Recombinant Human Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1 (KLRB1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP621524HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP621524HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP621524HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP621524HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP621524HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:KLRB1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:C-type lectin domain family 5 member B; CD161; CLEC5B; HNKR-P1a; Killer Cell Lectin like Receptor Subfamily B Member 1; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1; KLRB1; KLRB1_HUMAN; Natural killer cell surface protein P1A; NKR; NKR P1; NKR-P1A; NKRP1; NKRP1A
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays an inhibitory role on natural killer (NK) cells cytotoxicity. Activation results in specific acid sphingomyelinase/SMPD1 stimulation with subsequent marked elevation of intracellular ceramide. Activation also leads to AKT1/PKB and RPS6KA1/RSK1 kinases stimulation as well as markedly enhanced T-cell proliferation induced by anti-CD3. Acts as a lectin that binds to the terminal carbohydrate Gal-alpha(1,3)Gal epitope as well as to the N-acetyllactosamine epitope. Binds also to CLEC2D/LLT1 as a ligand and inhibits NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity as well as interferon-gamma secretion in target cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results show that susceptibility of normal articular chondrocytes to lysis by NK cells is modulated by NKR-P1A/LLT1 interactions. Thus, NKR-P1A/LLT1 interaction might provide some novel target for therapeutic interventions in the course of pathological cartilage injury. PMID: 29212911
- Blocking LLT1-NKRP1A interaction will make prostate cancer cells susceptible to killing by NK cells, suggesting a therapeutic option for treatment of prostate cancer. PMID: 27626681
