Recombinant Human Gap junction alpha-8 protein (GJA8), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP009449HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009449HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009449HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP009449HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP009449HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:GJA8
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:GJA8; Gap junction alpha-8 protein; Connexin-50; Cx50; Lens fiber protein MP70
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Structural component of eye lens gap junctions. Gap junctions are dodecameric channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjoining cells. They are formed by the docking of two hexameric hemichannels, one from each cell membrane. Small molecules and ions diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell via the central pore.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- this study identified the genetic susceptibility of GJA8 polymorphisms on ARC and provides new clues for fully understanding the pathological mechanism of GJA8 variants in affecting lens opacity PMID: 30349978
- The mutation c.139G>A in the GJA8 gene detected in the present study was also previously reported in Caucasian and Chinese families but with different phenotypes, i.e. nuclear and nuclear pulverulent cataracts. Thus, the mutation c.139G>A in GJA8 appears to exhibit marked interfamilial phenotypic variability. PMID: 30262699
- The p.V44M mutation in the GJA8 gene was the most common mutation and was due to a founder effect within the Chinese congenital cataract cohort studied. PMID: 30078984
- GJA8 is the newly identified genetic cause of familial congenital cataract. PMID: 29434075
- Data indicate de novo heterozygous mutations affecting the same codon of gap junction alpha-8 protein (GJA8) p.(Gly94Glu) and p.(Gly94Arg) )in 2 of the probands, in addition to the p.(Asp51Asn) mutation previously identified in the third case. PMID: 28455998
- Study identified two novel missense mutations within P59 and R76 of Cx50 that are associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataracts (ADCC). Functional analysis showed that Cx50R76H localized at appositional membranes forming gap junctions with enormous cytoplasmic protein accumulation, whereas the Cx50P59A mutation was found inefficient at forming detectable plaques. PMID: 27216975
- The novel insert mutation in the TM2 domain of Cx50 protein, which impairs its trafficking to the cell membrane and gap-junction function, is associated with the cataract formation in this Chinese pedigree. PMID: 29489419
- study demonstrates that the mutant protein localized to the plasma membrane and formed functional intercellular channels. These data suggest that GJA8 c.658A>G is most likely a benign rare variant PMID: 28827829
- The missense mutation c.139G > A in GJA8 gene is associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataract in a six-generation Chinese family. The result of this present study provides further evidence that the p. D47N mutation in CX50 is a hot-spot mutation. PMID: 28526010
- The c.433G > T (p.G145W) mutation in the GJA8 gene was first reported to our best knowledge. The results of our study would further broaden the mutation spectrum of GJA8 associated with congenital cataract. PMID: 27785597
- These results indicated that the mutant Cx50 (S276F) might inhibit the function of gap junction channel in a dominant negative manner, but inhibit the hemichannel function in a recessive negative manner. PMID: 26174669
- GJA8 mutation (p.V44A) is associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataract. PMID: 25517998
- This is a novel missense mutation [c.829C > T, (p.H277Y)] identified in exon 2 of Cx50. PMID: 25947639
- We have used trio-based exome sequencing to uncover a recurrent missense mutation in CRYGD and two novel missense mutations in GJA8 associated with autosomal dominant cataract in three nuclear families. PMID: 25403472
- Tthe molecular consequences of the p.P88T mutation in GJA8 include changes in connexin 50 protein localization patterns. PMID: 24535056
- A recurrent missense mutation c.773C>T (p.S258F) in exon 2 of the gap junction protein alpha 8 gene (GJA8) was identified in the proband with nuclear cataract. PMID: 25301372
- structural bases of the varied functional consequences of Cx50 missense mutations, were determined. PMID: 25003127
- Exome sequencing in developmental eye disease leads to identification of causal variants in GJA8, CRYGC, PAX6 and CYP1B1. PMID: 24281366
- The results provide a molecular basis for the formation of various cataract phenotypes in human patients with Cx50 mutations. PMID: 24005045
