Recombinant Human Apolipoprotein C-II (APOC2)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP001932HU
-
规格:¥1344
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
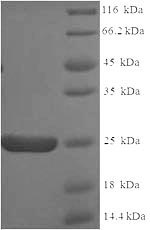
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:APC 2; APC2; Apo CII; Apo-CII; APOC 2; ApoC II; ApoC-II; APOC2; APOC2 protein; APOC2_HUMAN; ApoCII; Apolipoprotein C II; Apolipoprotein C II precursor; Apolipoprotein C2; ApolipoproteinCII; MGC75082; ProapoC-II; Proapolipoprotein C-II
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:24.9kDa
-
表达区域:23-101aa
-
氨基酸序列TQQPQQDEMPSPTFLTQVKESLSSYWESAKTAAQNLYEKTYLPAVDEKLRDLYSKSTAAMSTYTGIFTDQVLSVLKGEE
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Component of chylomicrons, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) in plasma. Plays an important role in lipoprotein metabolism as an activator of lipoprotein lipase. Both proapolipoprotein C-II and apolipoprotein C-II can activate lipoprotein lipase. In normolipidemic individuals, it is mainly distributed in the HDL, whereas in hypertriglyceridemic individuals, predominantly found in the VLDL and LDL.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results from this exploratory analysis suggest that regulatory element methylation levels within the larger TOMM40-APOE-APOC2 gene region correlate with AD-related biomarkers and TOMM40 or APOE gene expression in AD. PMID: 29371683
- Triglyceride-raising variant alleles of the APOC2 encoding apo C-II, associated with clinical Cardiovascular endpoints. PMID: 28534127
- The results demonstrate the important role of both intra- and inter-subunit charge interactions in stabilizing apoC-II amyloid fibrils, a process that may be a key factor in determining the general ability of proteins to form amyloid fibrils. PMID: 28229588
- The results highlight the importance of charge-pair interactions within the apoC-II fibril core PMID: 26196342
