Recombinant Human LIM homeobox transcription factor 1-beta (LMX1B)
-
货号:CSB-YP013019HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013019HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013019HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP013019HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP013019HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:LMX1B
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:LIM homeo box transcription factor 1 beta; LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta; LIM homeobox transcription factor 1-beta; LIM-homeobox protein 1.2; LIM/homeobox protein 1.2; LIM/homeobox protein LMX1B; LMX 1.2; LMX-1.2; LMX1.2; LMX1B; LMX1B_HUMAN; MGC138325; MGC142051; NPS 1; NPS1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-402
-
氨基酸序列MDIATGPESL ERCFPRGQTD CAKMLDGIKM EEHALRPGPA TLGVLLGSDC PHPAVCEGCQ RPISDRFLMR VNESSWHEEC LQCAACQQAL TTSCYFRDRK LYCKQDYQQL FAAKCSGCME KIAPTEFVMR ALECVYHLGC FCCCVCERQL RKGDEFVLKE GQLLCKGDYE KEKDLLSSVS PDESDSVKSE DEDGDMKPAK GQGSQSKGSG DDGKDPRRPK RPRTILTTQQ RRAFKASFEV SSKPCRKVRE TLAAETGLSV RVVQVWFQNQ RAKMKKLARR HQQQQEQQNS QRLGQEVLSS RMEGMMASYT PLAPPQQQIV AMEQSPYGSS DPFQQGLTPP QMPGDHMNPY GNDSIFHDID SDTSLTSLSD CFLGSSDVGS LQARVGNPID RLYSMQSSYF AS
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Essential for the specification of dorsal limb fate at both the zeugopodal and autopodal levels.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study reports two additional families with 18 affected individuals with nail patella-like renal disease (NPLRD). The predominant LMX1B mutation is the previously reported R246Q mutation. PMID: 28059119
- Study identified a novel heterozygous in-frame indel mutation of LMX1B in a family of Nail patella syndrome. PMID: 29290531
- 9q33.3q34.11 microdeletion including LMX1b gene identified in four patients with intellectual disability, epilepsy, nail dysplasia and bone malformations. PMID: 26395556
- Report progression of autosomal dominant renal-limited disease with LMX1B mutation. PMID: 26560070
