Recombinant Rat Beta-nerve growth factor (Ngf), partial
In Stock-
中文名称:大鼠Ngf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015779RA1
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
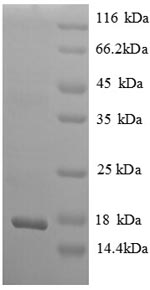
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Ngf; Ngfb; Beta-nerve growth factor; Beta-NGF
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:17.2kDa
-
表达区域:124-241aa
-
氨基酸序列THPVFHMGEFSVCDSVSVWVGDKTTATDIKGKEVTVLGEVNINNSVFKQYFFETKCRAPNPVESGCRGIDSKHWNSYCTTTHTFVKALTTDDKQAAWRFIRIDTACVCVLSRKAARRG
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Nerve growth factor is important for the development and maintenance of the sympathetic and sensory nervous systems. Extracellular ligand for the NTRK1 and NGFR receptors, activates cellular signaling cascades to regulate neuronal proliferation, differentiation and survival. The immature NGF precursor (proNGF) functions as ligand for the heterodimeric receptor formed by SORCS2 and NGFR, and activates cellular signaling cascades that lead to inactivation of RAC1 and/or RAC2, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and neuronal growth cone collapse. In contrast to mature NGF, the precursor form (proNGF) promotes neuronal apoptosis (in vitro). Inhibits metalloproteinase-dependent proteolysis of platelet glycoprotein VI. Binds lysophosphatidylinositol and lysophosphatidylserine between the two chains of the homodimer. The lipid-bound form promotes histamine relase from mast cells, contrary to the lipid-free form.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- proinflammatory cytokines suppressed the TGFbetamediated expression of NGF in PDLderived fibroblasts through the inactivation of TGFbetainduced Smad2/3 and p38 MAPK signaling. PMID: 29901090
- Impairments in the extracellular maturation of proNGF are sufficient to cause a somatodendritic retrograde degeneration o fdegeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. PMID: 29609077
- McGill APP transgenic rats exhibit differential dysregulation in NGF and BDNF neurotrophins. At early stages, intraneuronal Abeta leads to significant reductions in BDNF mRNA expression, which correlate with learning and memory deficits. At later stages, deficits in the NGF metabolic pathway could explain the paradoxical upregulation of proNGF in the absence of changes in NGF mRNA. PMID: 28865749
- p75NTR is sufficient to mediate the modulation of myogenic cells differentiation by NGF in terms of structural, metabolic and functional changes. PMID: 29202822
- NGF protects GECs against IND-induced injury. Mitochondria are major targets of both INDO-induced injury and NGF afforded protection of GECs. TrkA expression in the mitochondria of GECs indicates that the protection afforded by NGF is partly mediated by its direct action on mitochondria. NGF prevents MMP depolarization and increases expression of IGF-1 protein in GECs. PMID: 28843696
- The results suggest that NGF is a prominent hyperalgesic mediator in the trigeminal system and plays a role in trigeminal neuropathic pain PMID: 27392124
- Early and late behavioral changes in sciatic nerve injury may be modulated by nerve growth factor and substance P in rats PMID: 28685530
- A higher level of nerve growth factor in the early days post-transvaginal mesh implantation is associated with a shorter voiding interval and a smaller bladder capacity, which represents abnormal lower urinary tract symptoms following transvaginal mesh implantation. PMID: 27762470
- Findings might aid in identifying effective treatment windows for nerve growth factor (NGF)-based strategies to counteract retinal and/or optic-nerve degeneration. PMID: 28067793
- The aim of our study was to investigate the influence of two mild stressors, acute and chronic exposure to forced swim (FS) or high-light open field (HL-OF), on neurons containing NGF. PMID: 27978417
- This work sheds light on the role of miR-132 in bladder overactivity, bladder hypertrophy, NGF signaling and expression of inflammatory mediators. Findings demonstrate that aberrant expression of NGF and miR-132 is involved in voiding dysfunctions. PMID: 27789288
- Data indicate the effects of vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation across three consecutive generations on brain neurotrophins like brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); nerve growth factor (NGF) and cognitive performance in the third generation male offspring. PMID: 27569259
- This study demonstrated that Age-dependent changes in the density of NGF-ir neurons in stressed rats are probably caused by ageing processes and they may point to dysregulation of excitatory control exerted by the amygdala. PMID: 26724365
- Data indicate that nerve growth factor precursors and nerve growth factor (ProNGF and NGF) and the downstream effector proteins play an important role in the growth, differentiation, and apoptosis of oligodendrocyte (OLG). PMID: 26681653
- NGF in the facet joint contributes to the development of injury-induced joint pain. Localized blocking of NGF signaling in the joint may provide potential treatment for joint pain. PMID: 26521746
- This study deminstrated that elevated NGF after peripheral nerve injury induces neurite sprouting and the formation of synapse-like structures within the contralateral DRG, leading to the development of chronic mirror-image pain. PMID: 26121254
