Recombinant Human Aquaporin-4 (AQP4), partial
-
货号:CSB-BP001964HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP001964HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP001964HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
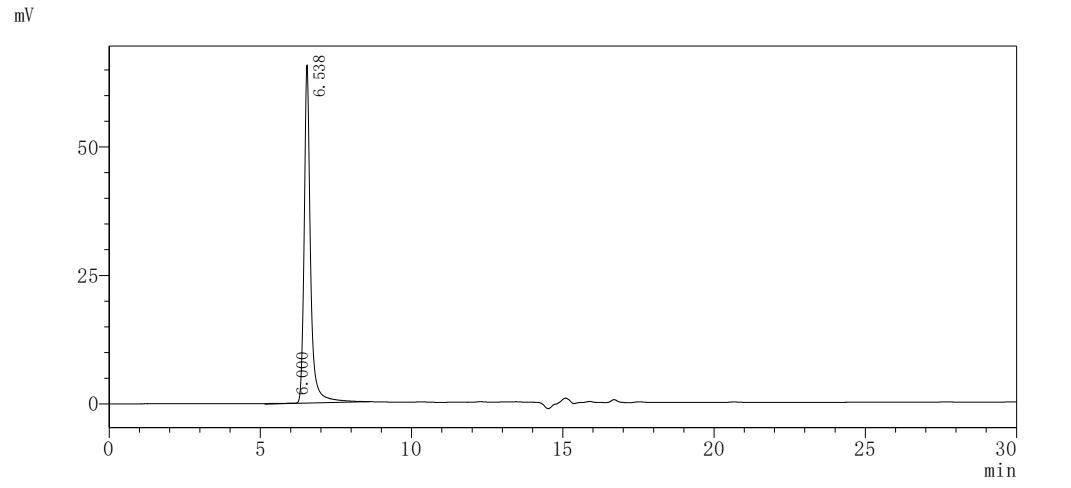
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:Name:AQP4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:AQP 4; AQP-4; AQP4; AQP4_HUMAN; Aquaporin type 4; Aquaporin-4; Aquaporin4; HMIWC 2; HMIWC2; Mercurial insensitive water channel; Mercurial-insensitive water channel; MGC22454; MIWC; WCH 4; WCH4
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
表达区域:253-323
-
氨基酸序列CPDVEFKRRFKEAFSKAAQQTKGSYMEVEDNRSQVETDDLILKPGVVHVIDVDRGEEKKG KDQSGEVLSSV
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Forms a water-specific channel. Plays an important role in brain water homeostasis and in glymphatic solute transport. Required for a normal rate of water exchange across the blood brain interface. Required for normal levels of cerebrospinal fluid influx into the brain cortex and parenchyma along paravascular spaces that surround penetrating arteries, and for normal drainage of interstitial fluid along paravenous drainage pathways. Thereby, it is required for normal clearance of solutes from the brain interstitial fluid, including soluble beta-amyloid peptides derived from APP. Plays a redundant role in urinary water homeostasis and urinary concentrating ability.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- AQP4 genetic variation moderates the relationship between sleep and brain Abeta-amyloid burden. PMID: 29479071
- our results suggested that miRNA-320a could suppress the aggressive capacity of tumors by targeting AQP4, and that miRNA-320a could serve as a new effective therapeutic target for glioma surgical and therapeutic strategies. PMID: 29484417
- This study demonstrated that Concentrations of microparticles expressing GFAP and AQP4 were significantly higher in the traumatic brain injury group compared with healthy controls. PMID: 28972406
- Review speculated that the diverse expression of AQP4 isoforms and complement regulatory factors may determine individual susceptibility to disease onset, the expression difference in AQP4 isoforms and complement regulatory factors in different organs may determine the extent of involvement and the severity of the disease. AQP4-IgG-mediated immune injury in peripheral organs may not be rare. PMID: 29141819
- Hypothermia-mediated increase in AQP4 surface abundance on human astrocytes, which was blocked using either calmodulin antagonist; TRPV4 antagonist or calcium chelation. A TRPV4 agonist mimicked the effect of hypothermia compared with untreated normothermic astrocytes. Hypothermia increased surface localization of AQP4 in human astrocytes likely through TRPV4 calcium channels and calmodulin activation. PMID: 28925524
- AQP4 expression was significantly increased 24 hours after mTBI. mTBI resulted in a significant increase in the cell swelling within 30 min of mTBI, which was significantly reduced in the presence of AZA. PMID: 27623738
- the overall results of this study allowed us to provide the first description of the localization of AQP4 in human SGs and indicate an abnormal distribution of AQP4 in SGs from SS patients, which could be responsible for the decreased saliva secretion in these patients. PMID: 28648105
- CC genotype of rs72878794 associated with sudden infant death syndrome PMID: 28520217
- Aquaporin 4 (AQP-4) are recognized as essential for two unique functions, namely, neurovascular coupling and glymphatic flow, the brain equivalent of systemic lymphatics [Review]. PMID: 28820467