- a novel G>A mutation of GJA8 in a three-generation Chinese pedigree was associated with perinuclear opacities of the lens involving the nucleus PMID: 23555834
- Data indicate that after inhibition of new protein synthesis with cycloheximide, CX50fs disappeared much more rapidly than CX50, suggesting increased degradation of the mutant. PMID: 23720739
- A novel connexin 50 gene (GJA8) mutation, resulting in the amino substitution p. D47H in a Chinese family with nuclear and zonular pulverulent congenital cataracts, is reported. PMID: 23592913
- A PDZ-binding motif and ZO-1 protein are necessary for Cx50 intercellular channel formation PMID: 21965293
- A missense D47N mutation in GJA8 is associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataract in a Chinese family. PMID: 21921990
- Mutations in GJA8 and CRYAA were identified in three Chinese families with cataract and microcornea. PMID: 21686328
- The G46V and W45S mutations of connexin 50 are in adjacent amino acids. W45S inhibits gap junctional channel function while G46V reduces cell viability by forming open hemichannels. PMID: 21228318
- Two novel nonsynonymous variations and four reported variations in CRYAB, CRYGC, CRYGD, and GJA8, were observed. PMID: 21423869
- the gap junction protein-alpha 8 polymorphisms may have a role in age-related cataracts PMID: 20582632
- The D47N mutation of Cx50 causes the hereditary nuclear cataract in this family in an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance with incomplete penetrance. PMID: 21174522
- This report is the first to relate p.R198W mutation in GJA8 with congenital cataract-microcornea syndrome. PMID: 20806042
- This study has identified a novel missense mutation located in the carboxyl terminus of GJA8 (S258F) associated with autosomal dominant nuclear cataract. PMID: 20597646
- A novel mutation in GJA8 was detected in a Chinese family with autosomal dominant congenital nuclear cataract, providing clear evidence of a relationship between the genotype and the corresponding cataract phenotype. PMID: 20019893
- the C-terminus of human Cx50 is involved in pHi sensitivity, but has little influence over single-channel conductance, voltage dependence, or gating kinetics. PMID: 11944087
- Study confirmed that GJA8 plays a vital role in the maintenance of human lens transparency and its mutation could be the genetic defect causing autosomal dominant congenital cataract . PMID: 15696487
- The pulverulent cataract described in this family is associated with a novel GJA8 mutation and has a different clinical phenotype from previously described GJA8 mutants. PMID: 16397066
- This is the first report of mutations in GJA8 (connexin50) to be associated with autosomal dominant cataract and microcornea. PMID: 16604058
- Resultsdemonstrated that Cx50 hemichannels gating control can be cooperated by CaM and Ca2+. PMID: 16740131
- Matched case-control and family study indicate that Cx50 may play a role in the genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. PMID: 17412882
- Mutation of the gap junction protein alpha 8 (GJA8) gene causes autosomal recessive cataract. PMID: 17601931
- Five novel mutations in CRYAA, CRYGD, and GJA8 genes were detected in congenital cataract in association with microcornea PMID: 17724170
- Pulverulent cataracts present in members of a family are associated with a novel mutation, Cx50D47N, that acts as a loss-of-function mutation. The consequent decrease in lens intercellular communication may contribute to cataract formation. PMID: 18006672
- A novel disease-causing mutation (D47Y) of GJA8 gene in a Chinese family with ADCC is reported. PMID: 18247306
- This is a novel mutation identified in the first transmembrane domain (M1) of GJA8. PMID: 18334946
- A novel GJA8 gene mutation was found to be associated with hereditary cataract in a Chinese congenital cataract family. PMID: 18334966
- The ins776G mutation most likely causes a recessive triangular cataract with variable expressivity of a weak phenotype in heterozygotes. PMID: 18483562
- A p.P88Q mutation in GJA8 associated with Y-sutural cataract in a family of Indian origin, is reported. PMID: 18587493
- The biochemical results indirectly suggest a potential novel mechanism by which connexin mutants could lead to cataracts. PMID: 19684000
- Direct sequencing of the PCR product produced from lens cDNA showed that the proband was heterozygous for a G>T transition at position 741 of the GJA8 gene, encoding the exchange of methionine for isoleucine at position 247 of CX50. PMID: 19756179
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Cataract 1, multiple types (CTRCT1)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, gap junction.