- Purified soluble NKR-P1 is homogeneous, deglycosylatable, crystallizable and monomeric in solution, as shown by size-exclusion chromatography, multi-angle light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation. PMID: 28757467
- A subset of virus-specific CD161(+) T cells selectively express the multidrug transporter MDR1 and are resistant to chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. PMID: 27821506
- CD161 expression levels were reduced in some NK and T cell subpopulations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, suggesting possible important role of CD161 and CD161-expressing immune cells in the SLE pathogenesis. PMID: 26590595
- A novel population of highly functional, memory CD8+ T cells enriched within the gut expresses CD161. PMID: 26220166
- Our results reveal that in combination with IGRAs, CD161-based indices provide a novel, fast diagnostic solution addressing the limitation of current tuberculosis diagnostics. PMID: 26643453
- these data suggest that LLT1-CD161 interactions play a novel and important role in B cell maturation within the Germinal center in humans. PMID: 26829983
- The regulation of NK cell homeostasis and activation apparently differs between carriers of the CC and TT variant of CD161. PMID: 26309225
- We suggest modulation of human Th17 responsiveness by CD39 and CD161 and describe novel molecular mechanisms integrating elements of both extracellular nucleotide and sphingolipid homeostasis--{REVIEW} PMID: 26059452
- percentage of alveolar CD3(+)CD161(+) T lymphocytes that produced IFN-gamma/IL-17 was significantly higher than those in the peripheral blood PMID: 25906076
- these results suggest that the CD8(+) subset of CD161(+) T cells may have regulatory effects and that they provide a basis for predicting the occurrence of aGVHD after allogeneic SCT. PMID: 25543092