- In neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder-AQP4 patients, gender impacts on disease onset age and site of attack PMID: 27760862
- Report the value of spinal cord biopsy in the diagnosis of aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. PMID: 24192218
- identified that TMZ might have therapeutic potential for controlling proliferation, invasion of malignant glioma by inhibiting AQP4 expression through activation of p38 signal transduction pathway PMID: 28569417
- The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not aquaporin-4 (AQP4) gene mutations are related to the pathogenesis of inflammatory demyelinating diseases in the central nervous system. PMID: 25895050
- Comparative molecular dynamics study of neuromyelitis optica-immunoglobulin G binding to AQP4 extracellular domains has been presented. PMID: 28477975
- Osmotic water permeabilities of aquaporins AQP4, AQP5, and GlpF from near-equilibrium simulations have been presented. PMID: 28455098
- A clear correlation between AQP4 expression and ADCmax values in grade I meningioma was identified. PMID: 27357591
- Peritumoral brain edema in patients with meningiomas may depend on AQP4 expression grades and not on tumor grade, tumor volume, Ki-67 expression, and cell count. PMID: 27552812
- AQP4 antibodies were higher in neuromyelitis optica Chinese Han patients with circulating auto-antibodies. PMID: 27988051
- Retinal nerve fiber layer may be better preserved in MOG-IgG versus AQP4-IgG optic neuritis. PMID: 28125740
- AQP4-autoantibody serostatus correlated with poor visual outcome in neuromyelitis optica (Meta-analysis) PMID: 28071581
- Data show that aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) autoantibodies double positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) patients had a multiphase disease course with a high annual relapse rate. PMID: 26920678
- In this study, altered AQP4 expression was associated with aging brains. PMID: 27893874
- Results suggest that pain is an important factor in the quality of life experienced by both AQP4-Ab positive and negative transverse myelitis patients and suggest an even greater association than disability PMID: 27538606
- The major findings in this study were (1) a higher AQP4 immunogold labeling density over parenchymal astrocytic membranes in human subjects than in mice, and (2) a lower degree of AQP4 immunogold polarization to perivascular astrocytic endfoot membranes in humans compared with mice. In the human individuals, endfoot AQP4 polarization did not differ between capillary and arteriolar vessel segments. PMID: 28317216
- Upregulation of Aquaporin 4 is associated with Astrocytomas. PMID: 27483250
- No characteristic MRI brain features were observed in the Malaysian AQP4 seropositive idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating disease patients versus those who are seronegative PMID: 28283103
- the T allele of rs2075575 is a risk for AQP4-Ab-positive NMO. PMID: 27012886
- A reduction was found in the aquaporin-4 levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with intracranial hypertension. PMID: 26853804
- Study concludes from direct measurement of deterministic molecular dynamics in conjunction with applied-field metadynamics that the intrinsic electric field within the AQP4 channel points along the +z-axis, such that externally applied static fields in this direction serve to "open" the channel in the selectivity-filter and the asparagine-proline-alanine region. PMID: 27586951
- Results indicate that T-cells bearing characteristics of both Th1 and Th17 T-cells and targeting specific immunodominant epitopes of the AQP4 protein might be involved in the pathogenesis of Neuromyelitis optica PMID: 27063619
- AQP4 antibody associated optic neuritis tends to involve the posterior optic pathway. PMID: 26163068
