-
中文名称:大鼠胆囊收缩素/肠促胰酶肽(CCK)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E08114r
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3900/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Rat CCK ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Rat CCK protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 3.9 pg/mL .
-
别名:CckCholecystokinin ELISA kit; CCK) [Cleaved into: Cholecystokinin-39 ELISA kit; CCK39); Cholecystokinin-33 ELISA kit; CCK33); Cholecystokinin-22 ELISA kit; CCK22); Cholecystokinin-12 ELISA kit; CCK12); Cholecystokinin-8 ELISA kit; CCK8)] ELISA kit
-
缩写:CCK
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Metabolism
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat CCK in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 93 Range % 88-97 1:2 Average % 95 Range % 90-99 1:4 Average % 97 Range % 93-101 1:8 Average % 84 Range % 80-92 -
回收率:
The recovery of rat CCK spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 103 96-108 EDTA plasma (n=4) 90 85-94 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 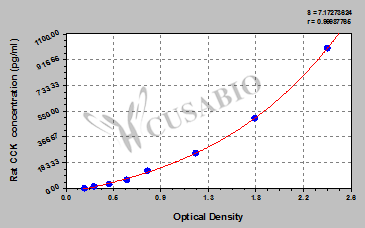
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 1000 2.449 2.351 2.400 2.209 500 1.783 1.692 1.738 1.547 250 1.212 1.182 1.197 1.006 125 0.789 0.739 0.764 0.573 62.5 0.549 0.596 0.573 0.382 31.2 0.409 0.420 0.415 0.224 15.6 0.267 0.278 0.273 0.082 0 0.185 0.197 0.191 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Exploring the Role of Duodenal Resurfacing in Diabetes Improvement L Nie,DIABETES OBESITY & METABOLISM,/
- Regulation of gastrointestinal hormones during laxative activity of gallotannin-enriched extract isolated from Galla Rhois in loperamide-induced constipation of SD rats Kim JE, et al,Lab Anim Res,2018
- Changes in ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in a hypoxia-induced anorexia rat model Duraisamy AJ. et al,Endokrynol Pol,2015
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:This peptide hormone induces gall bladder contraction and the release of pancreatic enzymes in the gut. Its function in the brain is not clear. Binding to CCK-A receptors stimulates amylase release from the pancreas, binding to CCK-B receptors stimulates gastric acid secretion.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study provides the first direct comparative and quantitative data showing that presynaptic GABAB receptors exert differential inhibition at cholecystokinin (CCK) and parvalbumin (PV) basket cell (BC) synapses, resulting from a higher surface expression of the receptor at all CCK BC terminals and a lower protein density present in a subpopulation of boutons of PV BCs. PMID: 28466358
- The two projections from CCK(NTS) neurons reduce food intake through opposite motivational states; one pathway signals positive valence (CCK(NTS)-->paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus ) and the other signals negative valence (CCK(NTS)-->parabrachial nucleus). PMID: 28684275
- Taken together, these results demonstrate that DMH NPY descending signals affect CCK-induced satiety, at least in part, via modulation of NTS catecholaminergic neuronal signaling. PMID: 27534875
- We conclude that only a small fraction of neuronal CCK is nonsulfated. The intracellular distribution of nonsulfated CCK in neurons suggests that they contribute only modestly to the CCK transmitter activity. PMID: 27535680
- The favorable treatment strategy for acute pancreatitis is to keep the pancreas at rest during an early stage followed by pancreatic stimulation by promoting endogenous CCK release. PMID: 26167074
- Cardiac expression of pro-cholecystokinin is cell-specific, which differentiates the expression from that of intestinal endocrine cells and cerebral neurons. PMID: 25627687
- Estrogen-induced anxiolytic effects were associated with changes of the cholecystokinin system in brain regions controlling anxiety-like behavior. PMID: 24732637
- All together, this study clearly demonstrates an important protective role of cholecystokinin against sepsis induced by Staphylococcus aureus. PMID: 24487953
- Data suggest that Cck (here synthetic peptide fragment Cck 1-8; but not peptide YY 3-36 or glucagon-like peptide 1) mediates anorexic behavioral responses of peripheral sensory neurons (presumably vagal afferent nerves in mucosa of small intestines). PMID: 25117406
- CCK-8 octapeptide attenuates the effects of morphine and saline on hippocampal long-term potentiation through CCK2 receptors, suggesting an ameliorative function of CCK-8 on morphine-induced memory impairment. PMID: 24309294
- findings suggest that the fibroblast growth factor system is poised to modulate both CCK and FGF-R1 expression in the ventral tegmental area PMID: 24121132
- Data suggest that Apo AIV (apolipoprotein AIV) in NTS (nucleus of the solitary tract) or/and peripheral Cck require vagal Cck1r (cholecystokinin receptor 1) signaling to elicit satiation; high-fat diet reduces satiating capacity of these signals. PMID: 24564397
- CCK-8 antagonizes electroacpuncture modulation of sympathoexcitatory cardiovascular responses through an opioid mechanism and that inhibition of CCK-8 can convert animals that initially are unresponsive to EA to become responsive. PMID: 23785073
- A biliopancreatic diversion model in rats finds a pathophysiological mechanism of action resulting from weight loss and villi elongation. PMID: 22813405
- Cholecystokinin has cellular actions within the periaqueductal gray that can both oppose and reinforce opioid and cannabinoid modulation of pain and anxiety within this brain structure. PMID: 21525858
- Rats on a medium high-fat diet had significantly higher plasma leptin but lower cholecystokinin levels than rats on a low-fat diet. This corresponded to attenuated or reversed splanchnic nerve responses to cholecystokinin and leptin. PMID: 21239630
- Unlike in the dorsal vagal complex (DVC), CCK-8 was only able to activate the myenteric neurons in older rats. This delayed activation compared to the DVC may reflect a delayed role for these neurons in CCK-related functions. PMID: 21093507
- High dose lithium reduces the expression of cholecystokinin in hippocampal neurons. PMID: 16535834
- Our results provide a cellular and molecular mechanism to explain the roles of CCK in the brain. PMID: 20392936
- CaR is the beta 51-63 peptide sensor responsible for the stimulation of CCK secretion in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. PMID: 19896983
- Cholecystokinin induces caspase activation and mitochondrial dysfunction in pancreatic acinar cells PMID: 11964411
- Basal endogenous levels of cholecystokinin appear to play an important role in the anxiety-related behaviors in rats. PMID: 12450740
- Cholecystokinin has a role in stimulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase through activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Yes, and protein kinase C PMID: 12496267
- neurons in the rat basolateral amygdala contain cholecystokinin. PMID: 12763251
- leptin induces the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)-1/2 proteins and increases cholecystokinin release PMID: 12829630
- cholecystokinin system may play important role in expressing the symptopathology of the chronic stress responses such as depression, abnormality of food intake or anxiety-related disorders PMID: 12914981
- CCK-IR cells represent one interneuron type that assists in the maturation of glutamatergic synapses (activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors) via GABAergic depolarization of principal cell dendrites. PMID: 12927199
- Significant downregulation of CCK transcription is noted in the hippocampus and contralateral cortex 1 day after entorhinal cortex lesioning and an increased signal in ipsilateral cortex, followed by up-regulated CCK mRNA expression at postlesional day 5. PMID: 12946704
- Spinal cord injury increases levels of cholecystokinin mRNA in the cortex, diencephalon, and mesencephalon of rats. Animals that developed pain post-injury had higher CCK levels than animals that did not develop pain. PMID: 14559369
- The degree of colocalization of the prohormone convertase (PC) enzymes PC1, PC2, and PC5 with CCK in rat brain is regionally specific. PMID: 14608596
- in rat retina, CCK induces tyrosine phosphorylation of p130(Cas), in a time and concentration-dependent manner. PMID: 14698681
- Plasma levels CCK and CGRP were significantly increased through 3 hours and 7 days postinjury, with the peak at 72 hours. CCK in jejunum changed as in plasma. PMID: 15040036
- procholecystokinin undergoes parallel pathways of proteolytic cleavages PMID: 15260493
- Data suggest that cholecystokinin may play a role in the generation of negative affective states indexed by 22-kilohertz (kHz) ultrasonic calls in certain regions of the brain. PMID: 15464747
- Co-expression patterns of the neuropeptides vasoactive intestinal peptide and cholecystokinin with the transduction molecules alpha-gustducin and T1R2 in rat taste receptor cells. PMID: 15561439
- A study of the hypothesis that CCK in the rostral ventromedial medulla may engage descending pain facilitatory pathways to enhance spinal nociceptive transmission and attenuate morphine antinociception. PMID: 15647484
- CCK preadministration to obese rats did not affect ghrelin-induced food intake. PMID: 15890776
- Elevated CCK levels in the posterior cortex may be related to negative aspects of play, while lower CCK levels in the hypothalamus may reflect the more positive valenced aspects of play during bouts of juvenile social-play fighting. PMID: 16143427
- Intra-nucleus accumbens administration of a CCK2 receptor antagonist inhibited not only the development but also the expression of chronic morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance. PMID: 16837074
- stimulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-protein kinase A signaling pathway by CCK-8 through CCK-1R and CCK-2R inhibits the LPS-induced activation of p38 kinase and NF-kappaB to block the IL-1beta production in rat pulmonary interstitial macrophages PMID: 17505309
- CCK increased the frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and currents. This effect was blocked by tetrodotoxin, indicating that the CCK effect is likely mediated by direct excitation of GABAergic interneurons. PMID: 17904218
- These data show that CCK is an initiating factor in acute pancreatitis in the rat. PMID: 18297100
- Results show that CCK plays a role in regulating the access of leptin to the brain via CCK1 receptors. PMID: 18587446
- Report effects of cholecystokinin-58 on type 1 cholecystokinin receptor function and regulation. PMID: 18776046
- Results show that synaptophysin-containing cells co-expressed vesicular-associated membrane protein 2 and cholecystokinin. PMID: 19253017
- Duodenal Cholecystokinin requires the activation of the gut Cholecystokinin-A receptor and a gut-brain-liver neuronal axis to lower glucose production. PMID: 19656488
- assessed whether leptin signaling in hindbrain also enhances these responses to CCK PMID: 19726710
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Gastrin/cholecystokinin family
-
组织特异性:The shortest form (CCK8) is predominantly found in the brain, whereas the larger ones are found in the intestine.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













