Recombinant Human Extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1)
-
货号:CSB-YP007383HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP007383HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP007383HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP007383HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP007383HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:ECM1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ECM 1; Ecm1; ECM1_HUMAN; Extracellular matrix protein 1; Secretory component p85; URBWD
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Extracellular domain
-
表达区域:20-540
-
氨基酸序列A SEGGFTATGQ RQLRPEHFQE VGYAAPPSPP LSRSLPMDHP DSSQHGPPFE GQSQVQPPPS QEATPLQQEK LLPAQLPAEK EVGPPLPQEA VPLQKELPSL QHPNEQKEGT PAPFGDQSHP EPESWNAAQH CQQDRSQGGW GHRLDGFPPG RPSPDNLNQI CLPNRQHVVY GPWNLPQSSY SHLTRQGETL NFLEIGYSRC CHCRSHTNRL ECAKLVWEEA MSRFCEAEFS VKTRPHWCCT RQGEARFSCF QEEAPQPHYQ LRACPSHQPD ISSGLELPFP PGVPTLDNIK NICHLRRFRS VPRNLPATDP LQRELLALIQ LEREFQRCCR QGNNHTCTWK AWEDTLDKYC DREYAVKTHH HLCCRHPPSP TRDECFARRA PYPNYDRDIL TIDIGRVTPN LMGHLCGNQR VLTKHKHIPG LIHNMTARCC DLPFPEQACC AEEEKLTFIN DLCGPRRNIW RDPALCCYLS PGDEQVNCFN INYLRNVALV SGDTENAKGQ GEQGSTGGTN ISSTSEPKEE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in endochondral bone formation as negative regulator of bone mineralization. Stimulates the proliferation of endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis. Inhibits MMP9 proteolytic activity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- the present study demonstrated the association between ECM1 gene mutation and patients with LP. Patients with LP exhibited one homozygous point mutation (C220G) as previously reported, one novel homozygous mutation (c.508insCTG) and two heterozygous mutations (C220G/P.R481X and c.507delT/c.l473delT). PMID: 29693130
- The results showed a significant upregulation of ECM1 and ITGB3, and a significant downregulation for FBLN5 in pelvic organ prolapse patients. PMID: 29729708
- Three patients with homozygous mutations in sixth and seventh exons of the ECM1 gene had a drug-resistant course at the end of long-term follow-up PMID: 28434238
- This proteome analysis indicate that ECM1 is a potential novel plasma protein biomarker for the detection of primary ESCC and evaluation of neoplasms progression PMID: 28493612
