Recombinant Rat Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 (Kcna1)
-
中文名称:大鼠Kcna1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-CF012005RA
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:Kcna1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Kcna1; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1; RBKI; RCK1; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.1
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-495
-
氨基酸序列MTVMSGENADEASAAPGHPQDGSYPRQADHDDHECCERVVINISGLRFETQLKTLAQFPN TLLGNPKKRMRYFDPLRNEYFFDRNRPSFDAILYYYQSGGRLRRPVNVPLDMFSEEIKFY ELGEEAMEKFREDEGFIKEEERPLPEKEYQRQVWLLFEYPESSGPARVIAIVSVMVILIS IVIFCLETLPELKDDKDFTGTIHRIDNTTVIYTSNIFTDPFFIVETLCIIWFSFELVVRF FACPSKTDFFKNIMNFIDIVAIIPYFITLGTEIAEQEGNQKGEQATSLAILRVIRLVRVF RIFKLSRHSKGLQILGQTLKASMRELGLLIFFLFIGVILFSSAVYFAEAEEAESHFSSIP DAFWWAVVSMTTVGYGDMYPVTIGGKIVGSLCAIAGVLTIALPVPVIVSNFNYFYHRETE GEEQAQLLHVSSPNLASDSDLSRRSSSTISKSEYMEIEEDMNNSIAHYRQANIRTGNCTA TDQNCVNKSKLLTDV
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain and the central nervous system, but also in the kidney. Contributes to the regulation of the membrane potential and nerve signaling, and prevents neuronal hyperexcitability. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane. Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6, KCNA7, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel. Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation of delayed rectifier potassium channels. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA1 forms a delayed-rectifier potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by slow spontaneous channel closure. In contrast, a heterotetrameric channel formed by KCNA1 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation. Regulates neuronal excitability in hippocampus, especially in mossy fibers and medial perforant path axons, preventing neuronal hyperexcitability. Response to toxins that are selective for KCNA1, respectively for KCNA2, suggests that heteromeric potassium channels composed of both KCNA1 and KCNA2 play a role in pacemaking and regulate the output of deep cerebellar nuclear neurons. May function as down-stream effector for G protein-coupled receptors and inhibit GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons. May contribute to the regulation of neurotransmitter release, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release. Plays a role in regulating the generation of action potentials and preventing hyperexcitability in myelinated axons of the vagus nerve, and thereby contributes to the regulation of heart contraction. Required for normal neuromuscular responses. Regulates the frequency of neuronal action potential firing in response to mechanical stimuli, and plays a role in the perception of pain caused by mechanical stimuli, but does not play a role in the perception of pain due to heat stimuli. Required for normal responses to auditory stimuli and precise location of sound sources, but not for sound perception. The use of toxins that block specific channels suggest that it contributes to the regulation of the axonal release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Required for normal postnatal brain development and normal proliferation of neuronal precursor cells in the brain. Plays a role in the reabsorption of Mg(2+) in the distal convoluted tubules in the kidney and in magnesium ion homeostasis, probably via its effect on the membrane potential.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our findings provide direct evidence that N-glycans of Kv3.1 splice variants contribute to the placement of these glycoproteins in the plasma membrane of neuronal-derived cells while those of Kv1.1 were absent. PMID: 26348848
