Mouse Programmed Death 1(PD-1)ELISA Kit
-
中文名称:
小鼠程序性死亡-1(PD-1)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:
CSB-E13586m
-
规格:
96T/48T
-
价格:
¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse PDCD1 ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse PDCD1 protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL and the sensitivity is 0.078 ng/mL.
-
别名:
Pdcd1 ELISA Kit; Pd1 ELISA Kit; Programmed cell death protein 1 ELISA Kit; Protein PD-1 ELISA Kit; mPD-1 ELISA Kit; CD antigen CD279 ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates
-
检测范围:
0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL
-
灵敏度:
0.078 ng/mL
-
反应时间:
1-5h
-
样本体积:
50-100ul
-
检测波长:
450 nm
-
研究领域:
Cell Biology
-
测定原理:
quantitative
-
测定方法:
Sandwich
-
精密度:
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% | | | | |
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | | |
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% | | | | |
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | | | |
| | | | | | | |
-
线性度:
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse PD-1 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | |
| | Sample | Serum(n=4) | | |
| 1:1 | Average % | 97 | | |
| Range % | 92-101 | | |
| 1:2 | Average % | 91 | | |
| Range % | 85-96 | | |
| 1:4 | Average % | 84 | | |
| Range % | 80-88 | | |
| 1:8 | Average % | 95 | | |
| Range % | 95-99 | | |
-
回收率:
| The recovery of mouse PD-1 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | |
|
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | | |
| Serum (n=5) | 101 | 96-107 | | |
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 95 | 90-100 | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
-
标准曲线:
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | |
|
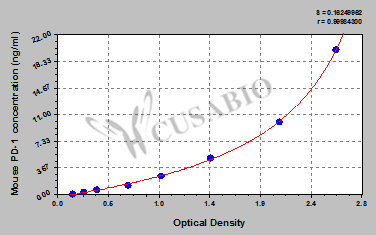 | ng/ml | OD1 | OD2 | Average | Corrected | | | | 20 | 2.652 | 2.528 | 2.590 | 2.430 | | | | 10 | 2.121 | 2.009 | 2.065 | 1.905 | | | | 5 | 1.439 | 1.417 | 1.428 | 1.268 | | | | 2.5 | 0.994 | 0.952 | 0.973 | 0.813 | | | | 1.25 | 0.651 | 0.680 | 0.666 | 0.506 | | | | 0.625 | 0.384 | 0.375 | 0.380 | 0.220 | | | | 0.312 | 0.256 | 0.261 | 0.259 | 0.099 | | | | 0 | 0.163 | 0.156 | 0.160 | | | |
|
-
本试剂盒所含材料:
- A micro ELISA plate --- The 96-well plate has been pre-coated with an anti-human PD-1 antibody. This dismountable microplate can be divided into 12 x 8 strip plates.
- Two vials lyophilized standard ---Dilute a bottle of the standard at dilution series, read the OD values, and then draw a standard curve.
- One vial Biotin-labeled PD-1 antibody (100 x concentrate) (120 μl/bottle) ---Act as the detection antibody.
- One vial HRP-avidin (100 x concentrate) (120 μl/bottle) ---Bind to the detection antibody and react with the TMB substrate to make the solution chromogenic.
- One vial Biotin-antibody Diluent (15 ml/bottle) ---Dilute the Biotin-antibody.
- One vial HRP-avidin Diluent (15 ml/bottle) ---Dilute the HRP-avidin solution.
- One vial Sample Diluent (50 ml/bottle)---Dilute the sample to an appropriate concentration.
- One vial Wash Buffer (25 x concentrate) (20 ml/bottle) ---Wash away unbound or free substances.
- One vial TMB Substrate (10 ml/bottle) ---Act as the chromogenic agent. TMB interacts with HRP, eliciting the solution turns blue.
- One vial Stop Solution (10 ml/bottle) ---Stop the color reaction. The solution color immediately turns from blue to yellow.
- Four Adhesive Strips (For 96 wells) --- Cover the microplate when incubation.
- An instruction manual
显示更多
收起更多
-
本试剂盒不含材料:
- A microplate reader capable of measuring absorbance at 450 nm, with the correction wavelength set at 540 nm or 570 nm.
- An incubator can provide stable incubation conditions up to 37°C±5°C.