- The TT genotype of ECM1 gene rs3737240 SNP significantly increased susceptibility for Ulcerative Colitis and azathioprine use in Ulcerative Colitis patients in a Turkish population. PMID: 28699600
- our work has identified a novel function of ECM1 in inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model PMID: 27316685
- Our results indicate that although mutation in ECM1gene is responsible for lipoid proteinosis, it is likely that this is not the only gene causing this disease and probably other genes may be involved in the pathogenesis of the LP disease. PMID: 27241643
- ECM1, which displayed a high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens, was closely associated with clinicopathologic data and may promote migration and invasion of HCC cells by inducing epithelia-mesenchymal transition. PMID: 27460906
- Cell invasion (matrigel) was reduced only in the Hs578T cells (p < 0.01). Silencing decreased the expression of the prometastatic molecules S100A4 and TGFbetaR2 in both cell lines and CD44 in Hs578T cells. We conclude that ECM1 is a key player in the metastatic process and regulates the actin cytoskeletal architecture of aggressive breast cancer cells at least in part via alterations in S100A4 and Rho A. PMID: 27770373
- Overexpression of miR-486-3p inhibited cell growth and metastasis by targeting ECM1. PMID: 27133046
- For 1q21 loci, we confirmed gene ECM1 as the most plausible gene from this region to be involved in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease PMID: 26738999
- In conclusion, the domain-specific anti-ECM1 MAbs produced in this study should provide a useful tool for investigating ECM1's biological functions, and cellular pathways in which it is involved. PMID: 26826312
- Lipoid proteinosis is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in ECM1, encoding extracellular matrix protein 1, a glycoprotein expressed in many organs and which has important protein-protein interactions in tissue homeostasis PMID: 26564090
- MMP-2 protein and ECM1 gene are useful preoperative markers for defining malignancy in suspicious thyroid nodules PMID: 25812648