- Our results suggest that AQP5 but not AQP4 contributes to salivary secretion in patients with Sjogren's syndrome, including those with neuromyelitis optica complicated with Sjogren's syndrome. PMID: 26375433
- Administration of E1 + P1 and E1 + P2 decreased the inhibitory effect of E1 on the IL-6 levels and AQP4 protein expression PMID: 26638215
- Study shows that the processing of AQP4 by antigen presenting cells in Lewis rats produces a highly encephalitogenic AQP4 epitope (AQP4268-285) PMID: 26530185
- The induction of antibodies to an AQP4 epitope in mice immunized with the TAX1BP1-derived peptide suggests that a latent HTLV-1 infection could lead to TAX1BP1 antigen presentation and the production of anti-AQP4 antibodies in human neuromyelitis optica. PMID: 26287441
- This study demonstrated that Subcellular localization of Aqp4 was compared between cortical and white matter astrocytes in postmortem specimens of patients with focal ischemic stroke versus controls. PMID: 26419740
- Anti-AQP-4 antibodies correlate with active neuromyelitis optica disease activity and animal models PMID: 25913278
- AQP4 antibody was highly prevalent (almost 54%) in Egyptian idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating central nervous system patients PMID: 25677878
- Study identified two AQP4 genomic variants, rs11661256 and rs1058427, as significant predictors of combined intracerebral hemorrhage and perihematomal edema volume after intracerebral hemorrhage PMID: 26000774
- Measurements of the membrane water permeability of MDCK cells expressing human AQP4 mutants provide the first evidencethat the rate of water flow can also be controlled by small movements of single-amino acid side chains lining the water pore. PMID: 26512424
- Phosphorylation at serine 276 is necessary for AQP4 translocation in response to changes of tonicity. PMID: 26013827
- Case Report: relapsing inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion associated with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders, in an anti-aquaporin-4 antibody positive 14-year-old girl. PMID: 24866202
- Case Report: anti-aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with hypothalamic lesions and sudden onset of sleep. PMID: 25160125
- Data suggest that preventing neuromyelitis optica (NMO)-IgG aquaporin-4 (AQP4) binding would represent a strategy for a NMO therapy. PMID: 25839357
- The idea is that sudden, disorderly, and excessive neuronal discharges activates NOX2 with O(2)(-) production, leading to lipid peroxidation. The resulting generation of HNE targets AQP4, affecting water and ion balance. PMID: 25460197
- This review focuses on the role of AQP4 in ischemic brain edema, and its prospect as a therapeutic target--{REVIEW} PMID: 25306413
- analysis of how aquaporin 4 extracellular domains mutations affect restricted binding patterns of pathogenic neuromyelitis optica IgG PMID: 25792738
- In conclusion, the present study provides evidence for possible involvement of genetic variations in AQP4 gene in the functional outcome, but not in initial severity or presence of intracranial hemorrhages of patients with TBI. PMID: 24999750
- results suggest that AQP4 is internalized and the lysosome is involved in degrading the internalized AQP4 post-intracerebral hemorrhage PMID: 25257965
- AQP4 is mainly targeted to the lipid rafts fraction of the plasma membrane and a change of subcellular localization of AQP4 by the treatment with cholesterol-lowering agents significantly reduces the cytotoxic effects of NMO-IgG PMID: 25128605
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome membrane. Cell membrane, sarcolemma; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection.