- Conformational rearrangement of apoC-II at lipoprotein surfaces promotes interaction with LPL. PMID: 26026161
- Large deletion in APOC2 caused by Alu-Alu homologous recombination is associated with with apolipoprotein C-II deficiency. PMID: 25172036
- No APOC2 mutations were identified in a cohort of patients with diabetic lipemia. PMID: 25131724
- STAT1 bound on multienhancer 2 cooperates with RXRalpha located on apoCII promoter and upregulates apoCII expression only in macrophages. PMID: 22808166
- Mutations in GPIHBP1 are rare but the associated clinical phenotype of hypertriglyceridaemia is severe PMID: 22239554
- These results support a predictive change in the ratio of plasma ApoCIII to ApoCII in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia. PMID: 21321243
- Substoichiometric concentrations of cyc[60-70] significantly delayed fibril formation by the fibrillogenic, linear peptides apoC-II[60-70] and apoC-II[56-76]. PMID: 22244853
- Activation of apoC-II fibrils by submicellar lipid (NBD-lyso-12-phosphocholine) is catalytic with release of monomer- and tetramer-bound lipid accompanying fibril elongation and growth. PMID: 21985034
- Physiological shear flow conditions and conditions experienced during apoC-II manufacturing exert significant effects on apoC-II conformation, leading to protein misfolding, aggregation, and amyloid fibril formation. PMID: 21476595
- Includes the observation of APOC4-APOC2 read-through transcription PMID: 8530039
- Our structural model for apoC-II fibrils suggests that apoC-II monomers fold and self-assemble to form a stable cross-beta-scaffold containing relatively unstructured connecting loops. PMID: 21146539
- Results describe the functional role of the secondary structure in the lipoprotein lipase-binding portion of apolipoprotein CII. PMID: 20042600
- Human apolipoprotein C-II (apoC-II) slowly forms amyloid fibers in lipid-free solutions at physiological pH and salt concentrations PMID: 11751863