- Results suggest the induction of NGF represents an adaptive response against immune-mediated neuroinflammation in the dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord that likely contributes to the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis attenuation PMID: 25801841
- elevation of plasma norepinephrine in neonatal colonic inflammation induces NGF expression in the gastric fundus. PMID: 26608656
- NGF acts directly on photoreceptors survival and prevents photoreceptor degeneration. PMID: 25897972
- Identify nerve growth factor as a binding partner for MOG and demonstrate that this interaction is capable of sequestering NGF from TrkA-expressing neurons to modulate axon growth and survival. PMID: 26347141
- Let-7 microRNAs regulate peripheral nerve regeneration by targeting nerve growth factor. PMID: 25394845
- Ginger extract has a synaptogenic effect via NGF-induced ERK/CREB activation, resulting in memory enhancement. PMID: 25049196
- Chronic heart failure impairs the expression of nerve growth factor in the sympathetic and sensory nerves. PMID: 24913185
- Vibration significantly increases total-NGF mRNA in interverterbal discs. Protein expression of BDNF increases by nearly 10-fold, especially in the inner annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus. PMID: 24921856
- NGF exhibits anti-oxidative and hepatoprotective effects and is suggested to be therapeutically applicable in treating cholestatic liver diseases. PMID: 25397406
- Activation of microtubule dynamics increases neuronal growth via the NGF- and Galpha s-mediated signaling pathways. PMID: 25691569
- NGF was increased 12, 24, and 48 hours in hippocampus after sepsis induction PMID: 24978930
- Findings revealed that NGF may play a pivotal role of anti-apoptosis in spinal cord neurons through retrograde transport of NF-kappaB in Schwann cells following sciatic nerve injury in rats PMID: 24620979
- Maternal separation decreased NGF levels in the hippocampus which was reversed with methamphetamine. PMID: 24407463
- the level of NGF expression did not display a meaningful change throughout the immobilization period PMID: 24154957
- Spinal nerve afferents are important in sustaining and up-regulating the expression of NGF in the sensory neurons innervating the heart in acute myocardial infarction. PMID: 24508054
- NGF played an important role in the activation of Akt and subsequent up-regulation of BDNF in the sensory neurons in visceral inflammation such as cystitis. PMID: 24303055
- The temporal mismatch in behaviour, skin [NGF] and phenotypic changes in sensory nerve fibres indicate that increased [NGF] does not cause hyperalgesia after partial mental nerve injury. PMID: 24380503
- Using gene expression as a functional read-out, our data demonstrate that the relative availability of NGF and proNGF in vivo might modulate the biological outcome of these ligands. PMID: 24713110
- The synergistic effects of grafting both NGF and GRGD ligands to PCL-CS scaffolds on the growth and differentiation of PC12 cells provide a new biomaterial for neural tissue engineering. PMID: 23468336
- Denervation causes age-dependent increases in NGF in the VP, which is a potential mechanism by which the autonomic nervous system may regulate prostate growth and lead to BPH/LUTS PMID: 23872662
- proBDNF accumulated in the hippocampus of aged rats. PMID: 23255148
- The effects of acute and chronic administration of branched-chain amino acids on protein levels and mRNA expression of nerve growth factor, was investigated. PMID: 23559405
- Suggest that nerve growth factor, which is elevated in the failing human heart, causes hypertrophy of neurons in cardiac ganglia. PMID: 23959444
- Hyperosmolarity induces apoptosis of pHCECs by activating JNK signaling. PMID: 24327613
- Environmental enrichment improves memory and increases nerve growth factor (NGF) concentration in the dentate gyrus. PMID: 23460346
- NGF contributes to the repair of nerve tissue and improves pain-related behavior after inferior alveolar nerve injury. PMID: 23190308
- Long-term casting induced heat hyperalgesia, and up-regulation and phenotypic change of NGF in dorsal root ganglia PMID: 23234417
- Data indicate that nerve growth factor (NGF) mRNA levels changed significantly during Leydig-cell regeneration in vivo. PMID: 23743199
- Upregulation of NGF in the amygdala promotes behavior of opioid reward and increases sensitivity to subsequent opioids. PMID: 22871918
- This study suggests that application of hADSCs with NGF-hydrogel on the CN might be a promising treatment for postprostatectomy ED. PMID: 22834730
- NGF increased expression of ASIC3 in DRG neurons. PMID: 22744968
- [REVIEW] Neuropathies and clinical presentations result from disruption of NGF signalling in hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathies (HSAN) type IV and HSAN type V. PMID: 23157347
- NGF gene expression is elevated during the whole course of cerebral concussion, especially in the early phase. PMID: 12857442
- There were much more Ngf-immunoreactive nerve cells expressed in the dorsal horn in sciatic nerve cryoneurolysis rats with hyperalgesia. PMID: 22580175
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted. Endosome lumen.
-
蛋白家族:NGF-beta family
-
组织特异性:Detected in the granule and pyramidal cell layer in the hippocampus.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:310738
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000022200
UniGene: Rn.22168
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)