- 38 different LMX1B polymorphisms have been found in 55 families with Nail-Patella Syndrome raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity. PMID: 25898926
- these results reveal a sustained and essential requirement of Lmx1b for the function of midbrain dopamine neurons PMID: 25915474
- A heterozygous microdeletion of the entire LMX1B gene using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) in a Chinese family with nail patella syndrome, is reported. PMID: 25380522
- Results demonstrate that loss of function may not be the only way that mutated LMX1b causes haploinsufficiency. Mutated LMX1b may interfere withdownsteam transcription events. PMID: 24720768
- In a large family with the two disorders with two novel frameshift TSC1 and LMX1B mutations, we describe the phenotypes PMID: 24477276
- LMX1B is a novel oncogene in ovarian cancer pathogenesis. PMID: 24056967
- this study identified two novel mutations of the LMX1B gene in three unrelated families with autosomaldominant Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and no extrarenal features. PMID: 23687361
- LMX1B is important in regulating type IV collagen gene expression in the GBM of the developing kidney and also has a likely role in regulating additional genes important in podocyte function and maintenance PMID: 23046462
- Data report on the association of LMX1B with autism, though it should be viewed with some caution considering the modest associations we report. PMID: 21901133
- c.194 A>C (Q65P) mutation is present in the LMX1B gene of the Chilean patients with nail-patella syndrome associated with glaucoma. PMID: 21850167
- effect of lmx1b on gene expression regulation in the brain PMID: 21246047
- The co-occurrence of nail-patella syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and major depressive disorder may be related to mesencephalic dopaminergic neurologic pathway abnormalities that are a consequence of LMX1B loss of function. PMID: 21184584
- Genetic variation in LMX1B may increase the risk of developing schizophrenia. PMID: 20570600