- During amyloidosis under oxidizing conditions, cysteine-containing apolipoprotein C-II (apoC-II) derivatives form fibrils more rapidly and become extensively tangled compared to wild-type apoC-II. PMID: 12450397
- Three categories of global constraints, together with the local classical NMR constraints, define the 3D structure of the apoCII-SDS micelle complex and give important clues toward a possible mechanism for the activation of lipoprotein lipase by apoCII. PMID: 12590574
- regions of lipoprotein lipase that are responsive to activation by apoC-II PMID: 12682050
- Hydrolysis activated by APOC2 was faster compared with the LPL-mediated lipolysis of emulsion triolein. The binding density of APOC2 was less for small emulsion surfaces than for large ones. PMID: 12782148
- Different levels of secreted apoC-II had little effect on LDL and HDL protein degradation by HepG2 cells. Compared to controls, cells under-expressing apoC-II showed a 160% higher capacity to selectively take up HDL-CE. PMID: 15778093
- Results show that purified human HDL and recombinant apolipoprotein A-I lipid particles bind directly to amyloid beta and apolipoprotein C-II amyloid fibrils. PMID: 16432277
- No relationship was found between ApoCII polymorphism and coronary disease in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 16459141
- Decrease of LPL activity in the heart, along with the inhibitory effects of excess apolipoprotein C-II, may contribute to the hypertriglyceridemia observed in apolipoprotein c-ii transgenic mice. PMID: 17018885
- Taken together these data demonstrate an interaction between antichymotrypsin and apolipoprotein C-II that accelerates fibrillogenesis and indicates a specific role for accessory proteins in protein aggregation. PMID: 17174330
- These results suggested that T-->A substitution at position -190 in the apoC-II gene promoter only partly affected transcriptional activity of the apoC-II promoter, leading to decrease of apoC-II expression in quantity. PMID: 17222387
