-
中文名称:小鼠葡萄糖激酶(GCK)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-EL009319MO
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse GCK ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse GCK protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 3.9 pg/mL.
-
别名:Gck ELISA Kit; Gk ELISA Kit; Hexokinase-4 ELISA Kit; HK4 ELISA Kit; EC 2.7.1.1 ELISA Kit; Glucokinase ELISA Kit; Hexokinase type IV ELISA Kit; HK IV ELISA Kit; Hexokinase-D ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates
-
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Metabolism
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse GCK in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 96 Range % 87-99 1:2 Average % 94 Range % 86-98 1:4 Average % 93 Range % 82-97 1:8 Average % 100 Range % 90-105 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse GCK spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 102 92-105 EDTA plasma (n=4) 104 95-108 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 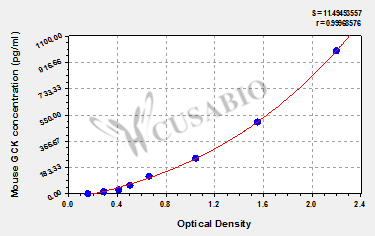
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 1000 2.252 2.156 2.204 2.026 500 1.588 1.529 1.559 1.381 250 1.032 1.084 1.058 0.880 125 0.687 0.662 0.675 0.497 62.5 0.515 0.528 0.522 0.344 31.25 0.426 0.435 0.431 0.253 15.6 0.300 0.311 0.306 0.128 0 0.180 0.176 0.178 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Different roles of insulin receptor a and b in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis in zebrafish Yulong Gong .et al,General and Comparative Endocrinology,2018
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexose, such as D-glucose, D-fructose and D-mannose, to hexose 6-phosphate (D-glucose 6-phosphate, D-fructose 6-phosphate and D-mannose 6-phosphate, respectively). Compared to other hexokinases, has a weak affinity for D-glucose, and is effective only when glucose is abundant. Mainly expressed in pancreatic beta cells and the liver and constitutes a rate-limiting step in glucose metabolism in these tissues. Since insulin secretion parallels glucose metabolism and the low glucose affinity of GCK ensures that it can change its enzymatic activity within the physiological range of glucose concentrations, GCK acts as a glucose sensor in the pancreatic beta cell. In pancreas, plays an important role in modulating insulin secretion. In liver, helps to facilitate the uptake and conversion of glucose by acting as an insulin-sensitive determinant of hepatic glucose usage. Required to provide D-glucose 6-phosphate for the synthesis of glycogen. Mediates the initial step of glycolysis by catalyzing phosphorylation of D-glucose to D-glucose 6-phosphate.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data also imply an etiological role of GCK in diet-induced diabetes. PMID: 29915142
- Long-term treatment with octanoic acid increased cellular glucose uptake in MIN6 cells by up-regulating the expression of glucokinase (GK). PMID: 29885841
- a nuclear import of glucokinase mediated by a redundant mechanism, involving a nuclear localization signal, and which is modulated by its SUMOylation, is reported. PMID: 28648619
- Glucokinase governs an alpha-cell metabolic pathway that suppresses secretion at or above normoglycemic levels; abnormal suppression of glucagon secretion deregulates hepatic glucose metabolism and, over time, induces a pre-diabetic phenotype. PMID: 29416045
- GCK-dependent glycolysis regulates Treg cell migration. PMID: 29166588
- GCK expression is regulated by nutrient-sensing O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosaminylation cycling in liver. PMID: 27520373
- Absence of Gck expression did not prevent the glucose responsiveness of glucose-excited or glucose-inhibited Sf1 neurons in either sex. Thus Gck in the VMN plays a sex-specific role in the glucose-dependent control of autonomic nervous activity; this is, however, unrelated to the control of the firing activity of classical glucose-responsive neurons. PMID: 27422385
- Using a mutant GCK gene (GCK 262) with a knocked out cytosine at position 2643 results in lower protein expression and more ubiquitination-led protein degradation compared with wild-type GCK (GCK 261) PMID: 26752353
- lncLGR facilitates the recruitment of hnRNPL to the GCK promoter and suppresses GCK transcription. PMID: 26904944
- Given that acetylated GKRP may affiliate with type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), understanding the mechanism of GKRP acetylation in the liver could reveal novel targets within the GK-GKRP pathway, for treating T2DM and other metabolic pathologies. PMID: 26620281
- These results suggest a mechanism for integrative control over GCK activation and, therefore, glucose metabolism and insulin secretion through regulation of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels. PMID: 26698632
- GHR knockdown caused increased glucokinase mRNA and protein levels. PMID: 26015548
- results suggest that chronic suppression of hepatic glucokinase has a small influence on intertissue (liver-to-BAT as well as liver-to-beta-cell) metabolic communication PMID: 25817793
- Atf3-silencing reversed ethanol-mediated Gck down-regulation and beta-cell dysfunction, followed by the amelioration of impaired glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. PMID: 25074928
- Suggest heterozygous glucokinase knockout mouse as a translatable model of human type 2 diabetes. PMID: 24772483
- Chronic treatment with glucose kinase activators in animal models of diabetes provided sustained lowering of blood glucose. PMID: 24772484
