Recombinant Human Fizzy-related protein homolog (FZR1)
-
货号:CSB-YP892473HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP892473HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP892473HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP892473HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:CDC20 like 1b; CDC20 like protein 1; CDC20-like protein 1; CDC20C; CDH1; Cdh1/Hct1 homolog; Fizzy related protein 1; Fizzy related protein; Fizzy related protein homolog; Fizzy-related protein homolog; Fizzy/cell division cycle 20 related 1; FYR; FZR 1; FZR 2; Fzr; FZR_HUMAN; Fzr1; Fzr1 protein; FZR2; HCDH 1; HCDH; hCDH1; KIAA1242
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-496
-
氨基酸序列MDQDYERRLL RQIVIQNENT MPRVTEMRRT LTPASSPVSS PSKHGDRFIP SRAGANWSVN FHRINENEKS PSQNRKAKDA TSDNGKDGLA YSALLKNELL GAGIEKVQDP QTEDRRLQPS TPEKKGLFTY SLSTKRSSPD DGNDVSPYSL SPVSNKSQKL LRSPRKPTRK ISKIPFKVLD APELQDDFYL NLVDWSSLNV LSVGLGTCVY LWSACTSQVT RLCDLSVEGD SVTSVGWSER GNLVAVGTHK GFVQIWDAAA GKKLSMLEGH TARVGALAWN AEQLSSGSRD RMILQRDIRT PPLQSERRLQ GHRQEVCGLK WSTDHQLLAS GGNDNKLLVW NHSSLSPVQQ YTEHLAAVKA IAWSPHQHGL LASGGGTADR CIRFWNTLTG QPLQCIDTGS QVCNLAWSKH ANELVSTHGY SQNQILVWKY PSLTQVAKLT GHSYRVLYLA MSPDGEAIVT GAGDETLRFW NVFSKTRSTK VKWESVSVLN LFTRIR
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Substrate-specific adapter for the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex. Associates with the APC/C in late mitosis, in replacement of CDC20, and activates the APC/C during anaphase and telophase. The APC/C remains active in degrading substrates to ensure that positive regulators of the cell cycle do not accumulate prematurely. At the G1/S transition FZR1 is phosphorylated, leading to its dissociation from the APC/C. Following DNA damage, it is required for the G2 DNA damage checkpoint: its dephosphorylation and reassociation with the APC/C leads to the ubiquitination of PLK1, preventing entry into mitosis. Acts as an adapter for APC/C to target the DNA-end resection factor RBBP8/CtIP for ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Through the regulation of RBBP8/CtIP protein turnover, may play a role in DNA damage response, favoring DNA double-strand repair through error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) over error-free, RBBP8-mediated homologous recombination (HR).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Cdh1-dependent degradation of FoxM1 is required to shut down transcriptional activation of mitotic regulators during exit from mitosis. PMID: 18758239
- Cdh1 reciprocally regulates the Rb pathway through competing with E2F1 to bind the hypophosphorylated form of Rb. PMID: 19477924
- Data report that a nuclear-localized portion of the stress-activated kinase JNK is degraded by the APC/C(Cdh1) during exit from mitosis and the G1 phase of the cell cycle. PMID: 20581839
- We identified the known APC/C regulator Cdh1 and the F-box protein Fbxl15 as specific modulators of N-cyclin B1-luciferase steady-state levels and turnover. Collectively, our studies suggest that analyzing the steady-state levels of luciferase fusion proteins in parallel facilitates identification of specific regulators of protein turnover. PMID: 28296622