- The ozone oxidation product of cholesterol, 3beta-hydroxy-5-oxo-5,6-secocholestan-6-al, rapidly promotes human apolipoprotein (apo) C-II amyloid fibril formation in vitro. PMID: 17429947
- Both common and rare DNA variants of APOC2 gene were found in 10% patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia PMID: 17717288
- Phospholipid interaction induces molecular-level polymorphism in APOC2 amyloid fibrils via alternative assembly pathways. PMID: 18005990
- The concentration-dependent kinetics of apolipoprotein C-II amyloid fibril formation and correlated this with the final size distribution of the fibrils determined by sedimentation velocity experiments, is studied. PMID: 18206908
- lipids promote on-pathway intermediates of apoC-II fibril assembly and the accumulation of a discrete tetrameric intermediate depends on the molecular state of the lipid PMID: 18852267
- No significant differences were found between the acute hypertriglyceridaemic pancreatitis cases and controls with severe hypertriglyceridaemia in terms of LPL activity and mass, hepatic lipase activity, CII and CIII mass, or apo E polymorphisms. PMID: 19534808
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Hyperlipoproteinemia 1B (HLPP1B)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Apolipoprotein C2 family
-
组织特异性:Liver and intestine.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 609
OMIM: 207750
KEGG: hsa:344
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000466775
UniGene: Hs.75615
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
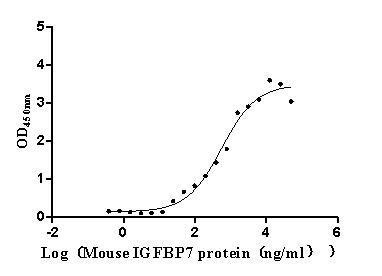
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
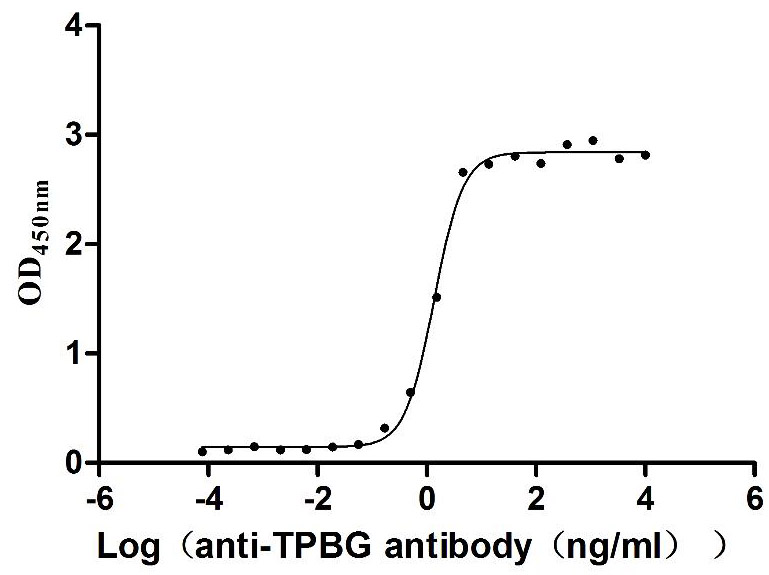
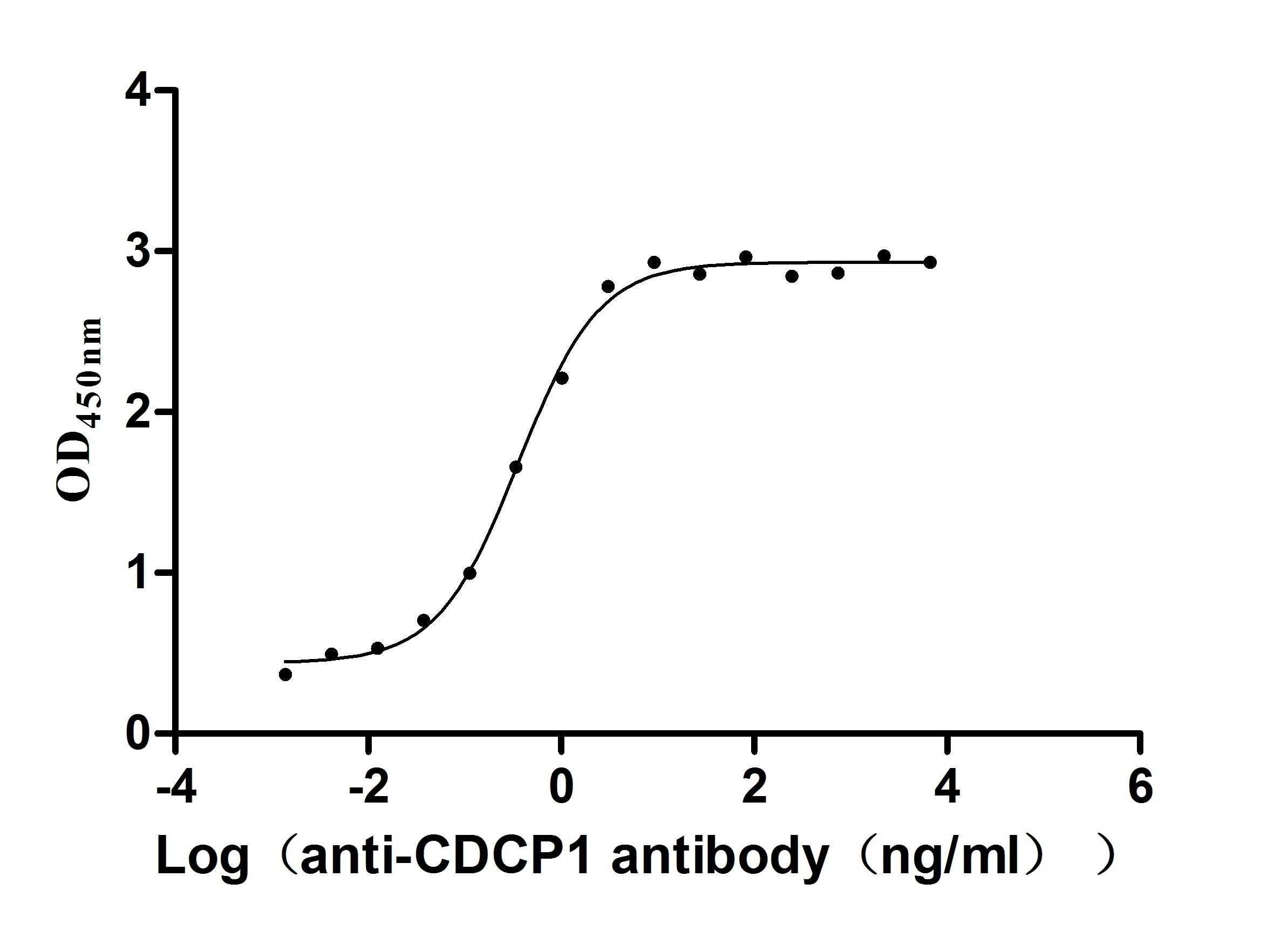
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
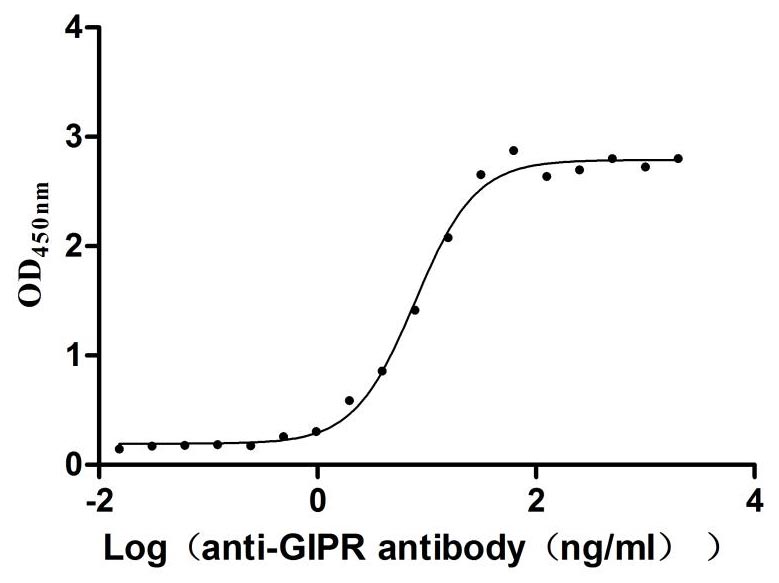
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
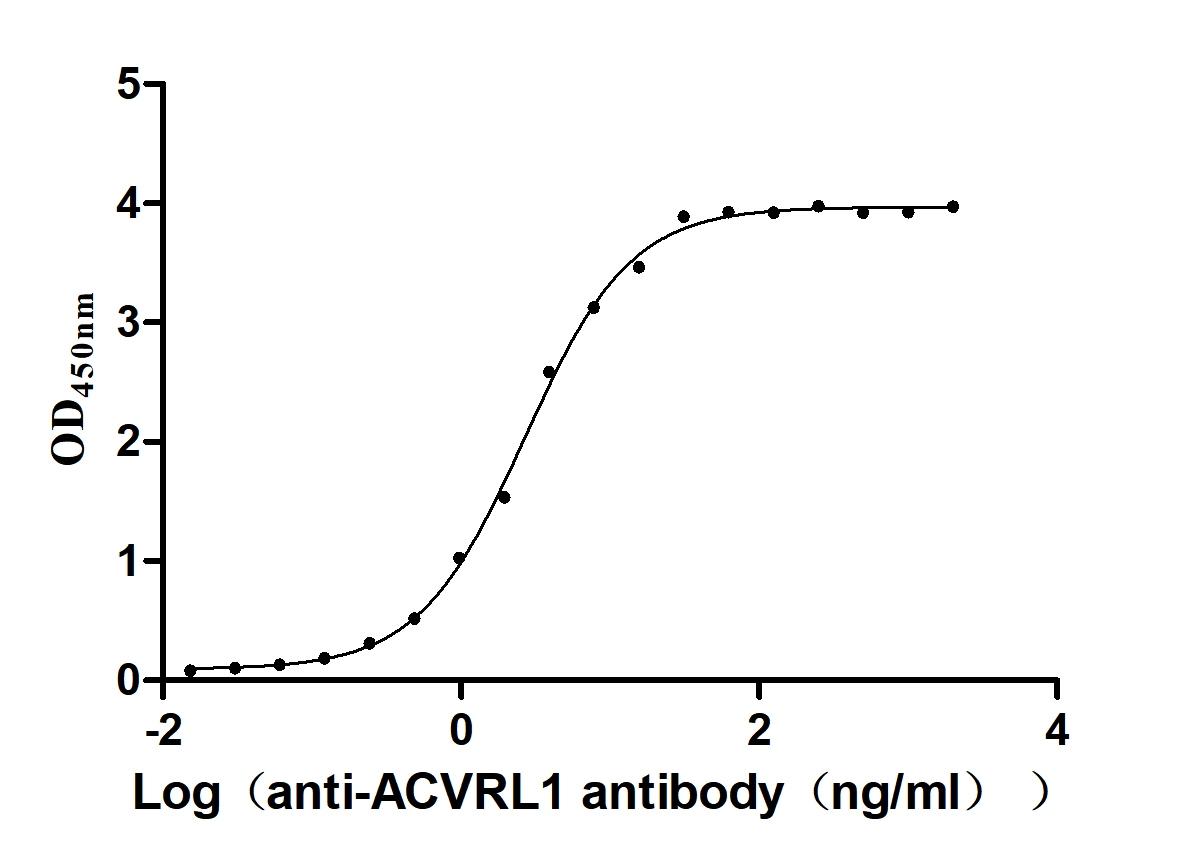
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)