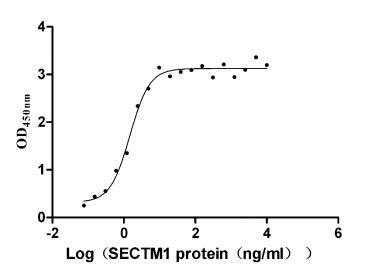
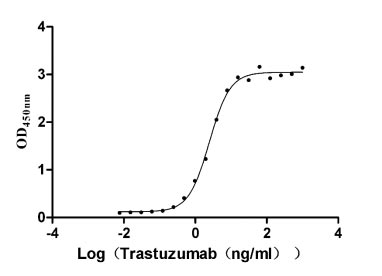
Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2 (Aplp2), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2(Aplp2),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP001912MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2(Aplp2),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP001912MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2(Aplp2),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP001912MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2(Aplp2),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP001912MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Amyloid-like protein 2(Aplp2),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP001912MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Aplp2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Aplp2; APPL2; Amyloid beta precursor like protein 2; Amyloid beta; A4 precursor-like protein 2; Amyloid protein homolog; Amyloid-like protein 2; APLP-2; CDEI box-binding protein; CDEBP; Sperm membrane protein YWK-II
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:May play a role in the regulation of hemostasis. The soluble form may have inhibitory properties towards coagulation factors. May interact with cellular G-protein signaling pathways. May bind to the DNA 5'-GTCACATG-3'(CDEI box). Inhibits trypsin, chymotrypsin, plasmin, factor XIA and plasma and glandular kallikrein. Modulates the Cu/Zn nitric oxide-catalyzed autodegradation of GPC1 heparan sulfate side chains in fibroblasts.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- APLP2 couples retina development and synaptic genes and present the first evidence that APLP2 expression may be linked to synaptic disease. PMID: 27267879
- These data support the notion that APP and APLP2 facilitate transmitter release, likely through the interaction with the neurotransmitter release machinery. PMID: 26551565