- Findings document the differential expression, subcellular localization and cell-cycle-regulatory activity of alternatively spliced human CDH1 isoforms. PMID: 12797865
- upon infection of quiescent cells human cytomegalovirus not only activates the E2F-dependent G(1)/S transcription program but also facilitates protein accumulation of APC/C substrates by rapid Cdh1 dissociation PMID: 16138013
- Cell cycle regulation of Six1 occurs both transcriptionally and post-translationally via phosphorylation PMID: 17130831
- Cdh1 may act as an important component in tumor suppression and could be considered as a novel biomarker in breast cancer. PMID: 18381934
- Reduced Cdh1 levels have no effect on destruction of many APC/C substrates during mitotic exit but strongly and specifically stabilize Aurora kinases. PMID: 18976910
- Low Cdh1 expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 19350629
- Glycolysis-promoting enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, isoform 3 (PFKFB3), is degraded by the E3 ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1. PMID: 20080744
- DDB1 modulates the function of APC/C(Cdh1) in a manner independent of the Cul4-DDB1 complex PMID: 20395298
- Proteolysis of Rad17 by Cdh1/APC regulates checkpoint termination and recovery from genotoxic stress PMID: 20424596
- APC/CCdh1 is a master G0/G1 regulator and involved in differentiation and development processes. (Review) PMID: 21497201
- The deubiquitinase USP37 binds CDH1 and removes degradative polyubiquitin from cyclin A. USP37 was induced by E2F factors in G1, peaked at G1/S, and was degraded in late mitosis. Phosphorylation of USP37 by CDK2 stimulated its full activity. PMID: 21596315
- Ect2 is subject to proteasomal degradation after mitosis, following ubiquitination by the APC/C complex and its co-activator Cdh1 PMID: 21886810
- studies uncover a cell-cycle-independent function of Cdh1, establishing Cdh1 as an upstream component that governs Smurf1 activity PMID: 22152476
- In senescent cells, the DNA damage response induces proteasomal degradation of G9a and GLP, histone methyltransferases, through Cdc14B- and p21(Waf1/Cip1)-dependent activation of APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase. PMID: 22178396
- APC/CCdh1 is able to ubiquitylate E2F3A in vitro, and that the degradation of E2F3A is stimulated by Cdh1, but not by Cdc20. PMID: 22580460
- The effect of Cdh1 on E2F1 degradation is blocked upon DNA damage. PMID: 22580462
- show that the Gas2l3 protein is targeted for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis by the APC/C(Cdh1) complex, but not by the APC/C(Cdc20) complex, and is phosphorylated by Cdk1 in mitosis PMID: 23469016
- Data indicate that regulation of Rad17 turnover is through the Cdh1/anaphase-promoting complex pathway in breast cancer cells. PMID: 23637229
- NEDL2 is a novel substrate of APC/C-Cdh1 as cells exit mitosis and functions as a regulator of the metaphase to anaphase transition PMID: 24163370