- Genetic testing of theECM1 gene showed a homozygous nonsense mutation c.1441C > T (p.Arg481X) in exon 10, confirming the diagnosis of lipoid proteinosis. PMID: 24079542
- Lipoidproteinosis results from a large homozygous deletion of ECM1 gene in a Chinese family. PMID: 25518807
- High extracellular matrix protein-1 expression is associated with the growth, metastasis and angiogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma PMID: 25824756
- This large cohort revealed extensive phenotypic variability in individuals with the same mutation in ECM1. PMID: 25529926
- Lipoid proteinosis (LP) is a rare autosomal recessive genodermatosis caused by mutations in extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) that involves deposition of basement membrane-like material in the skin and other organs. PMID: 23534907
- ECM1 induced the expression of genes that promote the Warburg effect, such as glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha). PMID: 25446258
- Report a global loss of 5hmC identified three new genes (ECM1, ATF5, and EOMES) with potential anti-cancer functions that may promote the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. PMID: 25517360
- High extracellular matrix protein 1 expression is correlated to carcinogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of gastric cancer PMID: 24779890
- The data supports the conclusion that the c.742G>T mutation nonsense mutation in ECM1 is the pathological cause of lipoid proteinosis. PMID: 24413997
- homozygous missense mutation p.C220G of ECM1 was identified by Sanger sequencing, which is a major allele in Chinese patients with LP PMID: 24708644
- splicing mutation in Chinese lipoid proteinosis family PMID: 23682690
- Clinical assays for ECM1 and TEX101 have the potential to replace most of the diagnostic testicular biopsies and facilitate the prediction of outcome of sperm retrieval procedures, increasing the reliability and success of assisted reproduction techniques PMID: 24259048
- role for TFAP2C in melanoma via its regulation of ECM1 PMID: 24023917
- Suggest that ECM1 plays promotive roles in the occurrence, development and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma. PMID: 23696932