- This paper demonstrates an important role for APLP2 in refractive development in mice and humans, suggesting a high level of evolutionary conservation of the signaling pathways underlying refractive eye development. PMID: 26313004
- Study provides compelling evidence for an essential role of both APP and APLP2 for neuronal and synaptic morphology as well as hippocampal function and suggest an acute and specific function of endogenous APPsalpha to facilitate synaptic plasticity PMID: 25432317
- The study investigates the subcellular distribution patterns of the metal ions Cu, Zn, Fe, and Ca in individual neurons derived from APP and APLP2 knockout mice brains to further define their role in metal homeostasis. PMID: 25098278
- This study further highlights the distinct and essential role of APLP2 at NMJ synapses that cannot be compensated by APP. PMID: 24998676
- Amyloid precursor protein (APP)/APP-like protein 2 (APLP2) expression is required to initiate endosome-nucleus-autophagosome PMID: 24898256
- The study investigated copper, iron, zinc and manganese levels in APP and APLP-2 single knockout mice as well as homozygous:hemizygous knockout mice at 3, 12 and 18 plus months of age. PMID: 24448592
- Data reveal that APLP2 is specifically required for proper cell cycle exit of neuronal progenitors, and thus has a distinct role in priming cortical progenitors for neuronal differentiation. PMID: 23345401
- APLP2 and the intracellular domain of APP are not essential for coherent activity patterns in the hippocampus, but have subtle effects on synaptic plasticity and fine-tuning of network oscillations. PMID: 23585881
- Gain and loss of function experiments demonstrate that miR-153 suppresses expression of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and APLP2. PMID: 22510281
- These studies highlight the so far underestimated functional importance of APLP2 for CNS physiology. PMID: 21931985
- [review] Studies of protein expression in knock-out mice demonstrate that APP and APLP2 do indeed play an important role in synaptic plasticity. PMID: 22006270