- CD161-expressing Th17 cells are enriched at sites of autoinflammation, are highly proinflammatory and resistant to Treg-mediated suppression suggesting their important pathogenic role in rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 26062995
- Expression of CD161 hence identifies a transcriptional and functional phenotype, shared across human T lymphocytes. PMID: 25437561
- Elevated expression of CD69 and CD161 on NK cells can be considered as immunological risk markers in RSA and IVF failure. PMID: 24975965
- CD39 and CD161 modulate human Th17 responses in CD through alterations in purinergic nucleotide-mediated responses and ASM catalytic bioactivity, respectively. PMID: 25172498
- CD161+ Th17/CD161+ Th1-cell imbalance may contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 24392804
- Here we present a distinct population of Treg, defined by CD161 expression, as the major source of FoxP3+ Treg-derived proinflammatory cytokines. PMID: 23355538
- The fraction of CD161high T cells is significantly higher in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis in relapse than those of controls. PMID: 23599932
- CD161+CD4+ T lymphocytes, differentiated into Th1 cells and Th17 cells, are involved in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. PMID: 22833233
- LLT1 and CD161 have roles in modulating immune responses to pathogens; and interferon-gamma contributes to modulate immune responses PMID: 21930700
- our results indicate that KLRB1 gene expression is altered in multiple sclerosis (MS) and likely to be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease, whereas rs4763655 in KLRB1 seems to have a minimal role in MS susceptibility. PMID: 21610746
- expression defines IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells PMID: 21909091
- Molecular basis for LLT1 protein recognition by human CD161 protein (NKRP1A/KLRB1). PMID: 21572041
- Th17 cells from patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma downregulate the Th17 cell surface receptor CD161 in peripheral blood as well as in primary tumors and especially in metastatic lymph nodes. PMID: 21570678
