-
中文名称:小鼠嗜环蛋白/亲环素A(CyPA)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E09282m
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3200/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse PPIA ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse PPIA protein in serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 3.9 pg/mL .
-
别名:Ppia ELISA Kit; Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A ELISA Kit; PPIase A ELISA Kit; EC 5.2.1.8 ELISA Kit; Cyclophilin A ELISA Kit; Cyclosporin A-binding protein ELISA Kit; Rotamase A ELISA Kit; SP18) [Cleaved into: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A ELISA Kit; N-terminally processed] ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Signal Transduction
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse CyPA in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 90 Range % 86-93 1:2 Average % 93 Range % 89-97 1:4 Average % 95 Range % 91-97 1:8 Average % 100 Range % 96-103 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse CyPA spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 95 90-97 EDTA plasma (n=4) 95 91-98 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 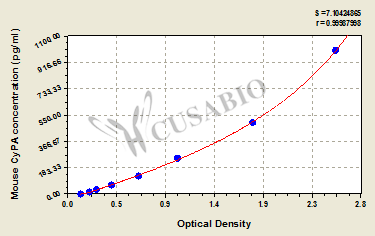
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 1000 2.582 2.566 2.574 2.431 500 1.782 1.776 1.779 1.636 250 1.055 1.073 1.064 0.921 125 0.682 0.695 0.689 0.546 62.5 0.431 0.437 0.434 0.291 31.2 0.292 0.282 0.287 0.144 15.6 0.224 0.216 0.220 0.077 0 0.144 0.142 0.143 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Intracellular and Extracellular Cyclophilin a Promote Cardiac Fibrosis Through Tgf-Β Signaling in Response to Angiotensin Ii M Cao,Available at SSRN,2023
- Extracellular cyclophilin A induces cardiac hypertrophy via the ERK/p47phox pathway M Cao,Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2020
- Prognosis of sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture in mice improved by anti-Clonorchis Sinensis cyclopholin a antibodies Song T. et al,Parasit Vectors,2015
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides. Exerts a strong chemotactic effect on leukocytes partly through activation of one of its membrane receptors BSG/CD147, initiating a signaling cascade that culminates in MAPK/ERK activation. Activates endothelial cells (ECs) in a proinflammatory manner by stimulating activation of NF-kappa-B and ERK, JNK and p38 MAP-kinases and by inducing expression of adhesion molecules including SELE and VCAM1. Induces apoptosis in ECs by promoting the FOXO1-dependent expression of CCL2 and BCL2L11 which are involved in EC chemotaxis and apoptosis. In response to oxidative stress, initiates proapoptotic and antiapoptotic signaling in ECs via activation of NF-kappa-B and AKT1 and up-regulation of antiapoptotic protein BCL2. Negatively regulates MAP3K5/ASK1 kinase activity, autophosphorylation and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis mediated by MAP3K5/ASK1. Necessary for the assembly of TARDBP in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) complexes and regulates TARDBP binding to RNA UG repeats and TARDBP-dependent expression of HDAC6, ATG7 and VCP which are involved in clearance of protein aggregates. Plays an important role in platelet activation and aggregation. Regulates calcium mobilization and integrin ITGA2B:ITGB3 bidirectional signaling via increased ROS production as well as by facilitating the interaction between integrin and the cell cytoskeleton. Binds heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Extracellular cyclophilin A augments platelet-dependent thrombosis and thromboinflammation. PMID: 28981554
- Endothelial cell-derived CypA (especially AcK-CypA) causes pulmonary artery hypertension by a presumptive mechanism involving increased EC apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. PMID: 28450293
- ox-LDL-induced CyPA secretion requires vesicle transportation, actin remodeling and ROCK-dependent diphosphorylation of myosin light chains in vascular smooth muscle cells. PMID: 27825172
- knockdown of CD147 on Hepa1-6 cells resulted in significantly increased T cells chemotaxis induced by CypA both in vivo and in vitro. PMID: 27133068
- CypA dually exerts pro-osteogenic and anti-osteoclastic effects. PMID: 26932182
- Extracellular CyPA activates platelets via cluster of differentiation 147-mediated phosphoinositid-3-kinase/Akt-signaling, leading to enhanced adhesion and thrombus formation independently of intracellular CyPA. PMID: 25550208
- CypA provided stability for NF-kappaB p65 and promoted NF-kappaB p65 nuclear translocation, resulting in increased nuclear accumulation and enhanced NF-kappaB activity. PMID: 25119989
- Newborn CypA-deficient pups exhibited generalized, pronounced skeletal defects, while high-resolution micro-computed tomography analyses of the femurs and lumbar vertebrae revealed delayed or incomplete endochondral ossification. PMID: 25870110