- APLP2 appears not to be essential for maintenance of dendritic structure, spine density, or synaptic function PMID: 22353605
- proteolytic cleavage sites of the amyloid precursor-like protein 2 by the proteases ADAM10, BACE1 and gamma-secretase PMID: 21695060
- Collectively, these data show that APLP2 and APP are synergistically required to mediate neuromuscular transmission, spatial learning and synaptic plasticity. PMID: 21522131
- Data show there were no differences in expression were detectable between wt and floxed alleles. PMID: 20140888
- role in inducing neuronal death is mediated by impairment of the neuroprotective calcium/calmodulin protein kinase IV-dependent signaling pathway PMID: 11877414
- The levels of APLP2 proteolytic products were decreased in BACE KO mice, but increased in BACE transgenic mice. Overexpression of BACE in cultured cells led to increased APLP2 processing. PMID: 15080893
- The APLP2 gene has both a GAGA sequence and a CAGA box immediately upstream of a position corresponding to the APP gene CAGA box. PMID: 15208260
- These findings provide evidence for the role of amyloid-beta precursor protein in copper homeostasis and support the hypothesis that amyloid-beta precursor protein and amyloid precursor-like protein-2 are copper-binding proteins with interchangeable roles PMID: 15447675
- Data describe a relationship between heparan sulfate and copper binding of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2) in the modulation of nitroxyl anion-catalyzed heparan sulfate degradation in glypican-1. PMID: 15677459
- Mice deficient in APlP2 exhibit aberrant apposition of presynaptic marker proteins with postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors and excessive nerve terminal sprouting. APLP2 is a key regulators of structure & function of developing neuromuscular synapses. PMID: 15689559