- Centrifuge
- Vortex
- Squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, or automated microplate washer
- Absorbent paper for blotting the microtiter plate
- 50-300ul multi-channel micropipette
- Pipette tips
- Single-channel micropipette with different ranges
- 100ml and 500ml graduated cylinders
- Deionized or distilled water
- Timer
- Test tubes for dilution
显示更多
收起更多
-
数据处理:
-
货期:
3-5 working days
靶点详情
-
功能:
Inhibitory receptor on antigen activated T-cells that plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self. Delivers inhibitory signals upon binding to ligands, such as CD274/PDCD1L1 and CD273/PDCD1LG2. Following T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement, PDCD1 associates with CD3-TCR in the immunological synapse and directly inhibits T-cell activation. Suppresses T-cell activation through the recruitment of PTPN11/SHP-2: following ligand-binding, PDCD1 is phosphorylated within the ITSM motif, leading to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN11/SHP-2 that mediates dephosphorylation of key TCR proximal signaling molecules, such as ZAP70, PRKCQ/PKCtheta and CD247/CD3zeta. The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and facilitate tumor survival.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Oncolytic herpes virotherapy and PD-1 blockade in a murine rhabdomyosarcoma model is an efficient treatment strategy. PMID: 28539588
- These results show that PD-1 plays an inhibitory role during the naive-to-effector CD8 T cell transition and that the PD-1 pathway can also be modulated at this stage of T cell differentiation. PMID: 29654146
- Blockade of CCR5-mediated myeloid derived suppressor cell accumulation enhances anti-PD1 efficacy in gastric cancer PMID: 29303012
- T-cell activation mediates the immunopreventive effects of anti-PD-1; PD-1 on T cells interacts with the PD-1 ligand PD-L1 on cancer cells PMID: 29018057
- these data show that PD-1 expression is an intrinsic property of brain-resident memory CD8 T cells in a persistent CNS viral infection PMID: 28829048
- Our results demonstrate that entinostat enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 targeting through functional inhibition of MDSCs and a transition away from an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment. These data provide a mechanistic rationale for the clinical testing and potential markers of response of this novel combination in solid tumor patients. PMID: 28698201
- synergism in cell death by Caspase-1- and RipK3 resulted in restriction of PD-1 and TIM3 expression on primed CD8(+) T cells, which promoted the survival of activated CD8(+) T cells. PMID: 28686578
- Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways play critical roles in regulating CD8(+) T cell function and maintaining normal pregnancy. PMID: 28331165
- Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy inhibited CMT167 orthotopic lung tumors by 95%. .Silencing PD-L1 expression in CMT167 cells resulted in smaller orthotopic tumors that remained sensitive to anti-PD-L1 therapy, whereas implantation of CMT167 cells into PD-L1(-) mice blocked orthotopic tumor growth, indicating a role for PD-L1 in both the cancer cell and the microenvironment. PMID: 28819064
- Combination therapies that depend on checkpoint inhibitor antibodies (Abs) such as for PD-1 or its ligand (PD-L1) together with immune stimulatory agonist Abs like anti-OX40 are being tested in the clinic to achieve improved antitumor effects PMID: 28848055
- Inhibition of Fut8, a core fucosyltransferase, by genetic ablation or pharmacologic inhibition reduced cell-surface expression of PD-1 and enhanced T cell activation, leading to more efficient tumor eradication. PMID: 28768188
- An examination of the mechanisms of immunity behind this long-term protection in PD-1 knockout mice showed a key role for parasite-specific CD8(+) T cells even when CD4(+) T cells and B cells responded to re-infection. PMID: 27217330
- To test the in vivo activity of REGN2810, which does not cross-react with murine PD-1, knock-in mice were generated to express a hybrid protein containing the extracellular domain of human PD-1, and transmembrane and intracellular domains of mouse PD-1 PMID: 28265006
- The combination of tumor vaccination to induce high avidity tumor specific T cell responses and PD-1 blockade synergises to provide tumor therapy and 85% survival in the aggressive B16 melanoma model. PMID: 27825115
- Blockade of PD-1 with monoclonal antibody may be an effective treatment during the postoperative period for restoring surgery-induced immunosuppression. PMID: 28320090
- Data suggest that genetic or environmental factors that even moderately affect the expression of both PD-1 and FoxP3 can cause life-threatening autoimmune diseases by disrupting the T-cell homeostasis. PMID: 27410049
- Data (including data from studies in transgenic/knockout mice) suggest that T-cell expression of Mirn155 is required to limit melanoma growth; miR-155, Pdcd1, Pdcd1l1, and Ctla4 appear to regulate overlapping pathways promoting antitumor immunity. [Mirn155 = microRNA 155; Pdcd1 = programmed cell death 1 protein; Pdcd1l1 = programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 protein; Ctla4 = cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4] PMID: 28912267
- PD-1 plays a vital role in brain inflammation via regulation of Fgl-2 after ICH, and that manipulation of PD-1 might be a promising therapeutical target in ICH. PMID: 27717876
- The identification of the role for PD-1 in regulating B cell-dependent antitumor immunity to Tn antigen highlights an opportunity to develop new therapeutic strategies targeting tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens PMID: 27856425