- Results showed evidence that Wip1 underwent Cdh1-dependent proteolysis during mitosis and sustained Wip1 activity during mitosis, resulting in mitotic delay at the metaphase to anaphase transition. PMID: 25649870
- Using biochemistry and live cell imaging of single cells s found that Cdh1 knockdown (kd) leads to strong nuclear stabilization of the substrates cyclin A and B and deregulated kinetics of DNA replication. PMID: 26455319
- Low Cdh1 expression may be important in AML biology by contributing to the differentiation block and response to therapy depending on differences in the microenvironment and the additional genetic background. PMID: 27374082
- APC/C(Cdc20), and APC/C(Cdh1) act successively to ensure that the disappearance of licensing inhibitors coincides exactly with a peak of Cdt1 and Cdc6. PMID: 23775192
- The Cells lacking Cdh1 have been shown to accumulate deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage, suggesting that it may play a previously unrecognized role in maintaining genomic stability. PMID: 21768287
- APC/C(Cdc20) or APC/C(Cdh1) complexes regulate RAP80 stability during mitosis to the G(1) phase, and these events are critical for a novel function of RAP80 in mitotic progression. PMID: 22426463
- the sequential actions of the APC-c(Cdc20) and APC-c(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligases regulate the clearance of Mps1 levels and are critical for Mps1 functions during the cell cycle in human cells. PMID: 20729194
- Study shows that nuclear PTEN interacts with APC/C, promotes APC/C association with CDH1, and thereby enhances the tumor-suppressive activity of the APC-CDH1 complex. PMID: 21241890
- APC-Cdh1 establishes a stimulus-response relationship that promotes S phase. PMID: 24356446
- The levels of CDC20 and CylinB1 increased and the levels of Ku70 and APC3 decreased after irradiation. APC/C(Cdh1) is involved in regulation of radiosensitivity in human NPC CNE-1 cells. PMID: 28004426
- Data show that FZR1 (Fzr), a cofactor of the multi-subunit E3 ligase complex anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), represents PMID: 27655696
- APC/C and pRB interact with each other via the co-activator of APC/C, FZR1, providing an alternative pathway of regulation of G1 to S transition by pRB using a post-translational mechanism. Both pRB and FZR1 have complex roles and are implicated not only in regulation of cell proliferation but also in differentiation, quiescence, apoptosis, maintenance of chromosomal integrity and metabolism. PMID: 27402801
- FZR1 inhibits BRAF oncogenic functions via both APC-dependent proteolysis and APC-independent disruption of BRAF dimers, whereas hyperactivated ERK and CDK4 reciprocally suppress APC(FZR1) E3 ligase activity PMID: 28174173
- These findings identify a dynamic interplay between FZR1 and BRAF with strong implications for cell-fate determination and the tumor suppressor role of FZR1 PMID: 28373167
- results suggest that reduction of FZR1 increases therapeutic sensitivity of B-ALL and that transient rather than tonic inhibition of FZR1 may be a therapeutic strategy. PMID: 28143883