- cytokines induce significant up-regulation of NKG2D expression while only IFN-alpha induced significant up-regulation of CD161 PMID: 20800424
- marker of IL-17-producing T-cell subsets PMID: 20486123
- Results reveal a functional relationship between CD161 expression and NK cell cytotoxicity as well as NK cell reactivity to glycans and mutated citrullinated vimentin, providing new insight into the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 20359956
- CD161 expression on human CD8+ T cells defines a distinct functional subset with tissue-homing properties. PMID: 20133607
- There is a significant positive correlation of CD161 expression with NK cytotoxicity. PMID: 19711124
- Pl(A2) genotype is associated with a decreased risk of developing intermittent claudication. PMID: 14987913
- Engagement of CD161 on NK cells with LLT1 expressed on target cells inhibited NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma secretion. LLT1/CD161 interaction in the presence of a TCR signal enhanced IFN-gamma production by T cells PMID: 16339512
- LLT1 on target cells can inhibit NK cytotoxicity via interactions with CD161. LLT1 activates NFAT-GFP reporter cells expressing a CD3zeta-CD161 chimeric receptor; reciprocally, reporter cells with a CD3zeta-LLT1 chimeric receptor are stimulated by CD161 PMID: 16339513
- define a novel signal transduction pathway for the CD161 (NKR-P1A) receptor and provide fresh insights into NK and NKT cell biology PMID: 16455998
- NKRPIA binds to the alphaGal epitope of mouse laminin. Moreover, exposing NAcLac by removal of alphaGal resulted in an increase in binding. PMID: 16925668
- The results of this work demonstrated that the transcription of the KLRB1 was suppressed in tumor tissues in 68% patients with nonsmall-lung-cancer (p < 0.0001) and 57% patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (p = 0.0003). PMID: 18159636