- LMX1B mutations is associated with Nail-Patella syndrome. PMID: 20531206
- novel mutations in patients with nail patella syndrome PMID: 11668639
- Transcriptional induction of slit diaphragm genes by Lmx1b is required in podocyte differentiation. PMID: 11956244
- The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Lmx1b plays a crucial role in podocytes PMID: 11956245
- Review. Lmx1b is a homeodomain transcription factor required for glomerular basement membrane collagen expression by podocytes. Its absence in nail-patella syndrome causes abnormalities in many organ systems. PMID: 11978876
- LMX1B 17-bp deletion and A3243G mtDNA transition in a previously described PMID: 12646768
- These findings indicate that heterozygous mutations of LMX1B do not appear to dramatically affect the expression of type IV collagen chains, podocin, or CD2AP in nail-patella syndrome patients. PMID: 12819019
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms in LMX1B gene is associated with nail dysplasia in the nail patella syndrome PMID: 15638822
- This is the first study indicating that family history of nephropathy and mutation location might be important in precipitating individual risks for developing NPS renal disease PMID: 15928687
- Pathogenic mechanism resulting from the mutation is presumably haploinsufficiency rather than a dominant negative effect, which would explain the clinical variability in this family. PMID: 17515884
- familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) heterozygote mutation and nail-patella syndrome (NPS) in 3 members of a family with no pathologic mutation in the LMX1B gene PMID: 17710881
- The detection of two entire LMX1B gene deletions and one smaller exonic LMX1B deletion by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), is described. PMID: 18414507
- study reports a novel LMX1B gene mutation c.368_369delTG, p.C123X in a Japanese girl with the typical nail changes of nail-patella syndrome; the proband's father carried the same mutation, although his fingernails were intact PMID: 18562181
