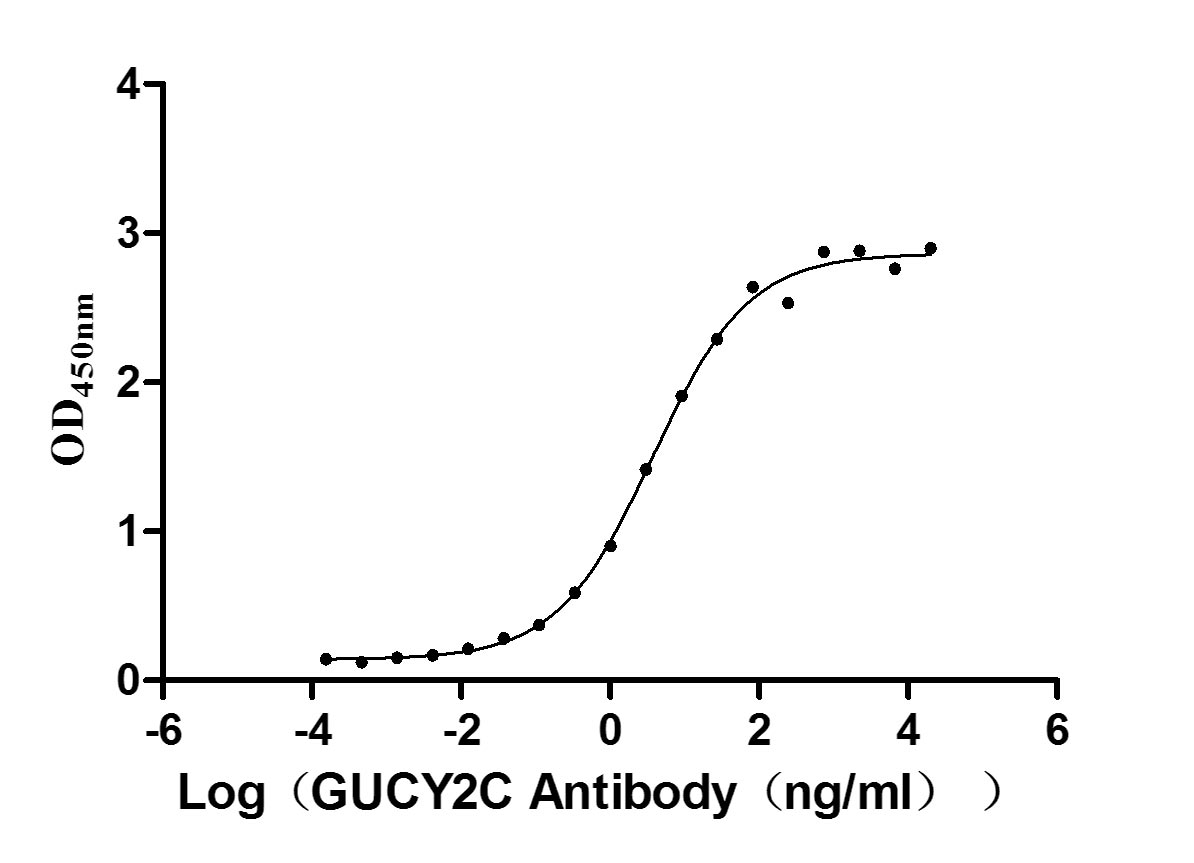
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
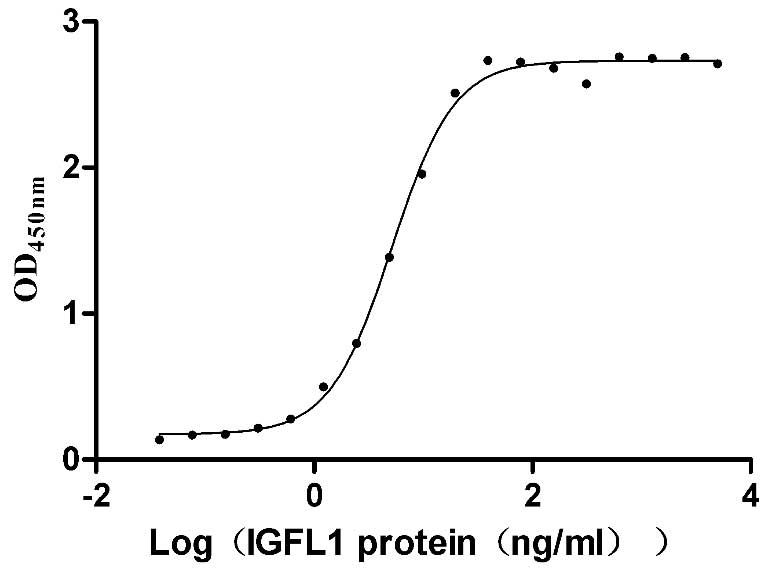
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
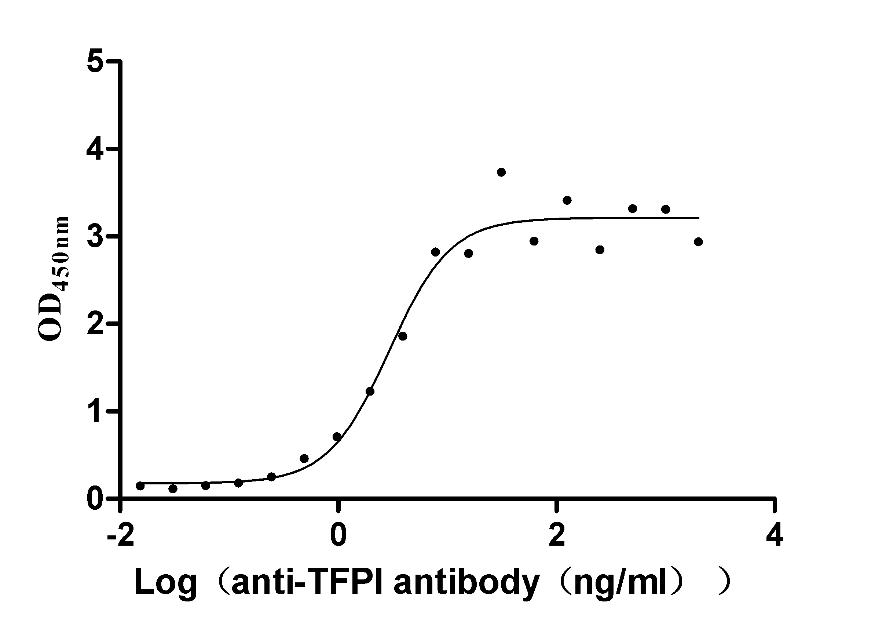