-
蛋白家族:MIP/aquaporin (TC 1.A.8) family
-
组织特异性:Detected in skeletal muscle. Detected in stomach, along the glandular base region of the fundic gland (at protein level). Detected in brain, lung and skeletal muscle, and at much lower levels in heart and ovary.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 637
OMIM: 600308
KEGG: hsa:361
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000372654
UniGene: Hs.315369
Most popular with customers
-
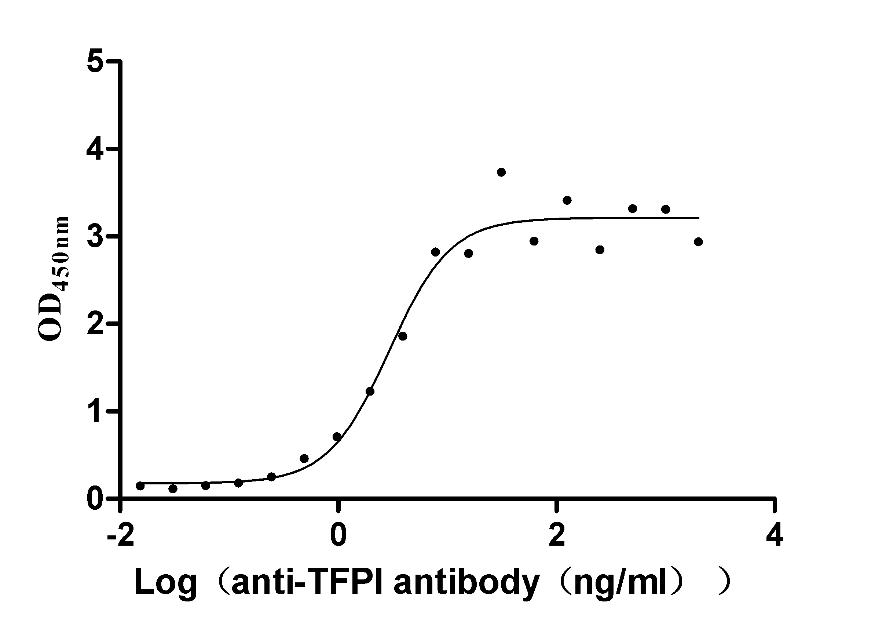
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