- This stuidy demonstrated that kainic-acid induced status epilepticus there are two phases of Kv1.1 repression: (1) an initial mTOR-dependent repression of Kv1.1 that is followed by (2) a miR-129-5p persistent reduction of Kv1.1. PMID: 25270294
- This study supports the possibility of alpha subunits being precisely arranged in Kv1 channels, rather than being randomly assembled. PMID: 23725331
- Overexpression of miR-129 represses Kv1.1 mRNA translation when mTORC1 kinase is inhibited. PMID: 23836929
- Endogenous H2S generating enzyme cystathionine-beta-synthetase was co-localized well with Kv1.1 and Kv1.4 in trigeminal ganglion neurons. PMID: 23413915
- This study demonistrated that Kcna1-mutant rats dominantly display myokymia, neuromyotonia and spontaneous epileptic seizures. PMID: 22206926
- Our study provides evidence that K(V)1.1 contributes to the control of peripheral sensory nerve excitability PMID: 21903165
- Kv1.1 channels are expressed in the beta-cells of several species PMID: 21483673
- Our data suggest that altered Kv1.1(I400V) RNA editing contributes to the reduced ictogenic potential of 4-AP in chronic epileptic rats. PMID: 21371023
- Electro-pharmacological profile of a mitochondrial inner membrane big-potassium channel from rat brain PMID: 20974108
- Kv1.1 or 1.2 homomers and their concatenated forms between the pairs of adjacently and diagonally arranged heterotetramers show differential sensitivity to tetraethylammonium. PMID: 20805574
- Kv1.1 potassium channels apparently contribute to cell-autonomous death of retinal ganglion cells through different components of the apoptotic machinery. PMID: 19696788
- mutations in KCNA1 increase neurotransmitter release in episodic ataxia type 1 PMID: 19779067
- Selective blockade of T-lymphocyte K(Ca)3.1 and K(v)1.3 channels may represent a novel alternative therapy for prevention of kidney allograft rejection. PMID: 19715983
- N-glycosylation affected gating properties both by altering surface potential sensed by the channel's activation gating machinery and by modifying conformational changes regulating cooperative subunit interactions during activation and inactivation PMID: 12879861
- KCNE4 beta-subunit has a drastic inhibitory effect on currents generated by Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 potassium channels PMID: 12944270
- Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels make a significant contribution to K+ efflux at the apical membrane of the choroid plexus. PMID: 14602579
- Age-related changes in the distribution of Kv1.1 in auditory neuron rat cochlear nuclei. PMID: 15949244
- Kv 1.1 was found in cochlear nucleus neuronal cell bodies at birth and postnatal day 21 through adulthood, labeling for potassium channel was in axonal processes, whereas the number of cell bodies labeled for Kv 1.1 decreased. PMID: 16122713