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
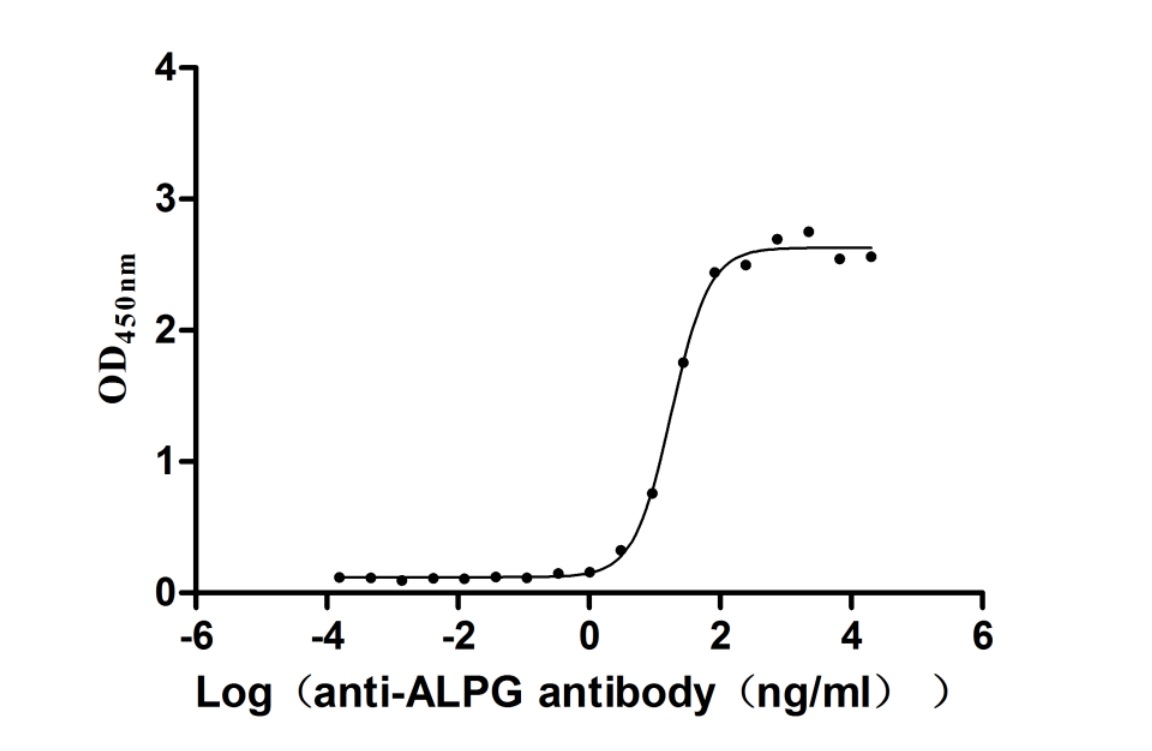
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
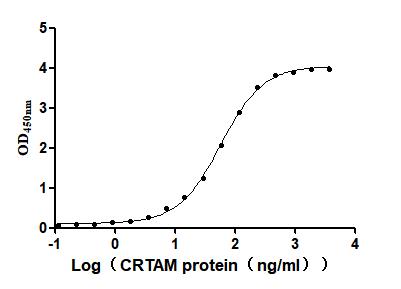