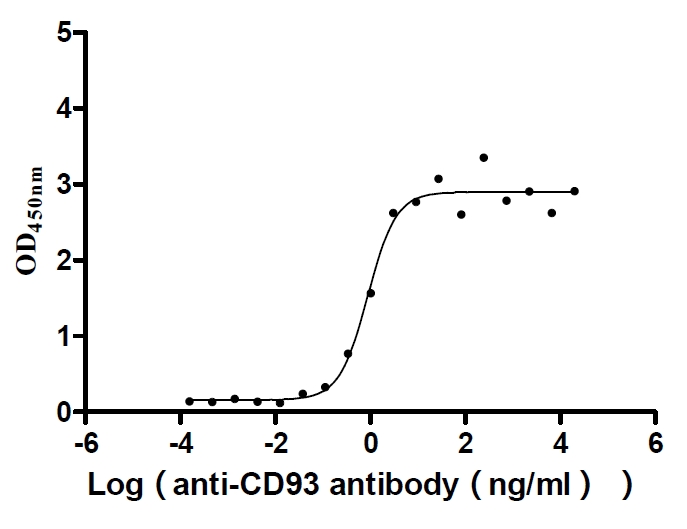
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
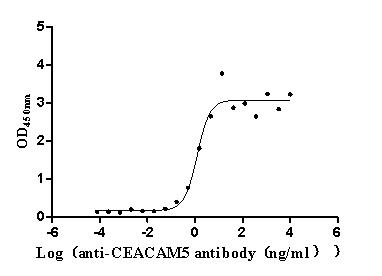
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
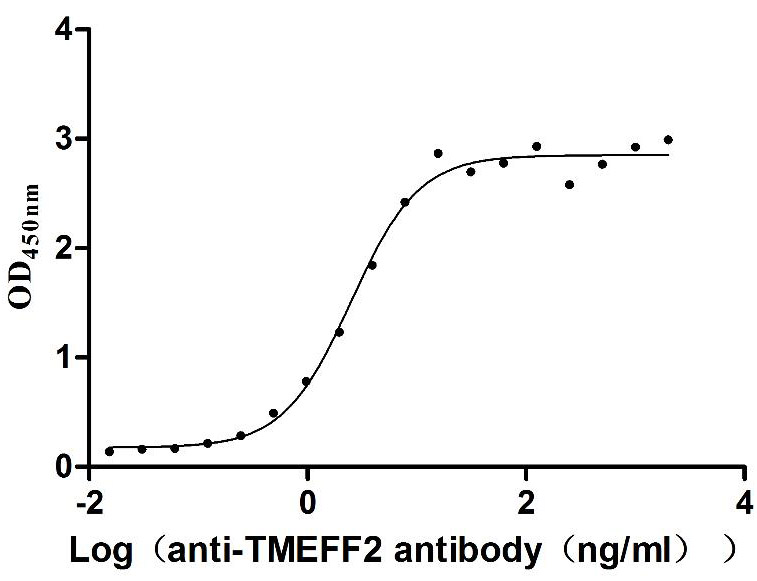
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
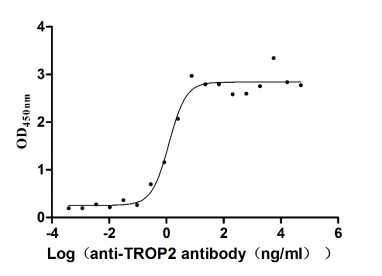
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
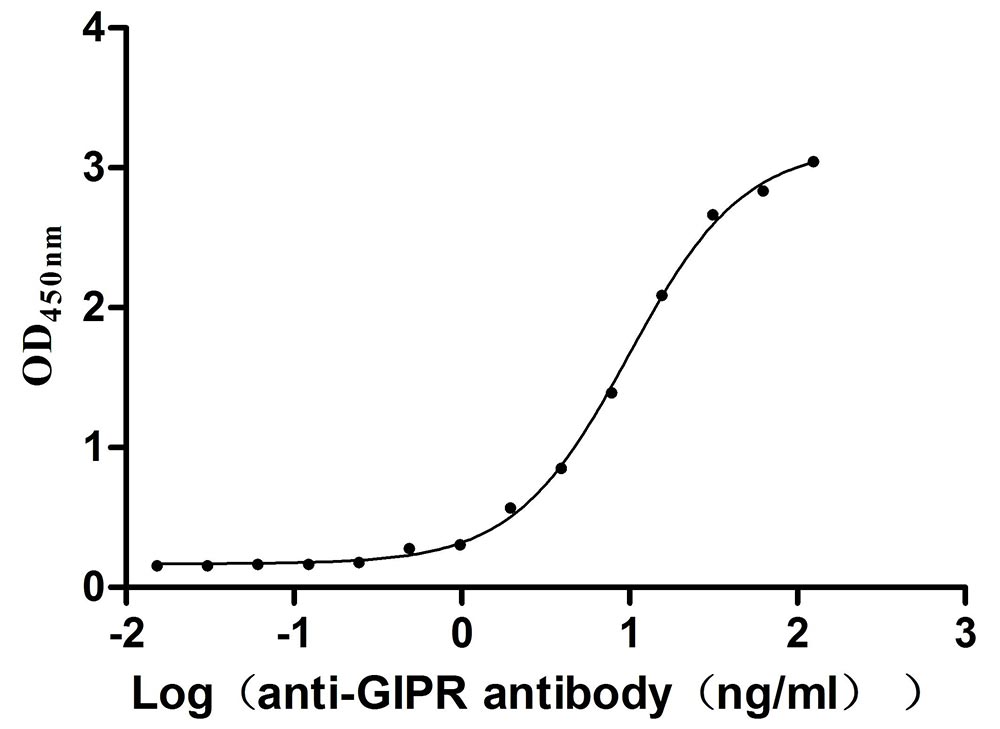
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
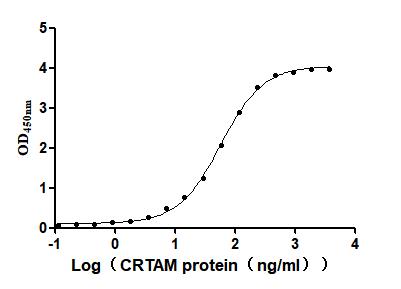
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)