-
蛋白家族:Connexin family, Alpha-type (group II) subfamily
-
组织特异性:Eye lens.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 4281
OMIM: 116200
KEGG: hsa:2703
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000240986
UniGene: Hs.632441
Most popular with customers
-
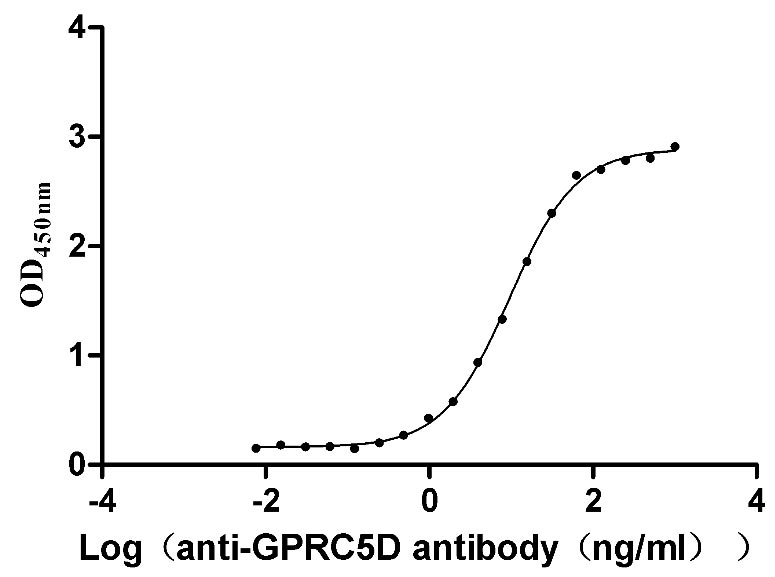
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