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
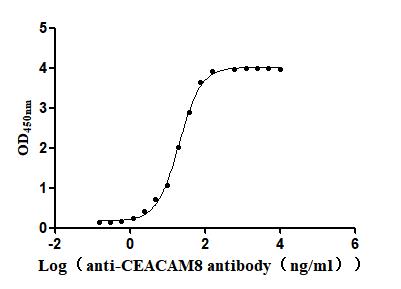
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
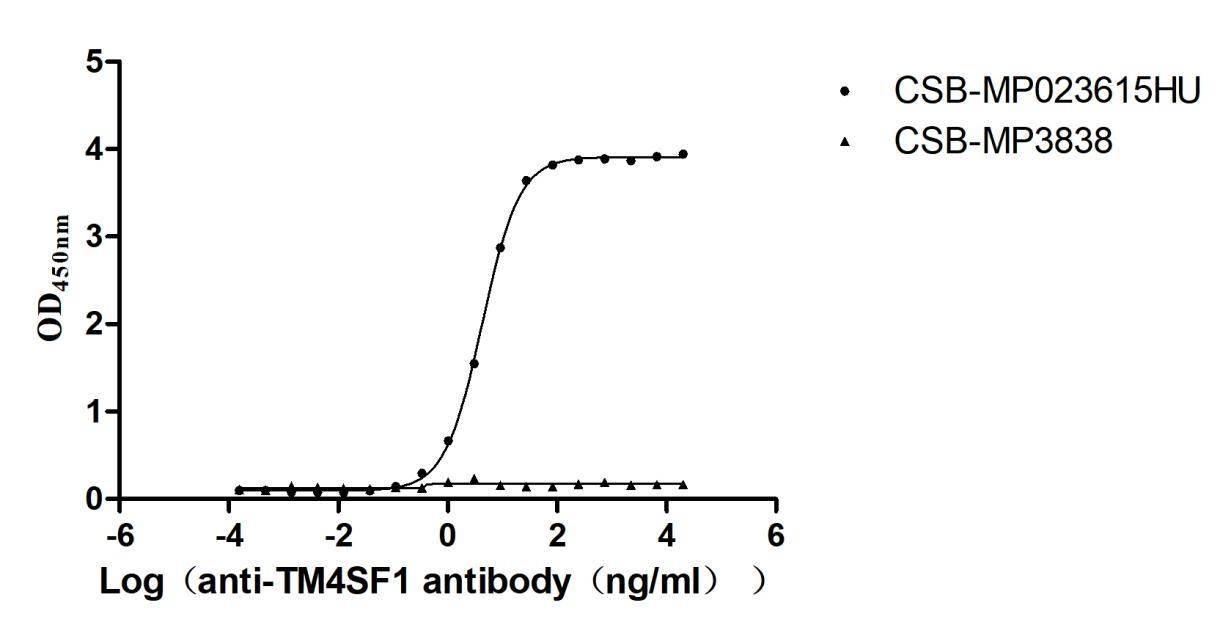
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)