- Occurrence of the YWK-II protein in the plasma membranes of mouse gametes suggests its involvement in sperm-egg interaction. PMID: 16177981
- findings demonstrate that the APLP2-intracellular C-terminal domains interact with CP2 transcription factor in the nucleus and induce the expression of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta PMID: 16645641
- specific domains of the extracellular region of YWK-II protein may be involved in sperm-egg interaction PMID: 16720320
- The results demonstrated that cell viability and neurite outgrowth of N2a cells undergoing knockdown of Aplp1 were significantly reduced, compared with N2a cells undergoing knockdown of either App or Aplp2. PMID: 16889988
- APLP2/MHC association is influenced by multiple domains of the MHC class I heavy chain and by beta(2)m's effects on the conformation of the heavy chain. PMID: 18452037
- APP and amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2) have a significant role in the development of synaptic function by the regulation of glutamatergic neurotransmission PMID: 18535156
- Amyloid precursor like protein-2 and amyloid beta protein precursor share overlapping anticoagulant functions with regard to regulating thrombosis after cerebral vascular injury. PMID: 19403832
- APP and amyloid precursor-like protein 2 are expressed by stromal cells of thymus and lymph nodes, but not by lymphocytes. PMID: 19710207
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:APP family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11804
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000072428
UniGene: Mm.19133
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
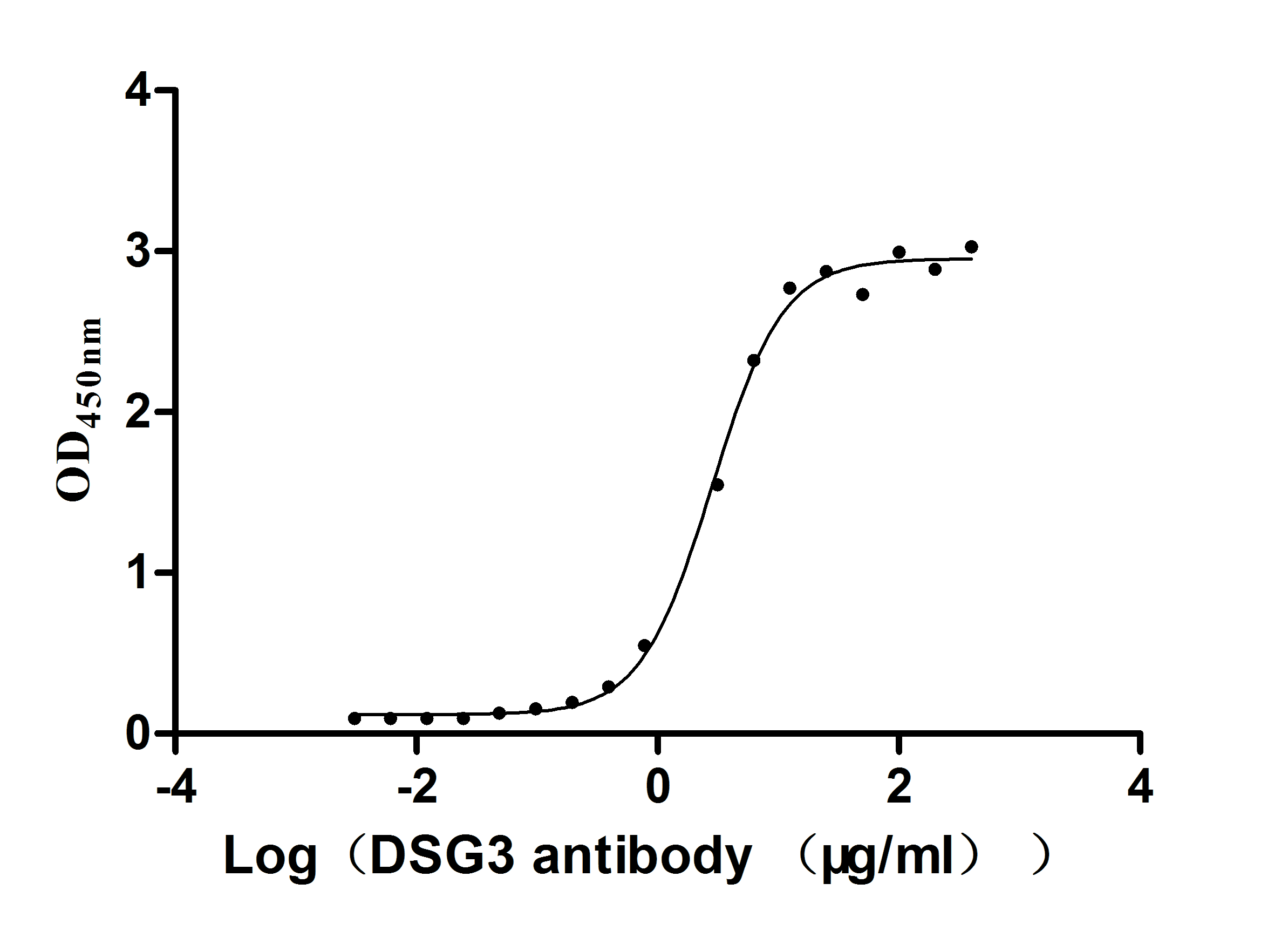
Recombinant Mouse Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
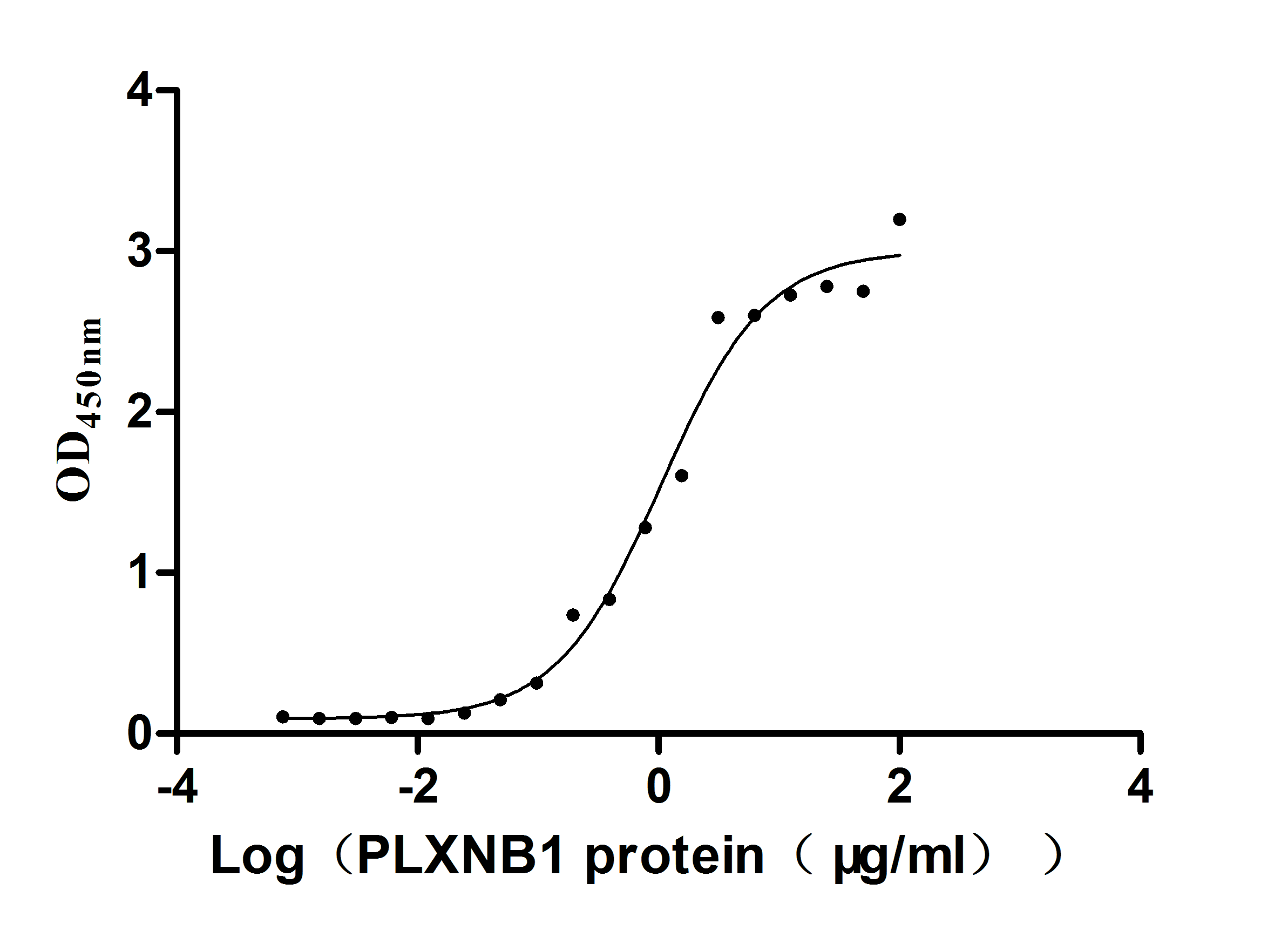
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
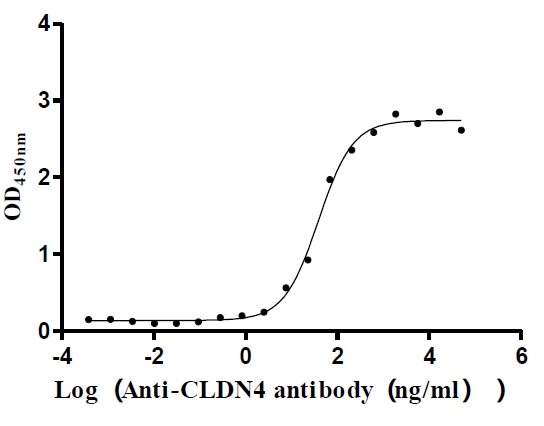
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
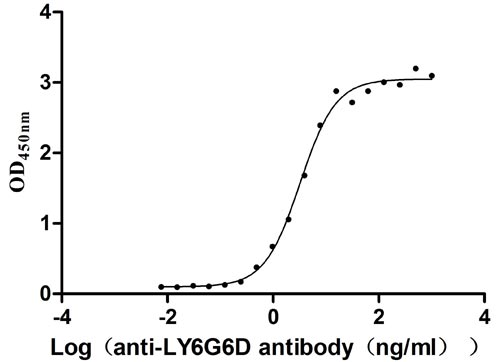
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)