- In the liver-specific glucokinase knockout mouse reduced expression of glucokinase in the liver induces diabetic cardiomyopathy. PMID: 24447392
- Glucokinase is regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system to avoid misfolding and reduced activity of the enzyme. PMID: 24028089
- IRS-2 signalling is important for maintaining the activity of liver glucokinase. PMID: 23560040
- Hepatic GK overexpression in obesity-resistant mice promoted weight gain, while hepatic GK knockdown in obesity-prone mice attenuated weight gain with increased adaptive thermogenesis. PMID: 23217261
- SUMOylation of pancreatic glucokinase regulates its cellular stability and activity PMID: 23297408
- Changes in gluconeogenesis, delayed development of GCK and impaired hepatic glycogen synthesis in the liver potentially lead to the onset and progression of MODY2. PMID: 23291412
- A novel Gck mutation in mice, with relevance in humans, leading to glycaemic disease. PMID: 22698525
- Fed LiRiKO mice displayed loss of Akt Ser473 phosphorylation and reduced glucokinase and SREBP1c activity in the liver. PMID: 22521878
- beta-cell glucokinase appears to be essential for liraglutide-mediated insulin secretion, but liraglutide may improve glycemic control, steatosis, and beta-cell death in a glucokinase-independent fashion PMID: 22569791
- Generation of N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) diabetes models in mice demonstrates genotype-specific action of glucokinase activators. PMID: 21921030
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 stimulates post-translational activation of glucokinase in pancreatic beta cells PMID: 21454584
- The findings indicate that the absence of glucokinase inhibition by glucose 6-phosphate probably led to increased glycolysis and blocked glyceroneogenesis in the mouse model. PMID: 20623219
- Data show that binding and activation of glucokinase by PFK-2/FBPase-2 in beta-cells is promoted by glucose, resulting in an enhancement of insulin secretion at stimulatory glucose concentrations, without affecting basal insulin secretion. PMID: 20702580
- GCK inactivation and down-regulation were mediated by ethanol metabolism-generated peroxynitrite. PMID: 20855893
- I. sinclarii is effective in lowering blood glucose due to the upregulation of glucokinase (Gk-rs1) and downregulation of hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase. PMID: 20954077
- results show that although HNF-6 is not required to open chromatin of the hepatic promoter of the glucokinase gene, it stimulates transcription of the glucokinase gene in the liver PMID: 12189444
- MRG1 and GK are cannabinoid-regulated genes and that they may be involved in the vascular and hypothalamic effects of cannabinoids, respectively. PMID: 12237329
- Insulin upregulates NO and causes S-nitrosylation of glucokinase(GK). Inhibition of NO synthase blocks insulin-stimulated changes in GK secretory granules and GK conformation. PMID: 12707306
- phosphorylation status of BAD protein helps regulate glucokinase activity PMID: 12931191
- Hepatic glucokinase is required for the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c on glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression PMID: 14985368
- glucokinase is an integral component of the insulin secretory granule and does not translocate during glucose stimulation. PMID: 15331544
- Hypothesis that the glucokinase gene might be expressed in the pituitary corticotrophic cells was therefore reexamined using mRNA in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical techniques but was not proven. PMID: 16804059
- Overexpression of insulin receptor substrate 2 in beta cells of high diet-fed glucokinase deficient(+/-) mice partially prevented diabetes by increasing beta cell mass. PMID: 17200721
- Glucokinase plays a key role in the neuroendocrine regulation of metabolic economy. PMID: 17218412
- The hepatic abundance of glucokinase is reduced in Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 deficient mice. PMID: 17267763
- Role of a bound glucokinase protein fraction in the regulation of insulin granule movement along tubulin filaments. PMID: 17287461
- PSN-GK1 is a potent glucokinase activaator and is active as an antidiabetic agent in diabetic animal models. PMID: 17415548
- inhibition to liver glucokinase probably is the primary pathogenesis in alloxan-induced diabetes, prompting elevation of serum glucose content that leads to a further decrease in insulin secretion PMID: 17768029
- adipocyte-derived Wnt signalling molecules regulate insulin secretion, glucokinase gene transcription and beta cell proliferation PMID: 17994217
- PFK-2/FBPase-2 protein rather than its product fructose 2,6-P(2) is the over-riding determinant of glucose-induced insulin secretion through regulation of glucokinase activity or subcellular targeting. PMID: 18039179
- Between these two strategies to activate glycogen deposition in the absence of GK, embryonic livers choose to express massive levels of HKI and HKII. PMID: 18165236
- mRNA levels of Gck, Glp1r, and Pdx1 were increased in pancreatic RNA from both CJC-1134-PC- and/or Ex-4-treated mice. PMID: 18313669
- HNF-4 and Foxo1 are required for reciprocal transcriptional regulation of glucokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase genes in response to fasting and feeding PMID: 18805788
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Mitochondrion.
-
蛋白家族:Hexokinase family
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