- results define a new APC/C(Cdh1) function that prevents cell cycle resumption after prolonged replication stress by inhibiting origin firing, which may act as an additional mechanism in safeguarding genome integrity. PMID: 26939887
- APC(Cdh1) inactivation is the commitment point when cells lose the ability to return to quiescence and decide to progress through the cell cycle. PMID: 27368103
- Data show that CDC20 homolog 1 (Cdh1) is O-GlcNAcylated in cultured cells. PMID: 27080259
- Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-CDH1, rather than Cdc20, promotes the degradation of BRSK2 in vivo. PMID: 23029325
- Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-Cdh1 coordinates glycolysis and glutaminolysis with transition to S phase in human T lymphocytes. PMID: 20921411
- Cdh1-depleted HeLa cells reduced stress fiber formation significantly. The GTP-bound active Rho protein was apparently decreased in the Cdh1-depleted cells. PMID: 20530197
- FZR1 is not required for the completion of mitosis, but is an important regulator of G1 phase and is required for efficient DNA replication in human and mouse somatic cells. PMID: 19861496
- Destruction-box specificities of APC/C(fzy) and APC/C(fzr)& successive activation of APC/C by fzy & fzr establish the temporal substrate degradation pattern, explaining why some endogenous RXXL substrates are degraded by fzy & others by fzr complexes. PMID: 12198152
- Results indicate that Cdh1 mediates its own degradation by activating the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome to degrade itself. PMID: 15029244
- Retinoic acid downregulates Rae1, hence facilitating APC(Cdh1)-mediated Skp2 degradation leading to the arrest of cell cycle progression and neuroblastoma differentiation. PMID: 18212744
- during endocycles, APC/C Fzr/Cdh1 functions to reduce the levels of the mitotic cyclins and Geminin in order to facilitate the relicensing of DNA replication origins and cell cycle progression PMID: 18321983
- In response to genotoxic stress in G2, the phosphatase Cdc14B translocates from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm and induces the activation of the ubiquitin ligase APC/C(Cdh1), with the consequent degradation of Plk1, a prominent mitotic kinase. PMID: 18662541
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 2]: Nucleus.; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:WD repeat CDC20/Fizzy family
-
组织特异性:Isoform 2 is expressed at high levels in heart, liver, spleen and some cancer cell lines whereas isoform 3 is expressed only at low levels in these tissues.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 24824
OMIM: 603619
KEGG: hsa:51343
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000378529
UniGene: Hs.413133
Most popular with customers
-
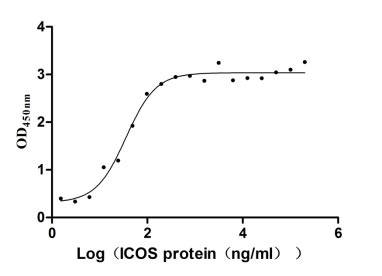
Recombinant Human ICOS ligand (ICOSLG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
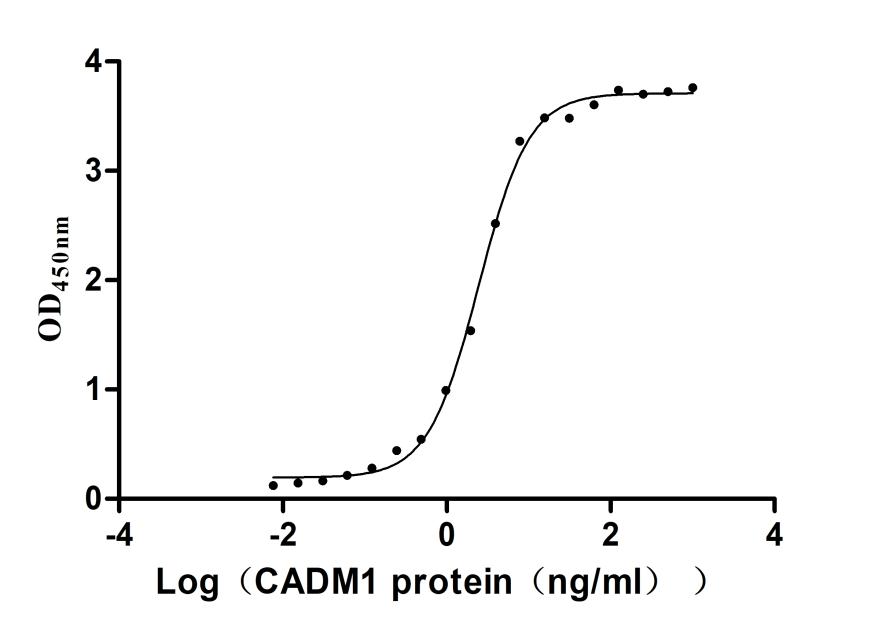
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
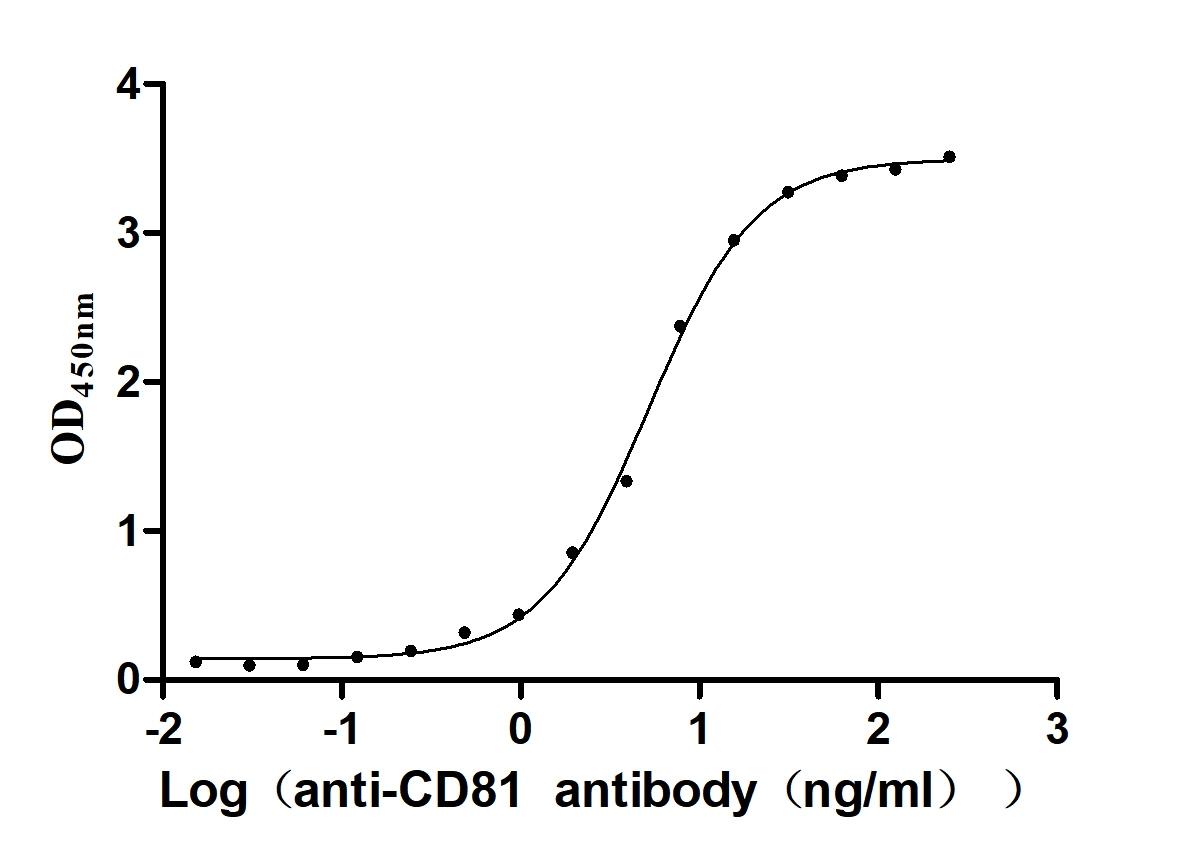
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
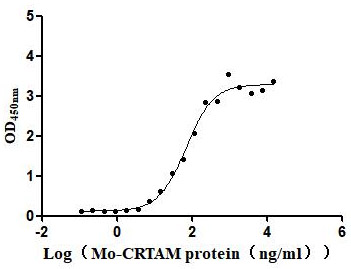
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)