- Expression of CD161 indicates a unique pattern of T cell differentiation that might help elucidate the mechanisms of hepatitis c virus immunity and pathogenesis. PMID: 18219672
- Interactions between NKR-P1A on NK cells and LLT1 on target cells inhibit NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and cytokine production PMID: 18453569
- PILAR signaling through CD161 supports CD3 antibody-dependent and antigen-specific T-cell proliferation by increasing the expression of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL and induces secretion of T helper type 1 cytokines PMID: 18550855
- all IL-17-producing cells originate from CD161(+) naive CD4(+) T cells of umbilical cord blood, as well as of the postnatal thymus PMID: 18663128
- These data identify CD161(+) CD4 T cells as a resting Th17 pool that can be activated by IL-23 and mediate destructive tissue inflammation. PMID: 19273624
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in a subset of NK cells predominantly in intestinal epithelium and liver. Detected in peripheral blood T-cells and preferentially in adult T-cells with a memory antigenic phenotype.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6373
OMIM: 602890
KEGG: hsa:3820
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000229402
UniGene: Hs.169824
Most popular with customers
-
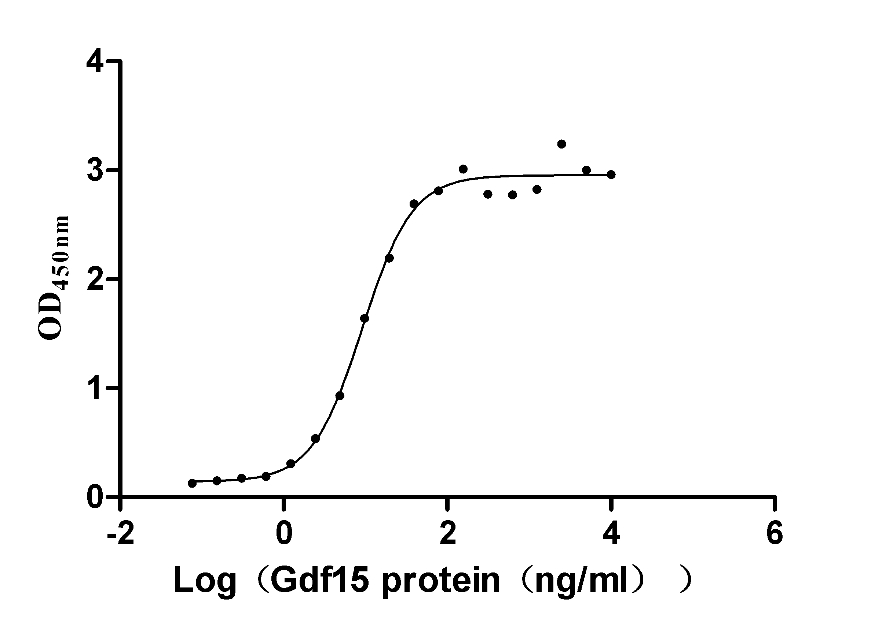
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
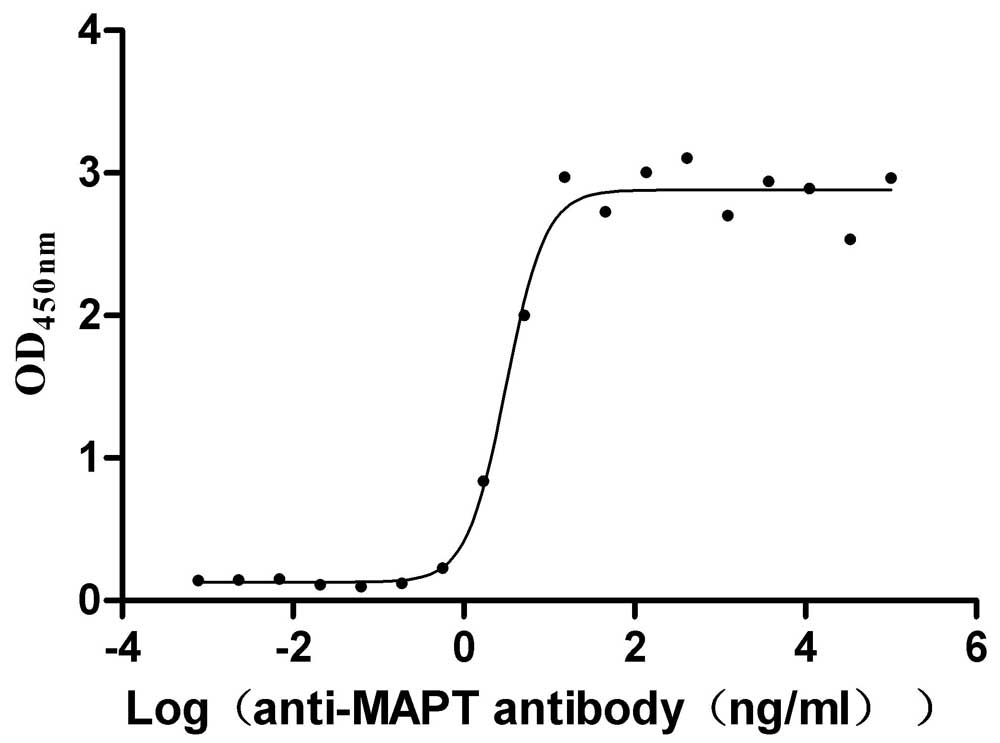
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
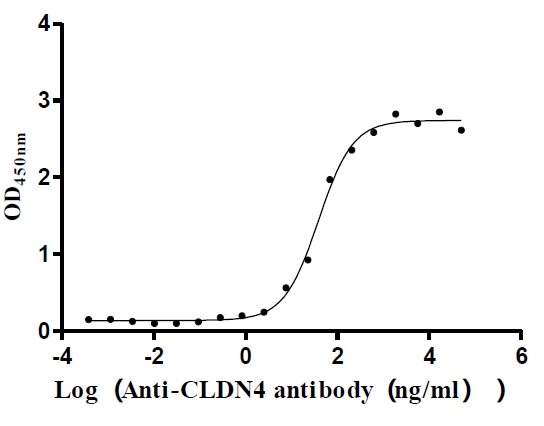
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
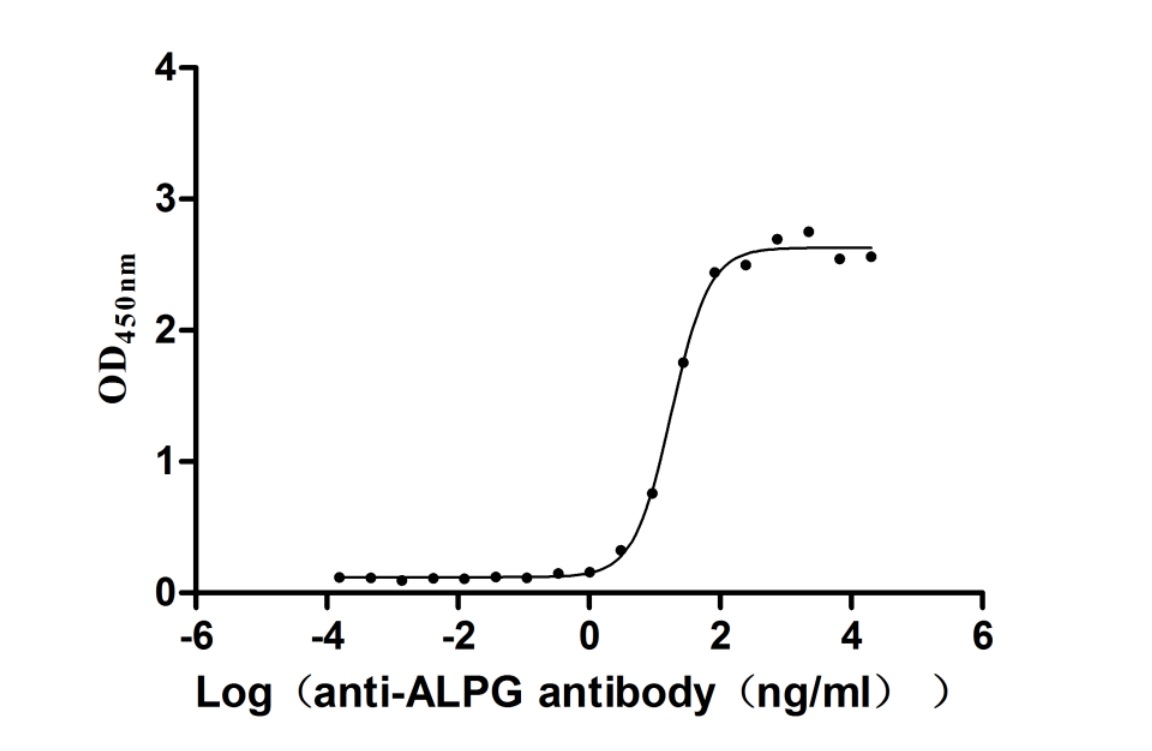
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
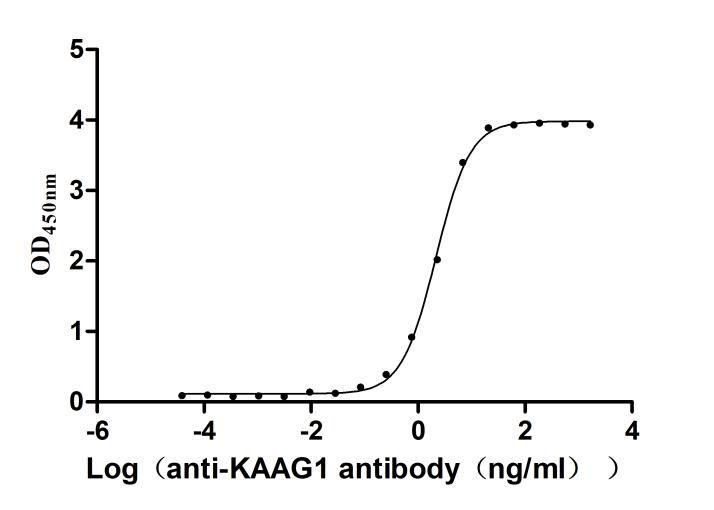
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
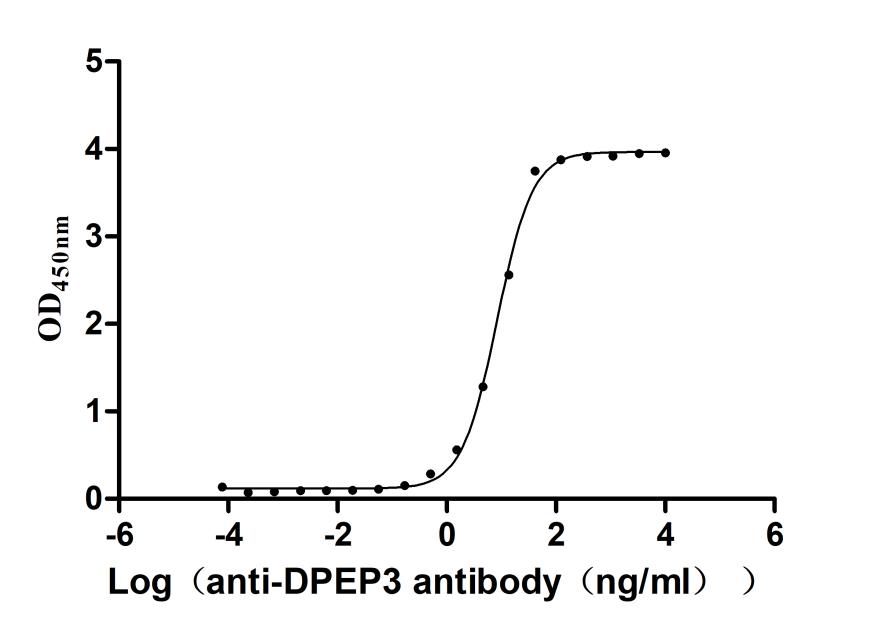
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
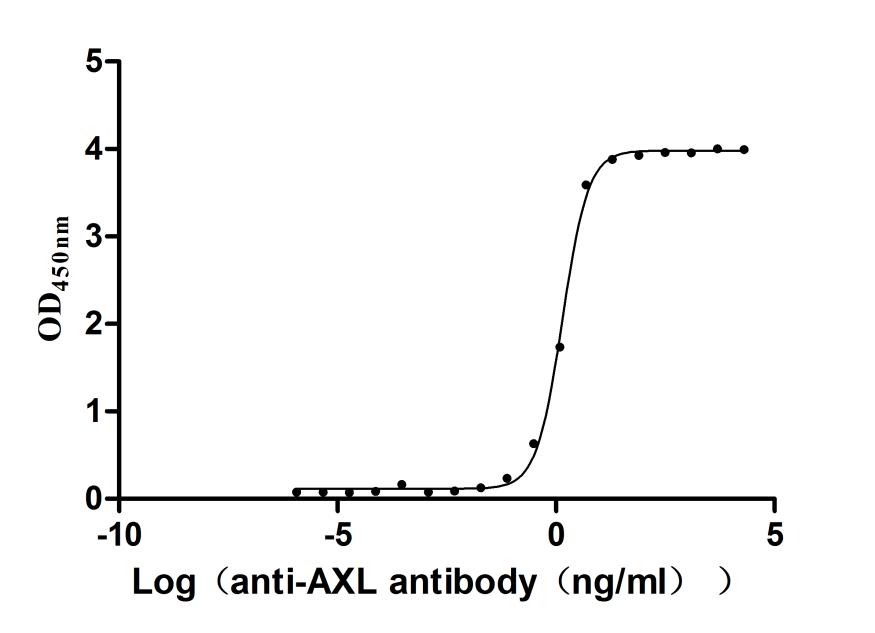
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)