- The expression of ECM1 was found to be an independent factor for predicting overall and disease-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 21128013
- Overexpression of ECM1 contributes to migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma. PMID: 22489696
- Case Report: a novel mutation in Pakistani family extends the body of evidence that supports the importance of ECM1 gene for the development of lipoid proteinosis. PMID: 21791056
- neurologic and neuroradiologic characteristics and ECM1 gene mutations of seven individuals with lipoid proteinosis (LP) from three unrelated consanguineous families PMID: 21349189
- ECM1 played an important role in the growth, metastasis and angiogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma. PMID: 16646403
- PLSCR1 interacts with the tandem repeat region of ECM1a in the dermal epidermal junction zone of human skin. PMID: 20870722
- The ECM/SULF1 and ECM/COLLAGEN metagenes showed inconsistent association with DMFS in the three prognostic data sets in both breast neoplasm subtypes, and the combined P values were not significant. PMID: 20805453
- A novel homozygous 62-bp insertion in exon 8 of ECM1 in this Pakistani family is a rare mutation affecting both alleles and it may help in further understanding the multifunctional role of ECM1 PMID: 19519837
- Extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1) mutations in lipoid proteinosis and genotype-phenotype correlation. Seven new homozygous nonsense or frameshift mutations. Exons 6 and 7 most common sites for ECM1 mutations. PMID: 12603844
- These results indicate that ECM1 tends to be preferentially expressed by metastatic epithelial tumors. PMID: 14550953
- Frther emphasizes the role of ECM-1 in lipoid proteinosis and highlights unresolved genotype-phenotype correlation in this disease. PMID: 16274456
- it is reported here that ECM1 interacts with MMP9 and that such interactions diminish the proteolytic activity of MMP9 PMID: 16512877
- We report here mutation analysis of the ECM1 gene in a Chinese family with lipoid proteinosis. PMID: 17721643
- This article provides an update on the molecular pathology of lipoid proteinosis, including the addition of 15 new mutations in ECM1 to the mutation database [review] PMID: 17927570