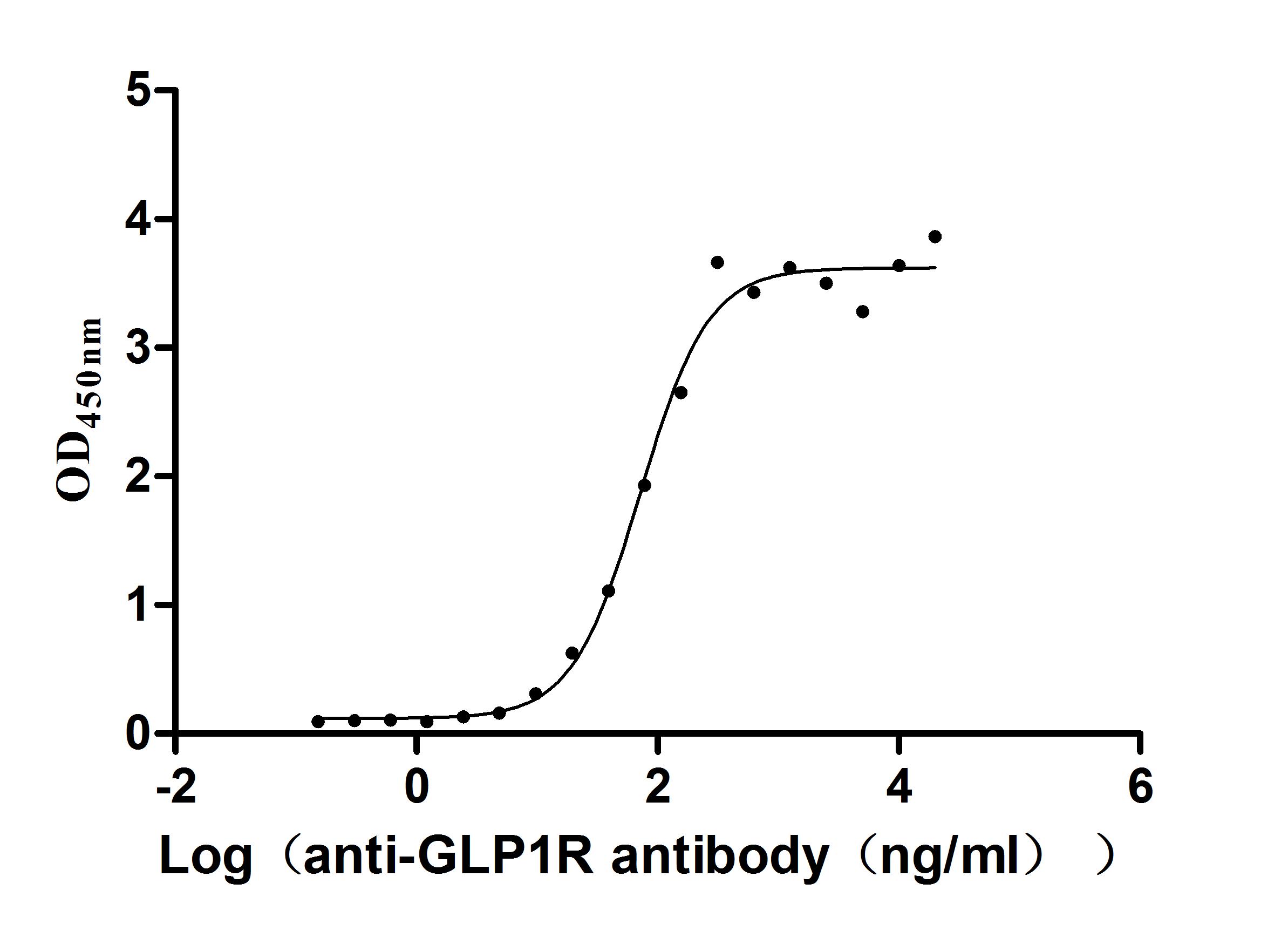
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
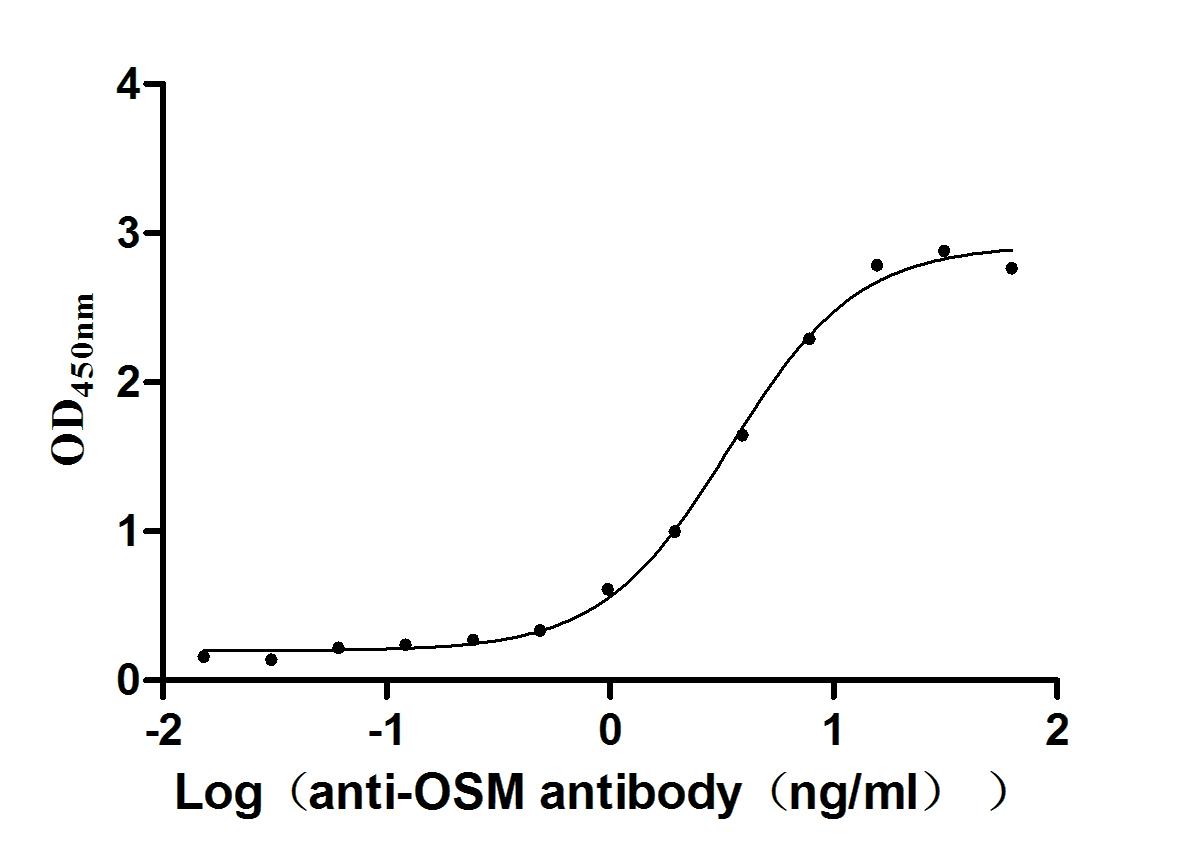
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