- a mutation in the LMX1B gene causes nail-patella syndrome in a Chinese population PMID: 18595794
- Familial, genetic proved ((missense mutation -G599A (R200Q)of LMX1B gene))of nail patella syndrome in a mother and her son PMID: 18634531
- LMX1B haplotypes influence susceptibility to glaucoma in the general population, suggesting altered LMX1B function predisposes to glaucomatous damage and that this role may be independent of raised intraocular pressure. PMID: 18952915
- These data demonstrate for the first time that LMX1B directly regulates transcription of a subset of NF-kappaB target genes in cooperation with nuclear p50/p65 NF-kappaB. PMID: 18996370
- podocin is specifically regulated by the transcription factor Lmx1b and by the functional polymorphism -116C/T. PMID: 19562271
- A synonymous genetic alteration of LMX1B in a family with nail-patella syndrome. PMID: 19721866
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Nail-patella syndrome (NPS)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in most tissues. Highest levels in testis, thyroid, duodenum, skeletal muscle, and pancreatic islets.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6654
OMIM: 161200
KEGG: hsa:4010
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000347684
UniGene: Hs.129133
Most popular with customers
-
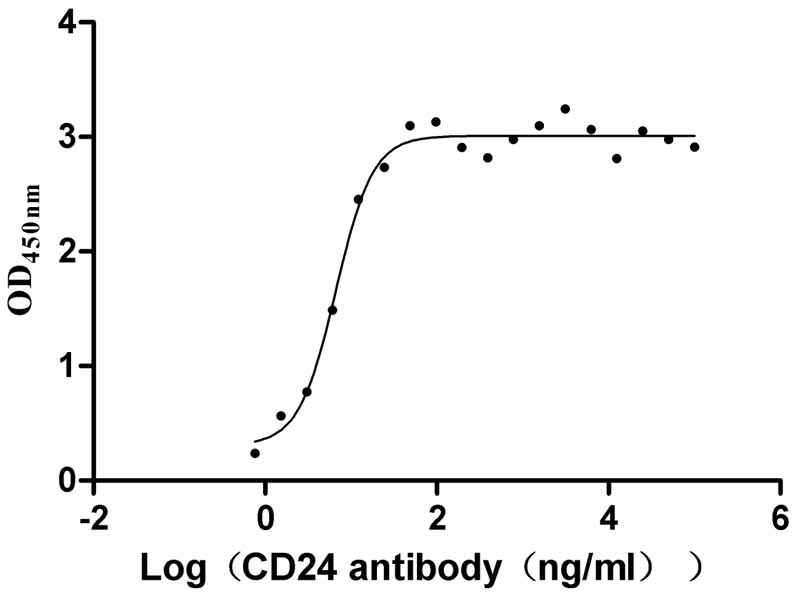
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
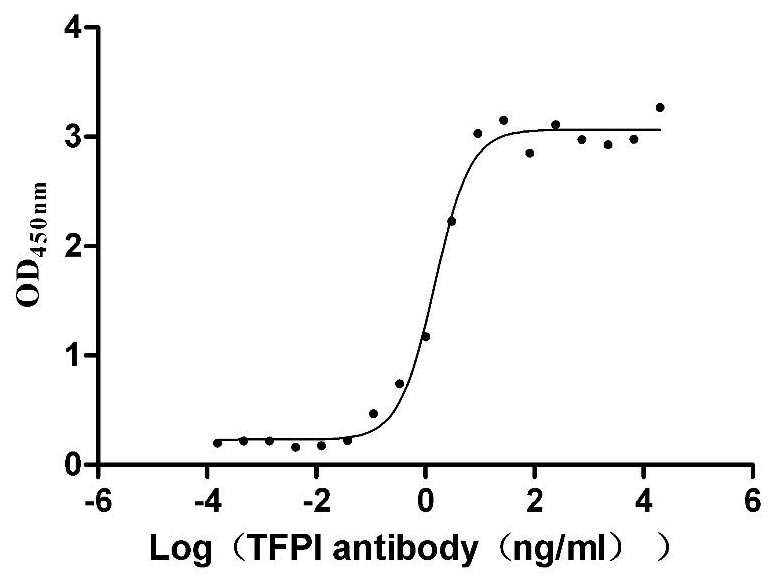
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
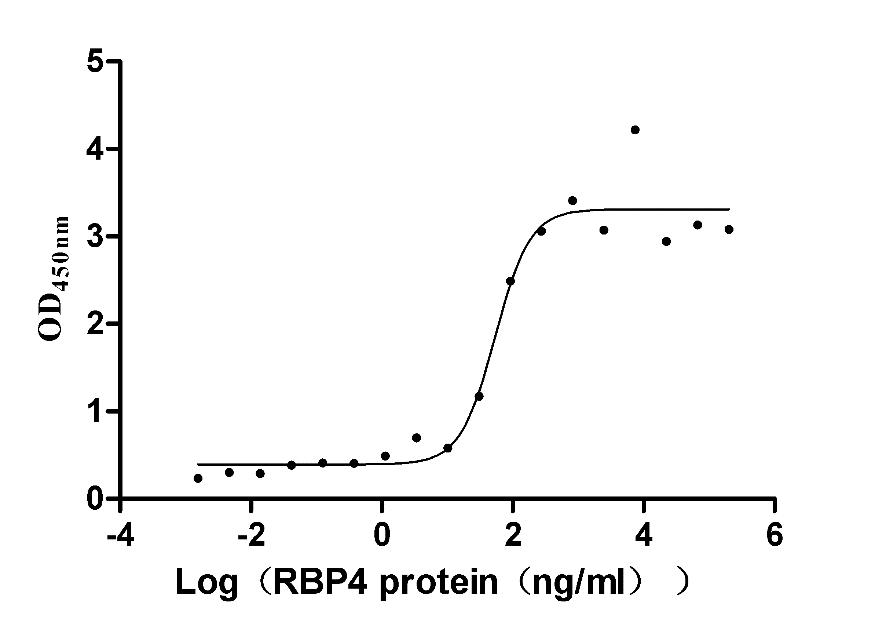
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
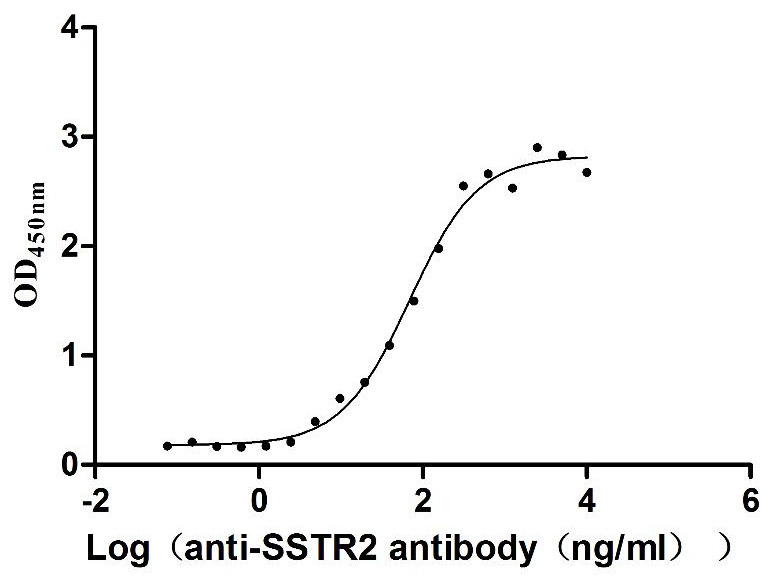
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
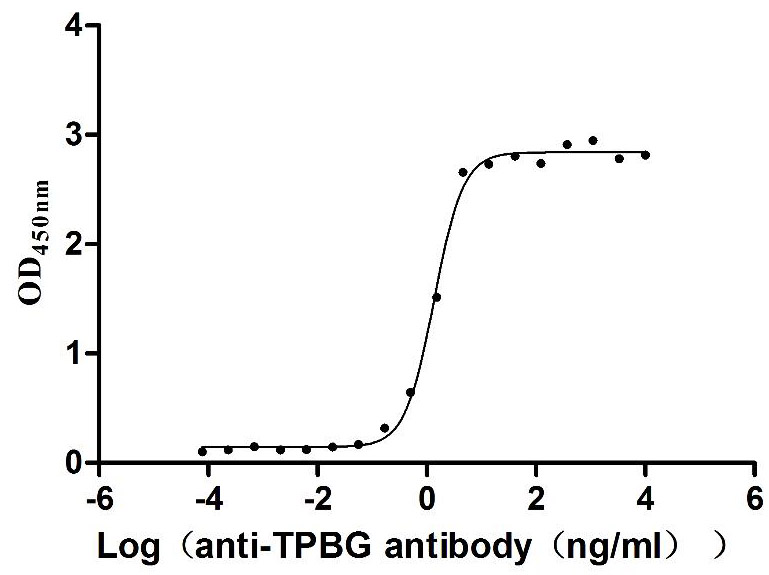
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
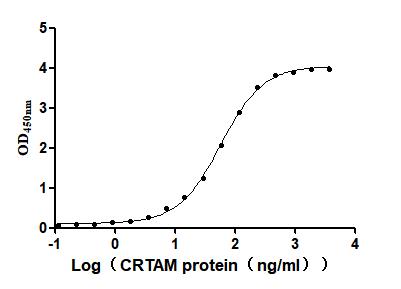
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
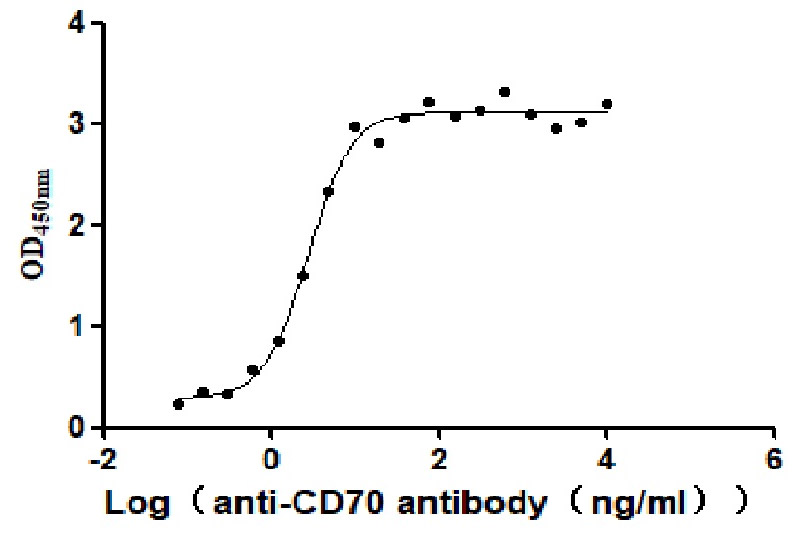
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
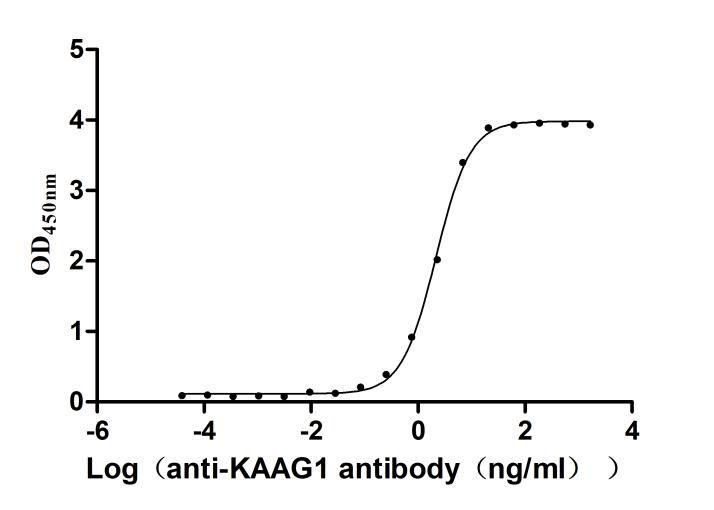
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)