- These findings suggest that PD-1 pathway blockade may reverse adaptive immune resistance following cyclic dinucleotide treatment, enhancing both local and systemic antitumor immunity. PMID: 27821498
- data suggest that increased expression of checkpoint blockade molecules PD-1 and CTLA-4 on donor T cells is not sufficient to prevent GvHD, and that cooperation between checkpoint blockade signaling by host cells and donor Tregs is necessary to limit GvHD in allo-HSCT recipients PMID: 28953925
- PD-1 Blockade Promotes Epitope Spreading in Anticancer CD8(+) T Cell Responses by Preventing Fratricidal Death of Subdominant Clones To Relieve Immunodomination PMID: 28939757
- Adoptive transfer of murine T cells expressing a chimeric-PD1-Dap10 receptor may induce a preferential cytokine profile and T-cell differentiation phenotype for anti-lymphoma therapies. PMID: 28670716
- soluble PD-1 is elevated in critical illness and may represent a potential biomarker for Acute respiratory distress syndrome. PMID: 27835962
- Together, our results suggest an important role of PD-1 in glioma-induced immune escape, and provide translational evidence for the use of PD-1 blocking antibodies in human malignant gliomas. PMID: 28681455
- study found that Bcl6 positively regulates PD-1 expression by inhibiting the ability of T-bet/Tbx21 to repress Pdcd1 transcription. PMID: 28586108
- PD-L1 selectively enhances T cell-mediated immune responses, driving graft-versus-host disease lethality and suggesting a context-dependent function of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis PMID: 27294527
- PD-1 is required for maintaining the number, and hence function, of KLRG1(+) Group 2 innate lymphoid cells. PMID: 28490441
- this study shows that PD-1 regulates early glycolytic and mitochondrial alterations in virus-specific CD8+ T cells generated during infection, and represses transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha PMID: 27496729
- Our results suggest that anti-PD-1 antibody treatment has little effect on afatinib-induced lung injury. PMID: 28756224
- both mouse and human tumour-associated macrophages (TAM) express PD-1; TAM PD-1 expression increases over time in mouse models of cancer and with increasing disease stage in primary human cancers PMID: 28514441
- These data implicate a critical role for conserved region C (CR-C), a promoter proximal cis-regulatory element that is critical to PD-1 expression in vitro, in governing PD-1 expression, and a subsequent role in guiding CD8 T cell differentiation PMID: 27895178
- we provide evidence that indicates that the PD-1(+) fraction of DN T cells represents self-reactive cells. PMID: 27060346
- PD-1 receptor has a role in interacting with programmed cell death ligands and B7-1 PMID: 28270509
- PD-1 is upregulated in CD4+ T cells in Schistosoma japonicum (S. japonicum)-infected mice. PMID: 27792733
- Findings indicated that METH induced the upregulation of PD-1 expression which altered the cytokine production as well as cytotoxic functions in mouse model of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. PMID: 27760221
- Taken together, our data demonstrate the importance of CD40 signaling in the conversion of CTL exhaustion and its ability to enhance PD-1 antagonist action in rescuing exhausted CTLs in chronic infection. PMID: 28153727
- Our proteogenomic analysis demonstrates a role of Smad4 loss in the PD-L1 immune evasion, as well as Il1rl1's role in CSC-like properties of NCC-S1M. PMID: 28153736
- These studies indicate that PD-1 is a critical homeostatic regulator for Tregs by modulating proliferation and apoptosis during IL-2 therapy. PMID: 28151427
- data defined PD-1(hi)IL-25R(hi) as an early checkpoint in Innate lymphoid cell development; results provide a perspective for exploring PD-1 and its ligand (PD-L1) in immunotherapy, and allow effective manipulation of the immune system for disease prevention and therapy PMID: 27749818
- s demonstrate that inactivation of the PD-1 gene in melanoma-reactive CD8(+) T cells and in fibrosarcoma-reactive polyclonal T cells enhanced the persistence of PD-1 gene-modified T cells at the tumor site and increased tumor control. PMID: 27197251
- PD-1/PD-L1 plays a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance induced by UVB-iDCs, as well as in actively controlling effector T cells specific to alloantigens. PMID: 27556047
- PD-1 dampens antigen-specific Th17 response, thus inhibiting autoimmune arthritis PMID: 27197661
- Tim-3(+) PD-1(+) CD8(+) T cells showed more evident properties associated with exhaustion than Tim-3(-) PD-1(+) CD8(+) T cells. PMID: 26750587
- that porcine islet-specific tolerance is dependent on PD-1, which could not be extended to skin grafts PMID: 26109574
- Programmed cell death-1 engagement followed by zymosan stimulation might primarily attenuate the phosphorylation of tyrosine residue in Programmed cell death-1 receptor/ligand. PMID: 26913605
- these data suggest a scenario in which microglia are involved in the regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing Th1-cell differentiation via the PD-L1-nitric oxide pathway. PMID: 26769487
- Blockade of TGFbeta downregulated PD-1 and PD-L1 expression and precipitated graft rejection. PMID: 26824266
- PD-1 regulates peripheral T-cell responses in both human and murine rheumatoid arthritis PMID: 26608464
- Decidual NK, NKT and gamma/delta T cells showed increased PD-1 expression and reduced cytotoxic potential when compared to the periphery. PMID: 26278059
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:
Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:
Thymus-specific.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers