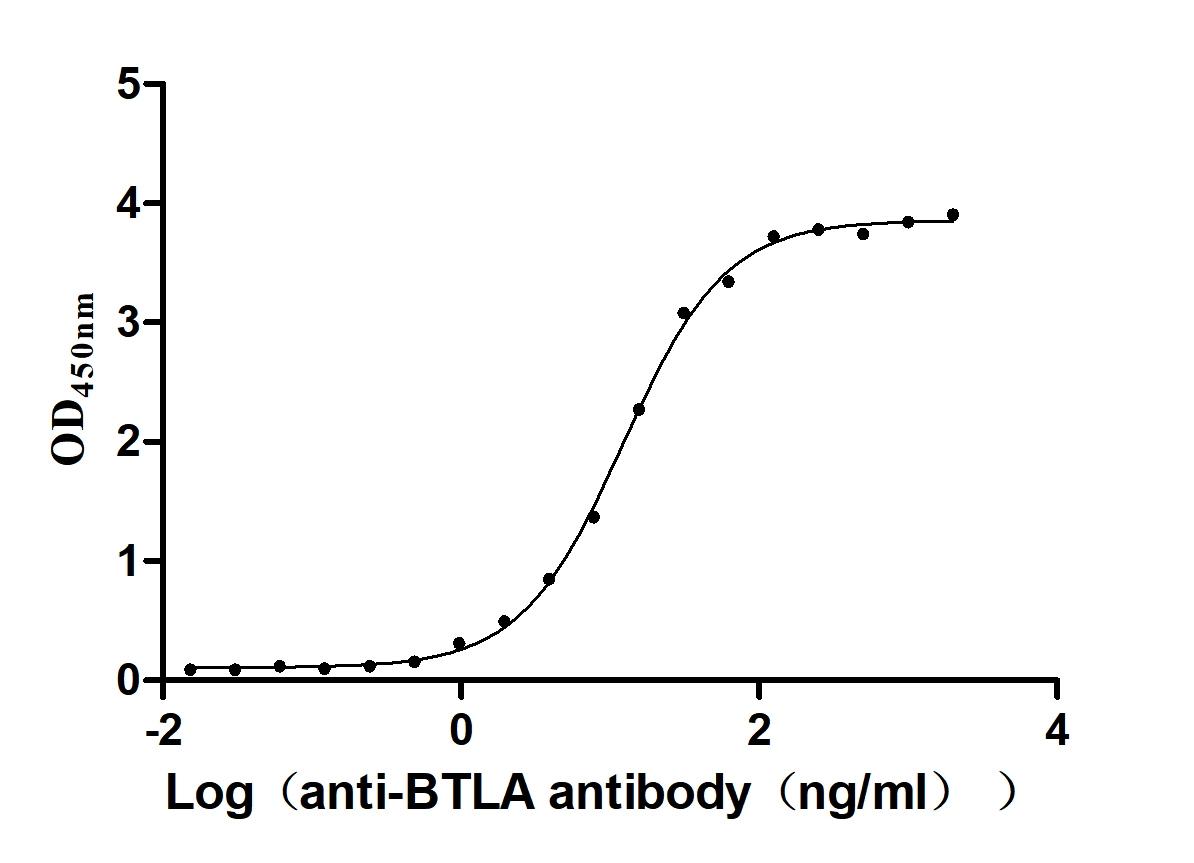
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
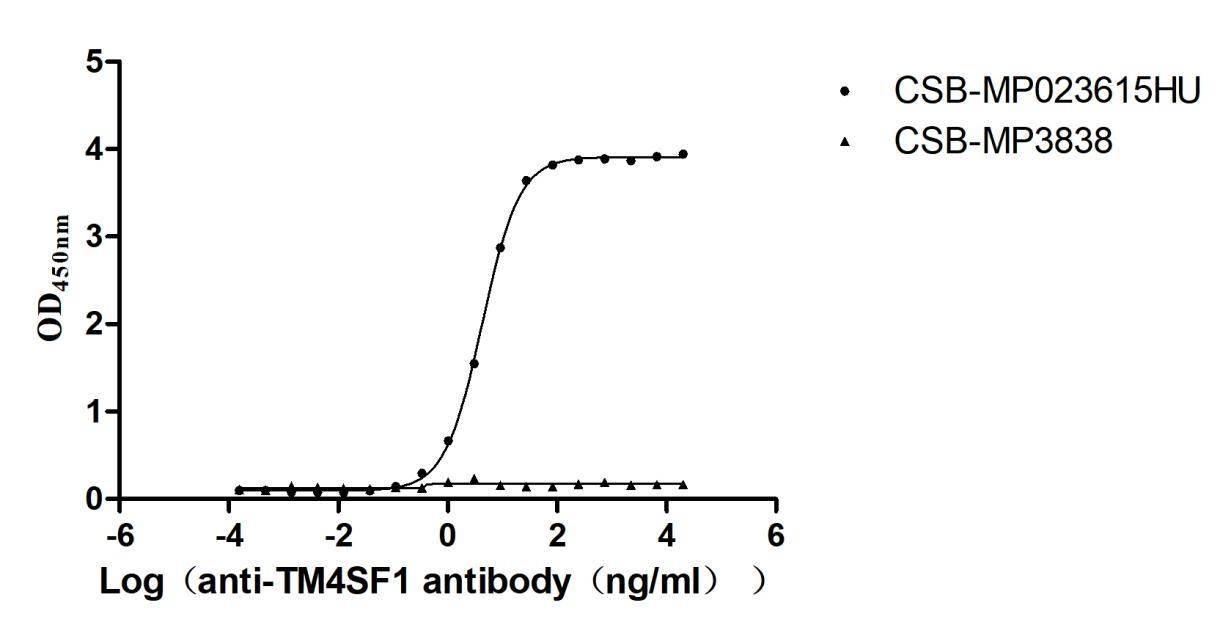
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)