- Cyclophilin A secretion was increased in lymphocytes from atherogenic mice. PMID: 25115246
- CD137-CD137L interactions mediated via regulation of CyPA contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis. PMID: 24520398
- Reactive oxygen species-dependent CypA secretion by endothelial cells is an important signaling mechanism through which endothelial cell reactive oxygen species regulate susceptibility of structural components of the aortic wall to aortic dissection. PMID: 24807872
- CyPA is an important regulator for AngII-induced ROS generation in VSMC through interaction with p47phox and cell cytoskeleton, which enhances the translocation of p47phox to caveolae. PMID: 23846495
- CYPA was identified as a novel host restriction factor that confered protection against rotavirus infection. PMID: 23303713
- CyPA expression increases and may modulate inflammatory cell adhesion and interleukin-6 expression inducing vascular smooth muscle cell migration and inflammatory cell extravasation in a time-dependent manner PMID: 23201430
- How does oxidative stress contribute to vascular disease? Data from vascular smooth muscle suggest that reduced glutathione peroxidase 1 (i.e., oxidative stress) promotes secretion of CypA which mediates paracrine inflammation of vasculature. PMID: 21782974
- CsA inhibits BKV replication through CypA and NFAT, which may be potential targets of anti-BKV treatment PMID: 22642569
- CyPA is an important Ca(2+) regulator in platelets, a critical mechanism for arterial thrombosis. PMID: 22740452
- CypA is a key target for treating APOE4-mediated neurovascular injury and the resulting neuronal dysfunction and degeneration PMID: 22622580
- truncated CyPA detected in brain following prion infection may have an important role in the activation of brain-derived primary astroglia and microglia in prion disease and perhaps other neurodegenerative or neuroinflammatory diseases. PMID: 22179611
- Disrupting the EMMPRIN (CD147)-cyclophilin A interaction reduces infarct size and preserves systolic function after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. PMID: 21441138
- CyPA is required for Ang II-mediated cardiac hypertrophy by directly potentiating ROS production, stimulating the proliferation and migration of cardiac fibroblasts, and promoting cardiac myocyte hypertrophy in ApoE deficient mice. PMID: 21330604
- data define a role for CyPA in atherosclerosis and suggest CyPA as a target for cardiovascular therapies PMID: 21173104
- The CyPA/EMMPRIN activation pathway may play a relevant role in promoting the vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. PMID: 19758589
- a novel function of CypA is required in the processing of RA-induced neuronal differentiation in p19 embryonal carcinoma cells PMID: 15047706
- CyPA is a novel paracrine and autocrine modulator of EC functions in immune-mediated vascular disease PMID: 15111303
- CyPA is highly expressed in in atherosclerotic plaques from the ApoE-/- mouse. It has proinflammatory effects on EC and may play an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. PMID: 15130913
- CyP-A may perform a general function related to the binding of cargo for retrograde movement along microtubules PMID: 15496417
- Among multiple potential intracellular ligands of T cells, CypA is the primary mediator of immunosuppression by cyclosporine. PMID: 15879096
- CypA has an epigenetic function in protecting the paternal allele of Peg3 from DNA methylation and inactive histone modifications PMID: 17071620
- These results show that MCMV replication depends upon cellular CyPA pathways in neural stem and progenitor cell (in a specific cell type-dependent fashion), that CyPA plays an important role in viral infection in this cell type. PMID: 17553872
- lethal translocation of AIF to the nucleus requires interaction with CypA, suggesting a model in which two proteins that normally reside in separate cytoplasmic compartments acquire novel properties when moving together to the nucleus PMID: 17635954
- CyPA plays a crucial role in vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation, and inflammatory cell accumulation, thus regulating flow-mediated vascular remodeling and intima formation. PMID: 18541741
- Apoe-/-Ppia-/- mice are completely protected from AngII-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm formation PMID: 19430489
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Secreted. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Cyclophilin-type PPIase family, PPIase A subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the kidney thick ascending limb (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and motor neurons (at protein level). Expressed in platelets.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