- ECM1 is a basement membrane protein of the skin PMID: 18200062
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in ECM1 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis PMID: 18438406
- A survey of ECM1 expression in different tumors indicated that ECM1, although not tumor specific, is significantly elevated in many malignant epithelial tumors that give rise to metastases, emphasizing its relevance in the cancer process. Review. PMID: 18443958
- ECM1 variation was not associated with Crohn's disease. PMID: 19068216
- ECM proteins such as EDBFN and collagen are upregulated in ERM and PDR, and are regulated by TGF-beta. PMID: 19219685
- Functional and structural characterisation of human colostrum free secretory component. PMID: 19230975
- ECM1 is a multifunctional binding core and/or a scaffolding protein interacting with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. PMID: 19275936
- Overexpression of ECM1 is associated with invasive breast carcinomas. PMID: 19521735
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Lipoid proteinosis (LiP)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in breast cancer tissues. Little or no expression observed in normal breast tissues. Expressed in skin; wide expression is observed throughout the dermis with minimal expression in the epidermis.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3153
OMIM: 247100
KEGG: hsa:1893
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000358045
UniGene: Hs.81071
Most popular with customers
-
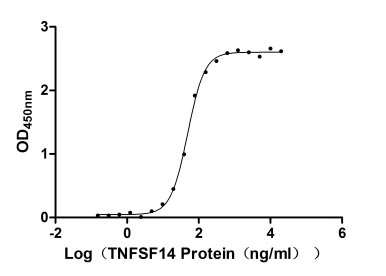
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
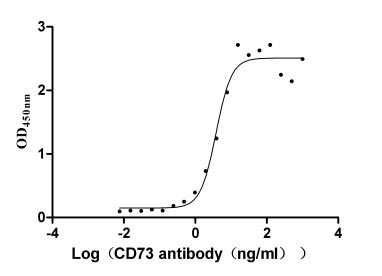
Recombinant Human 5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
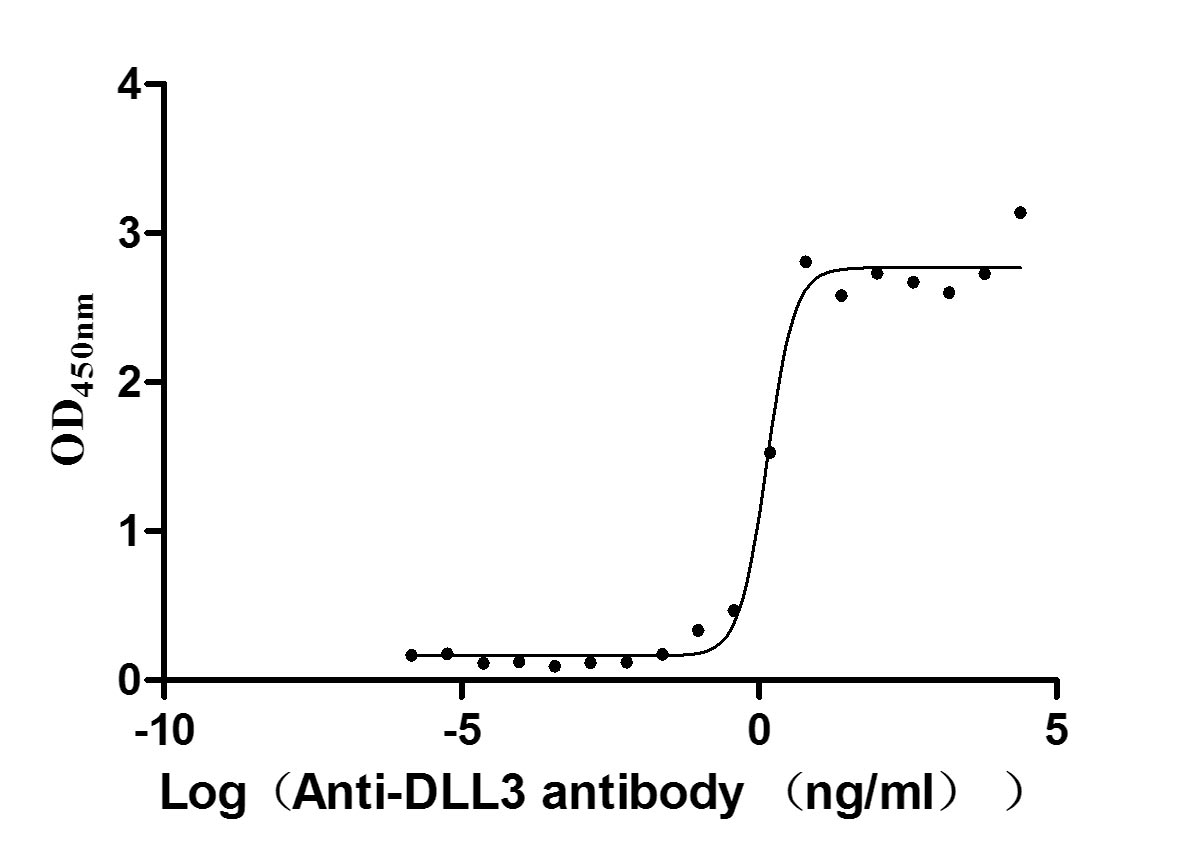
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
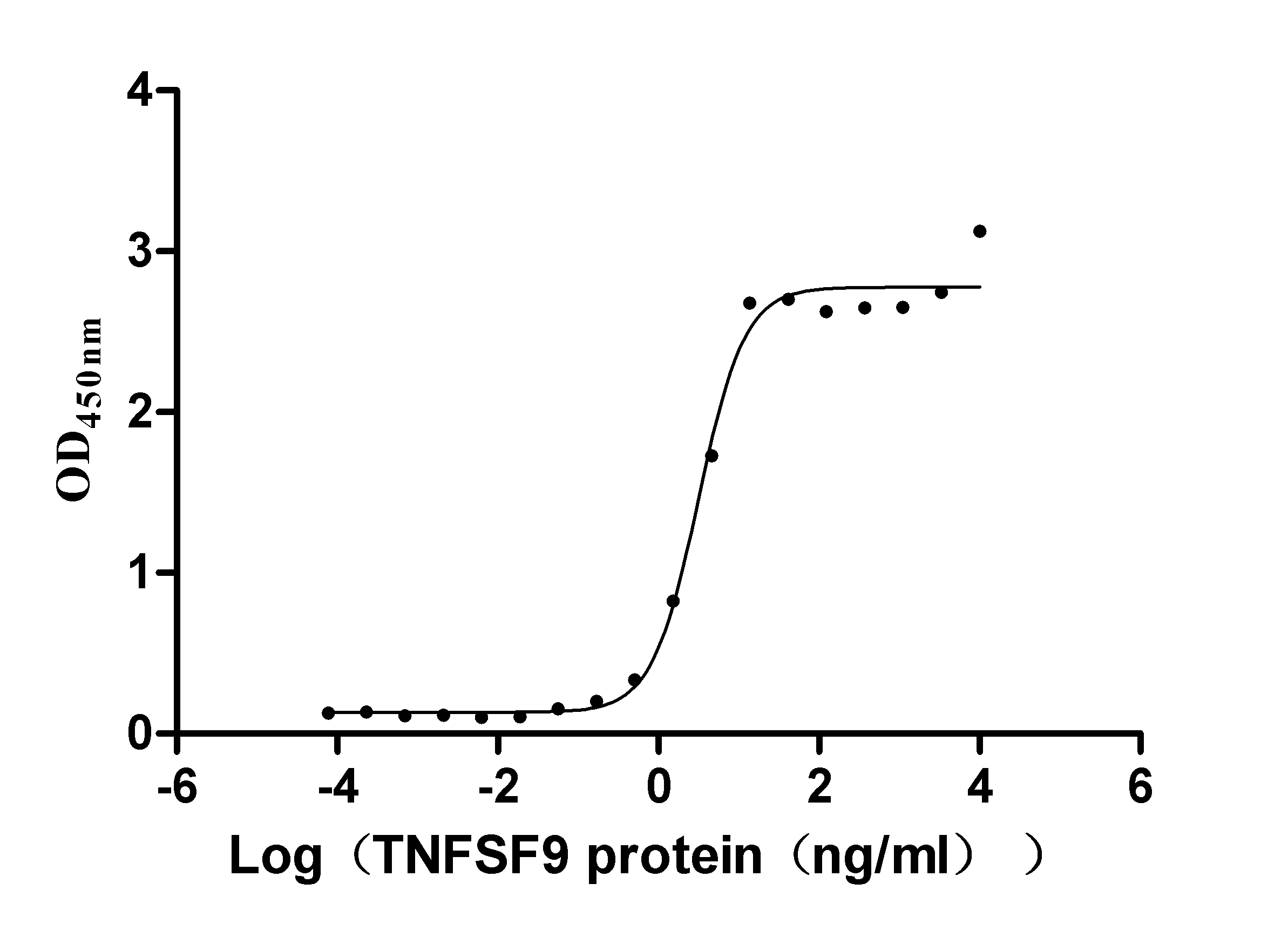
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human T-cell surface protein tactile (CD96), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
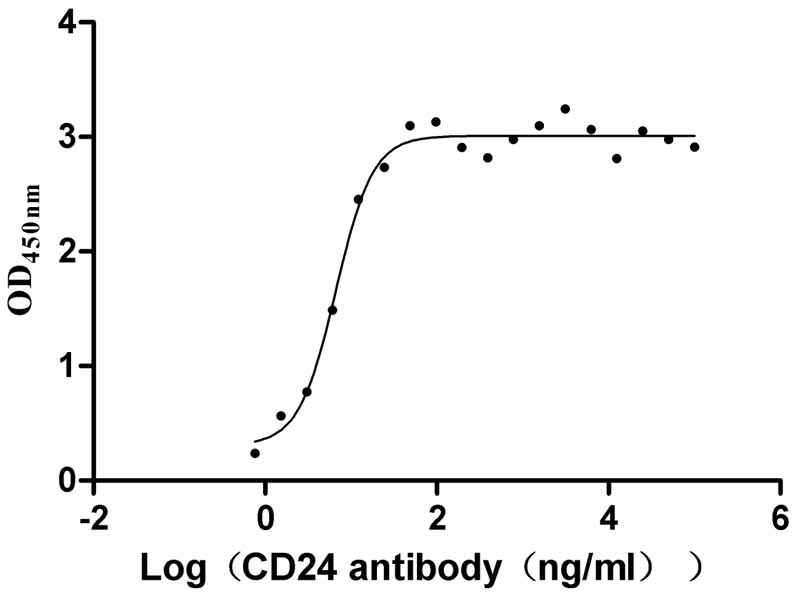
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Claudin-18 (Cldn18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
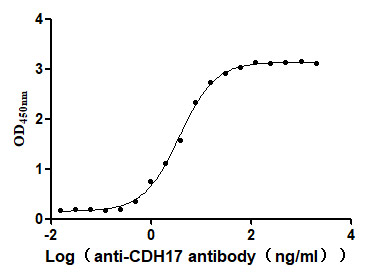
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)