- study shows that activation of presynaptic mu opioid receptors primarily attenuates GABAergic synaptic inputs to central nucleus of the amygdala-projecting neurons in the basolateral amygdala through a signaling mechanism involving Kv1.1 & Kv1.2 channels PMID: 16306173
- Kv1.1 is expressed in gastric epithelial cells and function as growth modulators. PMID: 16331678
- Consistent with these findings, strong immunoreactivities for Kv1.1 and Kv1.6, among 4-AP-sensitive and low-voltage-activated Kv1 family examined, were detected in the soma but not in the stem axon of MTN neurons. PMID: 16624997
- inhibition of mTOR increased Kv1.1 in hippocampal neurons & promoted Kv1.1 surface expression on dendrites without altering its axonal expression; synaptic excitation may cause local suppression of dendritic Kv1 channels by reducing their local synthesis PMID: 17023663
- Here we investigated the role of a highly conserved cytoplasmic C-terminal charged region of five amino acids (HRETE) of the S6 transmembrane domain in the protein and conductance expression of Kv1.1, Kv1.2, and Kv1.4 channels. PMID: 17520476
- Kv1.1 plays an important role in limiting AP firing and that siRNA may be a useful approach to establish the role of specific ion channels in the absence of selective antagonists. PMID: 17855588
- The numbers of Kv1.1 channel are higher in DRs than VRs. PMID: 18053989
- cofactor oxidation by Kvbeta1 is regulated by membrane potential, presumably via voltage-dependent structural changes in Kv1.1 channels PMID: 18222921
- In the rat cerebellar granule cell the protein kinase C pathway promotes neuronal apoptosis through an increase in the levels of expression of Kv1.1 alpha subunit. PMID: 18466331
- This study has revealed the specific expression of Kv1.1 in microglia AND was localized in the microglia in the rat brain between postnatal day 1 and day 10 then progressively reduced with age and was hardly detected at day 14 and day 21 in microglia. PMID: 19118603
- alterations of Kv1.1 and Kv2.1 might contribute to glutamate-induced toxicity in hippocampal neurons PMID: 19472219
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane. Cell projection, axon. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Perikaryon. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cell projection, dendrite. Cell junction. Cell junction, synapse. Cell junction, synapse, presynapse. Cell junction, synapse, presynaptic cell membrane.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, A (Shaker) (TC 1.A.1.2) subfamily, Kv1.1/KCNA1 sub-subfamily
-
组织特异性:Detected in hippocampus, in the middle third of the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus and in stratum radiatum and stratum oriens. Detected in the mossy fiber zone in the hippocampus CA3 region, at or near axon terminals. Detected in brain cortex, at ba
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:24520
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000026731
UniGene: Rn.9769
Most popular with customers
-
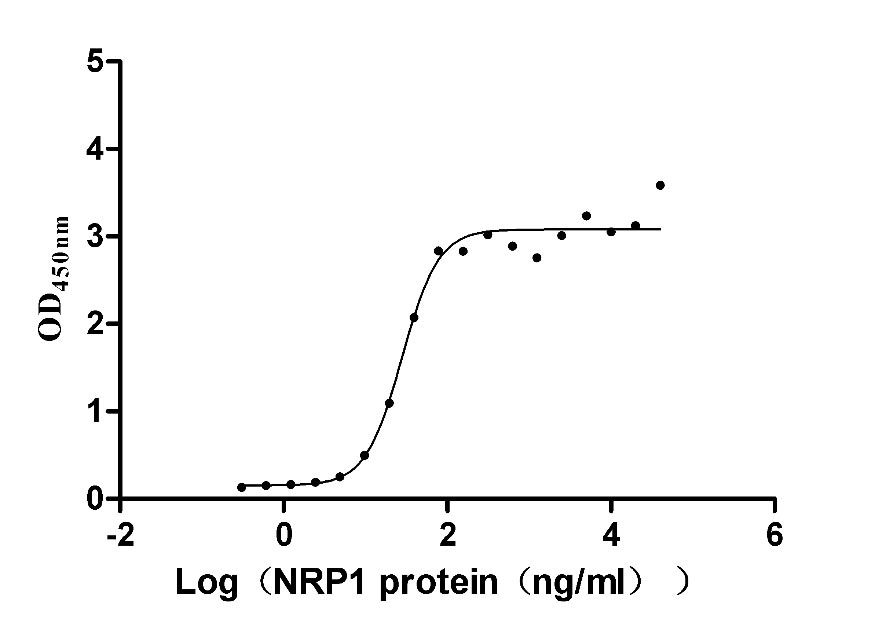
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
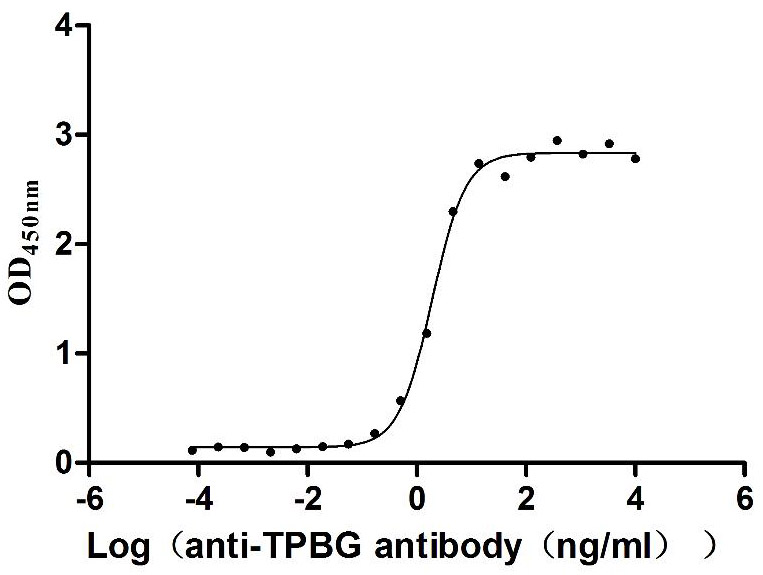
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
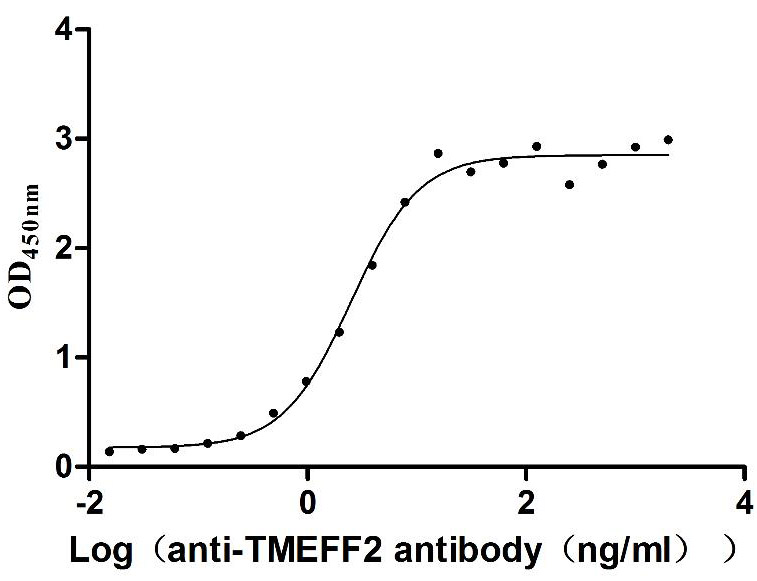
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
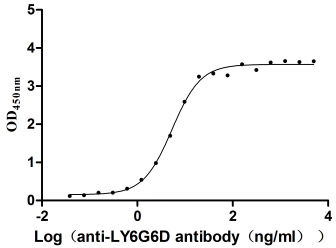
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)

-AC1.jpg)